In Vitro Effect of the Common Culinary Herb Winter Savory (Satureja montana) against the Infamous Food Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
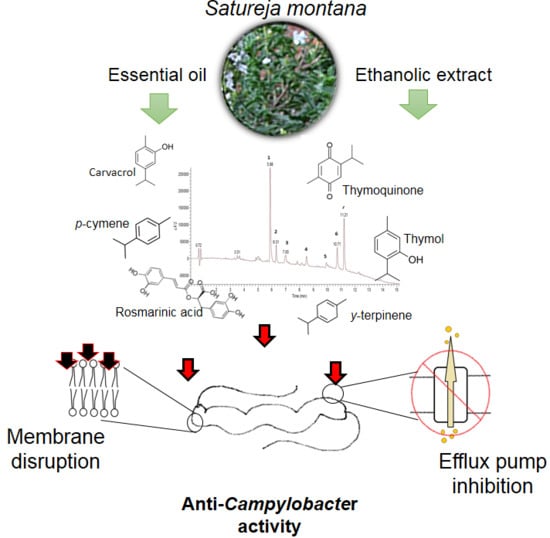
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethanolic Extract and Essential Oil Preparation and Chemical Analysis
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.3. Preparation of the C. jejuni 11168ΔcmeG Mutant Strain
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity Assay
2.5. Checkerboard Assay
2.6. Ethidium Bromide Accumulation Assay
2.7. Membrane Integrity Assay
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Analysis
3.2. Anti-Campylobacter Activity of S. montana Ethanolic Extract and Essential Oil
3.3. Synergistic Activity of the Six Pure Compounds
3.4. Efflux Pump Inhibition in C. jejuni
3.5. Disruption of Membrane Integrity in C. jejuni
3.6. Involvement of Efflux Systems in Resistance of C. jejuni to S. montana Ethanolic Extract and Essential Oil and Their Six Major Constituents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05500. [Google Scholar]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global epidemiology of Campylobacter infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nachamkin, I.; Allos, B.M.; Ho, T. Campylobacter species and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panel on Biological Hazards. European Food Safety Authority Scientific opinion on Campylobacter in broiler meat production: Control options and performance objectives and/or targets at different stages of the food chain. EFSA J. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA; ECDC. The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05598. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, B.; Wang, Y.; Hao, H.; Barton, Y.-W.; Zhang, Q. Contribution of CmeG to antibiotic and oxidative stress resistance in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Michel, L.O.; Zhang, Q. CmeABC functions as a multidrug efflux system in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Akiba, M.; Sahin, O.; Zhang, Q. CmeR functions as a transcriptional repressor for the multidrug efflux pump CmeABC in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, A.; Ramesh, A.; Seddon, A.M.; Karlyshev, A.V. CmeABC multidrug efflux pump contributes to antibiotic resistance and promotes Campylobacter jejuni survival and multiplication in Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lumpert, M.; Kreft, S. Folk use of medicinal plants in Karst and Gorjanci, Slovenia. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2017, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrier, J.; Saciragic, L.; Trakić, S.; Chen, E.C.H.; Gendron, R.L.; Cuerrier, A.; Balick, M.J.; Redžić, S.; Alikadić, E.; Arnason, J.T. An ethnobotany of the Lukomir Highlanders of Bosnia & Herzegovina. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2015, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grasser, S.; Schunko, C.; Vogl, C.R. Gathering “tea”—From necessity to connectedness with nature. Local knowledge about wild plant gathering in the Biosphere Reserve Grosses Walsertal (Austria). J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2012, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pieroni, A.; Rexhepi, B.; Nedelcheva, A.; Hajdari, A.; Mustafa, B.; Kolosova, V.; Cianfaglione, K.; Quave, C.L. One century later: The folk botanical knowledge of the last remaining Albanians of the upper Reka Valley, Mount Korab, Western Macedonia. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2013, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano, C.; Matos, O.; Teixeira, B.; Ramos, C.; Neng, N.; Nogueira, J.; Nunes, M.L.; Marques, A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Satureja montana L. extracts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćetković, G.S.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.M.; Djilas, S.M.; Tumbas, V.T.; Markov, S.L.; Cvetković, D.D. Antioxidant potential, lipid peroxidation inhibition and antimicrobial activities of Satureja montana L. subsp. kitaibelii Extracts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilijević, B.; Mitić-Ćulafić, D.; Djekic, I.; Marković, T.; Knežević-Vukčević, J.; Tomasevic, I.; Velebit, B.; Nikolić, B. Antibacterial effect of Juniperus communis and Satureja montana essential oils against Listeria monocytogenes in vitro and in wine marinated beef. Food Control 2019, 100, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, T.L.C.; de Araújo Soares, R.; Ramos, E.M.; das Graças Cardoso, M.; Alves, E.; Piccoli, R.H. Antimicrobial activity of Satureja montana L. essential oil against Clostridium perfringens type A inoculated in mortadella-type sausages formulated with different levels of sodium nitrite. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 144, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Taylor, D.E. Natural transformation in Campylobacter species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klančnik, A.; Smole Možina, S.; Zhang, Q. Anti-Campylobacter activities and resistance mechanisms of natural phenolic compounds in Campylobacter. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, M.H.; Yu, C.M.; Yu, V.L.; Chow, J.W. Synergy assessed by checkerboard. A critical analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1993, 16, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. Terminology relating to methods for the determination of susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2000, 6, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovač, J.; Šimunović, K.; Wu, Z.; Klančnik, A.; Bucar, F.; Zhang, Q.; Smole Možina, S. Antibiotic resistance modulation and modes of action of (-)-α-pinene in Campylobacter jejuni. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zgórka, G.; Głowniak, K. Variation of free phenolic acids in medicinal plants belonging to the Lamiaceae family. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 26, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, S.E.; Ebrahimi, S.N.; Gafner, F.; Ochola, J.B.; Marubu, R.M.; Lwande, W.; Frei Haller, B.; Salehi, P.; Hamburger, M. Metabolite profiling for caffeic acid oligomers in Satureja biflora. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Ricci, A.; Serio, A.; Chaves-Lopez, C.; Mazzarrino, G.; D’Amato, S.; Sterzo, C.L.; Paparella, A. Characterization of essential oils obtained from abruzzo autochthonous plants: Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities assessment for food application. Foods 2018, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Alphen, L.B.; Burt, S.A.; Veenendaal, A.K.J.; Bleumink-Pluym, N.M.C.; van Putten, J.P.M. The natural antimicrobial carvacrol inhibits Campylobacter jejuni motility and infection of epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, C.; Gundogdu, O.; Pircalabioru, G.; Cean, A.; Scates, P.; Linton, M.; Pinkerton, L.; Magowan, E.; Stef, L.; Simiz, E.; et al. The in vitro and in vivo effect of carvacrol in preventing Campylobacter infection, colonization and in improving productivity of chicken broilers. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Arsi, K.; Wagle, B.R.; Upadhyaya, I.; Shrestha, S.; Donoghue, A.M.; Donoghue, D.J. Trans-cinnamaldehyde, carvacrol, and eugenol reduce Campylobacter jejuni colonization factors and expression of virulence genes in vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaieb, K.; Kouidhi, B.; Jrah, H.; Mahdouani, K.; Bakhrouf, A. Antibacterial activity of thymoquinone, an active principle of Nigella sativa and its potency to prevent bacterial biofilm formation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, Z.; Laughlin, T.F.; Kady, I.O. Thymoquinone inhibits Escherichia coli ATP synthase and cell growth. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchese, A.; Arciola, C.R.; Barbieri, R.; Silva, A.S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Tsetegho Sokeng, A.J.; Izadi, M.; Jafari, N.J.; Suntar, I.; Daglia, M.; et al. Update on monoterpenes as antimicrobial agents: A particular focus on p-cymene. Materials 2017, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, S.A.; Vlielander, R.; Haagsman, H.P.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A. Increase in activity of essential oil components carvacrol and thymol against Escherichia coli O157:H7 by addition of food stabilizers. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekambaram, S.P.; Perumal, S.S.; Balakrishnan, A.; Marappan, N.; Gajendran, S.S.; Viswanathan, V. Antibacterial synergy between rosmarinic acid and antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 5, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanachaikunsopon, P.; Phumkhachorn, P. Assessment of factors influencing antimicrobial activity of carvacrol and cymene against Vibrio cholerae in food. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavaric, N.; Smole Možina, S.; Kladar, N.; Bozin, B. Chemical profile, antioxidant and antibacterial activity of thyme and oregano essential oils, thymol and carvacrol and their possible synergism. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2015, 18, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, G. Biological activities of three essential oils of the Lamiaceae family. Medicines 2017, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovač, J.; Gavaric, N.; Bucar, F.; Smole Možina, S. Antimicrobial and resistance modulatory activity of Alpinia katsumadai seed phenolic extract, essential oil and post-distillation extract. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 52, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- La Storia, A.; Ercolini, D.; Marinello, F.; Di Pasqua, R.; Villani, F.; Mauriello, G. Atomic force microscopy analysis shows surface structure changes in carvacrol-treated bacterial cells. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumbwe, L.; Randall, L.P.; Woodward, M.J.; Piddock, L.J.V. Evidence for multiple-antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter jejuni not mediated by CmeB or CmeF. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, Q.; Lu, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhang, R.; Wen, G.; Wang, H.; Luo, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Correlation between gyrA and CmeR box polymorphism and fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni isolates in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00422-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Treatment | MIC (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| Ethanolic extract | 250 |
| Essential oil | 1000 |
| Carvacrol | 31.25 |
| Thymol | 31.25 |
| Thymoquinone | 31.25 |
| p-cymene | 1000 |
| γ-terpinene | 1000 |
| Rosmarinic acid | 250 |
| Combination | MIC (mg/L) | FICi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Compounds | Mixed Compounds | |||||
| Compound A | Compound B | Apurea | Bpureb | Amixc | Bmixd | |
| Carvacrol | Thymol | 62.5 | 31.25 | 7.81 | 1.95 | 0.2 |
| Thymoquinone | 62.5 | 31.25 | 15.62 | 7.81 | 0.5 | |
| p-cymene | 62.5 | 500 | 62.5 | 500 | 2.0 | |
| γ-terpinene | 31.25 | 2000 | 31.25 | 2000 | 2.0 | |
| Rosmarinic acid | 31.25 | 250 | 31.25 | 250 | 2.0 | |
| Thymol | Thymoquinone | 31.25 | 31.25 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 0.3 |
| p-cymene | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 2 | |
| γ-terpinene | 125 | 1000 | 62.5 | 1000 | 1.5 | |
| Rosmarinic acid | 31.25 | 250 | 31.25 | 250 | 2 | |
| Thymoquinone | p-cymene | 15.62 | 1000 | 7.81 | 1000 | 1.5 |
| γ-terpinene | 31.25 | 1000 | 7.81 | 500 | 0.8 | |
| Rosmarinic acid | 31.25 | 250 | 7.81 | 62.50 | 0.5 | |
| p-cymene | γ-terpinene | 250 | 1000 | 125 | 1000 | 1.5 |
| Rosmarinic acid | 1000 | 250 | 500 | 125 | 1.0 | |
| γ-terpinene | Rosmarinic acid | 1000 | 250 | 1000 | 125 | 1.5 |
| Treatment | ΔcmeB | ΔcmeR | ΔcmeF | ΔcmeG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (mg/L) | FCa | MIC (mg/L) | FCa | MIC (mg/L) | FCa | MIC (mg/L) | FCa | |
| Ethanolic extract | 31.25 | 4 | 125 | 1 | 62.5 | 2 | 31.25 | 4 |
| Essential oil | 1000 | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 500 | 2 |
| Carvacrol | 15.25 | 2 | 7.81 | 4 | 15.62 | 2 | 0.97 | 32 |
| Thymol | 7.81 | 4 | 7.81 | 4 | 31.25 | 1 | 1.95 | 16 |
| Thymoquinone | 15.25 | 2 | 7.81 | 4 | 15.62 | 2 | 0.97 | 32 |
| p-cymene | 1000 | 1 | 500 | 2 | 500 | 2 | 500 | 2 |
| γ-terpinene | 500 | 2 | 250 | 4 | 250 | 4 | 500 | 2 |
| Rosmarinic acid | 62.5 | 4 | 125 | 4 | 125 | 2 | 125 | 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šimunović, K.; Bucar, F.; Klančnik, A.; Pompei, F.; Paparella, A.; Smole Možina, S. In Vitro Effect of the Common Culinary Herb Winter Savory (Satureja montana) against the Infamous Food Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni. Foods 2020, 9, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040537
Šimunović K, Bucar F, Klančnik A, Pompei F, Paparella A, Smole Možina S. In Vitro Effect of the Common Culinary Herb Winter Savory (Satureja montana) against the Infamous Food Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni. Foods. 2020; 9(4):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040537
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠimunović, Katarina, Franz Bucar, Anja Klančnik, Francesco Pompei, Antonello Paparella, and Sonja Smole Možina. 2020. "In Vitro Effect of the Common Culinary Herb Winter Savory (Satureja montana) against the Infamous Food Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni" Foods 9, no. 4: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040537
APA StyleŠimunović, K., Bucar, F., Klančnik, A., Pompei, F., Paparella, A., & Smole Možina, S. (2020). In Vitro Effect of the Common Culinary Herb Winter Savory (Satureja montana) against the Infamous Food Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni. Foods, 9(4), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040537