The Bioactive Potential of Functional Products and Bioavailability of Phenolic Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
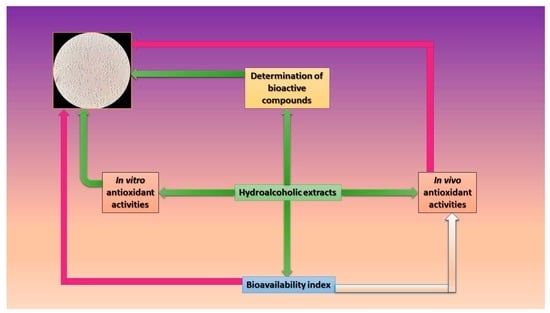
2.2. Determination of Bioactive Compounds
2.3. Assessment of the In Vitro Antioxidant Potential
2.4. Determination of the In Vivo Antioxidant Potential
2.5. Bioavailability Index Quantification
2.6. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Determination of Bioactive Compounds
3.2. Determination of In Vitro Antioxidant Activities
3.3. Determination of Bioavailability Index
3.4. Determination of In Vivo Antioxidant Activities after the Assimilation Process
3.5. Determination of Human Cell Viability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarko, T.; Duda-Chodak, A.; Sroka, P.; Satora, P.; Michalik, J. Transformation of Phenolics in Alimentary Tract. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 47, 456–463. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/58f2/23fafbe920b79ce4dbff4ec194e94b33007e.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Vamanu, E.; Gatea, F.; Sârbu, I.; Pelinescu, D. An In Vitro Study of the Influence of Curcuma longa Extracts on the Microbiota Modulation Process, In Patients with Hypertension. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarboui, R.; Baati, H.; Fetoui, F.; Gargouri, A.; Gharsallah, N.; Ammar, E. Yeast performance in wastewater treatment: Case study ofRhodotorula mucilaginosa. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamanu, E. Polyphenolic Nutraceuticals to Combat Oxidative Stress Through Microbiota Modulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aqil, F.; Munagala, R.; Jeyabalan, J.; Vadhanam, M.V. Bioavailability of phytochemicals and its enhancement by drug delivery systems. Cancer Lett. 2013, 334, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Archivio, M.; Filesi, C.; Varì, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Masella, R. Bioavailability of the Polyphenols: Status and Controversies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1321–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulić, J.; Šeregelj, V.; Kalušević, A.; Lević, S.; Nedović, V.; Tumbas Šaponjac, V.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Ćetković, G. Bioavailability and Bioactivity of Encapsulated Phenolics and Carotenoids Isolated from Red Pepper Waste. Molecules 2019, 24, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vamanu, E.; Gatea, F.; Sârbu, I. In Vitro Ecological Response of the Human Gut Microbiome to Bioactive Extracts from Edible Wild Mushrooms. Molecules 2018, 23, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, M.B.; Hassan, S.; Waheed, M.; Javed, A.; Farooq, M.A.; Tahir, A. Bioavailability and Metabolic Pathway of Phenolic Compounds, Plant Physiological Aspects of Phenolic Compounds; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vamanu, E.; Gatea, F. Correlations between Microbiota Bioactivity and Bioavailability of Functional Compounds: A Mini-Review. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteban-Torres, M.; Santamaría, L.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Plaza-Vinuesa, L.; Crispie, F.; De las Rivas, B.; Cotter, P.; Muñoz, R. A Diverse Range of Human Gut Bacteria Have the Potential To Metabolize the Dietary Component Gallic Acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01558-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyśkiewicz, K.; Konkol, M.; Kowalski, R.; Rój, E.; Warmiński, K.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Gil, Ł.; Stolarski, M.J. Characterization of bioactive compounds in the biomass of black locust, poplar and willow. Trees 2019, 33, 1235–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, Isolation, and Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Plant Extracts. Plants 2017, 22, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobek, M.; Frąc, M.; Cybulska, J. Plant Biostimulants: Importance of the Quality and Yield of Horticultural Crops and the Improvement of Plant Tolerance to Abiotic Stress—A Review. Agronomy 2019, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Jiao, R.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.M.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lei, L.; Ma, K.Y.; et al. Biology of ageing and role of dietary antioxidants. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patterson, T.L.; Mausbach, B.T. Measurement of functional capacity: A new approach to understanding functional differences and real-world behavioral adaptation in those with mental illness. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2010, 6, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lourenço, S.C.; Moldão-Martins, M.; Alves, V.D. Antioxidants of Natural Plant Origins: From Sources to Food Industry Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skrovankova, S.; Sumczynski, D.; Mlcek, J.; Jurikova, T.; Sochor, J. Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Different Types of Berries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24673–24706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Foligné, B.; Alexandraki, V.; Kazou, M.; Pot, B.; Tsakalidou, E. Discovering probiotic microorganisms: In Vitro, In Vivo, genetic and omics approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: http://scitechconnect.elsevier.com/bioavailability-bioaccessibility-bioactivity-food-components/ (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Available online: http://abc.herbalgram.org/site/PageServer (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- Ajuwon, O.R.; Katengua-Thamahane, E.; Van Rooyen, J.; Oguntibeju, O.O.; Marnewick, J.L. Protective Effects of Rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) and/or Red Palm Oil (Elaeis guineensis) Supplementation on tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Oxidative Hepatotoxicity in Wistar Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 984273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paschoin de Oliveira Campos, M.; Riechelmann, R.; Martins, L.C.; Hassan, B.J.; Branco Assunção Casa, F.; Del Giglio, A. Guarana (Paullinia cupana) Improves Fatigue in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Systemic Chemotherapy. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2011, 17, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misle, E.; Garrido, E.; Contardo, H.; González, W. Maqui [Aristotelia chilensis (Mol.) Stuntz] the Amazing Chilean Tree: A Review. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. B 2011, 1, 473–482. [Google Scholar]
