Identification of Cold Spots Using Non-Destructive Hyperspectral Imaging Technology in Model Food Processed by Coaxially Induced Microwave Pasteurization and Sterilization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
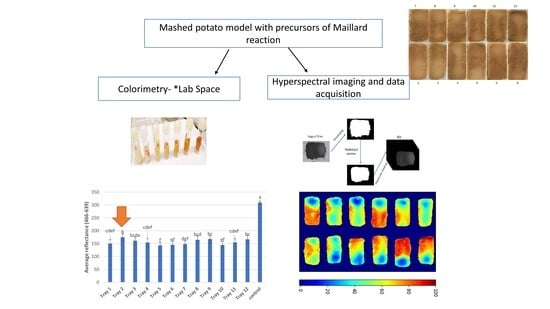
2.1. Mashed Potato Model Food Preparation
2.2. CiMPAS Treatment
2.3. Hyperspectral Imaging System
2.4. Image Segmentation
2.5. Colorimetric Analysis
2.6. Validation: Effect of Temperature Increase on Browning
2.7. Data Analysis
2.7.1. Statistical Analysis of Images
2.7.2. Visualization
2.7.3. Statistical Analysis of Colorimetry Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Kinetic Assay to Understand the Effect of Heat on Browning
3.2. Identification of Cold Spots Post CiMPAS Processing
3.3. Hyperspectral Image Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lund, D. Effects of heat processing on nutrients. In Nutritional Evaluation of Food Processing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988; pp. 319–354. [Google Scholar]
- Giroux, M.; Lacroix, M. Nutritional adequacy of irradiated meat—A review. Food Res. Int. 1998, 31, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickman, J.C.; Bruhn, C.M.; Barrett, D.M. Nutritional comparison of fresh, frozen, and canned fruits and vegetables II. Vitamin A and carotenoids, vitamin E, minerals and fiber. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Smith, J.; Thompson, A.; Brightwell, G. Microwave-induced thermal sterilization—A review on history, technical progress, advantages and challenges as compared to the conventional methods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Medina-Meza, I.; Candoğan, K.; Bermúdez-Aguirre, D. Advanced retorting, microwave assisted thermal sterilization (MATS), and pressure assisted thermal sterilization (PATS) to process meat products. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. Unlocking Potentials of Microwaves for Food Safety and Quality. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, E1776–E1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pistolesi, D.; Mascherpa, V. F0 A Technical Note; Fedegari: Albuzzano, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, D.; Tang, J.; Pedrow, P.D.; Liu, F.; Tang, Z. Analysis of electric field distribution within a microwave assisted thermal sterilization (MATS) system by computer simulation. J. Food Eng. 2016, 188, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadivambal, R.; Jayas, D. Non-uniform temperature distribution during microwave heating of food materials—A review. Food. Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Sun, D.-W.; Cheng, J.-H.; Han, Z. Non-destructive Detection and Screening of Non-uniformity in Microwave Sterilization Using Hyperspectral Imaging Analysis. Food Anal. Methods. 2018, 11, 1568–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, J.; Liu, F.; Bohnet, S.; Tang, Z. Chemical marker M2 (4-hydroxy-5-methyl-3 (2H)-furanone) formation in egg white gel model for heating pattern determination of microwave-assisted pasteurization processing. J. Food Eng. 2014, 125, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, D.; Tang, J.; Pedrow, P.D.; Liu, F.; Tang, Z. Using mobile metallic temperature sensors in continuous microwave assisted sterilization (MATS) systems. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atuonwu, J.C.; Tassou, S.A. Quality assurance in microwave food processing and the enabling potentials of solid-state power generators: A review. J. Food Eng. 2018, 234, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.; Tang, J.; Taub, I.; Yang, T.; Edwards, C.; Mao, R. Kinetics of chemical marker formation in whey protein gels for studying microwave sterilization. J. Food Eng. 2003, 60, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, R.B.; Tang, J.; Mikhaylenko, G.; Liu, F. Kinetics of chemical marker M-2 formation in mashed potato—A tool to locate cold spots under microwave sterilization. J. Food Eng. 2006, 76, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhorst, E.R.; Tang, J.; Sablani, S.S.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Thermal pasteurization process evaluation using mashed potato model food with Maillard reaction products. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarayreh, M.; Reis, M.M.; Yan, W.Q.; Klette, R. Deep spectral-spatial features of snapshot hyperspectral images for red-meat classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Image and Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ), Auckland, New Zealand, 19–21 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, M.M.; Van Beers, R.; Al-Sarayreh, M.; Shorten, P.; Yan, W.Q.; Saeys, W.; Klette, R.; Craigie, C. Chemometrics and hyperspectral imaging applied to assessment of chemical, textural and structural characteristics of meat. Meat Sci. 2018, 144, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravikanth, L.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D.; Fields, P.G.; Sun, D.-W. Extraction of spectral information from hyperspectral data and application of hyperspectral imaging for food and agricultural products. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, P.M.; Chen, Y.-R.; Kim, M.S.; Chan, D.E. Development of hyperspectral imaging technique for the detection of apple surface defects and contaminations. J. Food Eng. 2004, 61, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariana, D.P.; Lu, R.; Guyer, D.E. Near-infrared hyperspectral reflectance imaging for detection of bruises on pickling cucumbers. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2006, 53, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, K.C.; Windham, W.R.; Park, B.; Buhr, R.J. Hyperspectral imaging for poultry contaminant detection. NIR News 2001, 12, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q.; Wang, X. Protein content evaluation of processed pork meats based on a novel single shot (snapshot) hyperspectral imaging sensor. J. Food Eng. 2019, 240, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrener, J.; Posch, K.; Leitner, R. Hyperspectral fruit and vegetable classification using convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreschi, F.; Moyano, P.; Kaack, K.; Granby, K. Color changes and acrylamide formation in fried potato slices. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uan, D.G.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J. Dielectric Properties of Mashed Potatoes Relevant to Microwave and Radio-frequency Pasteurization and Sterilization Processes. J. Food. Sci. 2004, 69, FEP30–FEP37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Jiang, H. Effect of salt and sucrose content on dielectric properties and microwave freeze drying behavior of re-structured potato slices. J. Food Eng. 2011, 106, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, P.W.; Loh, Z.; Liew, C.V.; Lee, C. Dielectric properties of pharmaceutical materials relevant to microwave processing: Effects of field frequency, material density, and moisture content. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 941–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.I.; Jongen, W.M.; Van Boekel, M.A. A review of Maillard reaction in food and implications to kinetic modelling. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soni, A.; Al-Sarayreh, M.; Reis, M.M.; Smith, J.; Tong, K.; Brightwell, G. Identification of Cold Spots Using Non-Destructive Hyperspectral Imaging Technology in Model Food Processed by Coaxially Induced Microwave Pasteurization and Sterilization. Foods 2020, 9, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060837
Soni A, Al-Sarayreh M, Reis MM, Smith J, Tong K, Brightwell G. Identification of Cold Spots Using Non-Destructive Hyperspectral Imaging Technology in Model Food Processed by Coaxially Induced Microwave Pasteurization and Sterilization. Foods. 2020; 9(6):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060837
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoni, Aswathi, Mahmoud Al-Sarayreh, Marlon M. Reis, Jeremy Smith, Kris Tong, and Gale Brightwell. 2020. "Identification of Cold Spots Using Non-Destructive Hyperspectral Imaging Technology in Model Food Processed by Coaxially Induced Microwave Pasteurization and Sterilization" Foods 9, no. 6: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060837
APA StyleSoni, A., Al-Sarayreh, M., Reis, M. M., Smith, J., Tong, K., & Brightwell, G. (2020). Identification of Cold Spots Using Non-Destructive Hyperspectral Imaging Technology in Model Food Processed by Coaxially Induced Microwave Pasteurization and Sterilization. Foods, 9(6), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060837