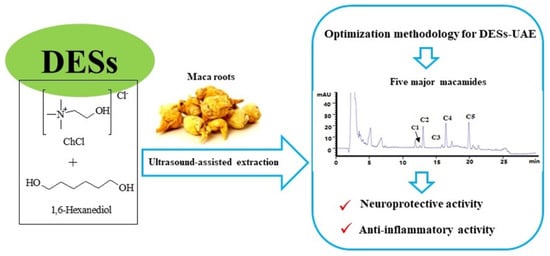
Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Strategy for Simultaneous Extraction of Five Macamides from Lepidium meyenii Walp and In Vitro Bioactivities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. DES Preparation
2.3. HPLC Quantification
2.4. Extraction Procedure
2.5. DES–UAE Process Optimization
2.5.1. Single-Factor Optimization
2.5.2. BBD Optimization
2.6. Other Extraction Methods for Comparison
2.7. Recovery of Target Macamides from DES Extracts
2.8. Evaluation of Neuroprotective Activities
2.9. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Activities
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Single-Factor Experimentation
3.1.1. Screening of DESs
3.1.2. Screening of UAE Parameters
3.2. BBD Optimization of Extraction Process Conditions
5.94X12 − 6.47X22 − 3.86X32
− 82.95X12 − 78.10X22 − 26.69X32
5.90X12 − 7.06X22 − 3.20X32
11.07X2X3 − 106.67X12 − 79.47X22 − 24.07X32
73.02X2X3 − 126.45X12 − 129.17X22 − 61.55X32
3.3. Validation of HPLC Analysis
3.4. Model Verification
3.5. Comparison of Extraction Efficiency
3.5.1. Petroleum Ether and DESs
3.5.2. Heating, Heating + Stirring, and UAE
3.6. Recovery of Target Macamides
3.7. Pharmacological Activities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; McNeil, B.; Harvey, L.M. Maca: An Andean crop with multi-pharmacological functions. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Fan, L. The nutritional composition of maca in hypocotyls (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) cultivated in different regions of China. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 3749627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Wei, J.; Gao, Y. A review of the study of active components and their pharmacology value in Lepidium meyenii (Maca). Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6706–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Chemical composition and health effects of maca (Lepidium meyenii). Food Chem. 2019, 288, 422–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.R.; Zhang, R.R.; Liu, J.H.; Li, Z.R.; Zhou, L.; Qiu, M.H. Lepithiohydimerins A-D: Four pairs of neuroprotective thiohydantoin dimers bearing a disulfide bond from maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.). Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2738–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, N.S.L.; Bortoluzzi, L.C.P.; Marques, L.L.M.; Formigoni, M.; Fuchs, R.H.B.; Droval, A.A.; Cardoso, F.A.R. Medicinal effects of Peruvian maca (Lepidium meyenii) a review. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenci, B.; Mannelli, L.D.; Maresca, M.; Micheli, L.; Pieraccini, G.; Mulinacci, N.; Ghelardini, C. Effects of a water extract of Lepidium meyenii root in different models of persistent pain in rats. Z. Nat. C J. Biosci. 2017, 72, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, B.; Hua, H.; Liu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yao, W.; Qian, H. Macamides: A review of structures, isolation, therapeutics and prospects. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.X.; Li, K.K.; Pubu, D.; Jiang, S.P.; Chen, B.; Chen, L.R.; Yang, Z.; Ma, C.; Gong, X.J. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction, HPLC and UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS analysis of main macamides and macaenes from Maca (cultivars of Lepidium meyenii Walp). Molecules 2017, 22, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.; Wei, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, R. Antioxidant and antitumoral activities of isolated macamide and macaene fractions from Lepidium meyenii (Maca). Talanta 2021, 221, 121635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Huang, J.