- Heck, C.I.; De Mejia, E.G. Yerba Mate Tea (Ilex paraguariensis): A Comprehensive Review on Chemistry, Health Implications, and Technological Considerations. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Rojas, D.F.; De Souza, C.R.; Oliveira, W.P. Clove (Syzygium aromaticum): A precious spice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaconeasa, Z.; Iuhas, C.I.; Ayvaz, H.; Rugină, D.; Stanilă, A.; Dulf, F.V.; Bunea, A.; Socaci, S.A.; Socaciu, C.; Pintea, A. Phytochemical Characterization of Commercial Processed Blueberry, Blackberry, Blackcurrant, Cranberry, and Raspberry and Their Antioxidant Activity. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanali, C.; Della Posta, S.; Vilmercati, A.; Dugo, L.; Russo, M.; Petitti, T.; Mondello, L.; De Gara, L. Extraction, Analysis, and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Phenolic Compounds in Different Italian Extra-Virgin Olive Oils. Molecules 2018, 23, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vamanu, E.; Nita, S. Antioxidant Capacity and the Correlation with Major Phenolic Compounds, Anthocyanin, and Tocopherol Content in Various Extracts from the Wild Edible Boletus edulis Mushroom. BioMed Res. Int. 2012, 2013, 313905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raudone, L.; Vilkickyte, G.; Pitkauskaite, L.; Raudonis, R.; Vainoriene, R.; Motiekaityte, V. Antioxidant Activities of Vaccinium vitis-idaea L. Leaves within Cultivars and Their Phenolic Compounds. Molecules 2019, 24, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoibe, M.; Chy, M.N.U.; Alam, M.; Adnan, M.; Islam, M.Z.; Nihar, S.W.; Rahman, N.; Suez, E. In Vitro and In Vivo Biological Activities of Cissus adnata (Roxb.). Biomedicines 2017, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celep, E.; Akyüz, S.; İnan, Y.; Yesilada, E. Assessment of potential bioavailability of major phenolic compounds in Lavandula stoechas L. ssp. Stoechas. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 118, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, M.M.; Holban, A.M.; Giurcăneanu, C.; Popa, L.G.; Buzea, M.; Filipov, M.; Lazǎr, V.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Popa, M.I. Identification and Phenotypic Characterization of the Most Frequent Bacterial Etiologies in Chronic Skin Ulcers. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55, 1401–1408. Available online: http://www.rjme.ro/RJME/resources/files/55041414011408.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2020). [PubMed]
- Vamanu, E.; Pelinescu, D.; Gatea, F.; Sârbu, I. Altered in Vitro Metabolomic Response of the Human Microbiota to Sweeteners. Genes 2019, 10, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonilla, J.; Sobral, P.J.A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of ethanolic extracts of guarana, boldo, rosemary and cinnamon Propriedades antioxidante e antimicrobiana de extratos etanólicos de guaraná, boldo, alecrim e canela. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2017, 20, e2016024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghasemzadeh, A.; Jaafar, H.Z.E.; Rahmat, A. Antioxidant Activities, Total Phenolics and Flavonoids Content in Two Varieties of Malaysia Young Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Molecules 2010, 15, 4324–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, J.P.; Rees, S.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K.L. Principles of early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quispe-Fuentes, I.; Vega-Gálvez, A.; Aranda, M. Evaluation of phenolic profiles and antioxidant capacity of maqui (Aristotelia chilensis) berries and their relationships to drying methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4168–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lam, K.L.; Hu, J.; N Ge, S.; Zhou, A.; Zheng, B.; Zeng, S.; Lin, S. Chlorogenic acid alleviates obesity and modulates gut microbiota in high-fat-fed mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonthier, M.P.; Verny, M.A.; Besson, C.; Rémésy, C.; Scalbert, A. Chlorogenic Acid Bioavailability Largely Depends on Its Metabolism by the Gut Microflora in Rats. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calhelha, R.C.; Falcão, S.I.; Queiroz, M.J.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Ferreira, I.C. Cytotoxicity of Portuguese Propolis: The Proximity of the In Vitro Doses for Tumor and Normal Cell Lines. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 897361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Webster, D.; Cao, J.; Shao, A. The safety of green tea and green tea extract consumption in adults—Results of a systematic review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 95, 412–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal Pharmaceutical Society. Available online: https://www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/1-what-is-a-nutraceutical/20002095.article?firstPass=false (accessed on 7 February 2020).
