Non-Thermal Plasma Decontamination Using a Multi-Hollow Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge: Impact of Food Matrix Composition on Bactericidal Efficacy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Supplemented Agar Media Preparation
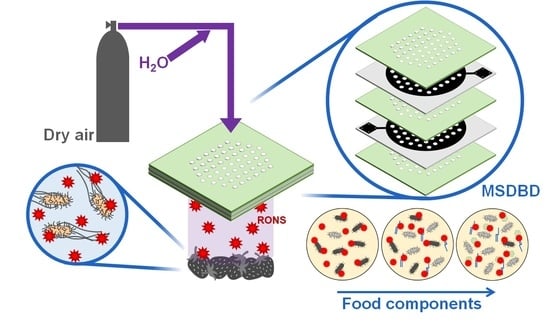
2.2. Plasma Treatment
2.3. Strain Preparation
2.4. Sample Handling
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Characterization
3.2. NTP Inactivation with Dry and Humid Air Plasma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knorr, D.; Watzke, H. Food Processing at a Crossroad. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alzamora, S.M.; López-Malo, A.; Tapia, M.S.; Welti-Chanes, J. Minimally Processed Foods. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Academic Press: Kidlington, Oxford, UK, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 767–771. ISBN 9780123849533. [Google Scholar]
- Barba, F.J.; Orlien, V.; Mota, M.J.; Lopes, R.P.; Pereira, S.A.; Saraiva, J.A. Implementation of Emerging Technologies. In Innovation Strategies in the Food Industry; Academic Press: Kidlington, Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 121–143. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, H.B.; Annapure, U.S.; Deshmukh, R.R. Non-Thermal Technologies for Food Processing. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khouryieh, H.A. Novel and Emerging Technologies Used by the U.S. Food Processing Industry. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 67, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COST Action CA19110 (PlAgri). WG5 Technical Roadmap—Key Food Applications and Standardized Procedures. 2022. Available online: https://plagri.eu/wg5-applications-of-plasma-processes-and-technologies-in-food-industry/ (accessed on 2 December 2022).
- Surowsky, B.; Schlüter, O.; Knorr, D. Interactions of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma with Solid and Liquid Food Systems: A Review. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 7, 82–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. Oscillations in Ionized Gases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1928, 14, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourke, P.; Ziuzina, D.; Boehm, D.; Cullen, P.J.; Keener, K. The Potential of Cold Plasma for Safe and Sustainable Food Production. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitehead, J.C. Plasma-Catalysis: The Known Knowns, the Known Unknowns and the Unknown Unknowns. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 243001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, A. Introduction to Theoretical and Applied Plasma Chemistry. In Plasma Chemistry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, N.N.; Ziuzina, D.; Cullen, P.J.; Keener, K.M. Characterization of a Novel Cold Atmospheric Air Plasma System for Treatment of Packaged Liquid Food Products; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2012; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, J.C. The Chemistry of Cold Plasma. In Cold Plasma in Food and Agriculture: Fundamentals and Applications; Misra, N.N., Schlüter, O., Cullen, P.J., Eds.; Academic Press, 2016; pp. 53–81. ISBN 9780128013656. [Google Scholar]
- von Woedtke, T.; Reuter, S.; Masur, K.; Weltmann, K.D. Plasmas for Medicine. Phys Rep 2013, 530, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, H.; Hinton, A.; Zhang, J. Influence of In-Package Cold Plasma Treatment on Microbiological Shelf Life and Appearance of Fresh Chicken Breast Fillets. Food Microbiol 2016, 60, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowsky, B.; Bußler, S.; Schlüter, O.K. Cold Plasma Interactions With Food Constituents in Liquid and Solid Food Matrices. In Cold Plasma in Food and Agriculture: Fundamentals and Applications; Misra, N.N., Schlüter, O., Cullen, P.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Kidlington, Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 179–203. ISBN 9780128013656. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Yun, H.-S.; Eom, S.-H.; Sung, B.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Jeon, S.-M.; Chin, S.-W.; Lee, M.-S. Bactericidal Action Mechanism of Nonthermal Plasma: Denaturation of Membrane Proteins. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2018, 2, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Jo, C. Applications of Cold Plasma Technology for Microbiological Safety in Meat Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 64, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleugels, M.; Shama, G.; Deng, X.T.; Greenacre, E.; Brocklehurst, T.; Kong, M.G. Atmospheric Plasma Inactivation of Biofilm-Forming Bacteria for Food Safety Control. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2005, 33, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, S.; Feichtinger, J.; Hertel, C. Characterization of Bacillus Subtilis Spore Inactivation in Low-Pressure, Low-Temperature Gas Plasma Sterilization Processes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baerdemaeker, K.; van der Linden, I.; Nikiforov, A.; Zuber, S.; de Geyter, N.; Devlieghere, F. Non-Thermal Plasma Inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium on Different Matrices and the Effect of Selected Food Components on Its Bactericidal Efficacy. Food Res. Int. 2022, 151, 110866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.M.; Chen, C.K.; Hsu, C.L. Non-Thermal Atmospheric Gas Plasma for Decontamination of Sliced Cheese and Changes in Quality. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2020, 26, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-Y.; Song, W.-J.; Eom, S.; Kim, S.B.; Kang, D.-H. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Cold Plasma Treatment against Food-Borne Pathogens on Various Foods. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 204003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuzina, D.; Han, L.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Cold Plasma Inactivation of Internalised Bacteria and Biofilms for Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium, Listeria Monocytogenes and Escherichia Coli. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 210, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, N.; Yagyu, Y. Treatment of Protein Using Oxygen Plasma Produced by RF Discharge. Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 33, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarangapani, C.; Ryan Keogh, D.; Dunne, J.; Bourke, P.; Cullen, P.J. Characterisation of Cold Plasma Treated Beef and Dairy Lipids Using Spectroscopic and Chromatographic Methods. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gross, K.C.; Wang, Y.; Saltveit, M. The Commercial Storage of Fruits, Vegetables, and Florist and Nursery Stocks; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; Volume 66. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, M.Y.; Dar, T.A.; Rajendrakumar Singh, L. Casein Proteins: Structural and Functional Aspects. In Milk Proteins—From Structure to Biological Properties and Health Aspects; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunstone, F.D.; Harwood, J.L.; Dijkstra, A.J. The Lipid Handbook with CD-ROM, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera, C.S.; Dardanelli, J.L. Water Deficit Modulates the Relationship between Temperature and Unsaturated Fatty Acid Profile in Soybean Seed Oil. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 3179–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obando, M.; Soto, E.; de Meulenaer, B. Influence of Oxidized Oils on Digestibility of Caseins in O/W Emulsions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1700331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, C.; Yoon, J. Kinetics and Mechanisms of DMSO (Dimethylsulfoxide) Degradation by UV/H2O2 Process. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekárek, S. Non-Thermal Plasma Ozone Generation. Acta Polytech. 2003, 43, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Moiseev, T.; Misra, N.N.; Cullen, P.J.; Mosnier, J.P.; Keener, K.M.; Bourke, P. Influence of High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma Process Parameters and Role of Relative Humidity on Inactivation of Bacillus Atrophaeus Spores inside a Sealed Package. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 88, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquali, F.; Stratakos, A.C.; Koidis, A.; Berardinelli, A.; Cevoli, C.; Ragni, L.; Mancusi, R.; Manfreda, G.; Trevisani, M. Atmospheric Cold Plasma Process for Vegetable Leaf Decontamination: A Feasibility Study on Radicchio (Red Chicory, Cichorium Intybus L.). Food Control 2016, 60, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmons, C.; Pai, K.; Jacob, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, L.M. Inactivation of Salmonella Enterica, Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli, and Listeria Monocytogenes by a Novel Surface Discharge Cold Plasma Design. Food Control 2018, 84, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuzina, D.; Misra, N.N.; Han, L.; Cullen, P.J.; Moiseev, T.; Mosnier, J.P.; Keener, K.; Gaston, E.; Vilaró, I.; Bourke, P. Investigation of a Large Gap Cold Plasma Reactor for Continuous In-Package Decontamination of Fresh Strawberries and Spinach. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 59, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.I.