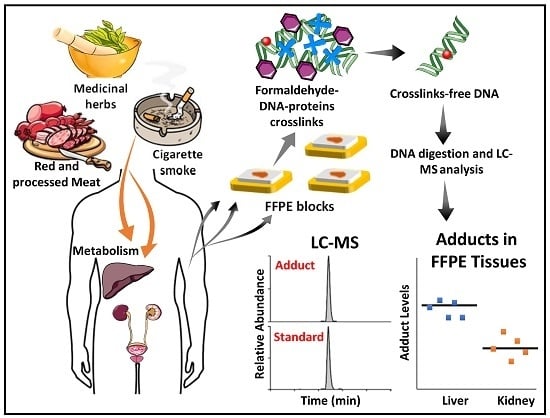
Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues—An Untapped Biospecimen for Biomonitoring DNA Adducts by Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Metabolism, Bioactivation, and DNA Adducts as Biomarkers of Exposure and Health Risk
1.1. Xenobiotic Metabolism and Bioactivation of Procarcinogens
1.2. Methods to Measure DNA Adducts
2. Overview and the History of Formalin Fixation Process
Technical Challenges and Breakthrough Technology in DNA Recovery from FFPE Tissues
3. Measurement of DNA Adducts in FFPE Tissues by IHC, 32P-Postlabeling, and LC-MS
3.1. IHC Detection of DNA Adducts
3.2. DNA Measurements in FFPE Tissues by 32P-Postlabeling
3.3. Measurement of DNA Adducts in FFPE Tissues of Rodents and Human by LC-MS
3.4. Rapid Throughput Method of DNA Extraction from FFPE Tissue
3.5. Future Applications of DNA Adduct Measurements in Human Tissues
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanley, L.A. Drug Metabolism. In Pharmacognosy: Fundamentals, Applications and Strategies; Badal, S., Delgoda, R., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 527–545. [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich, F.P. Cytochrome p450 and chemical toxicology. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, M.P. Bioactivation by Phase-II-Enzyme-Catalyzed Conjugation of Xenobiotics. In Encyclopedia of Drug Metabolism and Interactions; Lyubimov, A.V., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Dekant, W. The role of biotransformation and bioactivation in toxicity. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 57–86. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, E.C. Some current perspectives on chemical carcinogenesis in humans and experimental animals: Presidential address. Cancer Res. 1978, 38, 1479–1496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minchin, R.F.; Reeves, P.T.; Teitel, C.H.; McManus, M.E.; Mojarrabi, B.; Ilett, K.F.; Kadlubar, F.F. N-and O -acetylation of aromatic and heterocyclic amine carcinogens by human monomorphic and polymorphic acetyltransferases expressed in COS-1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 185, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thier, R.; Pemble, S.E.; Kramer, H.; Taylor, J.B.; Guengerich, F.P.; Ketterer, B. Human glutathione S-transferase T1-1 enhances mutagenicity of 1,2-dibromoethane, dibromomethane and 1,2,3,4-diepoxybutane in Salmonella typhimurium. Carcinogenesis 1996, 17, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.P.; Miller, D.W.; Von Tungeln, L.S.; Bryant, M.S.; Lay, J.O., Jr.; Huang, K.; Jones, L.; Evans, F.E. Formation of C8-modified deoxyguanosine and C8-modified deoxyadenosine as major DNA adducts from 2-nitropyrene metabolism mediated by rat and mouse liver microsomes and cytosols. Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, S.L.; Maggs, J.L.; Hammond, T.G.; Lambert, C.; Williams, D.P.; Park, B.K. Acyl glucuronides: The good, the bad and the ugly. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2010, 31, 367–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauwelaers, G.; Bessette, E.E.; Gu, D.; Tang, Y.; Rageul, J.; Fessard, V.; Yuan, J.M.; Yu, M.C.; Langouet, S.; Turesky, R.J. DNA adduct formation of 4-aminobiphenyl and heterocyclic aromatic amines in human hepatocytes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorenko, V.S.; Attaluri, S.; Zaitseva, I.; Iden, C.R.; Dickman, K.G.; Johnson, F.; Grollman, A.P. Bioactivation of the human carcinogen aristolochic acid. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1814–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reardon, D.B.; Prakash, A.S.; Hilton, B.D.; Roman, J.M.; Pataki, J.; Harvey, R.G.; Dipple, A. Characterization of 5-methylchrysene-1,2-dihydrodiol-3,4-epoxide-DNA adducts. Carcinogenesis 1987, 8, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penning, T.M. The aldo-keto reductases (AKRs): Overview. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 234, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marques, M.M.; Beland, F.A. Identification of tamoxifen-DNA adducts formed by 4-hydroxytamoxifen quinone methide. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osborne, M.R.; Hewer, A.; Hardcastle, I.R.; Carmichael, P.L.; Phillips, D.H. Identification of the major tamoxifen-deoxyguanosine adduct formed in the liver DNA of rats treated with tamoxifen. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guengerich, F.P. Comparisons of catalytic selectivity of cytochrome P450 subfamily enzymes from different species. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1997, 106, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turesky, R.J.; Constable, A.; Fay, L.B.; Guengerich, F.P. Interspecies differences in metabolism of heterocyclic aromatic amines by rat and human P450 1A2. Cancer Lett. 1999, 143, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.J.; Murray, B.P.; Murray, S.; Schulz, T.; Neubert, D.; Gant, T.W.; Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Boobis, A.R.; Davies, D.S. Contribution of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 to the activation of heterocyclic amines in monkeys and humans. Carcinogenesis 1994, 15, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelstein, M.W.; Boogaard, P.J.; Cadet, J.; Farmer, P.B.; Kim, J.H.; Martin, E.A.; Persaud, R.; Shuker, D.E. Creating context for the use of DNA adduct data in cancer risk assessment: II. Overview of methods of identification and quantitation of DNA damage. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2009, 39, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarabek, A.M.; Pottenger, L.H.; Andrews, L.S.; Casciano, D.; Embry, M.R.; Kim, J.H.; Preston, R.J.; Reddy, M.V.; Schoeny, R.; Shuker, D.; et al. Creating context for the use of DNA adduct data in cancer risk assessment: I. Data organization. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2009, 39, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Tobacco smoke and involuntary smoking. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2004, 83, 1–1438. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. Tobacco smoking IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1986, 38, 35–394.
