Identification of Illicit Conservation Treatments in Fresh Fish by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Chemometric Methods
Abstract
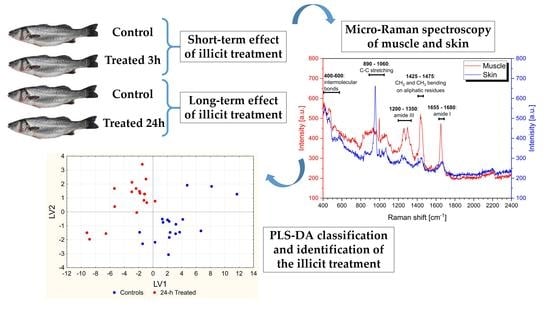
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Study Design and Sample Preparation
2.3. Micro-Raman Spectroscopy
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.4.2. Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
- (1)
- Short-term effects of the treatment on muscle: the dataset consisted in micro-Raman spectra collected on muscle from six control fish and six 3 h-treated fish (6 fish × 3 replicates = 18 control measurements; 6 fish × 3 replicates = 18 treated measurements).
- (2)
- Long-term effects of the treatment on muscle: the dataset consisted of micro-Raman spectra collected on muscle from six control fish and six 24 h-treated fish (6 fish × 3 replicates = 18 control measurements; 6 fish × 3 replicates = 18 treated measurements).
- (3)
- Short-term effects of the treatment on skin: the same as in (1) but spectra were collected on the skin samples;
- (4)
- Long-term effects of the treatment on skin: the same as in (2) but spectra were collected on the skin samples.
2.5. Software
3. Results
3.1. Micro-Raman Spectroscopy
3.2. PCA on the Overall Dataset
3.3. Classification Models
3.3.1. Muscle—Short-Term and Long-Term Treatment Effects
3.3.2. Skin—Short-Term and Long-Term Treatment Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; 244p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, A. Overview of Food Fraud in the Fisheries Sector; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Donlan, C.J.; Luque, G.M. Exploring the Causes of Seafood Fraud: A Meta-Analysis on Mislabeling and Price. Mar. Policy 2019, 100, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, A.; Malloggi, C.; Tinacci, L.; Nucera, D.; Armani, A. Mislabeling in Seafood Products Sold on the Italian Market: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Control 2023, 145, 109395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RASFF The Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed—Annual Report 2020; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021.
- Howes, B.D.; Milazzo, L.; Droghetti, E.; Nocentini, M.; Smulevich, G. Addition of Sodium Ascorbate to Extend the Shelf-Life of Tuna Meat Fish: A Risk or a Benefit for Consumers? J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 200, 110813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manimaran, U.; Shakila, R.J.; Shalini, R.; Sivaraman, B.; Sumathi, G.; Selvaganapathi, R.; Jeyasekaran, G. Effect of Additives in the Shelflife Extension of Chilled and Frozen Stored Indian Octopus (Cistopus indicus). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 53, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bisenius, S.; Ludmann, M.; Neuhaus, H.; Effkemann, S.; Heemken, O.; Bartelt, E.; Haunhorst, E.; Kehrenberg, C. The Impact of Food Additives on the Chemical Composition in Cod (Gadus morhua): A Comparative Study. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2019, 14, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiri, H.; Haghparast, S.; Shabanpour, B. Effects of Sodium Salt Solutions (Sodium Acetate, Lactate and Citrate) on Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Persian Sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) Fillets under Refrigerated Storage. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 13, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Food Fraud: What Does It Mean? Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/safety/agri-food-fraud/food-fraud-what-does-it-mean_it (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Gussow, K.E.; Mariët, A. The Scope of Food Fraud Revisited 1 3. Crime Law Soc. Change 2022, 78, 621–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration Federal Register: Economically Motivated Adulteration; Public Meeting; Request for Comment. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2009/04/06/E9-7843/economically-motivated-adulteration-public-meeting-request-for-comment (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Bozzetta, E.; Pezzolato, M.; Cencetti, E.; Varello, K.; Abramo, F.; Mutinelli, F.; Ingravalle, F.; Teneggi, E. Histology as a Valid and Reliable Tool to Differentiate Fresh from Frozen-Thawed Fish. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, R.; di Cesare, F.; Longo, F.; Abballe, F.; Panseri, S.; Bonanni, R.C.; Baccelliere, R.; Neri, B.; Chiesa, L.M. Undeclared (Poly)Phosphates Detection in Food of Animal Origin as a Potential Tool toward Fraud Prevention. Foods 2021, 10, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Koo, Y.J.; Lee, M.; Pack, E.C.; Jang, D.