Determination of Heavy Metal Ions in Infant Milk Powder Using a Nanoporous Carbon Modified Disposable Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Preparation of the SPE/NPC
2.4. Real Sample Preparations
2.5. Electrochemical Detection of Pb(II) and Cd(II)
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of NPC
3.2. Electrochemical Characterizations of the SPE/NPC
3.3. Parameter Optimization
3.4. Electrochemical Determination of Pb(II) and Cd(II)
3.5. Reproducibility, Stability, and Anti-Interference Performance of the SPE/NPC
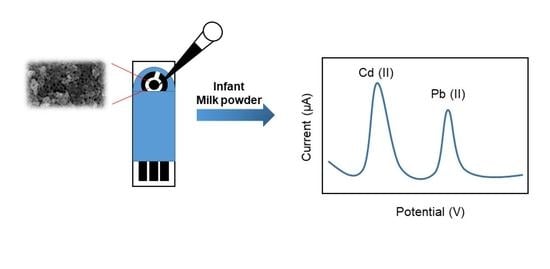
3.6. Real Samples Application
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sawan, S.; Maalouf, R.; Errachid, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in the voltammetric detection of heavy metals: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 106492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. Recent advances in nanomaterial-enabled screen-printed electrochemical sensors for heavy metal detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 115, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, N.; Su, C.; Wang, J.; Soyeurt, H. Relationships between Pb, As, Cr, and Cd in individual cows’ milk and milk composition and heavy metal contents in water, silage, and soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, J.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y. Determination of trace heavy metals in milk using an ionic liquid and bismuth oxide nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudebbouz, A.; Boudalia, S.; Bousbia, A.; Habila, S.; Boussadia, M.I.; Gueroui, Y. Heavy metals levels in raw cow milk and health risk assessment across the globe: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.M.; Raghunath, R.; Sastry, V.N.; Krishnamoorthy, T.M. Daily intake of heavy metals by infants through milk and milk products. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 227, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, C.S.; Arruda, A.F.; Da Cunha, L.R.; SouzaDe, J.R.; Braga, J.W.; Dorea, J.G. Toxic metals (Pb and Cd) and their respective antagonists (Ca and Zn) in infant formulas and milk marketed in Brasilia, Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 4062–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pan, D.; Zhu, R. Quantitative assessment on soil concentration of heavy metal-contaminated soil with various sample pretreatment techniques and detection methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, M. Recent developments of heavy metals detection in traditional Chinese medicine by atomic spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, F.; Palleschi, G. Screening and confirmatory methods for the detection of heavy metals in foods. In Persistent Organic Pollutants and Toxic Metals in Foods; Woodhead Publishing: Roma Tor Vergata, Italy, 2013; pp. 81–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, H.; He, M.; Hu, B. Facile Chip-Based Array Monolithic Microextraction System Online Coupled with ICPMS for Fast Analysis of Trace Heavy Metals in Biological Samples. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6878–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, B.; He, M.; Wang, H.; Tian, S.; Hu, B. Facile Design of Phase Separation for Microfluidic Droplet-Based Liquid Phase Microextraction as a Front End to Electrothermal Vaporization-ICPMS for the Analysis of Trace Metals in Cells. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10078–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burakham, R.; Srijaranai, S.; Grudpan, K. High-performance liquid chromatography with sequential injection for online precolumn derivatization of some heavy metals. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 2614–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F. Antibody developments for metal ions and their applications. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 1079–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Shu, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Fu, Z. An ultra-facile and label-free immunoassay strategy for detection of copper (II) utilizing chemiluminescence self-enhancement of Cu (II)-ethylenediaminetetraacetate chelate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Terakado, S.; Sasaki, K.; Aota, A.; Matsumoto, N.; Shiku, H.; Ino, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Matsue, T.; Ohmura, N. Microfluidic heavy metal immunoassay based on absorbance measurement. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 33, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compagnone, D.; Lupu, A.S.; Ciucu, A.; Magearu, V.; Cremisini, C.; Palleschi, G. Fast Amperometric Fia Procedure for Heavy Metal Detection Using Enzyme Inhibition. Anal. Lett. 2001, 34, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachan Upadhyay, L.S.; Verma, N. Enzyme Inhibition Based Biosensors: A Review. Anal. Lett. 2013, 46, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y. A ratiometric electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of multiple heavy metal ions based on ferrocene-functionalized metal-organic framework. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 310, 127756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Peng, X.; Fu, H.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Recent advances in the development of electrochemical aptasensors for detection of heavy metals in food. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 147, 111777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantao, L.; Diming, Z.; Qian, Z.; Yanli, L.; Jing, J.; Gang Logan, L.; Qingjun, L. Combining localized surface plasmon resonance with anodic stripping voltammetry for heavy metal ion detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Bansod, B.; Kumar, T.; Thakur, R.; Rana, S.; Singh, I. A review on various electrochemical techniques for heavy metal ions detection with different sensing platforms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based cyclic voltammetry system with graphene modified screen printed electrodes for glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragay, G.; Merkoçi, A. Nanomaterials application in electrochemical detection of heavy metals. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Rafols, C.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Serrano, N.; Diaz-Cruz, J.M.; Arino, C.; de Pablo, J.; Esteban, M. Ag Nanoparticles Drop-Casting Modification of Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Cu(II) and Pb(II). Sensors 2017, 17, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Rafols, C.; Serrano, N.; Diaz-Cruz, J.M.; Arino, C.; Esteban, M. New approaches to antimony film screen-printed electrodes using carbon-based nanomaterials substrates. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 916, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, G.; Huang, H.; Tian, J.