Using Hepatic Gene Expression Assays in English Sole (Parophrys vetulus) to Investigate the Effects of Metro Vancouver Wastewater Effluents
Abstract
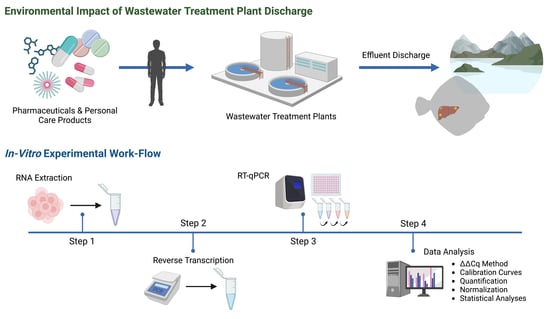
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling of Wild English Sole
2.2. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Primer Design
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. Data Analysis of Gene Expression
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Wild English Sole Health and Body Morphometrics
3.2. Gene Primer Set Design and Evaluation
3.3. RT-qPCR Gene Expression
4. Discussion
4.1. Examining the Health and Body Metrics of Resident English Sole
4.2. Influence of Urban Pollutants on Hepatic CYP1A Gene Expression
4.3. Exploring Sewage Effluent’s Potential Disruption of Thyroid Hormone Metabolism
4.4. Exploring Fatty acid Metabolism Transcripts as Promising Biomarkers of Sewage Effluent Exposure
4.5. Disruption of the Reproductive Endocrine Axis by Estrogenic Contaminant Exposure
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on Pollution and Health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehman, M.S.U.; Rashid, N.; Ashfaq, M.; Saif, A.; Ahmad, N.; Han, J.-I. Global Risk of Pharmaceutical Contamination from Highly Populated Developing Countries. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Bloom, R.A.; Nicell, J.A.; Laurenson, J.P. Risks Associated with the Environmental Release of Pharmaceuticals on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration “Flush List”. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xi, H.; Xu, L.; Jin, M.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H. Ecotoxicological Effects, Environmental Fate and Risks of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products in the Water Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- British Columbia Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy. British Columbia Approved Water Quality Guidelines: Aquatic Life, Wildlife & Agriculture—Guideline Summary; Water Quality Guideline Series, WQG-20; British Columbia Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2021.
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: Nonylphenol and its ethoxylates. In Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, J.C.G.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Barbosa, M.O.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. A Review on Environmental Monitoring of Water Organic Pollutants Identified by EU Guidelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.A.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Mills, K.H.; Palace, V.P.; Evans, R.E.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Flick, R.W. Collapse of a Fish Population after Exposure to a Synthetic Estrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8897–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, P.; Wheeler, J.R.; Weltje, L. A Review of the Evidence for Endocrine Disrupting Effects of Current-Use Chemicals on Wildlife Populations. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2017, 48, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Söffker, M.; Tyler, C.R. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Sexual Behaviors in Fish—A Critical Review on Effects and Possible Consequences. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2012, 42, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Detailed Review Paper on the State of the Science on Novel In Vitro and In Vivo Screening and Testing Methods and Endpoints for Evaluating Endocrine Disruptors; OECD: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENKON Environmental Limited. Burrard Inlet Ambient Monitoring Program 2017 Fish Community and Health; ENKON Environmental Limited: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nautilus Environmental. Metro Vancouver Ambient Burrard Inlet Monitoring Program Fish Health Survey; Nautilus Environmental: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- ENKON Environmental Limited. Burrard Inlet Ambient Monitoring Program 2012 Biota Monitoring; ENKON Environmental Limited: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart, K.; Ciannelli, L.; Waldo Wakefield, W. A Comparative Analysis of Sampling Methodologies for Assessing Abundance and Distribution of Young-of-the-Year Groundfishes in Nearshore Soft-Sediment Habitats. Fish. Res. 2023, 264, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levings, C.; Ong, S. Fish Communities and Life History Attributes of English Sole (Pleuronectes vetulus) in Vancouver Harbour. Mar. Environ. Res. 2004, 57, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittaro, P.M.; Finley, R.J.; Levin, P.S. Spatial and Temporal Patterns in the Contribution of Fish from Their Nursery Habitats. Oecologia 2009, 160, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, M.; Oliveira, C.; Pardo, B.G.; Martínez, P.; Foresti, F. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Order Pleuronectiformes (Teleostei) Based on Sequences of 12S and 16S Mitochondrial Genes. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2008, 31 (Suppl. S1), 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flores, A.; Wiff, R.; Díaz, E. Using the Gonadosomatic Index to Estimate the Maturity Ogive: Application to Chilean Hake (Merluccius Gayi Gayi). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 72, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowerre-Barbieri, S.K.; Ganias, K.; Saborido-Rey, F.; Murua, H.; Hunter, J.R. Reproductive Timing in Marine Fishes: Variability, Temporal Scales, and Methods. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2011, 3, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sol, S.Y.; Olson, O.P.; Lomax, D.P.; Johnson, L.L. Gonadal Development and Associated Changes in Plasma Reproductive Steroids in English sole, Pleuronectes vetulus, from Puget Sound, Washington. Fish. Bull. Natl. Ocean. Atmos. Adm. 1998, 96, 859–870. [Google Scholar]
- Goksøyr, A. Use of Cytochrome P450 1A (CYP1A) in Fish as a Biomarker of Aquatic Pollution. Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 1995, 17, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oris, J.T.; Roberts, A.P. Statistical ANALYSIS of cytochrome P4501A biomarker measurements in fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, L.A.; Armstrong, J.M.; Sakamoto, K.; Steinert, S.A.; Perkins, E.; Lomax, D.P.; Johnson, L.L.; Schlenk, D. The Relationships of Biochemical Endpoints to Histopathology and Population Metrics in Feral Flatfish Species Collected near the Municipal Wastewater Outfall of Orange County, California, USA. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Arena, M.; Kienzler, A. Fish Toxicity Testing for Identification of Thyroid Disrupting Chemicals. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, P.D.; Stapleton, H.M. PBDE Flame Retardants. Endocr. Disruptors 2014, 2, e29430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinling, J.; Houde, M.; Verreault, J. Environmental Exposure to a Major Urban Wastewater Effluent: Effects on the Energy Metabolism of Northern Pike. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 191, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard-Aitken, M.; Fournier, H.; Pariseau, R.; Marcogliese, D.J.; Cyr, D.G. Thyroid Disruption in Walleye (Sander vitreus) Exposed to Environmental Contaminants: Cloning and Use of Iodothyronine Deiodinases as Molecular Biomarkers. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 83, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares-Rubio, H.F.; Vega-López, A. Fatty Acid Metabolism in Fish Species as a Biomarker for Environmental Monitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Fent, K. Cardiovascular Drugs and Lipid Regulating Agents in Surface Waters at Global Scale: Occurrence, Ecotoxicity and Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.-S.; Metcalfe, C. Determination of Pharmaceuticals in Aqueous Samples Using Positive and Negative Voltage Switching Microbore Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 38, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.-S.; Metcalfe, C.D. Determination of Cholesterol-Lowering Statin Drugs in Aqueous Samples Using Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 998, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.B.D.; Miller, J.; Clarence, S.; McCallum, E.S.; Balshine, S.; Chandramouli, B.; Cosgrove, J.; Sherry, J.P. Altered Expression of Metabolites and Proteins in Wild and Caged Fish Exposed to Wastewater Effluents in Situ. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martyniuk, C.J.; Feswick, A.; Munkittrick, K.R.; Dreier, D.A.; Denslow, N.D. Twenty Years of Transcriptomics, 17alpha-Ethinylestradiol, and Fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 286, 113325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, H.; Uno, S.; Koyama, J.; Hiramatsu, N.; Todo, T.; Hara, A. Development of Specific Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Multiple Vitellogenins in Marbled Sole, Pleuronectes yokohamae. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 281, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.B.; Rapp, J.L.; Kandel, C.; Keefe, S.H.; Rice, J.; Westerhoff, P.; Bertolatus, D.W.; Vajda, A.M. Integrated Assessment of Wastewater Reuse, Exposure Risk, and Fish Endocrine Disruption in the Shenandoah River Watershed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3429–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.K.A.; Yu, R.M.K.; Islam, R.; Nguyen, T.H.T.; Bui, T.L.H.; Kong, R.Y.C.; O’Connor, W.A.; Leusch, F.D.L.; Andrew-Priestley, M.; MacFarlane, G.R. The Utility of Vitellogenin as a Biomarker of Estrogenic Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Molluscs. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, M.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shu, G.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. New Methods for Purification of Paralichthys olivaceus Lipovitellin and Immunoassay-Based Detection of Vitellogenin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, E.J.; Habibi, H.R. Estrogen Receptor Function and Regulation in Fish and Other Vertebrates. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.L.; Lomax, D.P.; Myers, M.S.; Olson, O.P.; Sol, S.Y.; O’Neill, S.M.; West, J.; Collier, T.K. Xenoestrogen Exposure and Effects in English Sole (Parophrys vetulus) from Puget Sound, WA. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 88, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osachoff, H.L.; Osachoff, K.N.; Wickramaratne, A.E.; Gunawardane, E.K.; Venturini, F.P.; Kennedy, C.J. Altered Burst Swimming in Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss Exposed to Natural and Synthetic Oestrogens. Fish Biol. 2014, 85, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlatt, V.L.; Bayen, S.; Castaneda-Cortès, D.; Delbès, G.; Grigorova, P.; Langlois, V.S.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Metcalfe, C.D.; Parent, L.; Rwigemera, A.; et al. Impacts of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals on Reproduction in Wildlife and Humans. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Site | Location | Coordinates (UTM) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIA-1 | Outer Harbour North | E 483752 N 5464073 | 1.5 km offshore to the south of Pacific Institute |
| BIA-2 | Outer Harbour South | E 482935 N 5460679 | 1.5 km north of Spanish Bank |
| BIA-3 | Inner Harbour | E 493841 N 5460963 | West of Loch Katrine Bank |
| BIA-5 | Port Moody Arm | E 506788 N 5459875 | East of Port Moody Narrows |
| BIA-6 | Indian Arm | E 505549 N 5464824 | Representative southern site |
| II-NF | Iona Island | E 478523 N 5453266 | 2–4 km north of Iona diffuser |
| II-FF | Iona Island | E 477283 N 5442000 | 8–10 km of south Iona diffuser |
| Target Gene | Accession ID | Primer Sequence | Tm (°C) | Amplicon Size | Efficiency (%) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Housekeeping Genes | ||||||
| 18S rRNA | XR_004613416.1 | F: GGTCTGTGATGCCCTTAGATG R: GCTTATGACCCGCGCTTAC | 55.8 | 210 | 104.5 | 0.972 |
| ACT | XM_035181811.1 | F: GACCAACTGGGATGACATGG R: GCGTACAGGGACAGCACAGC | 61 | 204 | 103 | 0.972 |
| Genes of Biological Interest | ||||||
| CYP1A | AJ310693.1 | F: TGTGAGGACAGGAAGCTGGA R: GCTCCAAACAGGTCGTTGACA | 58 | 86 | 96.9 | 0.992 |
| DIO1 | AB362421.1 | F: ACAGATGGTTGGGCCTTCAC R: TGACTTTCCCAGCCTGAAGC | 57.7 | 196 | 108.1 | 0.992 |
| eEF11 | XM_035620145.1 | F: AAGATCCACATCAACATCGTG R: CAAACTTCCACAGAGCGATG | 56.7 | 229 | 98.8 | 0.998 |
| ER | XM_035143352.1 | F: GCTGAGGGATTTGAGATGGCT R: ATGTAGTCATTGTGACCCTGGATG | 56.9 | 143 | 106.1 | 0.96 |
| FABP1 | XM_020099114.1 | F: GAAGGTCAAGGCGGTGGTTC R: ACATGCGTTTGCTCGTCCTC | 58.4 | 155 | 108.4 | 0.989 |
| FASN | XM_035162863.1 | F: GCAACGGCAATGACAAAGAGC R: TTTGTCTGGTTTCCGTGCCA | 57.6 | 143 | 107.8 | 0.952 |
| GLUT2 | AY521663.1 | F: CCGCGCTACCTCTACATCGT R: TGCTGCCTGTAGACGGAAGA | 58.6 | 182 | 102.6 | 0.969 |
| HSP70 | AF187726.1 | F: CAGTGCCCGCCTACTTCAAT R: TTCTGACCCAACCTTCTTGTCC | 57.3 | 143 | 111.7 | 0.971 |
| PPAR | XM_035158970.1 | F: GACCTCGCTCCACCCTTTAC R: TCCAAGCCCGAATGTGGAAC | 57.7 | 157 | 98.5 | 0.988 |
| PPAR | AJ243956.2 | F: TGTCAGTCACGCTCTGCTGAA R: TAGGAGATCAGGGTCCCGTCT | 58.8 | 176 | 102.4 | 0.988 |
| RPS4X | XM_034569090.1 | F: GTTTGATACTGCCAACCTGTGC R: TTGGAGAGCCTGGTAGCGAA | 57.5 | 150 | 99.7 | 0.976 |
| VTG | XM_035177204.1 | F: CAAGAGCCAGAGTTCACACA R: TGCAACAGCATAAGTCTCAAC | 57.3 | 143 | 103.6 | 0.971 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parekh, K.; Marlatt, V.L. Using Hepatic Gene Expression Assays in English Sole (Parophrys vetulus) to Investigate the Effects of Metro Vancouver Wastewater Effluents. Toxics 2023, 11, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080657
Parekh K, Marlatt VL. Using Hepatic Gene Expression Assays in English Sole (Parophrys vetulus) to Investigate the Effects of Metro Vancouver Wastewater Effluents. Toxics. 2023; 11(8):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080657
Chicago/Turabian StyleParekh, Karan, and Vicki L. Marlatt. 2023. "Using Hepatic Gene Expression Assays in English Sole (Parophrys vetulus) to Investigate the Effects of Metro Vancouver Wastewater Effluents" Toxics 11, no. 8: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080657
APA StyleParekh, K., & Marlatt, V. L. (2023). Using Hepatic Gene Expression Assays in English Sole (Parophrys vetulus) to Investigate the Effects of Metro Vancouver Wastewater Effluents. Toxics, 11(8), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080657