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, K.M.; Choi, D.W. An Optimised Method for the Rapid Analysis of Condensed Phosphates in Fishery and Processed Marine Food Products Using Ion Chromatography and Microwave Sample Processing. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 37, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.; Elliott, C.; Huisman, W.; Dean, M.; van Ruth, S. The 11 Sins of Seafood: Assessing a Decade of Food Fraud Reports in the Global Supply Chain. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3746–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hungerford, J.M. Scombroid Poisoning: A Review. Toxicon 2010, 56, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Parliament Parliamentary Question|Answer to Question No E-002605/16|E-002605/2016(ASW)|European Parliament. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/E-8-2016-002605-ASW_EN.html#ref2 (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Tepedino, V.; Ferri, M. Additivi Nel Pesce: Rispondono i Veterinari; Eurofishmarket: Bologna, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Piscopo, A. Additivi e Coadiuvanti. Utilizzo Di Cafodos, Perossido Di Idrogeno, e Di Cloro Nei Prodotti Della Pesca. Il Pesce 2010, 6, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Himonides, A.T.; Taylor, A.; Knowles, M.J. The Improved Whitening of Cod and Haddock Flaps Using Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.; Alves, V.R.; Pérez, S.O.; Ferreira, M.; Daguer, H.; de Oliveira, M.A.L.; Micke, G.A.; Vitali, L. Rapid Method for the Determination of Citrate, Phosphate and Sulfite in Seafood by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, B.; Vieira, H.; Lourenço, H.; Gonçalves, S.; Martins, M.F.; Mendes, R. Control of Phosphate Levels in Seafood Products from the Portuguese Market: Is There a Need for Concern? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 62, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, P.K.; Vatsa, S.; Srivastav, P.P.; Pathak, S.S. A Comprehensive Review on Freshness of Fish and Assessment: Analytical Methods and Recent Innovations. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bello, F.; Aigotti, R.; Zorzi, M.; Giaccone, V.; Medana, C. Multi-Analyte MS Based Investigation in Relation to the Illicit Treatment of Fish Products with Hydrogen Peroxide. Toxics 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Currò, S.; Fasolato, L.; Serva, L.; Boffo, L.; Ferlito, J.C.; Novelli, E.; Balzan, S. Use of a Portable Near-Infrared Tool for Rapid on-Site Inspection of Freezing and Hydrogen Peroxide Treatment of Cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis). Food Control 2022, 132, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, I.; Semeraro, A.; Scalise, F.; Calderari, I.; Stacchini, P. European official control of food: Determination of histamine in fish products by a HPLC–UV-DAD method. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaut, A.; Duthen, S.; Grard, T.; Krzewinski, F.; N’Guessan, A.; Brisabois, A.; Duflos, G. Development of an SPME-GC-MS method for the specific quantification of dimethylamine and trimethylamine: Use of a new ratio for the freshness monitoring of cod fillets. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3787–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, J.; Medina, I.; Bianchi, F.; Careri, M.; Mangia, A.; Musci, M. Study of the volatile compounds useful for the characterisation of fresh and frozen-thawed cultured gilthead sea bream fish by solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velioğlu, H.M.; Temiz, H.T.; Boyaci, I.H. Differentiation of Fresh and Frozen-Thawed Fish Samples Using Raman Spectroscopy Coupled with Chemometric Analysis. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhong, P.; Jiang, A.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lei, H. Raman Spectroscopy Coupled with Chemometrics for Food Authentication: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Tian, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Geng, X.; Wang, K.; Du, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, H. Rapid Identification of Fish Species by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Raman Spectroscopy Coupled with Machine Learning Methods. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallouchos, A.; Mikrou, T.; Gardeli, C. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolite Profiling for the Assessment of Freshness in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Foods 2020, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trocino, A.; Xiccato, G.; Majolini, D.; Tazzoli, M.; Bertotto, D.; Pascoli, F.; Palazzi, R. Assessing the Quality of Organic and Conventionally-Farmed European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Food Chem. 2012, 131, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, F.; Giraudo, A.; Cavallini, N.; Esposito, G.; Merlo, G.; Geobaldo, F.; Acutis, P.L.; Pezzolato, M.; Savorani, F.; Bozzetta, E. Differentiation between Fresh and Thawed Cephalopods Using NIR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Data Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallini, N.; Pennisi, F.; Giraudo, A.; Pezzolato, M.; Esposito, G.; Gavoci, G.; Magnani, L.; Pianezzola, A.; Geobaldo, F.; Savorani, F.; et al. Chemometric Differentiation of Sole and Plaice Fish Fillets Using Three Near-Infrared Instruments. Foods 2022, 11, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połomska, M.; Kubisz, L.; Wolak, J.; Hojan-Jezierska, D. Effects of Temperature on the FT NIR Raman Spectra of Fish Skin Collagen. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Ma, J.; Zhong, N. Raman spectroscopy combined with support vector regression and variable selection method for accurately predicting salmon fillets storage time. Optik 2021, 247, 167879. [Google Scholar]
- Wenyang, Z.; Ma, J.; Sun, D.-W. Raman spectroscopic techniques for detecting structure and quality of frozen foods: Principles and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2623–2639. [Google Scholar]
- Rabia, A.; Alansari, W.S.; Shamlan, G.; Eskandrani, A.A.; Howell, N.K. An investigation of green tea’s effect on mackerel (Scomber scombrus)’s protein structure during frozen storage by FT-Raman spectroscopy. Kuwait J. Sci. 2021, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.M. Raman spectroscopy a promising technique for quality assessment of meat and fish: A review. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuka, K.; Mayer, S.G.; Park, J.W. FT-IR and Raman spectroscopies determine structural changes of tilapia fish protein isolate and surimi under different comminution conditions. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero, A.M.; Carmona, P.; Careche, M. Raman spectroscopic study of structural changes in hake (Merluccius merluccius L.) muscle proteins during frozen storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunyaboon, S.; Thumanu, K.; Park, J.W.; Khongla, C.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Evaluation of lipid oxidation, volatile compounds and vibrational spectroscopy of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) during ice storage as related to the quality of its washed mince. Foods 2021, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiramis, S.; Howell, N.K. The effects of freeze-drying and storage on the FT-Raman spectra of Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) and horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt, B.J.; Wold, J.P. Raman analysis of fish: A potential method for rapid quality screening. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rašković, B.; Heinke, R.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. The potential of Raman spectroscopy for the classification of fish fillets. Food Anal. Met. 2016, 9, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunyaboon, S.; Thumanu, K.; Park, J.W.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Vibrational spectroscopy and biochemical changes in silver carp as related to quality of washed mince. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Tang, H.; Zou, X.; Meng, G.; Wu, N. Raman spectroscopy for food quality assurance and safety monitoring: A review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xu, W.; Qu, M.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Cheng, F. Recent advances in the application of Raman spectroscopy for fish quality and safety analysis. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3647–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, J.D.; Torley, P.J.; Blanch, E.W. Detection of biomarkers relating to quality and differentiation of some commercially significant whole fish using spatially off-set Raman spectroscopy. Molecules 2020, 25, 3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, T.; Xiang, C.; Xu, X.; Tian, X. Rapid identification of rainbow trout adulteration in Atlantic salmon by Raman spectroscopy combined with machine learning. Molecules 2019, 24, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, J.; Li, Z.; Cai, S. Freshness assessment of intact fish via 2D 1H J-resolved NMR spectroscopy combined with pattern recognition methods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xiang, W.; Fan, H.; Xie, J.; Qian, Y.