Impact of Milk Storage and Heat Treatments on In Vitro Protein Digestibility of Soft Cheese
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
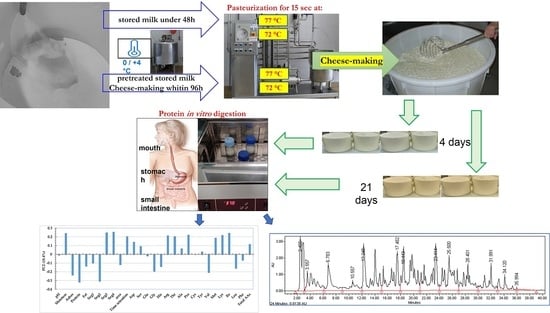
2.1. Cheese Production
- -
- Fresh milk (F) was processed within 48 h of the first milking,
- -
- Pre-treated stored milk (P) was thermized at 65 °C for 15 s upon receipt (within about 24 h of the first milking) and processed within 96 h of the first milking.
- -
- At 72 °C for 15 s, called minimal pasteurization (M), the minimum recommended level for milk pasteurization,
- -
- At 77 °C for 15 s, called strong pasteurization (S), a higher-temperature condition of pasteurization to test the effect on produced cheese.
2.2. Physico-Chemical Analyses of Cheeses
2.3. In Vitro Digestion Model
2.4. Peptide Profile Analysis before and after Digestion
2.5. Analysis of Amino Acids
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Cheese
3.2. Peptide Profile before and after In Vitro Digestion
3.2.1. Peptide Profile Comparison between Undigested and Digested Cheese
3.2.2. Changes in Peptide Profile Due to Heat Treatments
3.2.3. Peptide Profile Determination to Study Protein Digestion In Vitro
3.3. Amino Acid Content after In Vitro Digestion
3.3.1. Determining Total AA Content to Assess In Vitro Digestion
3.3.2. Individual AAs Released after Digestion
3.4. Influence of Heat Treatment and Microstructure on Protein Digestion
3.5. Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, P.C. Milk nutritional composition and its role in human health. Nutrition 2014, 30, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lieshout, G.A.; Lambers, T.T.; Bragt, M.C.; Hettinga, K.A. How processing may affect milk protein digestion and overall physiological outcomes: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2422–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto, A. Bioactive peptides: Production and functionality. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, L.; Gauthier, S.F.; Britten, M.; Turgeon, S.L. Invitro gastrointestinal digestion of liquid and semi-liquid dairy matrixes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, L.; Rioux, L.E.; Britten, M.; Turgeon, S.L. Invitro bioaccessibility of peptides and amino acids from yogurt made with starch, pectin, or β-glucan. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 46, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet-Cabero, A.I.; Mackie, A.R.; Wilde, P.J.; Fenelon, M.A.; Brodkorb, A. Structural mechanism and kinetics of in vitro gastric digestion are affected by process-induced changes in bovine milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 86, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, S.L.; Brisson, G. Symposium review: The dairy matrix—Bioaccessibility and bioavailability of nutrients and physiological effects. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 6727–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbé, F.; Ménard, O.; Le Gouar, Y.; Buffière, C.; Famelart, M.H.; Laroche, B.; Le Feunteun, S.; Dupont, D.; Rémond, D. The heat treatment and the gelation are strong determinants of the kinetics of milk proteins digestion and of the peripheral availability of amino acids. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Rioux, L.E.; Labrie, S.; Turgeon, S.L. Commercial cheeses with different texture have different disintegration and protein/peptide release rates during simulated in vitro digestion. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 56, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Rioux, L.E.; Labrie, S.; Turgeon, S.L. Disintegration and nutrients release from cheese with different textural properties during in vitro digestion. Food Res. Int. 2016, 88, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunick, M.H.; Ren, D.X.; Van Hekken, D.L.; Bonnaillie, L.; Paul, M.; Kwoczak, R.; Tomasula, P.M. Effect of heat and homogenization on in vitro digestion of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4124–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, L.; Cattaneo, S.; De Noni, I. Nutrition and Health: Effects of Processing on Protein Quality of Milk and Milk Products. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Fuquay, J.W., McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 1067–1074. ISBN 9780123744029. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, S.J.; Lim, B.O.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. In vitro human digestion models for food applications. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, S.; Palocci, G.; Contò, M.; Di Giovanni, S.; Tripaldi, C. Chemical characteristics, oxidation and proteolysis in cheese produced from fresh or stored milk subjected to heat treatments. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripaldi, C.; Rinaldi, S.; Palocci, G.; Di Giovanni, S.; Claps, S.; Buttazzoni, L. Effect of Storage and Heat Treatment of Milk Destined for Cheese Production on Its Oxidative Characteristics. Dairy 2021, 2, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Dairy Federation (IDF). Cheese and Processed Cheese Products. Determination of Dry Matter; FIL-IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists International (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC Intl.: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO 21543); International Dairy Federation (IDF 201). Milk Products-Guidelines for the Application of Near Infrared Spectrometry; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bordoni, A.; Picone, G.; Babini, E.; Vignali, M.; Danesi, F.; Valli, V.; Di Nunzio, M.; Laghi, L.; Capozzi, F. NMR comparison of in vitro digestion of Parmigiano Reggiano cheese aged 15 and 30 months. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, S61–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meira, M.M.S.; Daroit, D.J.; Helfer, V.E.; Corrêa, A.P.F.; Segalin, J.; Carro, S.; Brandelli, A. Bioactive peptides in water-soluble extracts of ovine cheeses from Southern Brazil and Uruguay. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrot, S.; Degraeve, P.; Curia, C.; Martial-Gros, A. In vitro study on digestion of peptides in Emmental cheese: Analytical evaluation and influence on angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Nahrung-Food 2003, 47, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Analysis System Institute (SAS). User’s Guide: Statistics; Version 9.4; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Waungana, A. Influence of heat treatment of milk on cheesemaking properties. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, V.K.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Magboul, A.A.A.; Fox, P.F. Proteolysis in Cheese during Rmaturation. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology; General Aspects; Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Cogan, T.M., Guinee, T.P., Eds.; Applied Science: London, UK, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Matar, C.; Amiot, J.; Savoie, L.; Goulet, J. The Effect of Milk Fermentation by Lactobacillus helveticus on the Release of Peptides during in Vitro Digestion. J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 79, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mant, C.T.; Zhou, N.E.; Hodges, R.S. Correlation of protein retention times in reversed-phase chromatography with polypeptide chain length and hydrophobicity. J. Chromatogr. 1989, 476, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, L.; Ménard, O.; Baumann, C.; Duerr, D.; Schlegel, P.; Stoll, P.; Vergères, G.; Dupont, D.; Portmann, R. Digestion of milk proteins: Comparing static and dynamic in vitro digestion systems with in vivo data. Food Res. Int. 2019, 118, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žolnere, K.; Arnold, M.; Hull, B.; Everett, D.W. Cheese proteolysis and matrix disintegration during in vitro digestion. Food Struct. 2019, 21, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caira, S.; Pinto, G.; Vitaglione, P.; Dal Piaz, F.; Ferranti, P.; Addeo, F. Identification of casein peptides in plasma of subjects after a cheese-enriched diet. Food Res. Int. 2016, 84, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf-Bolanz, K.A.; Schwander, F.; Gijs, M.; Vergéres, G.; Portmann, R.; Egger, L. Validation of an in vitro digestive system for studying macronutrient decomposition in humans. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.H.L.; Yamamoto, A. Penetration and enzymatic barriers to peptide and protein absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1990, 4, 171–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Mandalari, G.; Mollé, D.; Jardin, J.; Rolet-Répécaud, O.; Duboz, G.; Léonil, J.; Mills, C.E.N.; Mackie, A.R. Food processing increases casein resistance to simulated infant digestion. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinot, L.; Rioux, L.E.; Labrie, S.; Britten, M.; Turgeon, S.L. Identification of texture parameters influencing commercial cheese matrix disintegration and lipid digestion using an in vitro static digestion model. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, L.; Ménard, O.; Abbühl, L.; Duerr, D.; Stoffers, H.; Berthoud, H.; Meola, M.; Badertscher, R.; Blaser, C.; Dupont, D.; et al. Higher microbial diversity in raw than in pasteurized milk Raclette-type cheese enhances peptide and metabolite diversity after in vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Milk | Pasteurization | Storage | Interaction | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | M | S | 4 Days | 21 Days | m*p | m*s | p*s | m*p*s | |
| pH | 5.36 ± 0.52 | 5.19 ± 0.21 | 5.40 a ± 0.53 | 5.15 b ± 0.13 | 5.29 ± 0.40 | 5.27 ± 0.42 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Moisture (%) | 58.66 ± 2.74 | 58.44 ± 2.18 | 58.35 ± 3.05 | 58.75 ± 1.71 | 60.08 a ± 1.99 | 57.02 b ± 1.85 | 0.02 | ns | ns | ns |
| Ash (%) | 2.77 ± 0.40 | 2.78 ± 0.28 | 2.80 ± 0.32 | 2.76 ± 0.37 | 2.63 b ± 0.29 | 2.92 a ± 0.33 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Protein (%) | 18.40 b ± 0.63 | 18.79 a ± 0.64 | 18.80 a ± 0.73 | 18.39 b ± 0.52 | 18.18 b ± 0.58 | 19.01 a ± 0.45 | 0.002 | ns | ns | ns |
| Fat (%) | 21.21 ± 1.31 | 20.53 ± 1.61 | 21.31 a ± 1.79 | 20.43 b ± 0.96 | 20.40 b ± 1.23 | 21.33 a ± 1.61 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Parameters | Milk | Pasteurization | Storage | Interaction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | M | S | 4 Days | 21 Days | m*p | m*s | p*s | m*p*s | ||
| % | Min | ||||||||||
| seg1 | 1–12 | 23.68 ± 7.09 | 23.69 ± 6.16 | 23.82 ± 6.34 | 23.55 ± 6.93 | 29.80 a ± 1.43 | 17.56 b ± 0.75 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| seg2 | 12–24 | 21.95 ± 2.27 | 21.21 ± 2.68 | 21.05 ± 2.84 | 22.11 ± 1.98 | 19.60 b ± 1.78 | 23.56 a ± 0.72 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| seg3 | 24–36 | 34.36 ± 7.21 | 34.04 ± 7.72 | 34.59 ± 6.42 | 33.8 ± 8.37 | 27.36 b ± 2.02 | 41.04 a ± 0.80 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| seg4 | 36–42 | 20.02 ± 2.23 | 21.07 ± 3.84 | 20.54 ± 3.18 | 20.55 ± 3.20 | 23.24 a ± 1.89 | 17.86 b ± 0.49 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| total area (106) | 224.3 ± 60.1 | 205.3 ± 58.3 | 219.5 ± 67.9 | 210.0 ± 50.6 | 163.8 b ± 22.6 | 265.8 a ± 27.7 | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| mean retention time (min) | 23.88 ± 1.50 | 24.18 ± 1.00 | 23.95 ± 1.11 | 24.10 ± 1.43 | 22.94 ± 0.60 | 25.11 ± 0.50 | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Parameters | Milk | Pasteurization | Storage | Interaction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | M | S | 4 Days | 21 Days | m*p | m*s | p*s | m*p*s | ||
| % | min | ||||||||||
| seg1 | 1–12 | 24.37 b ± 3.55 | 26.79 a ± 1.79 | 24.33 b ± 2.81 | 26.83 a ± 2.78 | 23.90 b ± 3.16 | 27.25 a ± 1.67 | ns | 0.001 | ns | ns |
| seg2 | 12–24 | 48.60 ± 2.68 | 48.39 ± 3.34 | 49.49 a ± 2.00 | 47.49 b ± 3.48 | 46.03 b ± 2.03 | 50.95 a ± 0.62 | ns | ns | 0.007 | ns |
| seg3 | 24–36 | 25.01 ± 4.10 | 23.80 ± 3.10 | 24.62 ± 2.79 | 24.19 ± 4.40 | 27.52 a ± 1.66 | 21.29 b ± 1.53 | ns | ns | 0.02 | ns |
| seg4 | 36–42 | 2.03 a ± 1.64 | 1.02 b ± 0.64 | 1.56 ± 1.46 | 1.49 ± 1.24 | 2.55 a ± 1.12 | 0.50 b ± 0.11 | ns | 0.001 | ns | ns |