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, K.; Que, J. Maca (Lepidium meyenii) as a source of macamides and polysaccharide in combating of oxidative stress and damage in human erythrocytes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Jin, W.; Lv, X.; Dai, P.; Ao, Y.; Wu, M.; Deng, W.; Yu, L. Effects of macamides on endurance capacity and anti-fatigue property in prolonged swimming mice. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovska, L.; Law, C.; Lai, B.; Chung, T.; Nelson, K.; Day, S.; Haines, C. Maca reduces blood pressure and depression, in a pilot study in postmenopausal women. Climacteric. J. 2015, 18, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melnikovova, I.; Fait, T.; Kolarova, M.; Fernandez, E.C.; Milella, L. Effect of Lepidium meyenii Walp. on semen parameters and serum hormone levels in healthy adult men: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study. J. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 324369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCollom, M.M.; Villinski, J.R.; McPhail, K.L.; Craker, L.E.; Gafner, S. Analysis of macamides in samples of maca (Lepidium meyenii) by HPLC-UV-MS/MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2005, 16, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgud, F.K.; Narinç, D. Influences of dietary supplementation with Maca (Lepidium meyenii) on performance, parameters of growth curve and carcass characteristics in Japanese quail. Animals 2022, 12, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, Z.; Nicolussi, S.; Rau, M.; Lorántfy, L.; Forgo, P.; Hohmann, J.; Csupor, D.; Gertsch, J. Identification of endocannabinoid system-modulating N-alkylamides from Heliopsis helianthoides var. scabra and Lepidium meyenii. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.Q.; Ma, Z.H.; Yang, Q.F.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.Q.; Wu, R.F.; Ren, X.; Mu, L.J.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Zhou, M. Isolation and synthesis of a new benzylated alkamide from the roots of Lepidium meyenii. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2731–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Deng, J.L.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, H.J.; Lin, C.B. Simultaneous determination of macaenes and macamides in maca using an HPLC method and analysis using a chemometric method (HCA) to distinguish maca origin. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Cui, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, X.S.; Hao, J.Y.; Zheng, S.D.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, X.Z.; Wu, T.; Liu, Y.Y.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvents extraction of glabridin and isoliquiritigenin from Glycyrrhiza glabra: Optimization, extraction mechanism and in vitro bioactivities. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 83, 105946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparecida de Marco, B.; Saú Rechelo, B.; Gandolpho Tótoli, E.; Carolina Kogawa, A.; Regina Nunes Salgado, H. Evolution of green chemistry and its multidimensional impacts: A review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolo, M.R.V.; Martins, V.C.A.; Plepis, A.M.G.; Bogusz, S.J. Utilization of pomegranate peel waste: Natural deep eutectic solvents as a green strategy to recover valuable phenolic compounds. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 327, 129471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.W.; Zhao, J.; Lee, M.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, J. Enhanced extraction of bioactive natural products using tailor-made deep eutectic solvents: Application to flavonoid extraction from Flos sophorae. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Duan, M.H.; Yao, X.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhao, C.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Fu, Y.J. Green extraction of five target phenolic acids from Lonicerae Japonicae Flos with deep eutectic solvent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal-Abidin, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Jayakumar, N.S. New horizons in the extraction of bioactive compounds using deep eutectic solvents: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 979, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, O.A.O.; Almulgabsagher, G.A.A.; Ryder, K.S.; Abbott, A.P. Effect of solute polarity on extraction efficiency using deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 5097–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, S.; Chen, S.; Geng, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B. Ultrasound-assisted natural deep eutectic solvent extraction and bioactivities of flavonoids in Ampelopsis grossedentata leaves. Foods 2022, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, N.A.; Alam, P.; Alrehaily, A.J.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Akhtar, A.; Alhowiriny, T.A.; Almarfadi, O.M.; Mothana, R.A. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted parthenolide extraction from Tarchonanthus camphoratus leaves using response surface methodology: HPTLC and cytotoxicity analysis. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Lin, W.; Yang, J.; Feng, S.; Qin, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Bu, T.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of Cordyceps cicadae polyphenols: Optimization, LC-MS characterization, antioxidant and DNA damage protection activity evaluation. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H. Effective extraction of flavonoids from Lycium barbarum L. fruits by deep eutectic solvents-based ultrasound-assisted extraction. Talanta 2019, 203, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Li, G.; Ren, X.; Yin, W. Ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction of echinacoside and oleuropein from Syringa pubescens Turcz. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 151, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanović, M.; Albreht, A.; Krajnc, P.; Vovk, I.; Razboršeka, M.I. Sustainable ultrasound-assisted extraction of valuable phenolics from inflorescences of Helichrysum arenarium L. using natural deep eutectic solvents. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 160, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Jia, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P. (+)- and (–)-Corydecumbenines A and B, two pairs of novel quaternary protoberberine alkaloid cycloadduct enantiomers with anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective activities from the rhizomes of Corydalis decumbens. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 104, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Dou, L.L.; Guo, L.; Li, P.; Liu, E.H. Comprehensive evaluation of deep eutectic solvents in extraction of bioactive natural products. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A.; Sahraei, R. A green ultrasonic-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for the HPLC-UV determination of ferulic, caffeic and cinnamic acid from olive, almond, sesame and cinnamon oil. Talanta 2016, 150, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, L.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, H.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, F. Water based-deep eutectic solvent for ultrasound-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction of parabens in edible oil. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhong, Z.; Bian, G.; Cheng, X.; Li, D. Ultra-rapid, enhanced and eco-friendly extraction of four main flavonoids from the seeds of Oroxylum indicum by deep eutectic solvents combined with tissue-smashing extraction. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Feng, F.; Jiang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, T.; Voglmeir, J.; Chen, Z.G. Green and efficient extraction of rutin from tartary buckwheat hull by using natural deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.L.; Yan, H.; Xu, H.D.; Muhammad, N.; Yan, W.D. Preparation from Lepidium meyenii Walpers using high-speed counter current chromatography and thermal stability of macamidesin air at various temperatures. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mako´s, P.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as “green” extraction media for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1570, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino-Figueroa, A.; Nguyen, D.; Maher, T.J. Neuroprotective effects of Lepidium meyenii (Maca). Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1199, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugnani, K.S.; Vu, N.; Rondón-Ortiz, A.N.; Böhlke, M.; Maher, T.J.; Pino-Figueroa, A.J. Neuroprotective activity of macamides on manganese-induced mitochondrial disruption in U-87 MG glioblastoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 340, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzetti, M.; Rucci, N. Updates on osteoimmunology: What’s new on the cross-talk between bone and immune system. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Jin, W.; Fu, C.; Dai, P.; Yu, Y.; Huo, Q.; Yu, L. Discovering anti-osteoporosis constituents of maca (Lepidium meyenii) by combined virtual screening and activity verification. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, C.H.; Zhong, H.B.; Gong, Y.; Cui, Z.K.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Liang, C.; Cao, H.H.; Chen, X.R.; et al. N-(3- methoxybenzyl)-(9Z,12Z,15Z)-octadecatrienamide promotes bone formation via the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Jin, W.; Cui, Y.; Ao, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Yu, L. Protective effects of macamides from Lepidium meyenii Walp. against corticosterone-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 23096–23108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, R.; Hua, H.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Qian, H.; Du, P. The macamide relieves fatigue by acting as inhibitor of inflammatory response in exercising mice: From central to peripheral. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 917, 174758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Abbreviation | HBA | HBD | Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| DES-1 | Choline chloride | Levulinic acid | 1:2 |
| DES-2 | Propanedioic acid | 1:2 | |
| DES-3 | 1,4-Butanediol | 1:2 | |
| DES-4 | Glycerol | 1:2 | |
| DES-5 | Urea | 1:2 | |
| DES-6 | Triethylene glycol | 1:2 | |
| DES-7 | 1,6-Hexanediol | 1:2 | |
| DES-8 | Xylitol | 1:2 | |
| DES-9 | DL-Malic acid | 1:2 | |
| DES-10 | Ethyl glycol | 1:2 |
| Run | X1 (mL/g) | X2 (°C) | X3 (min) | Extraction Yield (μg/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | ||||
| 1 | 0 (10:1) | 0 (40) | 0 (30) | 77.50 | 602.14 | 57.08 | 719.40 | 1201.25 |
| 2 | 0 (10:1) | 0 (40) | 0 (30) | 78.60 | 622.04 | 58.13 | 710.43 | 1197.92 |
| 3 | −1 (8:1) | −1 (30) | 0 (30) | 71.14 | 504.41 | 49.35 | 568.32 | 1063.07 |
| 4 | 0 (10:1) | −1 (30) | 1 (40) | 67.69 | 486.67 | 43.71 | 607.95 | 962.07 |
