Changes in the Quality of Myofibrillar Protein Gel Damaged by High Doses of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate as Affected by the Addition of Amylopectin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Myofibrillar Proteins (MP) Extraction
2.3. Treatment of MP
2.4. Oxidation Degree of MP
2.5. Thiol Group Content of MP
2.6. Free Amino Group Content of MP
2.7. Solubility of MP
2.8. Surface Hydrophobicity of MP
2.9. Tryptophan Fluorescence of MP
2.10. Secondary Structure of MP
2.11. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis of MP Gels
2.12. Electrophoresis of MP
2.13. Dynamic Rheological Testing of MP
2.14. Preparation of MP Gel
2.15. Cooking Loss of MP Gel
2.16. Gel Strength of MP Gel
2.17. Microstructure of MP Gel
2.18. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
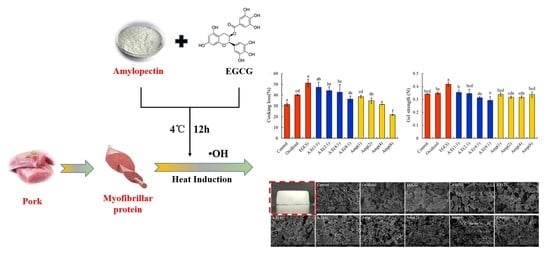
3.1. Cooking Loss and Gel Strength of the MP Gels
3.2. Chemical Properties of the MP
3.2.1. Carbonyl Content
3.2.2. Free Amino and Thiol Group
3.2.3. Solubility
3.3. Secondary and Tertiary Structure of the MP
3.3.1. Tryptophan Fluorescence
3.3.2. Surface Hydrophobicity
3.3.3. CD Spectrum
3.4. FTIR of MP
3.5. SDS-PAGE Patterns of the MP
3.6. Rheological Properties of the MP
3.7. Microstructure of the MP Gels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Suo, Z.; Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; et al. Inhibition of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate/Protein Interaction by Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin in Myofibrillar Protein Emulsion Gels under Oxidative Stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8094–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, H.; Sun, W.; Cui, C. Effects of oxidative modification on gel properties of isolated porcine myofibrillar protein by peroxyl radicals. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, C.P.; KjÆrsgård, I.V.; Jessen, F.; Jacobsen, C. Protein and Lipid Oxidation during Frozen Storage of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8118–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez, M. Protein carbonyls in meat systems: A review. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.C.; Chen, L.; Lei, N.; Wang, S.X.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Li, Z.X. Emulsifying Properties of Oxidatively Stressed Myofibrillar Protein Emulsion Gels Prepared with (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and NaCl. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, C.; Ullah, N.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Hackman, R.M.; Zhou, G.; Feng, X. Different physicochemical, structural and digestibility characteristics of myofibrillar protein from PSE and normal pork before and after oxidation. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.B.; Zhang, W.G.; Zou, Y.F.; Xing, L.J.; Zheng, H.B.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Influence of RosA-protein adducts formation on myofibrillar protein gelation properties under oxidative stress. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 67, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E.; Altay, F. A review on protein–phenolic interactions and associated changes. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongberg, S.; Terkelsen, L.; Miklos, R.; Lund, M.N. Green tea extract impairs meat emulsion properties by disturbing protein disulfide cross-linking. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Tan, C.; Zhang, X.; Feng, B.; Xia, S. Fabrication of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Nanocarrier Based on Glycosylated Casein: Stability and Interaction Mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4677–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Liu, R.; Wei, Q.; Su, R.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; He, Z. Interaction between lysozyme and procyanidin: Multilevel structural nature and effect of carbohydrates. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; True, A.D.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Dual Role (Anti- and Pro-oxidant) of Gallic Acid in Mediating Myofibrillar Protein Gelation and Gel In Vitro Digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Qiu, H.H.; Deng, X.R.; Mao, X.Y.; Guo, X.B.; Xu, C.J.; Zhang, J. Effect of Chlorogenic Acid on the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Coregonus Peled Myofibrillar Protein through Hydroxyl Radical Oxidation. Molecules 2019, 24, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.P.; Liu, C.K.; Wang, J.X.; Li, W.X.; Lin, B.Y.; Zhu, W.H.; Xu, Y.X.; Yi, S.M.; Mi, H.B.; Li, J.R. Tea Polyphenols Affect Oxidative Modification and Solution Stability of Myofibrillar Protein from Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Food Biophys. 2020, 15, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Lin, S.; Liu, D. The beneficial effects of rutin on myofibrillar protein gel properties and related changes in protein conformation. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Munir, S.; Yu, X.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Liu, R.; Xiong, S.; Hu, Y. Double-crosslinked effect of TGase and EGCG on myofibrillar proteins gel based on physicochemical properties and molecular docking. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Chlorogenic acid-mediated gel formation of oxidatively stressed myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, D.; Kong, B. Changes in the structural and gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein induced by catechin modification. Meat Sci. 2017, 127, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.Q.; Li, Y.Q.; Xia, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Huang, Q.R. Glycosylation of bovine serum albumin via Maillard reaction prevents epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced protein aggregation. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Damodaran, S.; Lucey, J.A. Formation of whey protein isolate (WPI)-dextran conjugates in aqueous solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7113–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterschoot, J.; Gomand, S.V.; Fierens, E.; Delcour, J.A. Production, structure, physicochemical and functional properties of maize, cassava, wheat, potato and rice starches. Starch-Starke 2015, 67, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Relationships between amylopectin internal molecular structure and physicochemical properties of starch. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Inouchi, N.; Nishinari, K. Structural, thermal and viscoelastic characteristics of starches separated from normal, sugary and waxy maize. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguleswaran, S.; Vasanthan, T.; Hoover, R.; Liu, Q. Structure and physicochemical properties of palmyrah (Borassus flabellifer L.) seed-shoot starch grown in Sri Lanka. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Gu, Z.B.; Li, Z.F. Properties of waxy corn starch and its application in food processing. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2005, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.C.; Li, C.; Ullah, N.; Hackman, R.M.; Zhou, G.H. Potential Biomarker of Myofibrillar Protein Oxidation in Raw and Cooked Ham: 3-Nitrotyrosine Formed by Nitrosation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10957–10964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.S.; Fan, X.J.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhu, B.; Ullah, N.; Feng, X.C. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate mediated self-assemble behavior and gelling properties of the ovalbumin with heating treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Alvarenga, M.S.; Martinez-Rodriguez, E.Y.; Garcia-Amezquita, L.E.; Olivas, G.I.; Zamudio-Flores, P.B.; Acosta-Muniz, C.H.; Sepulveda, D.R. Effect of Maillard reaction conditions on the degree of glycation and functional properties of whey protein isolate—Maltodextrin conjugates. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, B.; Feng, X. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate-mediated formation of myofibrillar protein emulsion gels under malondialdehyde-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Guo, C.; Zhou, D. Effect of hydroxyl radical induced oxidation on the physicochemical and gelling properties of shrimp myofibrillar protein and its mechanism. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, G. Insight into the mechanism of physicochemical influence by three polysaccharides on myofibrillar protein gelation. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 229, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xia, X.; Kong, B. Changes in myofibrillar protein gel quality of porcine longissimus muscle induced by its stuctural modification under different thawing methods. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Z.; Haworth, I.S.; Zhong, Z.; Chow, M.; Chow, A. Physicochemical and Structural Characterization of Quercetin-β-Cyclodextrin Complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.H.; Huan, H.Z.; Bu, Y.; Li, X.P.; Shiuan, D.; Li, J.R.; Sun, X.T. Effects of hydroxyl radical induced oxidation on water holding capacity and protein structure of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantle. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, L.; Lv, Y.Q.; Wang, S.X.; Suo, Z.Y.; Cheng, X.G.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Li, Z.X.; Feng, X.C. Inhibition of interaction between epigallocatechin-3-gallate and myofibrillar protein by cyclodextrin derivatives improves gel quality under oxidative stress. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aewsiri, T.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Eun, J.B.; Wierenga, P.A.; Gruppen, H. Antioxidative activity and emulsifying properties of cuttlefish skin gelatin modified by oxidised phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J. Oxidation-induced unfolding facilitates Myosin cross-linking in myofibrillar protein by microbial transglutaminase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8020–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Ying, D.Y.; Hlaing, M.M.; Ye, J.H.; Sanguansri, L.; Augustin, M.A. Development of broccoli by-products as carriers for delivering EGCG. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Q.; Qian, S.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Ullah, N.; Chen, L. The gelation properties of myofibrillar proteins prepared with malondialdehyde and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Yang, R.; Fan, X.; He, G.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Han, M.; Ullah, N.; et al. Changes in the Quality of Myofibrillar Protein Gel Damaged by High Doses of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate as Affected by the Addition of Amylopectin. Foods 2023, 12, 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091790
Chen L, Yang R, Fan X, He G, Zhao Z, Wang F, Liu Y, Wang M, Han M, Ullah N, et al. Changes in the Quality of Myofibrillar Protein Gel Damaged by High Doses of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate as Affected by the Addition of Amylopectin. Foods. 2023; 12(9):1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091790
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lin, Rong Yang, Xiaojing Fan, Gongchen He, Zhengshan Zhao, Fangqu Wang, Yaping Liu, Mengyuan Wang, Minyi Han, Niamat Ullah, and et al. 2023. "Changes in the Quality of Myofibrillar Protein Gel Damaged by High Doses of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate as Affected by the Addition of Amylopectin" Foods 12, no. 9: 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091790
APA StyleChen, L., Yang, R., Fan, X., He, G., Zhao, Z., Wang, F., Liu, Y., Wang, M., Han, M., Ullah, N., & Feng, X. (2023). Changes in the Quality of Myofibrillar Protein Gel Damaged by High Doses of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate as Affected by the Addition of Amylopectin. Foods, 12(9), 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091790