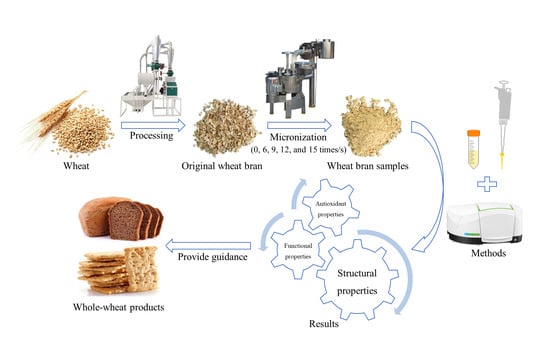
Micronization Effects on Structural, Functional, and Antioxidant Properties of Wheat Bran
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Wheat Bran
2.3. Particle Size Distribution
2.4. Main Chemical Components
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.7. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.8. Fatty Acids Value (FAC)
2.9. Lipase Activity (LA)
2.10. Lipoxygenase (LOX) Activity
2.11. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.12. Oil-Holding Capacity (OHC)
2.13. Swelling Capacity (SC)
2.14. Cholesterol-Adsorption Capacity (CAC)
2.15. Sodium Nitrite-Adsorption Capacity (SNAC)
2.16. Cation-Exchange Capacity (CEC)
2.17. DPPH• Scavenging Capacity
2.18. ABTS+• Scavenging Capacity
2.19. Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)
2.20. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size Distribution
3.2. Main Chemical Components
3.3. Surface Micromorphology
3.4. Crystalline Structure
3.5. Functional Group
3.6. Fatty Acid Value (FAV)
3.7. Lipase and Lipoxygenase Activities
3.8. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC), Oil-Holding Capacity (OHC), and Swelling Capacity (SC)
3.9. Cholesterol-Absorption Capacity (CAC) and Sodium Nitrite-Absorption Capacity (SNAC)
3.10. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
3.11. Antioxidant Activity In Vitro
3.12. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belcar, J.; Kaszuba, J.; Gorzelany, J. Effect of wheat and barley malt addition on the quality of the baking blend and wheat bread. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2022, 72, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcar, J.; Buczek, J.; Kapusta, I.; Gorzelany, J. Quality and pro-healthy properties of belgian witbier-style beers relative to the cultivar of winter wheat and raw materials used. Foods 2022, 11, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashaei, M.; Zare, L.; Sadrabad, E.K.; Hosseini Sharif Abad, A.; Mollakhalili-Meybodi, N.; Abedi, A.S. The impacts of salt reduction strategies on technological characteristics of wheat bread: A review. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 59, 4141–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delannoy-Bruno, O.; Desai, C.; Raman, A.S.; Chen, R.Y.; Gordon, J.I. Evaluating microbiome-directed fibre snacks in gnotobiotic mice and humans. Nature 2021, 595, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.; Ding, X.; Wu, G.; Lam, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, H.; Xue, X.; Lu, C.; Ma, J.; et al. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science 2018, 359, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazmiya, M.J.A.; Sultana, A.; Rahman, K.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Khan, S.; Appiah, S.C.Y. Current insights on bioactive molecules, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other pharmacological activities of cinnamomum camphora linn. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 9354555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onipe, O.O.; Jideani, A.I.O.; Beswa, D. Composition and functionality of wheat bran and its application in some cereal food products. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2016, 50, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdane, S.; Jacobs, P.J.; Dornez, E.; Verspreet, J.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) bran in bread making: A critical review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2016, 15, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, L. Effects of different particle sizes on the structure, functional properties and reconstitution stability of highland barley bran. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 54–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Huang, J.; Kawakami, K.; Liu, H.; Fujishima, T.; Qin, W.; Geng, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.T. Effects of particle size of glutinous rice flour on the quality attributes of sweet dumplings. J. Food Process. Pres. 2022, 46, e16388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Cui, Q. Effects of wheat bran micronization on the quality of reconstituted whole-wheat flour and its cooked noodles. Processes 2022, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gao, J.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Ying, J.; Zhou, W. Whole-wheat flour particle size influences dough properties, bread structure and in vitro starch digestibility. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3610–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Mu, T. Effects of extraction methods and particle size distribution on the structural, physicochemical, and functional properties of dietary fiber from deoiled cumin. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y. Effect of mechanical grinding on the physicochemical, structural, and functional properties of foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv) bran powder. Foods 2022, 11, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savlak, N.; Türker, B.; Yeşilkanat, N. Effects of particle size distribution on some physical, chemical and functional properties of unripe banana flour. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakos, A.; Kyriakakis, G.; Evageliou, V.; Protonotariou, S.; Mandala, I.; Ritzoulis, C. Influence of jet milling and particle size on the composition, physicochemical and mechanical properties of barley and rye flours. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Shang, G.; Zhu, H. Mechanical grinding alters physicochemical, structural, and functional properties of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) leaf powders. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 173, 114149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.3-2016; Food Safety National Standards for Determination of Moisture in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.4-2016; Food Safety National Standards for Determination of Ash in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.5-2016; Food Safety National Standards for Determination of Protein in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.6-2016; Food Safety National Standards for Determination of Fat in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- DB 43/T476-2009; Determination of Flavone in Vegetal Food. Hunan Quality and Technology Supervise Bureau of the People’s Republic of China: Changsha, China, 2009.
