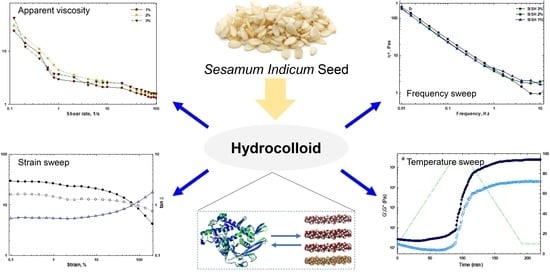
Effects of Concentration and Heating/Cooling Rate on Rheological Behavior of Sesamum indicum Seed Hydrocolloid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of SISH
2.3. Proximal Analysis
2.4. Functional Properties of Hydrocolloids
2.5. Rheological Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition and Functional Properties of SISH
3.2. Rheological Properties of SISH Dispersion at Different Concentrations
3.2.1. Apparent Viscosity Measurements
3.2.2. Strain Amplitude Sweep Measurements
3.2.3. Frequency Sweep Measurements
3.2.4. Temperature Sweep Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hesarinejad, M.; Razavi, S.M.; Koocheki, A. Alyssum homolocarpum seed gum: Dilute solution and some physicochemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laiho, S.; Williams, R.P.; Poelman, A.; Appelqvist, I.; Logan, A. Effect of whey protein phase volume on the tribology, rheology and sensory properties of fat-free stirred yoghurts. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 67, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafe, A.; Razavi, S.M. Scaling law, fractal analysis and rheological characteristics of physical gels cross-linked with sodium trimetaphosphate. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessada, S.M.; Barreira, J.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P. Pulses and food security: Dietary protein, digestibility, bioactive and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Rafe, A.; Shahidi, S.-A.; Hasan-Saraei, A.G. Functional Properties of Rice Bran Protein Isolate at Different pH Levels. Cereal Chem. 2016, 93, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafe, A.; Vahedi, E.; Hasan-Sarei, A.G. Rheology and microstructure of binary mixed gel of rice bran protein-whey: Effect of heating rate and whey addition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3890–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.; Rethinam, G.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Rout, J.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Nooruddin, T. Ozone enhanced production of potentially useful exopolymers from the cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. Polym. Test. 2020, 84, 106385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji-Tabasi, S.; Razavi, S.M.A. Functional properties and applications of basil seed gum: An overview. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafe, A. Improving Texture of Foods using Emerging Hydrocolloids. Emerg. Nat. Hydrocoll. 2019, 499–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanvand, E.; Rafe, A. Rheological and structural properties of rice bran protein-flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) gum complex coacervates. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Saini, C.S.; Punia, S.; Nain, V.; Sandhu, K.S. Sesame (Sesamum indicum) Seed. In Oilseeds: Health Attributes and Food Applications; Tanwar, B., Goyal, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 305–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dravie, E.E.; Kortei, N.K.; Essuman, E.K.; Tettey, C.O.; Boakye, A.A.; Hunkpe, G. Antioxidant, phytochemical and physicochemical properties of sesame seed (Sesamum indicum L.). Sci. Afr. 2020, 8, e00349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, N.; Almasi, H.; Pirouzifard, M.K.; Fathi, N.; Almasi, H.; Pirouzifard, M.K. Effect of ultraviolet radiation on morphological and physicochemical properties of sesame protein isolate based edible films. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, A.O.; Alashi, A.M.; Nwachukwu, I.D.; Fagbemi, T.N.; Aluko, R.E. Functional properties of sesame (Sesamum indicum Linn) seed protein fractions. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2021, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Nouri, L.; Daneshi, M.; Nafchi, A.M.; Nahidi, F. Effect of salt concentration and drying temperature on functional properties of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) meal protein isolate. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 4665–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouki, M.; Khazaei, N.; Jouki, A. Fabrication and characterization of an active biodegradable edible packaging film based on sesame seed gum (Sesamum indicum L.). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4748–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastra-Ripoll, S.E.; Quintana, S.E.; García-Zapateiro, L.A. Chemical, technological, and rheological properties of hydrocolloids from sesame (Sesamum indicum) with potential food applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafe, A.; Razavi, S.M.A. Dynamic viscoelastic study on the gelation of basil seed gum. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 48, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesarinejad, M.A.; Jokandan, M.S.