Causal Relationships between Air Pollutant Exposure and Bone Mineral Density and the Risk of Bone Fractures: Evidence from a Two-Stage Mendelian Randomization Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
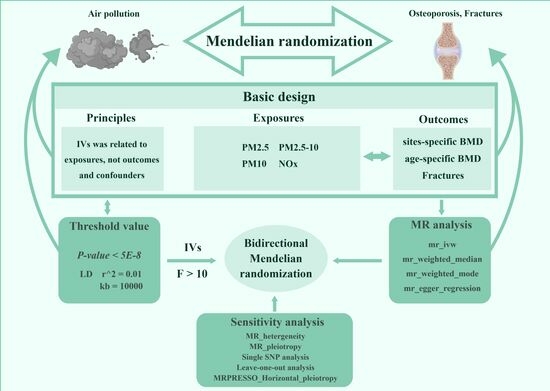
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Exposure Data Sources and IV Selection
2.3. Outcome Data Sources
2.4. Participant Overlap Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
TSMR Analysis
2.6. MVMR Analysis
Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Stage 1 Causal Associations between Air Pollutants and BMD and Bone Fracture Risk
3.3. Stage 2 Direct Causal Effects of Single Air Pollutants on Age-Specific TB-BMD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ensrud, K.E.; Crandall, C.J. Osteoporosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, ITC17–ITC32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.-L.; Cui, A.-Y.; Hsu, C.-J.; Peng, R.; Jiang, N.; Xu, X.-H.; Ma, Y.-G.; Liu, D.; Lu, H.-D. Global, Regional Prevalence, and Risk Factors of Osteoporosis According to the World Health Organization Diagnostic Criteria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 2137–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupsa, B.C.; Insogna, K. Bone Health and Osteoporosis. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 44, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grynpas, M. Age and Disease-Related Changes in the Mineral of Bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1993, 53 (Suppl. S1), S57–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfeir, J.G.; Drake, M.T.; Khosla, S.; Farr, J.N. Skeletal Aging. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2022, 97, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, W.; Zhu, G.; Liang, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, T. The Association between Hemoglobin Level and Osteoporosis in a Chinese Population with Environmental Lead and Cadmium Exposure. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrbaf, M.A.; Akbarzadeh, M.A.; Tabary, M.; Khaheshi, I. Air Pollution and Cardiac Arrhythmias: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R. Oxidative Stress and the Cardiovascular Effects of Air Pollution. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumtorntip, W.; Kasitanon, N.; Louthrenoo, W.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Potential Roles of Air Pollutants on the Induction and Aggravation of Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Cell to Bedside Studies. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, D.; Zhong, J.; Colicino, E.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.; Dagincourt, N.; Fang, S.C.; Kloog, I.; Zmuda, J.M.; Holick, M.; et al. Association of Air Particulate Pollution with Bone Loss over Time and Bone Fracture Risk: Analysis of Data from Two Independent Studies. Lancet Planet. Health 2017, 1, e337–e347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H.; Chang, M.-Y.; Muo, C.-H.; Wu, T.-N.; Hwang, B.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, T.-H.; Kao, C.-H. Exposure to Air Pollution Increases the Risk of Osteoporosis: A Nationwide Longitudinal Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Holmes, M.V. Meta-Analysis and Mendelian Randomization: A Review. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birney, E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2022, 12, a041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brion, M.-J.A.; Shakhbazov, K.; Visscher, P.M. Calculating Statistical Power in Mendelian Randomization Studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Robins, J.M. Instrumental Variables as Bias Amplifiers with General Outcome and Confounding. Biometrika 2017, 104, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Border, R.; O’Rourke, S.; de Candia, T.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M.; Yengo, L.; Jones, M.; Keller, M.C. Assortative Mating Biases Marker-Based Heritability Estimators. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eeftens, M.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Bellander, T.; Cesaroni, G.; Cirach, M.; Declercq, C.; Dėdelė, A.; Dons, E.; de Nazelle, A.; et al. Development of Land Use Regression Models for PM(2.5), PM(2.5) Absorbance, PM(10) and PM(Coarse) in 20 European Study Areas; Results of the ESCAPE Project. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11195–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian Randomization with Invalid Instruments: Effect Estimation and Bias Detection through Egger Regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.; Zheng-Bradley, X.; Smith, R.; Kulesha, E.; Xiao, C.; Toneva, I.; Vaughan, B.; Preuss, D.; Leinonen, R.; Shumway, M.; et al. The 1000 Genomes Project: Data Management and Community Access. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G.; CRP CHD Genetics Collaboration. Avoiding Bias from Weak Instruments in Mendelian Randomization Studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, A.E.; Steinberg, K.M.; Chiang, C.W.K.; Service, S.K.; Havulinna, A.S.; Stell, L.; Pirinen, M.; Abel, H.J.; Chiang, C.C.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Exome Sequencing of Finnish Isolates Enhances Rare-Variant Association Power. Nature 2019, 572, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lee, J.; Smelser, D.; Cade, B.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Kirchner, H.L.; Lin, X.; Mukherjee, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Neck Circumference Identifies Sex-Specific Loci Independent of Generalized Adiposity. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregson, C.L.; Armstrong, D.J.; Bowden, J.; Cooper, C.; Edwards, J.; Gittoes, N.J.L.; Harvey, N.; Kanis, J.; Leyland, S.; Low, R.; et al. UK Clinical Guideline for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Arch. Osteoporos. 2022, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Davies, N.M.; Thompson, S.G. Bias Due to Participant Overlap in Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Yu, K. Approximation of Bias and Mean-Squared Error in Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analyses. Biometrics 2020, 76, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Scott, R.A.; Timpson, N.J.; Davey Smith, G.; Thompson, S.G.; EPIC-InterAct Consortium. Using Published Data in Mendelian Randomization: A Blueprint for Efficient Identification of Causal Risk Factors. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuken, S.R.; McNerney, M.W. Costs and Benefits of Popular P-Value Correction Methods in Three Models of Quantitative Omic Experiments. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 2732–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E. Multivariable Mendelian Randomization and Mediation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Multivariable Mendelian Randomization: The Use of Pleiotropic Genetic Variants to Estimate Causal Effects. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.V.; Patsopoulos, N.A.; Salanti, G.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Critical Interpretation of Cochran’s Q Test Depends on Power and Prior Assumptions about Heterogeneity. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base Platform Supports Systematic Causal Inference across the Human Phenome. Elife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loxham, M.; Davies, D.E.; Holgate, S.T. The Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution. BMJ 2019, 367, l6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubrano, C.; Risi, R.; Masi, D.; Gnessi, L.; Colao, A. Is Obesity the Missing Link between COVID-19 Severity and Air Pollution? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zan, G.; Wei, Y.; Ge, X.; Cai, H.; Long, T.; Xie, L.; Tong, L.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; et al. Relationship of Multiple Metals Mixture and Osteoporosis in Older Chinese Women: An Aging and Longevity Study. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvaer, K.; Meyer, H.E.; Falch, J.A.; Nafstad, P.; Søgaard, A.J. Outdoor Air Pollution and Bone Mineral Density in Elderly Men—The Oslo Health Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2007, 18, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, D.; Crandall, C.J.; Kupsco, A.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.-A.; Stewart, J.D.; Liao, D.; Yanosky, J.D.; Ramirez, A.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Shen, Y.; et al. Air Pollution and Decreased Bone Mineral Density among Women’s Health Initiative Participants. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 57, 101864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavibaygei, S.R.; Bisadi, A.; ZareSakhvidi, F. Outdoor Air Pollution Exposure, Bone Mineral Density, Osteoporosis, and Osteoporotic Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 865, 161117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Xu, R.; Gong, M.; Zha, Y.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Risk of Ozone Exposure-Induced Fracture. Front. Public. Health 2023, 11, 1153256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, G.; Cattani, G.; Rossini, M.; Viapiana, O.; Olivi, P.; Orsolini, G.; Bertoldo, E.; Fracassi, E.; Gatti, D.; Fassio, A. Association between Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and Osteoporosis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briot, K.; Geusens, P.; Em Bultink, I.; Lems, W.F.; Roux, C. Inflammatory Diseases and Bone Fragility. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 3301–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.; Laurent, M.R.; Dubois, V.; Claessens, F.; O’Brien, C.A.; Bouillon, R.; Vanderschueren, D.; Manolagas, S.C. Estrogens and Androgens in Skeletal Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Fujikado, N.; Manaka, H.; Yasuda, H.; Iwakura, Y. IL-1 Plays an Important Role in the Bone Metabolism under Physiological Conditions. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Omaye, S.T. Air Pollutants, Oxidative Stress and Human Health. Mutat. Res. 2009, 674, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solleiro-Villavicencio, H.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Effect of Chronic Oxidative Stress on Neuroinflammatory Response Mediated by CD4+T Cells in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Mora-Tiscareño, A.; Francolira, M.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Peña-Cruz, B.; Palacios-López, C.; Zhu, H.; Kong, L.; Mendoza-Mendoza, N.; Montesinoscorrea, H.; et al. Exposure to Urban Air Pollution and Bone Health in Clinically Healthy Six-Year-Old Children. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2013, 64, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoenfelt, J.; Mitkus, R.J.; Zeisler, R.; Spatz, R.O.; Powell, J.; Fenton, M.J.; Squibb, K.A.; Medvedev, A.E. Involvement of TLR2 and TLR4 in Inflammatory Immune Responses Induced by Fine and Coarse Ambient Air Particulate Matter. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizabad, E.; Hossein-Nezhad, A.; Maghbooli, Z.; Ramezani, M.; Hashemian, R.; Moattari, S. Impact of Air Pollution on Vitamin D Deficiency and Bone Health in Adolescents. Arch. Osteoporos. 2017, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; He, T.; Gao, Z.-X.; Zhang, P.; Fang, Y.; Ge, M.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Pan, H.-F.; Wang, P. Causal Relationships between Air Pollutant Exposure and Bone Mineral Density and the Risk of Bone Fractures: Evidence from a Two-Stage Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Toxics 2024, 12, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010027
Hu X, Zhao Y, He T, Gao Z-X, Zhang P, Fang Y, Ge M, Xu Y-Q, Pan H-F, Wang P. Causal Relationships between Air Pollutant Exposure and Bone Mineral Density and the Risk of Bone Fractures: Evidence from a Two-Stage Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Toxics. 2024; 12(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiao, Yan Zhao, Tian He, Zhao-Xing Gao, Peng Zhang, Yang Fang, Man Ge, Yi-Qing Xu, Hai-Feng Pan, and Peng Wang. 2024. "Causal Relationships between Air Pollutant Exposure and Bone Mineral Density and the Risk of Bone Fractures: Evidence from a Two-Stage Mendelian Randomization Analysis" Toxics 12, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010027
APA StyleHu, X., Zhao, Y., He, T., Gao, Z. -X., Zhang, P., Fang, Y., Ge, M., Xu, Y. -Q., Pan, H. -F., & Wang, P. (2024). Causal Relationships between Air Pollutant Exposure and Bone Mineral Density and the Risk of Bone Fractures: Evidence from a Two-Stage Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Toxics, 12(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010027