Cerium Oxide Enhances the Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Lung Epithelial Cell Cultures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
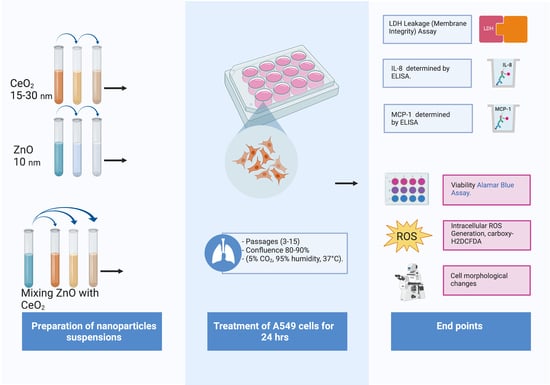
2.1. Characterization and Preparation of Nanomaterials Suspensions
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.3. Viability Assay
2.4. LDH Leakage
2.5. Reactive Oxygen Species
2.6. Cytokines and Chemokines
2.7. Interference of NPs with Cytotoxic Assays
2.8. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
3.2. Viability Assay
3.3. LDH Assay
3.4. ROS
3.5. Cytokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Simon, A.; Eshet, H.; Rabani, E. On the Phase Behavior of Binary Mixtures of Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, I.; Kumar, A. Including nanoparticle mixtures in human health risk assessment. Integr. Env. Assess. Manag. 2014, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomak, E.; Yazici, O.; Sam Parmak, E.; Gonultas, O. Influence of tannin containing coatings on weathering resistance of wood: Combination with zinc and cerium oxide nanoparticles. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 152, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrakala, H.N.; Ramaraj, B.; Shivakumaraiah; Madhu, G.M.; Siddaramaiah. The influence of zinc oxide–cerium oxide nanoparticles on the structural characteristics and electrical properties of polyvinyl alcohol films. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 8076–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S. 6 Destinations with Sunscreen Bans, and What You Need to Know. Available online: https://www.smartertravel.com/sunscreen-ban-destinations/ (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Kaluza, S.; Balderhaar, J.; Orthen, B.; Honnert, B.; Jankowska, E.; Pietrowski, P.; Rosell, M.; Tanarro, C.; Tejedor, J. Working Exposure to Nanoparticles; EU-OSHA—European Agency for Safety and Health at Work: Bilbao, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Monse, C.; Hagemeyer, O.; Raulf, M.; Jettkant, B.; van Kampen, V.; Kendzia, B.; Gering, V.; Kappert, G.; Weiss, T.; Ulrich, N.; et al. Concentration-dependent systemic response after inhalation of nano-sized zinc oxide particles in human volunteers. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandebriel, R.J.; De Jong, W.H. A review of mammalian toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossner, P.; Vrbova, K.; Strapacova, S.; Rossnerova, A.; Ambroz, A.; Brzicova, T.; Libalova, H.; Javorkova, E.; Kulich, P.; Vecera, Z.; et al. Inhalation of ZnO Nanoparticles: Splice Junction Expression and Alternative Splicing in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 168, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Ma, Y.; Shannon, K.B.; Chen, D.-R.; Huang, Y.-W. Toxicity of nano- and micro-sized ZnO particles in human lung epithelial cells. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 11, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Madler, L.; Gilbert, B.; Shi, H.; Yeh, J.I.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Reyes, G.; Rodea-Palomares, I.; Das, S.; Sakthivel, T.S.; Leganes, F.; Rosal, R.; Seal, S.; Fernandez-Pinas, F. Untangling the biological effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles: The role of surface valence states. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leibrock, L.; Wagener, S.; Singh, A.V.; Laux, P.; Luch, A. Nanoparticle induced barrier function assessment at liquid-liquid and air-liquid interface in novel human lung epithelia cell lines. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areecheewakul, S.; Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Givens, B.; Steines, B.; Wang, Y.; Meyerholz, D.; Parizek, N.; Altmaier, R.; Haque, E.; O’Shaughnessy, P.; et al. Toxicity assessment of metal oxide nanomaterials using in vitro screening and murine acute inhalation studies. NanoImpact 2020, 18, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, P.S. Inhalation toxicology models of endotoxin- and bioaerosol-induced inflammation. Toxicology 2000, 152, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Stebounova, L.V.; Kim, J.S.; Vorrink, S.U.; Ault, A.U.; O’Shaughnessy, P.T.; Grassian, V.H.; Thorne, P.S. Toxicity assessment of zinc oxide nanoparticles using sub-acute and sub-chronic murine inhalation models. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoid, G.M.; Cohen, J.M.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Demokritou, P. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro dosimetry of dispersed, engineered nanomaterials. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoid, G.; Cohen, J.M.; Darrah, T.; Derk, R.; Rojanasakul, L.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Wohlleben, W.; Demokritou, P. Estimating the effective density of engineered nanomaterials for in vitro dosimetry. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.J.; MacCormack, T.J.; Clark, R.J.; Ede, J.D.; Ortega, V.A.; Felix, L.C.; Dang, M.K.; Ma, G.; Fenniri, H.; Veinot, J.G.; et al. Widespread nanoparticle-assay interference: Implications for nanotoxicity testing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.S.; Koh, D.C.; Kong, I.C. Toxicity Evaluation of Individual and Mixtures of Nanoparticles Based on Algal Chlorophyll Content and Cell Count. Materials 2018, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, W.; Slaveykova, V.I. Effects of Mixtures of Engineered Nanoparticles and Metallic Pollutants on Aquatic Organisms. Environments 2020, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Su, Y.; Li, W.; Wilkinson, K.J.; Xie, B. Acute toxicity evaluation of nanoparticles mixtures using luminescent bacteria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, M. Principles and Practice of Mixtures Toxicology, 1st ed.; Mumtaz, M., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; p. 662. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Middleton, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Conolly, R.B. Bridging the Data Gap From in vitro Toxicity Testing to Chemical Safety Assessment Through Computational Modeling. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Pandey, A.K. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Induced Toxicity in Human Lung Cells: Role of ROS Mediated DNA Damage and Apoptosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 891934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.; Srividya, L. Evaluation of In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Zinc Oxide (Zno) Nanoparticles Using Human Cell Lines. J. Toxicol. Risk Assess. 2018, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila-Grana, A.; Diego-Gonzalez, L.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, A.; Simon-Vazquez, R. Synergistic Effect of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles on Cell Viability and Activation of MAP Kinases and NFkappaB. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, B.; Seog, J.H.; Graham, L.M.; Lee, S.B. Experimental considerations on the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Tong, T.; Xie, M.; Gaillard, J.-F. Lifetime and dissolution kinetics of zinc oxide nanoparticles in aqueous media. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 324001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Rupasinghe, T.; Wu, C.-M.; Grassian, V.H. Dissolution of ZnO Nanoparticles at Circumneutral pH: A Study of Size Effects in the Presence and Absence of Citric Acid. Langmuir 2012, 28, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, V.A.; Kumar, A. ZnO nanoparticles dissolution, penetration and toxicity in human epidermal cells. Influence of pH. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, B.; Xu, G.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Ju, X.; Bose, D.D.; Qiu, F.; et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles harness autophagy to induce cell death in lung epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; Kim, M.K.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, J.A.; Yu, J.; Chung, H.E.; Choi, S.J. Factors influencing the cytotoxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Particle size and surface charge. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 304, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wu, W.; Yan, Z. Reactive oxygen species trigger NF-kappaB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles in A549 cells. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, K.; Ordóñez Ramos, F.; Soria, D.B.; Pabón Gelves, E.; Di Virgilio, A.L. Cytotoxicity and DNA damage evaluation of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles. Uptake in lung cells in culture. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Karakoti, A.S.; Self, W.; Seal, S.; Singh, S. Redox-Sensitive Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Protect Human Keratinocytes from Oxidative Stress Induced by Glutathione Depletion. Langmuir 2016, 32, 12202–12211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S. Redox-dependent catalase mimetic cerium oxide-based nanozyme protect human hepatic cells from 3-AT induced acatalasemia. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 175, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saptarshi, S.R.; Feltis, B.N.; Wright, P.F.; Lopata, A.L. Investigating the immunomodulatory nature of zinc oxide nanoparticles at sub-cytotoxic levels in vitro and after intranasal instillation in vivo. J. Nanobiotechnology 2015, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holownia, A.; Wielgat, P.; Rysiak, E.; Braszko, J.J. Intracellular and Extracellular Cytokines in A549 Cells and THP1 Cells Exposed to Cigarette Smoke. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 910, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Castejon, G.; Brough, D. Understanding the mechanism of IL-1beta secretion. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazuda, D.J.; Lee, J.C.; Young, P.R. The kinetics of interleukin 1 secretion from activated monocytes. Differences between interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 8473–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santimano, M.C.; Martin, A.; Kowshik, M.; Sarkar, A. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Cause Morphological Changes in Human A549 Cell Line Through Alteration in the Expression Pattern of Small GTPases at mRNA Level. J. Bionanoscience 2013, 7, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, I.; Ellis, L.J.; Romer, I.; Tantra, R.; Carriere, M.; Allard, S.; Mayne-L’Hermite, M.; Minelli, C.; Unger, W.; Potthoff, A.; et al. Dispersion of Nanomaterials in Aqueous Media: Towards Protocol Optimization. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 130, e56074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betts, J.N.; Johnson, M.G.; Rygiewicz, P.T.; King, G.A.; Andersen, C.P. Potential for metal contamination by direct sonication of nanoparticle suspensions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Steines, B.R.; Jing, X.; Salem, A.K.; Thorne, P.S. Comparison of in vitro toxicity of aerosolized engineered nanomaterials using air-liquid interface mono-culture and co-culture models. NanoImpact 2020, 18, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Park, J.H.; Peters, T.M.; Thorne, P.S. Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in lung epithelial cells exposed at the air-liquid interface compared with in vivo assessment. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Rashaideh, T.; Metwali, N.; Perry, S.S.; Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Thorne, P.S. Cerium Oxide Enhances the Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Lung Epithelial Cell Cultures. Toxics 2022, 10, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090522
Al Rashaideh T, Metwali N, Perry SS, Adamcakova-Dodd A, Thorne PS. Cerium Oxide Enhances the Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Lung Epithelial Cell Cultures. Toxics. 2022; 10(9):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090522
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Rashaideh, Tasnim, Nervana Metwali, Sarah S. Perry, Andrea Adamcakova-Dodd, and Peter S. Thorne. 2022. "Cerium Oxide Enhances the Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Lung Epithelial Cell Cultures" Toxics 10, no. 9: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090522
APA StyleAl Rashaideh, T., Metwali, N., Perry, S. S., Adamcakova-Dodd, A., & Thorne, P. S. (2022). Cerium Oxide Enhances the Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Lung Epithelial Cell Cultures. Toxics, 10(9), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090522