| 5 | 0 (10:1) | 1 (50) | 1 (40) | 68.32 | 491.35 | 46.65 | 584.90 | 1047.88 |
| 6 | −1 (8:1) | 0 (40) | −1 (20) | 73.31 | 578.83 | 53.12 | 644.78 | 1123.30 |
| 7 | 0 (10:1) | 0 (40) | 0 (30) | 80.40 | 606.05 | 56.97 | 705.52 | 1223.63 |
| 8 | 0 (10:1) | 1 (50) | −1 (20) | 66.69 | 486.54 | 44.66 | 580.04 | 936.22 |
| 9 | 0 (10:1) | 0 (40) | 0 (30) | 79.02 | 598.54 | 54.50 | 707.97 | 1236.01 |
| 10 | 0 (10:1) | −1 (30) | −1 (20) | 73.09 | 550.41 | 50.62 | 647.35 | 1142.50 |
| 11 | 0 (10:1) | 0 (40) | 0 (30) | 80.82 | 613.87 | 56.69 | 699.71 | 1205.63 |
| 12 | −1 (8:1) | 1 (50) | 0 (30) | 65.71 | 463.57 | 42.64 | 528.33 | 953.95 |
| 13 | −1 (8:1) | 0 (40) | 1 (40) | 70.13 | 504.98 | 48.51 | 585.49 | 1066.53 |
| 14 | 1 (12:1) | 0 (40) | 1 (40) | 68.98 | 490.85 | 45.46 | 543.04 | 964.98 |
| 15 | 1 (12:1) | 0 (40) | −1 (20) | 65.49 | 420.89 | 43.22 | 538.13 | 944.76 |
| 16 | 1 (12:1) | 1 (50) | 0 (30) | 65.91 | 409.79 | 41.04 | 490.77 | 895.90 |
| 17 | 1 (12:1) | −1 (30) | 0 (30) | 64.71 | 412.15 | 41.83 | 502.41 | 916.16 |
| Variables | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value a | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value a | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value a | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value a | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value a | |
| Model | 56.34 | 37.07 | <0.0001 | 9358.95 | 76.79 | <0.0001 | 62.52 | 35.71 | <0.0001 | 10,744.64 | 106.55 | <0.0001 | 25,878.04 | 94.97 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 28.88 | 19.00 | 0.0033 | 12,649.25 | 103.79 | <0.0001 | 60.89 | 34.78 | 0.0006 | 7973.95 | 79.08 | <0.0001 | 29,409.19 | 107.93 | <0.0001 |
| X2 | 12.50 | 8.22 | 0.0241 | 1310.46 | 10.75 | 0.0135 | 13.83 | 7.90 | 0.0261 | 2520.15 | 24.99 | 0.0016 | 7803.13 | 28.64 | 0.0011 |
| X3 | 1.50 | 0.98 | 0.3541 | 493.29 | 4.05 | 0.0841 | 6.64 | 3.79 | 0.0924 | 988.35 | 9.80 | 0.0166 | 1386.54 | 5.09 | 0.0387 |
| X1X2 | 10.99 | 7.23 | 0.0311 | 370.18 | 3.04 | 0.1249 | 8.76 | 5.00 | 0.0603 | 200.93 | 1.99 | 0.2009 | 1974.02 | 7.24 | 0.0310 |
| X1X3 | 11.12 | 7.32 | 0.0304 | 5170.33 | 42.42 | 0.0003 | 11.73 | 6.70 | 0.0360 | 1030.41 | 10.22 | 0.0151 | 1481.87 | 5.44 | 0.0325 |
| X2X3 | 12.36 | 8.13 | 0.0246 | 1174.78 | 9.64 | 0.0172 | 19.80 | 11.31 | 0.0120 | 489.74 | 4.86 | 0.0634 | 21,329.14 | 78.27 | <0.0001 |
| X12 | 148.33 | 97.59 | <0.0001 | 28,972.43 | 237.72 | <0.0001 | 146.36 | 83.60 | <0.0001 | 47,913.24 | 475.15 | <0.0001 | 67,320.92 | 247.06 | <0.0001 |
| X22 | 176.00 | 115.79 | <0.0001 | 25,680.27 | 210.70 | <0.0001 | 210.06 | 119.99 | <0.0001 | 26,594.34 | 263.73 | <0.0001 | 70,253.80 | 257.82 | <0.0001 |
| X32 | 62.58 | 41.17 | 0.0004 | 2999.17 | 24.61 | 0.0016 | 43.14 | 24.64 | 0.0016 | 2439.79 | 24.19 | 0.0017 | 15,950.65 | 58.54 | 0.0001 |
| Lack of fit | 1.1100 | 0.6000 | 0.6464 | 165.1100 | 1.8500 | 0.2793 | 1.7200 | 0.9700 | 0.4900 | 165.6600 | 3.1700 | 0.1470 | 281.7500 | 1.0600 | 0.4586 |
| R2 | 0.9794 | 0.9900 | 0.9787 | 0.9928 | 0.9919 | ||||||||||
| Adj R2 | 0.9530 | 0.9771 | 0.9513 | 0.9834 | 0.9814 | ||||||||||
| Solvent | Extraction Yields (μg/g) | Total (μg/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | ||
| Petroleum ether | 60.93 ± 0.70 a | 420.73 ± 0.45 a | 48.75 ± 1.43 a | 593.99 ± 3.36 a | 776.32 ± 12.46 a | 1900.72 ± 9.64 a |
| DES-7 | 79.27 ± 1.21 b | 608.53 ± 2.47 b | 56.67 ± 1.54 b | 708.61 ± 4.85 b | 1212.89 ± 15.96 b | 2665.97 ± 11.26 b |
| Increment (%) | 30.1 | 44.6 | 16.2 | 19.3 | 56.2 | 40.3 |
| Macroporous Resins | Yields (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | |
| AB-8 | 82.75 | 79.26 | 75.40 | 85.32 | 87.88 |
| DM-130 | 86.12 | 80.74 | 78.87 | 65.08 | 81.23 |
| D-101 | 78.38 | 81.86 | 72.41 | 76.33 | 86.04 |