-F. Study on the mobility of water and its correlation with the spoilage process of salmon (Salmo solar) stored at 0 and 4 °C by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF NMR 1H). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 55, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.S.; Flores, I.S.; Ferri, P.H.; Lião, L.M. NMR Approach for Monitoring Caranha Fish Meat Alterations due to the Freezing-Thawing Cycles. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 2330–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Xiao, L.; Sun, X.; Xie, J. Evaluation of quality changes in big-eye tuna (Thunnus obesus) based on near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) and low field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR). J. Food Proc. Eng. 2021, 44, e13613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tang, M.; Dai, H.; Feng, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Dominating roles of protein conformation and water migration in fish muscle quality: The effect of freshness and heating process. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Chu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xie, J. Quality of frozen mackerel during storage as processed by different freezing methods. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A.; Pezzolato, M.; Robotti, E.; Biasibetti, E.; Poirier, A.; Dervilly, G.; Le Bizec, B.; Marengo, E.; Bozzetta, E. Profiling of transcriptional biomarkers in FFPE liver samples: PLS-DA applications for detection of illicit administration of sex steroids and clenbuterol in veal calves. Food Control. 2021, 128, 108149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V. Classification tools in chemistry. Part 1: Linear models. PLS-DA. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.M. Raman Spectroscopy for Monitoring Protein Structure in Muscle Food Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Colaianni, S.E.M.; Nielsen, O.F. Low-frequency Raman spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struc. 1995, 347, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Kitano, H. The structure of water in polymer systems as revealed by Raman spectroscopy. Spectroc. Acta Part A 1995, 51, 2433–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badii, F.; Howell, N.K. Effect of antioxidants, citrate, and cryoprotectants on protein denaturation and texture of frozen cod (Gadus morhua). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Raw Data | First Derivative | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° Variables | N° LV | %Acc | NER% | N° Variables | N° LV | %Acc | NER% | ||
| Muscle Short Term | Fitting | 38 | 10 | 86.11 | 86.11 | 61 | 5 | 100 | 100 |
| Cross-validation | 83.33 | 83.33 | 100 | 100 | |||||
| Muscle Long Term | Fitting | 558 | 6 | 100 | 100 | 314 | 1 | 100 | 100 |
| Cross-validation | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||
| Skin Short Term | Fitting | 470 | 7 | 100 | 100 | 273 | 2 | 100 | 100 |
| Cross-validation | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||
| Skin Long Term | Fitting | 294 | 7 | 100 | 100 | 108 | 3 | 100 | 100 |
| Cross-validation | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robotti, E.; Belay, M.H.; Calà, E.; Benedetto, A.; Cerruti, S.; Pezzolato, M.; Pennisi, F.; Abete, M.C.; Marengo, E.; Brizio, P. Identification of Illicit Conservation Treatments in Fresh Fish by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Chemometric Methods. Foods 2023, 12, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030449
Robotti E, Belay MH, Calà E, Benedetto A, Cerruti S, Pezzolato M, Pennisi F, Abete MC, Marengo E, Brizio P. Identification of Illicit Conservation Treatments in Fresh Fish by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Chemometric Methods. Foods. 2023; 12(3):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030449
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobotti, Elisa, Masho Hilawie Belay, Elisa Calà, Alessandro Benedetto, Simone Cerruti, Marzia Pezzolato, Francesco Pennisi, Maria Cesarina Abete, Emilio Marengo, and Paola Brizio. 2023. "Identification of Illicit Conservation Treatments in Fresh Fish by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Chemometric Methods" Foods 12, no. 3: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030449
APA StyleRobotti, E., Belay, M. H., Calà, E., Benedetto, A., Cerruti, S., Pezzolato, M., Pennisi, F., Abete, M. C., Marengo, E., & Brizio, P. (2023). Identification of Illicit Conservation Treatments in Fresh Fish by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Chemometric Methods. Foods, 12(3), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030449