Effects of In Vitro Fermentation of Polysialic Acid and Sialic Acid on Gut Microbial Community Composition and Metabolites in Healthy Humans
Abstract
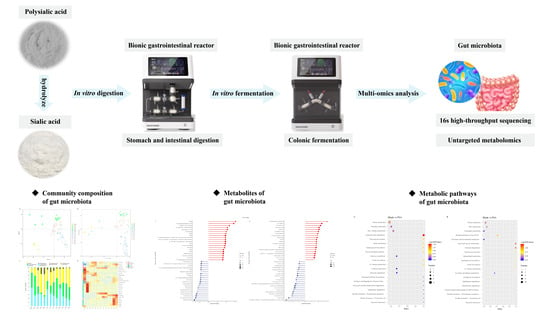
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation and Extraction of PSA and SA
2.3. Simulated Digestion Experiments
2.4. Preparation of Fecal Inoculum Solution
2.5. Fecal Fermentation in BGR
2.6. Determination of the Molecular Weight of PSA
2.7. Determination of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
2.8. Determination of Gut Microbiota
2.9. Determination of Metabolites
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Weight Changes of PSA in In Vitro Digestion
3.2. Consumption of PSA and SA in In Vitro Fermentation
3.3. Effects of SA and PSA on SCFA Content
3.4. Effects of PSA and SA on Gut Microbiota in In Vitro Fermentation
3.5. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3.6. Correlation Analysis between Differential Metabolites and Microbiota
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knight, R.; Callewaert, C.; Marotz, C.; Hyde, E.R.; Debelius, J.W.; McDonald, D.; Sogin, M.L. The Microbiome and Human Biology. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2017, 18, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Kim, Y.G.; Sham, H.P.; Vallance, B.A.; Puente, J.L.; Martens, E.C.; Nunez, G. Regulated Virulence Controls the Ability of a Pathogen to Compete with the Gut Microbiota. Science 2012, 336, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koropatkin, N.M.; Cameron, E.A.; Martens, E.C. How glycan metabolism shapes the human gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadpoor, M.; Peeters, C.; Henricks, P.A.J.; Varasteh, S.; Pieters, R.J.; Folkerts, G.; Braber, S. Anti-Pathogenic Functions of Non-Digestible Oligosaccharides In Vitro. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A.; Gagneux, P. Multifarious roles of sialic acids in immunity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1253, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stencel-Baerenwald, J.E.; Reiss, K.; Reiter, D.M.; Stehle, T.; Dermody, T.S. The sweet spot: Defining virus-sialic acid interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, J.K.; Moyne, O.; Rodionov, D.A.; Zengler, K. Carbohydrates great and small, from dietary fiber to sialic acids: How glycans influence the gut microbiome and affect human health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1869502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engfer, M.B.; Stahl, B.; Finke, B.; Sawatzki, G.; Daniel, H. Human milk oligosaccharides are resistant to enzymatic hydrolysis in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburg, D.S.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk glycans protect infants against enteric pathogens. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2005, 25, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colley, K.J.; Kitajima, K.; Sato, C. Polysialic acid: Biosynthesis, novel functions and applications. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 498–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, C.; Kitajima, K. Disialic, oligosialic and polysialic acids: Distribution, functions and related disease. J. Biochem. 2013, 154, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony Constantinou, A.A.E.; Hreczuk-Hirst, D.; Jain, S.; Deonarain, M.P. Modulation of Antibody Pharmacokinetics by Chemical Polysialylation. Bioconj. Chem. 2008, 19, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.; Shim, M.K.; Park, M.J.; Jang, E.H.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.H. Hydrophobically modified polysaccharide-based on polysialic acid nanoparticles as carriers for anticancer drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 520, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.; Hu, L.; Peng, B.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y. Polysialic acid-modifying liposomes for efficient delivery of epirubicin, in-vitro characterization and in-vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhong, J.; Long, J.; Zou, X.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Liang, Y.; Huang, R.; Wei, X.; et al. Hypoglycemic effects and mechanism of different molecular weights of konjac glucomannans in type 2 diabetic rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165 Pt B, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.H.; Xu, Y.X.; Li, Y.H.; Cao, J.; Song, F.L.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Yang, Y. Effects of konjac glucomannan with different molecular weights on gut microflora with antibiotic perturbance in in vitro fecal fermentation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.T.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhan, X.B.; Gao, M.J. New dynamic digestion model reactor that mimics gastrointestinal function. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 154, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Hu, G.A.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Z.C.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, M.J.; Zhan, X.B. In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation of highly resistant starch rice and its effect on the gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Xu, J.J.; Yin, Z.W.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z.T.; Zhan, X.B. Fractionation, preliminary structural characterization and prebiotic activity of polysaccharide from the thin stillage of distilled alcoholic beverage. Process Biochem. 2022, 118, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Zhan, X.; Lin, C.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L. A new polysialic acid production process based on dual-stage pH control and fed-batch fermentation for higher yield and resulting high molecular weight product. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2405–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Zhan, X.B.; Wu, J.R.; Lin, C.C.; Yu, D.F. An efficient and large-scale preparation process for polysialic acid by Escherichia coli CCTCC M208088. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 53, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.B.; Chen, X.S.; Wu, J.; Sun, L.J.; Yuan, L.X.; Yao, J. Separation and purification to prepare N-acetylneuraminic acid after oxalic acid hydrolysis of polysialic acid. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China 2020, 50, 605–611. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, Q.; You, X.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z. In vitro digestibility and prebiotic potential of curdlan (1-->3)-beta-d-glucan oligosaccharides in Lactobacillus species. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 188, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, M.; Eck, A.; Koenen, M.E.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Budding, A.E.; Venema, K. Evaluation of an optimal preparation of human standardized fecal inocula for in vitro fermentation studies. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 117, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.X.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.R.; Li, H.; Wu, C.C.; Yin, Z.W.; Xu, J.J.; Zhu, L.; Gao, M.J.; Zhan, X.B. Structural characterization and in vitro evaluation of the prebiotic potential of an exopolysaccharide produced by Bacillus thuringiensis during fermentation. LWT 2022, 163, 113532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Gevers, D.; Earl, A.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Ward, D.V.; Giannoukos, G.; Ciulla, D.; Tabbaa, D.; Highlander, S.K.; Sodergren, E.; et al. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yan, Y.; Mi, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, L.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y. Simulated Digestion and Fermentation in Vitro by Human Gut Microbiota of Polysaccharides from Bee Collected Pollen of Chinese Wolfberry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.V.; Frassetto, A.; Kowalik, E.J., Jr.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Lu, M.M.; Kosinski, J.R.; Hubert, J.A.; Szeto, D.; Yao, X.; Forrest, G.; et al. Butyrate and propionate protect against diet-induced obesity and regulate gut hormones via free fatty acid receptor 3-independent mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Buerger, M.; Stallmach, A.; Bruns, T. Effects of Antibiotics on Gut Microbiota. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Martinez-Medina, M. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii: From microbiology to diagnostics and prognostics. ISME J. 2017, 11, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.P.N.; Manneras-Holm, L.; Puschmann, R.; Wu, H.; Troise, A.D.; Nijsse, B.; Boeren, S.; Backhed, F.; Fiedler, D.; de Vos, W.M. Conversion of dietary inositol into propionate and acetate by commensal Anaerostipes associates with host health. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lyu, N.; Liu, F.; Liang, S.; Zhu, B. An examination of data from the American Gut Project reveals that the dominance of the genus Bifidobacterium is associated with the diversity and robustness of the gut microbiota. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, H.; Nagai, F.; Morotomi, M.; Tanaka, R. Sutterella parvirubra sp. nov. and Megamonas funiformis sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58 Pt 4, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobori, M.; Yoshida, M.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Shinmoto, H. Ergosterol peroxide from an edible mushroom suppresses inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages and growth of HT29 colon adenocarcinoma cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, A.N.; Masri, M.S.; Robbins, D.J.; Emerson, O.H.; Jones, F.T.; De Eds, F. The metabolic fate of gallic acid and related compounds. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 3014–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S.; Nunn, K.P. Vitamin B6 intakes and 24-hr 4-pyridoxic acid excretions of children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1977, 30, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.S.; Packer, L. Lipoic Acid. Energy, Production, Antioxidant Activity and Health Effects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, D.G.; Goligorsky, M.S.; Schmid, P.C.; Krebsbach, R.J.; Schmid, H.H.O.; Das, S.K.; Dey, S.K.; Arreaza, G.; Thorup, C.; Stefano, G.; et al. Production and physiological actions of anandamide in the vasculature of the rat kidney. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksnes, A.; Njaa, L.R. Absorption of methionine and methionine sulphoxide in rat intestine and the effect of glutathione. Br. J. Nutr. 1983, 50, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: Major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, Z.; Zhu, L.; Gao, M.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhan, X. Effects of In Vitro Fermentation of Polysialic Acid and Sialic Acid on Gut Microbial Community Composition and Metabolites in Healthy Humans. Foods 2024, 13, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030481
Yin Z, Zhu L, Gao M, Yu D, Zhang Z, Zhu L, Zhan X. Effects of In Vitro Fermentation of Polysialic Acid and Sialic Acid on Gut Microbial Community Composition and Metabolites in Healthy Humans. Foods. 2024; 13(3):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030481
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Zhongwei, Li Zhu, Minjie Gao, Dan Yu, Zijian Zhang, Ling Zhu, and Xiaobei Zhan. 2024. "Effects of In Vitro Fermentation of Polysialic Acid and Sialic Acid on Gut Microbial Community Composition and Metabolites in Healthy Humans" Foods 13, no. 3: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030481
APA StyleYin, Z., Zhu, L., Gao, M., Yu, D., Zhang, Z., Zhu, L., & Zhan, X. (2024). Effects of In Vitro Fermentation of Polysialic Acid and Sialic Acid on Gut Microbial Community Composition and Metabolites in Healthy Humans. Foods, 13(3), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030481