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Koocheki, A.; Razavi, S.M.A.; Ale, M.T.; Attar, F.R. The effects of concentration and heating-cooling rate on rheological properties of Plantago lanceolata seed mucilage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibañez, M.C.; Ferrero, C. Extraction and characterization of the hydrocolloid from Prosopis flexuosa DC seeds. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemists Official Methods of Analysis 21st ed. 2019. Available online: https://www.aoac.org/official-methods-of-analysis-21st-edition-2019/ (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Rafe, A.; Razavi, S.M.; Khan, S. Rheological and structural properties of β-lactoglobulin and basil seed gum mixture: Effect of heating rate. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesarinejad, M.A.; Koocheki, A.; Razavi, S.M.A. Dynamic rheological properties of Lepidium perfoliatum seed gum: Effect of concentration, temperature and heating/cooling rate. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 35, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koocheki, A.; Razavi, S.M.A.; Hesarinejad, M.A. Effect of Extraction Procedures on Functional Properties of Eruca sativa Seed Mucilage. Food Biophys. 2011, 7, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, B.A.; Yazdi, F.T.; Shahidi, F.; Hesarinejad, M.A.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Mohebbi, M. Plantago major seed mucilage: Optimization of extraction and some physicochemical and rheological aspects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karazhiyan, H.; Razavi, S.M.A.; Phillips, G.O.; Fang, Y.; Al-Assaf, S.; Nishinari, K. Physicochemical aspects of hydrocolloid extract from the seeds of Lepidium sativum. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Ghosal, P.; Thakur, S.; Lerouge, P.; Loutelier-Bourhis, C.; Driouich, A.; Ray, B. Polysaccharides from Sesamum indicum meal: Isolation and structural features. Food Chem. 2004, 90, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.; Beltrán, O.; Rincón, F.; de Pinto, G.L.; Igartuburu, J.M. New structural features of Acacia tortuosa gum exudate. Food Chem. 2015, 182, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Barraza, D.; Ortega-Ramos, A.; Torregroza-Fuentes, E.; Quintana, S.E.; García-Zapateiro, L.A. Rheological and Functional Properties of Hydrocolloids from Pereskia bleo Leaves. Fluids 2021, 6, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannasin, S.P.; Adzahan, N.M.; Mustafa, S.; Muhammad, K. Techno-functional properties and in vitro bile acid-binding capacities of tamarillo (Solanum betaceum Cav.) hydrocolloids. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayar, N.; Kriaa, M.; Kammoun, R. Extraction and characterization of three polysaccharides extracted from Opuntia ficus indica cladodes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatchi, A.; Kiani, H.; Labbafi, M. A new functional protein-polysaccharide conjugate based on protein concentrate from sesame processing by-products: Functional and physico-chemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 122, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Stabilising emulsion-based colloidal structures with mixed food ingredients. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 93, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoudhi, N.; Sessa, M.; Chouaibi, M.; Ferrari, G.; Donsì, F.; Hamdi, S. Assessment of emulsifying ability of almond gum in comparison with gum arabic using response surface methodology. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 37, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafe, A.; Glikman, D.; Rey, N.G.; Haller, N.; Kulozik, U.; Braunschweig, B. Structure-property relations of β-lactoglobulin/κ-carrageenan mixtures in aqueous foam. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeniuk, R.W.; Biliaderis, C.G. Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) Mucilage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, E.A.; Doxastakis, G.I. Surface tension of Phaseolus vulgaris and coccineus proteins and effect of polysaccharides on their foaming properties. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, L.; Xie, H.; Lei, Q.; Fang, W.; Lu, X. Structural transitions of ovalbumin/κ-carrageenan complexes under the effects of pH and composition. Chem. Phys. 2020, 533, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, S.; Hesarinejad, M.A.; Shekarforoush, E.; Mirzababaee, S.M.; Karimpour, F. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on the rheological properties and foams/emulsions stability of Alyssum homolocarpum seed gum. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5571–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, Z.; Razavi, S.M. Physicochemical, rheological and functional properties of Nettle seed (Urtica pilulifera) gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 112, 106304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, G.; Fratini, E.; Sacco, P.; Asaro, F.; Cuomo, F.; Donati, I.; Lopez, F. Structural characterization and physical ageing of mucilage from chia for food processing applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpizar-Reyes, E.; Román-Guerrero, A.; Gallardo-Rivera, R.; Varela-Guerrero, V.; Cruz-Olivares, J.; Pérez-Alonso, C. Rheological properties of tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) seed mucilage obtained by spray-drying as a novel source of hydrocolloid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffe, J.F. Rheological Methods in Food Process Engineering; Freeman Press: Dallas, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A.H. Structural and Mechanical Properties of Biopolymer Gels. In Food Polymers, Gels and Colloids; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 1991; pp. 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koocheki, A.; Hesarinejad, M.A.; Mozafari, M.R. Lepidium perfoliatum seed gum: Investigation of monosaccharide composition, antioxidant activity and rheological behavior in presence of salts. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Murphy, S.B. Rheological Methods. In Physical Techniques for the Study of Food Biopolymers; Ross-Murphy, S.B., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 343–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, F.; Muñoz, J.; de Pinto, G.L.; Alfaro, M.C.; Calero, N. Rheological properties of Cedrela odorata gum exudate aqueous dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Tabarsa, M.; Cao, R.; You, S.; Melito, H.S.J.; Behnam, S.; Rezaei, M. Compositional characterization and rheological properties of an anionic gum from Alyssum homolocarpum seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll, S.E.L.; Martínez, S.E.Q.; Zapateiro, L.A.G. Rheological and Microstructural Properties of Xanthan Gum-Based Coating Solutions Enriched with Phenolic Mango (Mangifera indica) Peel Extracts. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 16119–16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutlu, G.; Akcicek, A.; Bozkurt, F.; Karasu, S.; Tekin-Cakmak, Z.H. Rocket seed (Eruca sativa Mill) gum: Physicochemical and comprehensive rheological characterization. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e69620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Koocheki, A.; Shahidi, F. Physical modification of Lepidium perfoliatum seed gum using cold atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Theng, A.H.P.; Yang, D.; Yang, H. Influence of κ-carrageenan on the rheological behaviour of a model cake flour system. LWT 2020, 136, 110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical composition | Moisture | 7.76 ± 0.14 |
| Fat | 0.47 ± 0.04 | |
| Protein | 23.32 ± 0.67 | |
| Carbohydrate | 60.95 ± 1.28 | |
| Ash | 7.50 ± 0.70 | |
| Functional properties | WHC | 405.05 ± 27.38 |
| Emulsion ability | 100 ± 0.00 | |
| Emulsion stability | 96.47 ± 0.75 | |
| Solubility | 34.05 ± 3.45 | |
| Foaming ability | 61.35 ± 1.60 | |
| Foaming stability | 65.32 ± 2.31 |
| SISH Concentration (%) | G′LVE (Pa) | G″LVE (Pa) | Tan δLVE | τc (Pa) | γ0 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 23.96 ± 0.58 c | 12.93 ± 0.04 c | 0.51 ± 0.01 a | 5.86 ± 0.97 c | 29.87 ± 1.48 c |
| 2.0 | 25.91 ± 0.27 b | 14.93 ± 0.03 b | 0.54 ± 0.02 a | 8.43 ± 1.07 b | 43.79 ± 2.34 b |
| 3.0 | 28.15 ± 0.62 a | 16.73 ± 0.02 a | 0.56 ± 0.01 a | 12.57 ± 1.12 a | 59.63 ± 3.57 a |
| SISH Concentration (%) | q | k′ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 0.18 ± 0.02 c | 39.56 ± 0.79 c | 0.96 |
| 2.0 | 0.14 ± 0.01 b | 61.85 ± 0.84 b | 0.90 |
| 3.0 | 0.11 ± 0.02 a | 82.72 ± 1.09 a | 0.91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafe, A.; Shadordizadeh, T.; Hesarinejad, M.A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Abd El-Maksoud, A.A.; Cheng, W.; Mozafari, M.R.; Abedelmaksoud, T.G. Effects of Concentration and Heating/Cooling Rate on Rheological Behavior of Sesamum indicum Seed Hydrocolloid. Foods 2022, 11, 3913. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233913
Rafe A, Shadordizadeh T, Hesarinejad MA, Lorenzo JM, Abd El-Maksoud AA, Cheng W, Mozafari MR, Abedelmaksoud TG. Effects of Concentration and Heating/Cooling Rate on Rheological Behavior of Sesamum indicum Seed Hydrocolloid. Foods. 2022; 11(23):3913. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233913
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafe, Ali, Talieh Shadordizadeh, Mohammad Ali Hesarinejad, Jose M. Lorenzo, Ahmed Ali Abd El-Maksoud, Weiwei Cheng, M. R. Mozafari, and Tarek Gamal Abedelmaksoud. 2022. "Effects of Concentration and Heating/Cooling Rate on Rheological Behavior of Sesamum indicum Seed Hydrocolloid" Foods 11, no. 23: 3913. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233913
APA StyleRafe, A., Shadordizadeh, T., Hesarinejad, M. A., Lorenzo, J. M., Abd El-Maksoud, A. A., Cheng, W., Mozafari, M. R., & Abedelmaksoud, T. G. (2022). Effects of Concentration and Heating/Cooling Rate on Rheological Behavior of Sesamum indicum Seed Hydrocolloid. Foods, 11(23), 3913. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233913