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.; Alahakoon, A.U.; Kim, K.; Choe, W.; Jo, C. Evaluation of Pathogen Inactivation on Sliced Cheese Induced by Encapsulated Atmospheric Pressure Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critzer, F.J.; Kelly-Wintenberg, K.; South, S.L.; Golden, D.A. Atmospheric Plasma Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens on Fresh Produce Surfaces. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F. On the Action of Ozone on Proteins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 82, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Klebach, M.; Visser, M.; Hofman, Z. Amino Acid Availability of a Dairy and Vegetable Protein Blend Compared to Single Casein, Whey, Soy, and Pea Proteins: A Double-Blind, Cross-over Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, F.C. Mechanisms of Nitric Oxide-Related Antimicrobial Activity. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2818–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kikugawa, K.; Kato, T.; Okamoto, Y. Damage of Amino Acids and Proteins Induced by Nitrogen Dioxide, a Free Radical Toxin, in Air. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 16, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.; Vanier, N.L.; Moomand, K.; Pinto, V.Z.; Colussi, R.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Ozone Oxidation of Cassava Starch in Aqueous Solution at Different PH. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lii, C.; Liao, C.-D.; Stobinski, L.; Tomasik, P. Effect of Corona Discharges on Granular Starches. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2003, 1, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Thirumdas, R.; Kadam, D.; Annapure, U.S. Cold Plasma: An Alternative Technology for the Starch Modification. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, P.; Pu, H.; Zhang, B.; Su, J.; Chen, L.; Li, X. Structural Characteristics and Rheological Properties of Plasma-Treated Starch. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 34, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsagonsup, R.; Deeyai, P.; Chaiwat, W.; Horrungsiwat, S.; Leejariensuk, K.; Suphantharika, M.; Fuongfuchat, A.; Dangtip, S. Modification of Tapioca Starch by Non-Chemical Route Using Jet Atmospheric Argon Plasma. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xiong, S.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Xie, F.; Chen, L. Effect of Oxygen Glow Plasma on Supramolecular and Molecular Structures of Starch and Related Mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 37, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morent, R.; de Geyter, N.; Gengembre, L.; Leys, C.; Payen, E.; van Vlierberghe, S.; Schacht, E. Surface Treatment of a Polypropylene Film with a Nitrogen DBD at Medium Pressure. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys 2008, 43, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, R.W. The Action of Nitrogen Dioxide on Corn Starch and Its Fractions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanha, N.; Miano, A.C.; Jones, O.G.; Reuhs, B.L.; Campanella, O.H.; Augusto, P.E.D. Starch Modification by Ozone: Correlating Molecular Structure and Gel Properties in Different Starch Sources. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gunn, C.; Beckman, J.S. Bactericidal Activity of Peroxynitrite. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 298, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, P.; Sager, B.; Fa, A.; Liang, T.; Lozano, C.; Khazzam, M. Bactericidal Efficacy of Hydrogen Peroxide on Cutibacterium Acne. Bone Jt. Res. 2019, 8, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Prasad, K.; Fang, Z.; Speight, R.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Activated Water as a Prospective Disinfectant: The Crucial Role of Peroxynitrite. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5276–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.; Wenske, S.; Lackmann, J.W.; Lalk, M.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K. On the Liquid Chemistry of the Reactive Nitrogen Species Peroxynitrite and Nitrogen Dioxide Generated by Physical Plasmas. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.D.R.; Helbig, E.; de Moura, F.A.; Vargas, C.G.; Ciacco, C.F. Oxidation of Fermented Cassava Starch Using Hydrogen Peroxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Park, H.; Kim, P.; Jiang, Y.; Costello, C.E. Surface Oxidation under Ambient Air-Not Only a Fast and Economical Method to Identify Double Bond Positions in Unsaturated Lipids but Also a Reminder of Proper Lipid Processing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5697–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.J.; Silva, J.L.; Chamul, R.S.; Chen, T.C. Influence of Ozone, Hydrogen Peroxide, or Salt on Microbial Profile, TBARs and Color of Channel Catfish Fillets. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, W.A.; Lightsey, J.W. Mechanisms of Nitrogen Dioxide Reactions: Initiation of Lipid Peroxidation and the Production of Nitrous Acid. Science 1981, 214, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, N.; Kalyanaraman, B. Nitric Oxide and Lipid Peroxidation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1411, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rød, S.K.; Hansen, F.; Leipold, F.; Knøchel, S. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment of Ready-to-Eat Meat: Inactivation of Listeria Innocua and Changes in Product Quality. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niki, E.; Abe, K. CHAPTER 1. Vitamin E: Structure, Properties and Functions. In Food Chemistry, Function and Analysis No. 11; Royal Society of Chemistry: Croydon, UK, 2019; pp. 1–11. ISBN 978-1-78801-240-9. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.G.; Cooper, M.; Yost, A.; Paff, M.; Ercan, U.K.; Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Brooks, A.D. Nonthermal Dielectric-Barrier Discharge Plasma-Induced Inactivation Involves Oxidative DNA Damage and Membrane Lipid Peroxidation in Escherichia Coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benevides, C.M.D.J.; Veloso, M.C.D.C.; de Paula Pereira, P.A.; de Andrade, J.B. A Chemical Study of β-Carotene Oxidation by Ozone in an Organic Model System and the Identification of the Resulting Products. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Loh, T.-P. Catalytic and Direct Methyl Sulfonylation of Alkenes and Alkynes Using a Methyl Sul-fonyl Radical Generated from a DMSO, Dioxygen and Copper System. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4939–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, V.; Zanardi, I.; Travagli, V. Answer on Letter to Professor E. I. Nazarov (from Velio Bocci). Available online: http://ozonetherapy.org/answer-bocci-nazarov/ (accessed on 2 December 2022).
- Bocci, V.; Zanardi, I.; Travagli, V. Oxygen/Ozone as a Medical Gas Mixture. A Critical Evaluation of the Various Methods Clarifies Positive and Negative Aspects. Med. Gas Res. 2011, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, M.H.; Hong, Y.J.; Attri, P.; Sim, G.B.; Lee, G.J.; Panngom, K.; Kwon, G.C.; Choi, E.H.; Uhm, H.S.; Park, G. Analysis of the Antimicrobial Effects of Nonthermal Plasma on Fungal Spores in Ionic Solutions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Low Conc. 1 | Middle Conc. 1 | High Conc. 1 | Additional Chemicals 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | ||||
| Casein hydrolysate | 2.6 | 5.1 | 7.1 ± 0.2 | HCl and NaOH |
| Carbohydrates | ||||
| Glucose | 2.0 | 10.0 | 18.0 | - |
| Starch | 2.0 | 10.0 | 18.0 | - |
| Lipids 3 | ||||
| Stripped soybean oil | 4.5 | 21.0 | 37.5 | Tween 20 (2.0 m%) |
| Refined soybean oil | 4.6 | 21.7 | 38.7 | Tween 20 (2.0 m%) |
| Salt | ||||
| NaCl | 0.1 | 1.6 | 3.0 | - |
| Anti-oxidants | ||||
| β-carotene | 0.1 | 3.6 | 7.0 | DMSO (5.8 v/m%) and Tween 20 (1.2 v/m%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Baerdemaeker, K.; Van Reepingen, A.; Nikiforov, A.; De Meulenaer, B.; De Geyter, N.; Devlieghere, F. Non-Thermal Plasma Decontamination Using a Multi-Hollow Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge: Impact of Food Matrix Composition on Bactericidal Efficacy. Foods 2023, 12, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020386
De Baerdemaeker K, Van Reepingen A, Nikiforov A, De Meulenaer B, De Geyter N, Devlieghere F. Non-Thermal Plasma Decontamination Using a Multi-Hollow Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge: Impact of Food Matrix Composition on Bactericidal Efficacy. Foods. 2023; 12(2):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020386
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Baerdemaeker, Klaas, Amber Van Reepingen, Anton Nikiforov, Bruno De Meulenaer, Nathalie De Geyter, and Frank Devlieghere. 2023. "Non-Thermal Plasma Decontamination Using a Multi-Hollow Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge: Impact of Food Matrix Composition on Bactericidal Efficacy" Foods 12, no. 2: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020386
APA StyleDe Baerdemaeker, K., Van Reepingen, A., Nikiforov, A., De Meulenaer, B., De Geyter, N., & Devlieghere, F. (2023). Non-Thermal Plasma Decontamination Using a Multi-Hollow Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge: Impact of Food Matrix Composition on Bactericidal Efficacy. Foods, 12(2), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020386