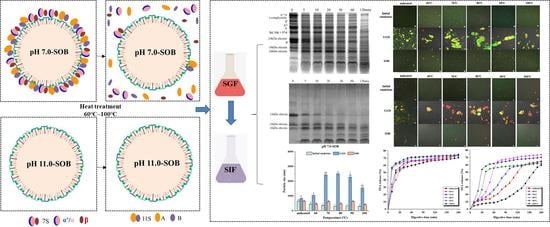
Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestive Characteristics of Different Soybean Oil Body Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extractions of pH 11.0-SOB and pH 7.0-SOB
2.3. Emulsion Preparation and Heat Treatment
2.4. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of SOBs
2.5. Zeta Potential
2.6. Droplet Size Analysis
2.7. Tricine-SDS-PAGE
2.8. Microscope Observation
2.9. Free Fatty Acid (FFA) Release
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein Compositions and Structures of pH 7.0- and pH 11.0-SOB Emulsions
3.2. Protein Hydrolysis in Stomach Digestion
3.3. Zeta Potential
3.4. Particle Size
3.5. Microstructures
3.6. The Release of FFAs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaaboul, F.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y. Soybean oil bodies: A review on composition, properties, food applications, and future research aspects. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 1097296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xu, Z.; Qi, B.; Cui, S.; Wang, T.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. Fabrication and characterization of soybean oil bodies encapsulated in maltodextrin and chitosan-EGCG conjugates: An in vitro digestibility study. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, R.; He, S.; Cheng, C.; Ma, Y. The stability and gastro-intestinal digestion of curcumin emulsion stabilized with soybean oil bodies. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 131, 109663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y. Macronutrients and micronutrients of soybean oil bodies extracted at different pH. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Liao, P.; Yang, H.; Tzen, J.T.C. Determination and analyses of the N-termini of oil-body proteins, steroleosin, caleosin and oleosin. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 43, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ying, Y.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y. The characterization of soybean oil body integral oleosin isoforms and the effects of alkaline pH on them. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallier, S.; Gordon, K.C.; Singh, H. Chemical and structural characterisation of almond oil bodies and bovine milk fat globules. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1996–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisk, I.D.; White, D.A.; Carvalho, A.; Gray, D.A. Tocopherol—An intrinsic component of sunflower seed oil bodies. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groopman, E.E.; Carmody, R.N.; Wrangham, R.W. Cooking increases net energy gain from a lipid-rich food. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2015, 156, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.; Zhao, L.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y. Behaviors of particle size and bound proteins of oil bodies in soymilk processing. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, A.; Li, X. Effect of water bath-assisted water extraction on physical and chemical properties of soybean oil body emulsion. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 6380–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Pan, Y.; Niu, Y.; Peng, D.; Huang, W.; Shen, W.; Jin, W.; Huang, Q. Modulating interfacial structure and lipid digestion of natural Camellia oil body by roasting and boiling processes. Food Chem. 2022, 402, 134198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Effects of preheat treatments on the composition, rheological properties, and physical stability of soybean oil bodies. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3150–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.H.C. Oleosins and oil bodies in seeds and other organs. Plant Physiol. 1996, 110, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capuano, E.; Pellegrini, N.; Ntone, E.; Nikiforidis, C.V. In vitro lipid digestion in raw and roasted hazelnut particles and oil bodies. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2508–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wen, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, R.; Yu, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. The physicochemical properties and gastrointestinal fate of oleosomes from non-heated and heated soymilk. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Wang, X.; Lin, Q.; Han, J.; Singh, H. Dynamic gastric stability and in vitro lipid digestion of whey-protein-stabilised emulsions: Effect of heat treatment. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, L. Digestive characteristics of oil body extracted from soybean aqueous extract at different pHs. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y. Comparison of two different natural oil body emulsions: In vitro gastrointestinal digestion. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yang, X.; Teng, Z.; Yin, S.; Zhu, J.; Qi, J. Stabilization of soybean oil body emulsions using κ, ι, λ-carrageenan at different pH values. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Z.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y. Physicochemical and rheological properties and oxidative stability of oil bodies recovered from soybean aqueous extract at different pHs. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhou, S.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Xiao, F. Investigation of curcumin emulsion stability and gastrointestinal digestion prepared with rapeseed oil body. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, 13566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, J.; Yin, S.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Qi, J.; Zheng, E. In vitro assessment of the bioaccessibility of fatty acids and tocopherol from soybean oil body emulsions stabilized with ι-carrageenan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhong, M.; Wu, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Qi, B. Loading natural emulsions with nutraceuticals by ultrasonication: Formation and digestion properties of curcumin-loaded soybean oil bodies. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallier, S.; Tate, H.; Singh, H. In vitro gastric and intestinal digestion of a walnut oil body dispersion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Katho, S.; Mothizuki, K. Influences of calcium and pH on protein solubility in soybean milk. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1993, 57, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Calcium sulphate-induced soya bean protein tofu-type gels: Influence of denaturation and particle size. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Jiang, L. Enzymatic activity and stability of soybean oil body emulsions recovered under neutral and alkaline conditions: Impacts of thermal treatments. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Li, Y. Review of in vitro digestion models for rapid screening of emulsion-based systems. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 32–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, D.; Gray, D.A.; Fisk, I.D.; Decker, E.A.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Extraction and characterization of oil bodies from soybeans: A natural source of pre-emulsified soybean oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8711–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y. Novel strategy for the demulsification of isolated sesame oil bodies by endogenous proteases. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Y.; Ding, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, L. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestive Characteristics of Different Soybean Oil Body Emulsions. Foods 2023, 12, 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152942
Yang X, Zhou L, Wu Y, Ding X, Wang W, Zhang D, Zhao L. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestive Characteristics of Different Soybean Oil Body Emulsions. Foods. 2023; 12(15):2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152942
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xufeng, Luyao Zhou, Yingying Wu, Xiuzhen Ding, Wentao Wang, Dajian Zhang, and Luping Zhao. 2023. "Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestive Characteristics of Different Soybean Oil Body Emulsions" Foods 12, no. 15: 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152942
APA StyleYang, X., Zhou, L., Wu, Y., Ding, X., Wang, W., Zhang, D., & Zhao, L. (2023). Effect of Heat Treatment on the Digestive Characteristics of Different Soybean Oil Body Emulsions. Foods, 12(15), 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152942