| total area (106) | 961 ± 247 | 1033 ± 242 | 1192 a ± 163 | 802 b ± 93 | 1036 ± 244 | 958 ± 244 | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| mean retention time (min) | 18.92 a ± 2.12 | 17.39 b ± 0.77 | 18.31 ± 1.59 | 17.99 ± 1.96 | 19.33 a ± 1.66 | 16.98 b ± 0.53 | ns | 0.002 | ns | ns | |
| mg/100 g | Milk | Pasteurization | Storage | Interaction | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | M | S | 4 Days | 21 Days | m*p | m*s | p*s | m*p*s | |
| Asp | 14.5 ± 3.1 | 14.0 ± 1.9 | 13.1 b ± 2.3 | 15.4 a ± 2.3 | 14.1 ± 2.2 | 14.4 ± 2.9 | 0.013 | ns | ns | ns |
| Ser | 50.4 ± 10.9 | 49.3 ± 6.8 | 45.1 b ± 5.4 | 54.7 a ± 9.3 | 47.4 ± 5.1 | 52.3 ± 11.3 | ns | ns | 0.014 | ns |
| Glu | 54.6 ± 7.7 | 54.0 ± 5.9 | 55.4 ± 6.7 | 53.3 ± 6.9 | 56.0 ± 7.2 | 52.6 ± 6.1 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Gly | 178.8 ± 30.3 | 182.2 ± 20.5 | 185.3 ± 19.4 | 175.7 ± 30.3 | 180.3 ± 24.5 | 180.7 ± 27.3 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| His | 37.2 ± 9.9 | 36.4 ± 9.9 | 33.8 ± 6.2 | 39.8 ± 11.7 | 33.2 ± 8.8 | 40.4 ± 9.5 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Arg | 1299.6 ± 120.2 | 1369.3 ± 128.0 | 1282.8 b ± 111.0 | 1386.1 a ± 123.8 | 1320.3 ± 94.3 | 1348.6 ± 155.4 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Thr | 134.3 ± 62.2 | 145.7 ± 57.5 | 103.2 b ± 33.0 | 176.8 a ± 56.7 | 126.3 ± 47.5 | 153.7 ± 67.8 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Ala | 124.5 ± 9.7 | 130.8 ± 12.4 | 122.1 b ± 10.5 | 133.1 a ± 9.7 | 127.0 ± 10.9 | 128.3 ± 12.2 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Pro | 221.2 ± 39.6 | 219.0 ± 18.6 | 221.6 ± 14.2 | 218.6 ± 41.4 | 229.9 ± 35.0 | 210.3 ± 22.0 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Cys | 243.0 ± 56.9 | 248.9 ± 48.5 | 258.4 ± 61.3 | 233.4 ± 38.7 | 246.1 ± 55.8 | 245.8 ± 49.9 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Tyr | 563.4 ± 106.2 | 564.2 ± 91.9 | 531.3 b ± 71.7 | 596.3 a ± 110.8 | 527.9 b ± 68.7 | 599.6 a ± 110.5 | ns | ns | 0.001 | ns |
| Val | 79.9 ± 9.1 | 81.4 ± 11.4 | 84.4 ± 8.5 | 76.9 ± 10.6 | 81.6 ± 9.87 | 79.7 ± 10.8 | 0.028 | ns | ns | ns |
| Met | 46.6 ± 19.2 | 55.0 ± 19.1 | 36.4 b ± 9.4 | 65.2 a ± 15.3 | 47.8 ± 15.1 | 53.8 ± 22.9 | ns | ns | 0.033 | ns |
| Lys | 555.8 ± 62.1 | 579.3 ± 45.2 | 548.6 ± 58.7 | 586.5 ± 44.4 | 569.6 ± 48.6 | 565.5 ± 61.8 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Ile | 202.6 ± 18.5 | 216.7 ± 35.8 | 200.7 ± 20.0 | 218.6 ± 34.0 | 215.5 ± 34.4 | 203.7 ± 21.7 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Leu | 537.0 ± 37.7 | 528.0 ± 43.9 | 528.3 ± 43.5 | 536.7 ± 38.3 | 517.8 ± 44.7 | 547.3 ± 30.3 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Phe | 966.7 ± 180.3 | 947.7 ± 140.9 | 905.7 b ± 175.5 | 1008.8 a ± 126.3 | 849.1 b ± 138.1 | 1065.3 a ± 89.5 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Total AAs | 5310.1 ± 443.6 | 5421.9 ± 381.5 | 5156.1 b ± 230.8 | 5575.8 a ± 446.9 | 5189.9 b ± 325.5 | 5542.1 a ± 418.9 | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rinaldi, S.; Di Giovanni, S.; Palocci, G.; Contò, M.; Steri, R.; Tripaldi, C. Impact of Milk Storage and Heat Treatments on In Vitro Protein Digestibility of Soft Cheese. Foods 2023, 12, 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081735
Rinaldi S, Di Giovanni S, Palocci G, Contò M, Steri R, Tripaldi C. Impact of Milk Storage and Heat Treatments on In Vitro Protein Digestibility of Soft Cheese. Foods. 2023; 12(8):1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081735
Chicago/Turabian StyleRinaldi, Simona, Sabrina Di Giovanni, Giuliano Palocci, Michela Contò, Roberto Steri, and Carmela Tripaldi. 2023. "Impact of Milk Storage and Heat Treatments on In Vitro Protein Digestibility of Soft Cheese" Foods 12, no. 8: 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081735
APA StyleRinaldi, S., Di Giovanni, S., Palocci, G., Contò, M., Steri, R., & Tripaldi, C. (2023). Impact of Milk Storage and Heat Treatments on In Vitro Protein Digestibility of Soft Cheese. Foods, 12(8), 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081735