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Facile preparation of polyethylenimine-tannins coated SiO2 hybrid materials for Cu2+ removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, K.; Ji, F.; Zhang, L. Enhanced Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals Using Swarming Biohybrid Adsorbents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1806340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ma, Y. Polyhedral-Like NiMn-Layered Double Hydroxide/Porous Carbon as Electrode for Enhanced Electrochemical Performance Supercapacitors. Small 2017, 13, 1702612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilian, A.T.E.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Hwang, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Jun, Y.S.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.K. Salt-templated three-dimensional porous carbon for electrochemical determination of gallic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Li, M.-Y.; Yin, Y.-X.; Li, J.-Y.; Li, G.; Wang, W.-P.; Peng, W.; Cao, F.-F.; Guo, Y.-G. Porous carbon for high-energy density symmetrical supercapacitor and lithium-ion hybrid electrochemical capacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.Y.; Son, Y.J.; Yoo, J.M.; Kang, J.S.; Ahn, C.Y.; Park, S.; Sung, Y.E. Coffee Waste-Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon as a Highly Active and Durable Electrocatalyst for Electrochemical Energy Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41303–41313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, J.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, G.; Zhang, M. Evaluation of trace heavy metal levels in soil samples using an ionic liquid modified carbon paste electrode. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4418–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Wu, H.; Ping, J. Simultaneous determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions in honey and milk samples using a single-walled carbon nanohorns modified screen-printed electrochemical sensor. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiqi, Z.; Yonghua, Y.; Jian, W. Detection of cadmium content of lily by carbon nanoparticles modified screen-printed electrode. Trans. CSAE 2015, 31, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y. Development of an electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified disposable bismuth film electrode and its application for stripping analysis of heavy metals in milk. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, H.; Bai, N.; Xiang, K.; Zhou, W.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.S. Porous carbons derived from microalgae with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 194, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, T.; Zhuang, X.; Guo, Z.; Jiao, K. An ionic liquid supported CeO2 nanoshuttles-carbon nanotubes composite as a platform for impedance DNA hybridization sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2417–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X.; Park, J.Y. A miniaturized and flexible cadmium and lead ion detection sensor based on micro-patterned reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotube/bismuth composite electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Yerga, D.; Alvarez-Martos, I.; Blanco-Lopez, M.C.; Henry, C.S.; Fernandez-Abedul, M.T. Point-of-need simultaneous electrochemical detection of lead and cadmium using low-cost stencil-printed transparency electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 981, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, L.; Vannini, A.; Monaci, F.; Loppi, S. Competition between heavy metal ions for binding sites in lichens: Implications for biomonitoring studies. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, S.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, E. High-sensitivity determination of lead and cadmium based on the Nafion-graphene composite film. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 649, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Ma, H. Ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions based on three-dimensional graphene-carbon nanotubes hybrid electrode materials. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 852, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, M.; Zhao, H.; Lan, M.; Yu, C. Combination of Microporous Hollow Carbon Spheres and Nafion for the Individual Metal-free Stripping Detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Cui, R.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; Dong, J.; Sun, B. Insights into the role of pyrrole doped in three-dimensional graphene aerogels for electrochemical sensing Cd(II). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 871, 114323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechotnek, F.; Follmann, H.D.M.; Silva, R. Mesoporous silica decorated with L-cysteine as active hybrid materials for electrochemical sensing of heavy metals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Belwal, T.; Luo, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Lin, X. Direct detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in juice and beverage samples using PDMS modified nanochannels electrochemical sensors. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Cd(II) | Pb(II) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added (μg L−1) | ICP-MS (μg L−1) | Our Method (μg L−1) | Recovery (%) | Added (μg L−1) | ICP-MS (μg L−1) | Our Method (μg L−1) | Recovery (%) | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | 0 | 0 | 0 | / |
| 30 | 33.23 ± 1.18 | 21.45 ± 1.38 | 71.5 | 30 | 27.25 ± 3.73 | 33.12 ± 1.48 | 110.4 | |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | 0 | 0 | 0 | / |
| 30 | 33.19 ± 0.42 | 25.83 ± 3.54 | 86.1 | 30 | 29.65 ± 0.82 | 34.06 ± 1.33 | 113.6 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | 0 | 0 | 0 | / |
| 30 | 33.24 ± 0.08 | 27.94 ± 2.88 | 93.2 | 30 | 27.17 ± 0.60 | 31.05 ± 1.85 | 103.5 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | 0 | 0 | 0 | / |
| 30 | 32.19 ± 0.07 | 23.39 ± 1.38 | 77.9 | 30 | 31.49 ± 1.56 | 36.13 ± 4.79 | 120.5 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | / | 0 | 0 | 0 | / |
| 30 | 33.57 ± 0.59 | 31.56 ± 3.90 | 105.2 | 30 | 37.69 ± 0.66 | 38.58 ± 3.39 | 128.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ping, J. Determination of Heavy Metal Ions in Infant Milk Powder Using a Nanoporous Carbon Modified Disposable Sensor. Foods 2023, 12, 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040730
Chen H, Yao Y, Zhang C, Ping J. Determination of Heavy Metal Ions in Infant Milk Powder Using a Nanoporous Carbon Modified Disposable Sensor. Foods. 2023; 12(4):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040730
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Han, Yao Yao, Chao Zhang, and Jianfeng Ping. 2023. "Determination of Heavy Metal Ions in Infant Milk Powder Using a Nanoporous Carbon Modified Disposable Sensor" Foods 12, no. 4: 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040730
APA StyleChen, H., Yao, Y., Zhang, C., & Ping, J. (2023). Determination of Heavy Metal Ions in Infant Milk Powder Using a Nanoporous Carbon Modified Disposable Sensor. Foods, 12(4), 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040730