- Zimmermann, A.; Hofer, S.; Pendl, T.; Kainz, K.; Madeo, F.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D. Yeast as a tool to identify anti-aging compounds. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18, foy020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, K.C.; De M B Costa, E.M.; Pazini, F.; Valadares, M.C.; De Oliveira, V. Bioconversion of quercetin and rutin and the cytotoxicity activities of the transformed products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajik, N.; Tajik, M.; Mack, I.; Enck, P. The potential effects of chlorogenic acid, the main phenolic components in coffee, on health: A comprehensive review of the literature. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 2215–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.F.; Borge, G.I.A.; Piskula, M.; Tudose, A.; Tudoreanu, L.; Valentová, K.; Williamson, G.; Santos, C.N. Bioavailability of Quercetin in Humans with a Focus on Interindividual Variation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Pino-García, R.; Rivero-Pérez, M.D.; González-SanJosé, M.L.; Croft, K.D.; Muñiz, P. Bioavailability of phenolic compounds and antioxidant effects of wine pomace seasoning after oral administration in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 25, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Compounds (mg/100 mL Extract) | Aspalathus linearis | Paullinia cupana | A. chilensis | Ilex paraguariensis | Syzygium aromaticum | Wild Berries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.21 ± 0.01 a | 0.60 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 14.38 ± 0.29 c | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.37 ± 0.01 a |
| Caffeic acid | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.01 ± 0.01 a | 0.005 ± 0.02 a | 0.19 ± 0.10 a | 0. 60 ± 0.08 b | 0.30 ± 0.01 b |
| Rutin | nd | nd | nd | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 b | 0.07 ± 0.08 b |
| Quercetin | 0.68 ± 0.04 c | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.96 ± 0.04 c | 4.67 ± 0.27 c | 0.21 ± 0.02 b |
| Kaempferol 7-glucoside | 0.04 ± 0.01 c | 0.06 ± 0.05 b | 0.04 ± 0.01 b | 2.88 ± 0.30 c | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 a |
| Kaempferol 3-galactoside | 0.02 ± 0.03 b | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.33 ± 0.05 c | 6.09 ± 0.29 | 1.07 ± 0.05 c | 0.01 ± 0.03 c |
| Kaempferol 3-rutinoside | 0.06 ± 0.02 a | 0.03 ± 0.05 a | 0.04 ± 0.02 a | 0.56 ± 0.41 | 0.10 ± 0.07 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 a |
| Kaempferol 3-rhamnoside | 0.01 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.05 a | nd | 0.24 ± 0.03 b | 0.04 ± 0.08 c | 0.08 ± 0.05 b |
| Myricetin 3-glucoside | 0.95 ± 0.08 b | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.04 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.40 ± 0.03 b | 0.002 ± 0.07 a |
| Quercetin 3-rhamnoside | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 1.84 ± 0.04 c | 0.31 ± 0.09 b | 40.52 ± 0.93 | 0.37 ± 0.01 b | 0.24 ± 0.01 a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabulici, C.M.; Sârbu, I.; Vamanu, E. The Bioactive Potential of Functional Products and Bioavailability of Phenolic Compounds. Foods 2020, 9, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070953
Dabulici CM, Sârbu I, Vamanu E. The Bioactive Potential of Functional Products and Bioavailability of Phenolic Compounds. Foods. 2020; 9(7):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070953
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabulici, Cristina Monica, Ionela Sârbu, and Emanuel Vamanu. 2020. "The Bioactive Potential of Functional Products and Bioavailability of Phenolic Compounds" Foods 9, no. 7: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070953
APA StyleDabulici, C. M., Sârbu, I., & Vamanu, E. (2020). The Bioactive Potential of Functional Products and Bioavailability of Phenolic Compounds. Foods, 9(7), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9070953