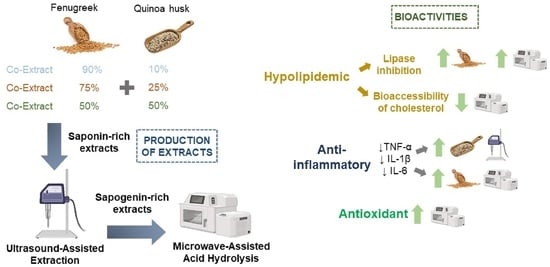
Combination of Fenugreek and Quinoa Husk as Sources of Steroidal and Triterpenoid Saponins: Bioactivity of Their Co-Extracts and Hydrolysates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Production of Saponin-Rich Co-Extracts
2.3. Production of Sapogenin-Rich Co-Extracts
2.4. Analysis and Quantification of Saponins and Sapogenins
2.5. Bioactivity Assessment of the Extracts and Co-Extracts
2.5.1. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition Assay
2.5.2. Hypocholesterolemic Effect via Inhibition of Cholesterol Bioaccessibility In Vitro
2.5.3. Cellular Antioxidant Activity
2.5.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Saponin and Sapogenin Content of the Extracts and Co-Extracts
3.2. Inhibition Activity against Pancreatic Lipase of Extracts and Co-Extracts
3.3. Effect of Extracts and Co-Extracts on the Bioaccessibility of Cholesterol
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Extracts and Co-Extracts
3.5. Antioxidant Cellular Effect of Co-Extracts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrera, T.; Navarro del Hierro, J.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Inhibitory effect of quinoa and fenugreek extracts on pancreatic lipase and α-amylase under in vitro traditional conditions or intestinal simulated conditions. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Fărcaș, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Tofana, M.; Diaconeasa, Z.M.; Pop, O.L.; Salanță, L.C. An Overview of Saponins—A Bioactive Group. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 77, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrose, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Maki, T.; Tsujii, H. Karaya root saponin exerts a hypocholesterolemic response in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, T.T.; Che, H.X.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xue, C.H.; Chang, Y.G.; Wang, Y.M. Saponins of sea cucumber attenuate atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice via lipid-lowering and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.N.; Feng, Z.M.; Jiang, J.S.; Zhang, P.C. Eight new triterpenoid saponins with antioxidant activity from the roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. Fitoterapia 2019, 133, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayasu, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Aoki, Y.; Yazaki, K.; Sugiyama, A. Triterpenoid and steroidal saponins differentially influence soil bacterial genera. Plants 2021, 10, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Gupta, N.; Chatterjee, S. Investigating Therapeutic Potential of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. as Our Defense Mechanism against Several Human Diseases. J. Toxicol. 2016, 2016, 1250387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, A.M.; Javadivala, Z.; Khalili, Y.; Khalili, M. Efects of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) on infammatory mediators: A systematic review of preclinical studies. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.N.; Cueva, C.; Tamargo, A.; Núñez-Gómez, E.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. In Vitro Colonic Fermentation of Saponin-Rich Extracts from Quinoa, Lentil, and Fenugreek. Effect on Sapogenins Yield and Human Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2020, 68, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Cantero-Bahillo, E.; Fernández-Felipe, M.T.; Martin, D. Microwave-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis vs. Conventional Hydrolysis to Produce Sapogenin-Rich Products from Fenugreek Extracts. Foods 2022, 11, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Idehen, E.; Sang, S. Steroidal saponins in oat bran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Sang, S. Triterpenoid Saponins in Oat Bran and Their Levels in Commercial Oat Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6381–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Ray, A.; Singhal, R.S. Co-extraction of turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) and dried coconut shreds by supercritical fluid extraction (SFE): Chemical and bioactivity profile. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, E.; García-Risco, M.R.; Jaime, L.; Reglero, G.; Fornari, T. Simultaneous extraction of rosemary and spinach leaves and its effect on the antioxidant activity of products. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2013, 82, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Bermejo, D.; de las Nieves Siles-Sánchez, M.; Hernández, D.M.; García-Risco, M.R.; Jaime, L.; Santoyo, S.; Fornari, T. Theoretical framework to evaluate antioxidant synergistic effects from the coextraction of marjoram, rosemary and parsley. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ma, C.; Chen, S.; Zhu, S.; Lou, Z.; Wang, H. Conversion of steroid saponins into diosgenin by catalytic hydrolysis 623 using acid-functionalized ionic liquid under microwave irradiation. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 79, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, E.; Savarino, P.; Claereboudt, E.J.S.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Deleu, M.; Lins, L.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. 626 Enhancing the Membranolytic Activity of Chenopodium quinoa Saponins by Fast Microwave Hydrolysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, T.; Navarro del Hierro, J.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Acid hydrolysis of saponin-rich extracts of quinoa, lentil, fenugreek and soybean to yield sapogenin-rich extracts and other bioactive compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3157–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Herrera, T.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The gastrointestinal behavior of saponins and its significance for their bioavailability and bioactivities. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzi, C.A.; Barin, J.S.; Hermes, A.L.; Mortari, S.R.; Flores, É.M.M. A Fast Microwave-Assisted Procedure for Loss on Drying Determination in Saccharides. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Del Hierro, J.; Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The hydrolysis of saponin-rich extracts from fenugreek and quinoa improves their pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity and hypocholesterolemic effect. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarič, L.; Šimko, P. The Comparison of HPLC and Spectrophotometric Method for Cholesterol Determination. J. Food Sci. 2020, 14, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, K.; Liu, R. Cellular Antioxidant Activity (CAA) Assay for Assessing Antioxidants, Foods, and Dietary Supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8896–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinarova, L.; Vinarov, Z.; Atanasov, V.; Pantcheva, I.; Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.; Stoyanov, S. Lowering of cholesterol bioaccessibility and serum concentrations by saponins: In vitro and in vivo studies. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. Chemical characterization and bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds from saponin-rich extracts and their acid-hydrolysates obtained from fenugreek and quinoa. Foods 2020, 9, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhansari, G.; Soltani-Zangbar, M.S.; Pourmoghadam, Z.; Kamrani, A.; Azizi, R.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Danaii, S.; Koushaeian, L.; Hojat-Farsangi, M.; Yousefi, M. Oxidative stress, inflammatory settings, and microRNA regulation in the recurrent implantation failure patients with metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2019, 82, e13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Shi, Z.; Ren, G. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Saponins from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Seeds in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages Cells. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, F.R.S.; Araújo-Filho, H.G.; Monteiro, B.S.; Shanmugam, S.; de Souza Araújo, A.A.; da Silva Almeida, J.R.G.; Thangaraj, P.; Júnior, L.J.Q.; de Souza Siqueira Quintans, J. Anti-inflammatory and modulatory effects of steroidal saponins and sapogenins on cytokines: A review of pre-clinical research. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 152842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Cui, S.; Zheng, T.; Ma, H.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, K.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; et al. Sarsasapogenin improves adipose tissue inflammation and ameliorates insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Yang, E.J.; Ku, S.K.; Song, K.S.; Bae, J.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of oleanolic acid on LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Inflammation 2013, 36, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, K.T.; Park, H.J. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Saponin and Sapogenins Obtained from the Stem of Akebia quinata. J. Med. Food 2005, 8, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Chang, S.K.C. Comparative study on antiproliferation properties and cellular antioxidant activities of commonly consumed food legumes against nine human cancer cell lines. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.G.; Park, H.M.; Yoon, K.S. Analysis of saponin composition and comparison of the antioxidant activity of various parts of the quinoa plant (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, P.; Ghaskadbi, S.; Mohan, H.; Devasagayam, P.A. Antioxidant Properties of Germinated Fenugreek Seeds. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ye, X.-L.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.-L.; Bai, H.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X.-D.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.-L.; Hai, C.-X. Antioxidant activities of oleanolic acid in vitro: Possible role of Nrf2 and MAP kinases. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 184, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Total Saponin Content (g/100 g) | Proportion (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steroidal | Triterpenoid | ||
| F100 | 39.9 ± 1.1 a | 100 | - |
| F90Q10 | 49.7 ± 0.5 b | 69.8 | 30.2 |
| F75Q25 | 53.5 ± 3.7 b | 54.6 | 45.4 |
| F50Q50 | 61.9 ± 3.6 c | 26.2 | 73.8 |
| Q100 | 71.9 ± 4.1 d | - | 100 |
| Sample | Total sapogenin content (g/100 g) | ||
| HF100 | 16.4 ± 3.1 A | 100 | - |
| HF90Q10 | 27.1 ± 1.8 AB | 31.9 | 68.1 |
| HF75Q25 | 23.4 ± 3.7 A | 16.7 | 83.3 |
| HF50Q50 | 39.3 ± 3.2 BC | 9.5 | 90.5 |
| HQ100 | 52.3 ± 6.7 C | - | 100 |
| Saponin-Rich Extracts and Co-Extracts | IC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| F100 | >1000 |
| F90Q10 | >1000 |
| F75Q25 | >1000 |
| F50Q50 | >1000 |
| Q100 | >1000 |
| Sapogenin-rich extracts and co-extracts | |
| HF100 | 234.2 ± 34.4 d |
| HF90Q10 | 226.2 ± 21.7 d |
| HF75Q25 | 393.3 ± 23.3 c |
| HF50Q50 | 331.7 ± 12.1 b |
| HQ100 | 505.7 ± 31.5 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cantero-Bahillo, E.; Navarro del Hierro, J.; de las Nieves Siles-Sánchez, M.; Jaime, L.; Santoyo, S.; Martin, D. Combination of Fenugreek and Quinoa Husk as Sources of Steroidal and Triterpenoid Saponins: Bioactivity of Their Co-Extracts and Hydrolysates. Foods 2024, 13, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040562
Cantero-Bahillo E, Navarro del Hierro J, de las Nieves Siles-Sánchez M, Jaime L, Santoyo S, Martin D. Combination of Fenugreek and Quinoa Husk as Sources of Steroidal and Triterpenoid Saponins: Bioactivity of Their Co-Extracts and Hydrolysates. Foods. 2024; 13(4):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040562
Chicago/Turabian StyleCantero-Bahillo, Emma, Joaquín Navarro del Hierro, María de las Nieves Siles-Sánchez, Laura Jaime, Susana Santoyo, and Diana Martin. 2024. "Combination of Fenugreek and Quinoa Husk as Sources of Steroidal and Triterpenoid Saponins: Bioactivity of Their Co-Extracts and Hydrolysates" Foods 13, no. 4: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040562
APA StyleCantero-Bahillo, E., Navarro del Hierro, J., de las Nieves Siles-Sánchez, M., Jaime, L., Santoyo, S., & Martin, D. (2024). Combination of Fenugreek and Quinoa Husk as Sources of Steroidal and Triterpenoid Saponins: Bioactivity of Their Co-Extracts and Hydrolysates. Foods, 13(4), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13040562