| NKA | – a | – | – | 9.72 | 6.58 |
| HPD-100 | 90.31 | 87.69 | 85.62 | 90.48 | 92.25 |
| HP-20 | – | – | – | – | 69.41 |
| D4020 | 77.56 | – | 79.68 | – | – |
| DM-301 | 78.46 | 81.26 | 80.52 | 85.71 | 87.36 |
| Group | Cell Viability (%) | Compared Group | p | Compared Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 100 ± 0.10 | - | - | - | - |
| Model | 52.14 ± 1.44 | Normal | ** | - | - |
| Nimodipine | 87.98 ± 2.68 | Model | *** | - | - |
| DES–UAE (5 μg/mL) | 76.51 ± 2.10 | Model | *** | - | - |
| PE-UAE (5 μg/mL) | 68.38 ± 3.04 | Model | ** | DES–UAE (5 μg/mL) | * |
| DES-Heating (5 μg/mL) | 58.16 ± 1.66 | Model | ** | DES–UAE (5 μg/mL) | *** |
| DES-Heating + Stirring (5 μg/mL) | 62.16 ± 1.32 | Model | *** | DES–UAE (5 μg/mL) | ** |
| DES–UAE (10 μg/mL) | 82.84 ± 1.68 | Model | **** | - | - |
| PE-UAE (10 μg/mL) | 72.66 ± 1.87 | Model | *** | DES–UAE (10 μg/mL) | ** |
| DES-Heating (10 μg/mL) | 62.44 ± 1.72 | Model | ** | DES–UAE (10 μg/mL) | *** |
| DES-Heating + Stirring (10 μg/mL) | 68.75 ± 2.04 | Model | *** | DES–UAE (10 μg/mL) | *** |
| DES–UAE (20 μg/mL) | 90.67 ± 2.16 | Model | **** | - | - |
| PE-UAE (20 μg/mL) | 86.12 ± 1.96 | Model | **** | DES–UAE (20 μg/mL) | ns |
| DES-Heating (20 μg/mL) | 65.72 ± 1.88 | Model | *** | DES–UAE (20 μg/mL) | *** |
| DES-Heating + Stirring (20 μg/mL) | 74.89 ± 2.26 | Model | *** | DES–UAE (20 μg/mL) | *** |
| Group | NO Inhibition (%) | Compared Group | p | Compared Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-Name | 76.35 ± 0.86 | - | - | - | - |
| DES–UAE (5 μg/mL) | 50.46 ± 0.78 | L-Name | **** | - | - |
| PE-UAE (5 μg/mL) | 38.16 ± 1.06 | L-Name | **** | DES–UAE (5 μg/mL) | *** |
| DES-Heating (5 μg/mL) | 18.65 ± 1.62 | L-Name | **** | DES–UAE (5 μg/mL) | *** |
| DES-Heating + Stirring (5 μg/mL) | 28.66 ± 1.25 | L-Name | **** | DES–UAE (5 μg/mL) | **** |
| DES–UAE (10 μg/mL) | 52.68 ± 1.39 | L-Name | *** | - | - |
| PE-UAE (10 μg/mL) | 41.55 ± 1.46 | L-Name | *** | DES–UAE (10 μg/mL) | *** |
| DES-Heating (10 μg/mL) | 19.86 ± 1.53 | L-Name | **** | DES–UAE (10 μg/mL) | **** |
| DES-Heating + Stirring (10 μg/mL) | 30.58 ± 0.96 | L-Name | **** | DES–UAE (10 μg/mL) | **** |
| DES–UAE (20 μg/mL) | 55.73 ± 1.66 | L-Name | ** | - | - |
| PE-UAE (20 μg/mL) | 43.81 ± 1.96 | L-Name | *** | DES–UAE (20 μg/mL) | ** |
| DES-Heating (20 μg/mL) | 21.33 ± 1.71 | L-Name | **** | DES–UAE (20 μg/mL) | **** |
| DES-Heating + Stirring (20 μg/mL) | 32.06 ± 1.64 | L-Name | *** | DES–UAE (20 μg/mL) | **** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Li, Z.; Men, L.; Li, J.; Gong, X. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Strategy for Simultaneous Extraction of Five Macamides from Lepidium meyenii Walp and In Vitro Bioactivities. Foods 2023, 12, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020248
Li K, Li Z, Men L, Li J, Gong X. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Strategy for Simultaneous Extraction of Five Macamides from Lepidium meyenii Walp and In Vitro Bioactivities. Foods. 2023; 12(2):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020248
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Keke, Zhongyu Li, Lei Men, Jiwen Li, and Xiaojie Gong. 2023. "Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Strategy for Simultaneous Extraction of Five Macamides from Lepidium meyenii Walp and In Vitro Bioactivities" Foods 12, no. 2: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020248
APA StyleLi, K., Li, Z., Men, L., Li, J., & Gong, X. (2023). Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Strategy for Simultaneous Extraction of Five Macamides from Lepidium meyenii Walp and In Vitro Bioactivities. Foods, 12(2), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020248