- Karakashov, B.; Grigorakis, S.; Loupassaki, S.; Makris, D.P. Optimisation of polyphenol extraction from Hypericum perforatum (St. John’s Wort) using aqueous glycerol and response surface methodology. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aroma. 2015, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ji, G.; Chen, X.; Han, L.; Gao, C. Effects on physicochemical properties of black tea by mechanical superfine and general grinding. T. Chin. Soc. Agr. Eng. 2016, 41, 1670–1677. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 15684-2015; Milled Cereal Products—Determination of Fat Acidity. Administration of Quality Supervision. Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB/T 5523-2008; Inspection of Grains and Oils—Determination of Lipase Activity of Grain and Oilseeds. Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection, and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Cato, L.; Halmos, A.L.; Small, D.M. Measurement of lipoxygenase in Australian white wheat flour: The effect of lipoxygenase on the quality properties of white salted noodles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Ma, C.; Mu, S.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hou, J. Comparison and characterization of the structure and physicochemical properties of three citrus fibers: Effect of ball milling treatment. Foods 2022, 11, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chu, J.; Lu, Z.; Lv, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, H. Physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from foxtail millet (Setaria italic) bran. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.33-2016; National Food Safety Standard for Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Aprotosoaie, A.C.; Miron, A.; Ciocârlan, N.; Brebu, M.; Roşu, C.M.; Trifan, A.; Vochiţa, G.; Gherghel, D.; Luca, S.V.; Niţă, A.; et al. Essential oils of Moldavian Thymus species: Chemical composition, antioxidant, anti-Aspergillus and antigenotoxic activities. Flavour Frag. J. 2019, 34, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Q.; Yao, C.; Zhu, R.Y.; Huang, Y.X.; Kang, W.Y.; Wang, J.M. Spectrum-effect relationship in antioxidant activity of Ligustri Lucidi Fructus based on DPPH, ABTS and FRAP assays. China J. of Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappelli, A.; Guerrini, L.; Parenti, A.; Palladino, G.; Cini, E. Effects of wheat tempering and stone rotational speed on particle size, dough rheology and bread characteristics for a stone-milled weak flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 91, 102879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, W.; Sun, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wei, X.; Luan, G.; Hu, Y.; Tatsumi, E. Grinding of maize: The effects of fine grinding on compositional, functional and physicochemical properties of maize flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 68, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Dang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X. Effects of ultrafine grinding on microstructure and functional properties of highland barley bran powder. T. Chinese Soc. Agr. Eng. 2020, 36, 278–283. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Lin, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Ying, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhou, W. How manipulation of wheat bran by superfine-grinding affects a wide spectrum of dough rheological properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 96, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Tian, L. Effects of superfine pulverization technology on the morphology, microstructure, and physicochemical properties of Apium graveolens L. root. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2022, 85, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, M.; Handa, S.; Mridula, D.; Singh, R.K. Physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) flour as influenced by particle size. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, N.; Isono, N.; Noda, T. Relationship of granule size distribution and amylopectin structure with pasting, thermal, and retrogradation properties in wheat starch. J. Agr. Food. Chem. 2020, 58, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Dong, K.; Chu, W.; Hu, X. Effects of microwave modification on the structure and functional properties of oat bran dietary fiber. J. Chin. I. Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 21, 30–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.-T.; Yang, Z.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhu, K.-X. Effect of superheated steam treatment on the lipid stability of whole wheat flour. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LS/T 3324-2015; Whole Wheat Flour. State Administration of Grain: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Ling, B.; Lyng, J.G.; Wang, S. Effects of hot air-assisted radio frequency heating on enzyme inactivation, lipid stability and product quality of rice bran. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wen, W.; Zhang, R.; Wei, Z.; Deng, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, M. Complex enzyme hydrolysis releases antioxidative phenolics from rice bran. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.; Chen, Z. Synthesis of binary and ternary intermetallic powders via a novel reaction ball milling technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 444, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liang, H.; Chen, N.; Shi, B.; Zeng, W. Potential of phenolic compounds in Ligustrum robustum (Rxob.) Blume as antioxidant and lipase inhibitors: Multi-spectroscopic methods and molecular docking. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Jin, X.; Gao, J.; Qiu, Z.; Zhou, W. Impact of wheat bran micronization on dough properties and bread quality: Part I—Bran functionality and dough properties. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Niu, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, S. Structural characteristics and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber modified by enzymatic and enzyme-micronization treatments. LWT. 2017, 75, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, G.; Liu, J.; Wen, J. Antioxidant Food and Health, 1st ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 112–228. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Parker, M.L.; Ng, A.; Waldron, K.W. The phenolic acid and polysaccharide composition of cell walls of bran layers of mature wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. Avalon) grains. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2005, 85, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal-Eldin, A.; George, N.; Sobti, B.; AlRashidi, N.; Ghnimi, S.; Ali, A.A.; Andersson, A.M.; Andersson, R.; Antony, A.; Hamed, F. Dietary fiber components, microstructure, and texture of date fruits (Phoenix dactylifera, L.). Sci. Rep 2020, 10, 21767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Yang, M.; Zhao, N.; Xie, F.; Zheng, P.; Simbo, J.; Yu, X.; Du, S.K. Structural, physicochemical, antioxidant and in vitro digestibility properties of banana flours from different banana varieties (Musa spp.). Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guo, X.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Huo, R.; Zhang, Y. Improving the adsorption characteristics and antioxidant activity of oat bran by superfine grinding. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 00, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, C.; Kapoor, H.C. Review Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables—The millennium’s health. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2001, 36, 703–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sample | D10 (µm) | D50 (µm) | D90 (µm) | Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 3.50 ± 0.04 e | 46.08 ± 0.09 a | 912.70 ± 3.42 a | 19.73 ± 0.03 a |
| B1 | 5.17 ± 0.04 d | 34.29 ± 0.09 b | 394.90 ± 3.36 b | 11.37 ± 0.09 b |
| B2 | 6.39 ± 0.05 c | 26.51 ± 0.04 c | 76.43 ± 1.40 c | 2.64 ± 0.05 c |
| B3 | 6.70 ± 0.09 b | 26.35 ± 0.03 d | 69.49 ± 0.50 d | 2.38 ± 0.01 d |
| B4 | 7.30 ± 0.11 a | 26.05 ± 0.10 e | 65.37 ± 1.43 d | 2.23 ± 0.04 e |
| Component | B0 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 9.95 ± 0.14 a | 9.82 ± 0.10 a | 7.78 ± 0.11 b | 6.58 ± 0.06 c | 5.59 ± 0.10 d |
| Crude Fat (%) | 4.92 ± 0.12 d | 5.22 ± 0.12 c | 5.39 ± 0.11 bc | 5.46 ± 0.09 b | 5.94 ± 0.10 a |
| Crude protein (%) | 15.36 ± 0.12 b | 15.44 ± 0.15 b | 15.52 ± 0.15 b | 15.56 ± 0.15 b | 15.86 ± 0.13 a |
| Ash (%) | 2.93 ± 0.09 a | 2.85 ± 0.09 a | 2.71 ± 0.05 b | 2.62 ± 0.06 bc | 2.49 ± 0.10 c |
| Total flavonoids (mg/g) | 2.94 ± 0.04 e | 3.16 ± 0.04 d | 3.46 ± 0.03 c | 3.55 ± 0.04 b | 3.63 ± 0.03 a |
| Total phenols (mg/g) | 2.36 ± 0.05 e | 2.5 ± 0.04 d | 2.66 ± 0.03 c | 2.74 ± 0.04 b | 2.81 ± 0.03 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Q. Micronization Effects on Structural, Functional, and Antioxidant Properties of Wheat Bran. Foods 2023, 12, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010098
Lai S, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Li G, Wang Y, Cui Q. Micronization Effects on Structural, Functional, and Antioxidant Properties of Wheat Bran. Foods. 2023; 12(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010098
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Sitong, Zhenjia Chen, Yanqing Zhang, Guang Li, Yuanmeng Wang, and Qingliang Cui. 2023. "Micronization Effects on Structural, Functional, and Antioxidant Properties of Wheat Bran" Foods 12, no. 1: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010098
APA StyleLai, S., Chen, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, G., Wang, Y., & Cui, Q. (2023). Micronization Effects on Structural, Functional, and Antioxidant Properties of Wheat Bran. Foods, 12(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010098