Ultrafine Particles Issued from Gasoline-Fuels and Biofuel Surrogates Combustion: A Comparative Study of the Physicochemical and In Vitro Toxicological Effects
Abstract
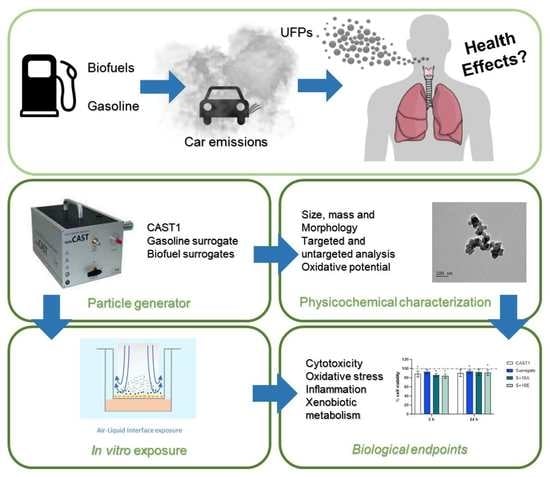
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Exposure System and Operating Conditions
2.3. Characteristics of Aerosols Emission
2.3.1. Particles Characterization: Size, Mass, and Morphology
2.3.2. Chemical Characterization
2.4. Oxidative Potential
2.4.1. Particle Suspension Preparation
2.4.2. Dithiothreitol (DTT) Assay
2.4.3. Antioxidant (AO) Depletion Measurement
2.5. Cell Culture and Exposures
2.6. Biological Endpoints
2.6.1. Cytotoxicity
2.6.2. ATP/ADP Quantification
Cell Sample Preparation
ATP/ADP Quantification
2.6.3. qRT-PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Aerosol Characterization
3.1.1. Particles’ Characterization: Size, Mass, and Morphology
3.1.2. Chemical Characterization
3.2. Oxidative Potential (AO Depletion Measurement and DTT Assay)
3.3. Cell Response after Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, R.; Hu, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, G.; Xu, D.; Chen, C. Beyond PM2.5: The Role of Ultrafine Particles on Adverse Health Effects of Air Pollution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 2844–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Bates, D.V.; Raizenne, M.E. Health Effects of Particulate Air Pollution: Time for Reassessment? Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizza, V.; Stabile, L.; Vistocco, D.; Russi, A.; Pardi, S.; Buonanno, G. Effects of the Exposure to Ultrafine Particles on Heart Rate in a Healthy Population. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraufnagel, D.E. The Health Effects of Ultrafine Particles. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, H.-S.; Ryu, M.H.; Carlsten, C. Ultrafine Particles: Unique Physicochemical Properties Relevant to Health and Disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Li, Y.-C.; Amesho, K.T.T.; Chou, F.-C.; Cheng, P.-C. Characterization and Quantification of PM2.5 Emissions and PAHs Concentration in PM2.5 from the Exhausts of Diesel Vehicles with Various Accumulated Mileages. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Diesel and Gasoline Engine Exhausts and Some Nitroarenes; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2013; ISBN 978-92-832-1210-2. [Google Scholar]
- Dahman, Y.; Syed, K.; Begum, S.; Roy, P.; Mohtasebi, B. 14—Biofuels: Their Characteristics and Analysis. In Biomass, Biopolymer-Based Materials, and Bioenergy; Verma, D., Fortunati, E., Jain, S., Zhang, X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Swanston, UK, 2019; pp. 277–325. ISBN 978-0-08-102426-3. [Google Scholar]
- Alalwan, H.A.; Alminshid, A.H.; Aljaafari, H.A.S. Promising Evolution of Biofuel Generations. Subject Review. Renew. Energy Focus 2019, 28, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lü, X. Chapter 1—General Introduction to Biofuels and Bioethanol. In Advances in 2nd Generation of Bioethanol Production; Lü, X., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Swanston, UK, 2021; pp. 1–7. ISBN 978-0-12-818862-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Rossow, B.; Modica, V.; Yu, X.; Wu, L.; Grisch, F. Laminar Flame Speed of Lignocellulosic Biomass-Derived Oxygenates and Blends of Gasoline/Oxygenates. Fuel 2017, 202, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohse-Höinghaus, K.; Oßwald, P.; Cool, T.A.; Kasper, T.; Hansen, N.; Qi, F.; Westbrook, C.K.; Westmoreland, P.R. Biofuel Combustion Chemistry: From Ethanol to Biodiesel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3572–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ge, Y.; Wang, X.; Thomas, D.; Su, S.; Li, H. An Assessment of How Bio-E10 Will Impact the Vehicle-Related Ozone Contamination in China. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Balasubramanian, R. Influence of Butanol–Diesel Blends on Particulate Emissions of a Non-Road Diesel Engine. Fuel 2014, 118, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leni, Z.; Künzi, L.; Geiser, M. Air Pollution Causing Oxidative Stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øvrevik, J. Oxidative Potential Versus Biological Effects: A Review on the Relevance of Cell-Free/Abiotic Assays as Predictors of Toxicity from Airborne Particulate Matter. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, J.T.; Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Zeng, L.; Weber, R.J.; Tolbert, P.E.; Abrams, J.Y.; Sarnat, S.E.; Klein, M.; Mulholland, J.A.; et al. Review of Acellular Assays of Ambient Particulate Matter Oxidative Potential: Methods and Relationships with Composition, Sources, and Health Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4003–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crobeddu, B.; Aragao-Santiago, L.; Bui, L.-C.; Boland, S.; Baeza Squiban, A. Oxidative Potential of Particulate Matter 2.5 as Predictive Indicator of Cellular Stress. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, I.C.; Sturrock, A.; Ghiassi, H.; Woller, D.J.; Deering-Rice, C.E.; Lighty, J.S.; Paine, R.; Reilly, C.; Kelly, K.E. Effects of Fuel Components and Combustion Particle Physicochemical Properties on Toxicological Responses of Lung Cells. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2018, 53, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An Emerging Discipline Evolving from Studies of Ultrafine Particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Verma, M.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Ultrafine Particles in Urban Ambient Air and Their Health Perspectives. Rev. Environ. Health 2013, 28, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, D.P.; Gomes, R.L.N.; Yoshizaki, K.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Matsuda, M.; Junqueira, M.D.S.; Teodoro, W.R.; Vasconcellos, P.D.C.; Pereira, D.C.D.A.; Da Conceição, P.R.; et al. Nrf2 Positively Regulates Autophagy Antioxidant Response in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Exposed to Diesel Exhaust Particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malorni, L.; Guida, V.; Sirignano, M.; Genovese, G.; Petrarca, C.; Pedata, P. Exposure to Sub-10nm Particles Emitted from a Biodiesel-Fueled Diesel Engine: In Vitro Toxicity and Inflammatory Potential. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 270, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seriani, R.; de Souza, C.E.C.; Krempel, P.G.; Frias, D.P.; Matsuda, M.; Correia, A.T.; Ferreira, M.Z.J.; Alencar, A.M.; Negri, E.M.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; et al. Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Exposed in Vitro to Diesel Exhaust Particles Exhibit Alterations in Cell Rheology and Cytotoxicity Associated with Decrease in Antioxidant Defenses and Imbalance in Pro- and Anti-Apoptotic Gene Expression. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 9862–9870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-J.; Cho, H.G.; Park, C.K.; Park, K.H.; Lim, H.B. Comparative In Vitro Biological Toxicity of Four Kinds of Air Pollution Particles. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 33, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juarez-Facio, A.T.; Castilla, C.; Corbière, C.; Lavanant, H.; Afonso, C.; Morin, C.; Merlet-Machour, N.; Chevalier, L.; Vaugeois, J.-M.; Yon, J.; et al. Development of a Standardized in Vitro Approach to Evaluate Microphysical, Chemical, and Toxicological Properties of Combustion-Derived Fine and Ultrafine Particles. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 113, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagnon, S.W.; Thion, S.; Nilsson, E.J.K.; Mehl, M.; Serinyel, Z.; Zhang, K.; Dagaut, P.; Konnov, A.A.; Dayma, G.; Pitz, W.J. Experimental and Modeling Studies of a Biofuel Surrogate Compound: Laminar Burning Velocities and Jet-Stirred Reactor Measurements of Anisole. Combust. Flame 2018, 189, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bescond, A.; Yon, J.; Ouf, F.X.; Ferry, D.; Delhaye, D.; Gaffié, D.; Coppalle, A.; Rozé, C. Automated Determination of Aggregate Primary Particle Size Distribution by TEM Image Analysis: Application to Soot. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Facio, A.T.; Yon, J.; Corbière, C.; Rogez-Florent, T.; Castilla, C.; Lavanant, H.; Mignot, M.; Devouge-Boyer, C.; Logie, C.; Chevalier, L.; et al. Toxicological Impact of Organic Ultrafine Particles (UFPs) in Human Bronchial Epithelial BEAS-2B Cells at Air-Liquid Interface. Toxicol. Vitr. 2021, 78, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrère, C.; Hubert-Roux, M.; Lange, C.M.; Rejaibi, M.; Kebir, N.; Désilles, N.; Lecamp, L.; Burel, F.; Loutelier-Bourhis, C. Solvent-Based and Solvent-Free Characterization of Low Solubility and Low Molecular Weight Polyamides by Mass Spectrometry: A Complementary Approach. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, J.; Carrasco, N.; Schmitz-Afonso, I.; Gautier, T.; Afonso, C. Comparison of Soluble and Insoluble Organic Matter in Analogues of Titan’s Aerosols. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 495, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Hajjar, C.; Rogez-Florent, T.; Seguin, V.; Verdin, A.; Garon, D.; Pottier, I.; André, V. Intrinsic Characteristics and Biological Effects of Standard Reference Indoor Dust SRM® 2585 and Its Inhalable Subfractions PM10 and PM2.5. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin de Lagarde, V.; Rogez-Florent, T.; Cazier, F.; Dewaele, D.; Cazier-Dennin, F.; Ollivier, A.; Janona, M.; Achard, S.; André, V.; Monteil, C.; et al. Oxidative Potential and in Vitro Toxicity of Particles Generated by Pyrotechnic Smokes in Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez-Facio, A.T.; Lagarde, V.; Monteil, C.; Vaugeois, J.-M.; Corbiere, C.; Rogez-Florent, T. Validation of a Fast and Simple HPLC-UV Method for the Quantification of Adenosine Phosphates in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bescond, A.; Yon, J.; Ouf, F.-X.; Rozé, C.; Coppalle, A.; Parent, P.; Ferry, D.; Laffon, C. Soot Optical Properties Determined by Analyzing Extinction Spectra in the Visible Near-UV: Toward an Optical Speciation According to Constituents and Structure. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 101, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.S.; Lobodin, V.V.; Rodgers, R.P.; McKenna, A.M.; Marshall, A.G. Compositional Boundaries for Fossil Hydrocarbons. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2174–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, R.S.; Korte, A.R.; Vertes, A.; Miller, J.H. The Molecular Composition of Soot. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4484–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmann, K.; Hepp, H.; Sattler, K. Reactive Dimerization: A New PAH Growth Mechanism in Flames. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1995, 109, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmann, K.; Sattler, K. Formation Mechanism for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Methane Flames. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 112, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünger, J.; Krahl, J.; Schröder, O.; Schmidt, L.; Westphal, G.A. Potential Hazards Associated with Combustion of Bio-Derived versus Petroleum-Derived Diesel Fuel. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2012, 42, 732–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Gao, K.; Zhang, C.; Lang, W. Chapter 2—Alternative Fuels for IC Engines and Jet Engines and Comparison of Their Gaseous and Particulate Matter Emissions. In Advanced Biofuels; Azad, A.K., Rasul, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Swanston, UK, 2019; pp. 17–64. ISBN 978-0-08-102791-2. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, O.; Krahl, J.; Munack, A.; Bünger, J. Environmental and Health Effects Caused by the Use of Biodiesel. SAE Trans. 1999, 108, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Roth, P.; Durbin, T.; Karavalakis, G. Impacts of Gasoline Aromatic and Ethanol Levels on the Emissions from GDI Vehicles: Part 1. Influence on Regulated and Gaseous Toxic Pollutants. Fuel 2019, 252, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Fang, T.; Xu, L.; Peltier, R.E.; Russell, A.G.; Ng, N.L.; Weber, R.J. Organic Aerosols Associated with the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Water-Soluble PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4646–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.K.; Sioutas, C.; Miguel, A.H.; Kumagai, Y.; Schmitz, D.A.; Singh, M.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Froines, J.R. Redox Activity of Airborne Particulate Matter at Different Sites in the Los Angeles Basin. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wyatt, A.; Kamens, R.M. Oxidant Generation and Toxicity Enhancement of Aged-Diesel Exhaust. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrogrande, M.C.; Russo, M.; Zagatti, E. Review of PM Oxidative Potential Measured with Acellular Assays in Urban and Rural Sites across Italy. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coufalík, P.; Matoušek, T.; Křůmal, K.; Vojtíšek-Lom, M.; Beránek, V.; Mikuška, P. Content of Metals in Emissions from Gasoline, Diesel, and Alternative Mixed Biofuels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 29012–29019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, G.; Bellance, N.; Jose, C.; Melser, S.; Nouette-Gaulain, K.; Rossignol, R. Multi-Site Control and Regulation of Mitochondrial Energy Production. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1797, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavanaugh, K.J.; Oswari, J.; Margulies, S.S. Role of Stretch on Tight Junction Structure in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2001, 25, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, X.; Su, H.; Ding, G.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z. Exposure to Ambient Fine Particles Causes Abnormal Energy Metabolism and ATP Decrease in Lung Tissues. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.; Zhang, J.; Valverde, M.; Rojas, E.; Shi, Z.-Z. Essential Role of Nrf2 in Protection against Hydroquinone- and Benzoquinone-Induced Cytotoxicity. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chu, H. Ambient Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Induces Oxidative Stress and pro-Inflammatory Response via up-Regulating the Expression of CYP1A1/1B1 in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells in Vitro. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2019, 839, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, A.; Bengalli, R.; Longhin, E.; Capasso, L.; Proverbio, M.C.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S.; Gualtieri, M.; Battaglia, C.; Camatini, M. Transcriptional Profiling of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell BEAS-2B Exposed to Diesel and Biomass Ultrafine Particles. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Ding, W.; Zhang, F. Indirect Effect of PM1 on Endothelial Cells via Inducing the Release of Respiratory Inflammatory Cytokines. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 57, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengalli, R.; Zerboni, A.; Marchetti, S.; Longhin, E.; Priola, M.; Camatini, M.; Mantecca, P. In Vitro Pulmonary and Vascular Effects Induced by Different Diesel Exhaust Particles. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 306, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengalli, R.; Longhin, E.; Marchetti, S.; Proverbio, M.C.; Battaglia, C.; Camatini, M. The Role of IL-6 Released from Pulmonary Epithelial Cells in Diesel UFP-Induced Endothelial Activation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, C.M.S.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Jiang, H.; Cullen, C.; Karavalakis, G.; Lin, Y.-H. Toxicological Responses in Human Airway Epithelial Cells (BEAS-2B) Exposed to Particulate Matter Emissions from Gasoline Fuels with Varying Aromatic and Ethanol Levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| CAST1 | Surrogate | S+10A | S+10E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propane (mL/min) | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Liquid fuel (mL/min) | 0 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Nitrogen (mL/min) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Oxidation air (L/min) | 1.5 | 1.52 | 1.46 | 1.5 |
| Dilution air (L/min) | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| CAST1 * | Surrogate | S+10A | S+10E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dm, geo (nm) | 114 | 124 | 123 | 123 |
| σgeo, Dm | 1.54 | 1.54 | 1.53 | 1.53 |
| Dp, geo (nm) | 26.6 | 43.3 | 35.5 | 34.9 |
| σp, geo | 1.31 | 1.34 | 1.39 | 1.45 |
| OC/TC (%) | 4.1 ± 3.5 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | 7.7 ± 0.9 |
| ATP | ADP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 h | 24 h | 3 h | 24 h | |
| Control | 23.60 ± 2.90 | 29.30 ± 6.29 | 2.07 ± 0.46 | 2.02 ± 0.68 |
| CAST1 | 23.65 ± 2.74 | 23.70 ± 2.94 | 1.79 ± 0.61 | 2.64 ± 1.31 |
| Control | 37.40 ± 2.66 | 38.62 ± 0.99 | 3.10 ± 0.15 | 4.14 ± 0.57 |
| Surrogate | 38.05 ± 1.36 | 37.40 ± 6.60 | 2.49 ± 0.33 | 4.84 ± 0.39 |
| Control | 32.52 ± 5.19 | 31.07 ± 2.04 | 1.87 ± 0.44 | 4.16 ± 0.80 |
| S+10A | 29.65 ± 6.96 | 26.90 ± 4.72 | 2.19 ± 0.42 | 2.89 ± 0.69 * |
| Control | 31.48 ± 5.05 | 18.87 ± 2.03 | 1.97 ± 0.74 | 1.91 ± 0.32 |
| S+10E | 22.27 ± 4.06 | 18.26 ± 5.02 | 1.69 ± 0.11 | 2.90 ± 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juárez-Facio, A.T.; Rogez-Florent, T.; Méausoone, C.; Castilla, C.; Mignot, M.; Devouge-Boyer, C.; Lavanant, H.; Afonso, C.; Morin, C.; Merlet-Machour, N.; et al. Ultrafine Particles Issued from Gasoline-Fuels and Biofuel Surrogates Combustion: A Comparative Study of the Physicochemical and In Vitro Toxicological Effects. Toxics 2023, 11, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010021
Juárez-Facio AT, Rogez-Florent T, Méausoone C, Castilla C, Mignot M, Devouge-Boyer C, Lavanant H, Afonso C, Morin C, Merlet-Machour N, et al. Ultrafine Particles Issued from Gasoline-Fuels and Biofuel Surrogates Combustion: A Comparative Study of the Physicochemical and In Vitro Toxicological Effects. Toxics. 2023; 11(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuárez-Facio, Ana Teresa, Tiphaine Rogez-Florent, Clémence Méausoone, Clément Castilla, Mélanie Mignot, Christine Devouge-Boyer, Hélène Lavanant, Carlos Afonso, Christophe Morin, Nadine Merlet-Machour, and et al. 2023. "Ultrafine Particles Issued from Gasoline-Fuels and Biofuel Surrogates Combustion: A Comparative Study of the Physicochemical and In Vitro Toxicological Effects" Toxics 11, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010021
APA StyleJuárez-Facio, A. T., Rogez-Florent, T., Méausoone, C., Castilla, C., Mignot, M., Devouge-Boyer, C., Lavanant, H., Afonso, C., Morin, C., Merlet-Machour, N., Chevalier, L., Ouf, F. -X., Corbière, C., Yon, J., Vaugeois, J. -M., & Monteil, C. (2023). Ultrafine Particles Issued from Gasoline-Fuels and Biofuel Surrogates Combustion: A Comparative Study of the Physicochemical and In Vitro Toxicological Effects. Toxics, 11(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010021