- Stiborova, M.; Arlt, V.M.; Schmeiser, H.H. DNA Adducts Formed by Aristolochic Acid Are Unique Biomarkers of Exposure and Explain the Initiation Phase of Upper Urothelial Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenquist, T.A.; Grollman, A.P. Mutational signature of aristolochic acid: Clue to the recognition of a global disease. DNA Repair 2016, 44, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wogan, G.N.; Kensler, T.W.; Groopman, J.D. Present and future directions of translational research on aflatoxin and hepatocellular carcinoma. A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2012, 29, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kensler, T.W.; Roebuck, B.D.; Wogan, G.N.; Groopman, J.D. Aflatoxin: A 50-year odyssey of mechanistic and translational toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120 (Suppl. 1), S28–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancar, A.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Unsal-Kacmaz, K.; Linn, S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 39–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randerath, K.; Reddy, M.V.; Gupta, R.C. 32P-labeling test for DNA damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6126–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.H. On the origins and development of the (32)P-postlabelling assay for carcinogen-DNA adducts. Cancer Lett. 2013, 334, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santella, R.M. Immunological methods for detection of carcinogen-DNA damage in humans. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1999, 8, 733–739. [Google Scholar]
- Poirier, M.C.; Santella, R.M.; Weston, A. Carcinogen macromolecular adducts and their measurement. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dizdaroglu, M.; Coskun, E.; Jaruga, P. Measurement of oxidatively induced DNA damage and its repair, by mass spectrometric techniques. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Farmer, P.B. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry: The future of DNA adduct detection. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaene, J.J.; Sharma, V.K.; Glick, J.; Vouros, P. The analysis of DNA adducts: The transition from (32)P-postlabeling to mass spectrometry. Cancer Lett. 2013, 334, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Mass spectrometry for the assessment of the occurrence and biological consequences of DNA adducts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7829–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tretyakova, N.; Goggin, M.; Sangaraju, D.; Janis, G. Quantitation of DNA adducts by stable isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2007–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Turesky, R.J. Human Biomonitoring of DNA Adducts by Ion Trap Multistage Mass Spectrometry. Curr. Protoc. Nucleic Acid Chem. 2016, 66, 7.24.21–7.24.25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shibutani, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Suzuki, N. 32P-Postlabeling DNA damage assays: PAGE, TLC, and HPLC. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 314, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfau, W.; Lecoq, S.; Hughes, N.C.; Seidel, A.; Platt, K.L.; Grover, P.L.; Phillips, D.H. Separation of 32 P-labelled nucleoside 3′,5′-bisphosphate adducts by HPLC. IARC Sci. Publ. 1993, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, D.H. DNA adducts as markers of exposure and risk. Mutat. Res. 2005, 577, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.H. Smoking-related DNA and protein adducts in human tissues. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 1979–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, D.H. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the diet. Mutat. Res. 1999, 443, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudo, A.; Peluso, M.; Munnia, A.; Lujan-Barroso, L.; Sanchez, M.J.; Molina-Montes, E.; Sanchez-Cantalejo, E.; Navarro, C.; Tormo, M.J.; Chirlaque, M.D.; et al. Aromatic DNA adducts and risk of gastrointestinal cancers: A case-cohort study within the EPIC-Spain. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilberson, T.; Peluso, M.E.; Munia, A.; Lujan-Barroso, L.; Sanchez, M.J.; Navarro, C.; Amiano, P.; Barricarte, A.; Quiros, J.R.; Molina-Montes, E.; et al. Aromatic adducts and lung cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) Spanish cohort. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricceri, F.; Godschalk, R.W.; Peluso, M.; Phillips, D.H.; Agudo, A.; Georgiadis, P.; Loft, S.; Tjonneland, A.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Palli, D.; et al. Bulky DNA adducts in white blood cells: A pooled analysis of 3600 subjects. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 3174–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, V.; Peacock, S.; Massey, T.E.; Godschalk, R.W.; van Schooten, F.J.; Chen, J.; King, W.D. Gene-diet interactions in exposure to heterocyclic aromatic amines and bulky DNA adduct levels in blood leukocytes. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, M.M.; John, K.; MacLean, A.B.; Afework, S.; Phillips, D.H.; Poirier, M.C. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) exposure and DNA adduct semi-quantitation in archived human tissues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2675–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumford, J.L.; Williams, K.; Wilcosky, T.C.; Everson, R.B.; Young, T.L.; Santella, R.M. A sensitive color ELISA for detecting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts in human tissues. Mutat. Res. 1996, 359, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divi, R.L.; Beland, F.A.; Fu, P.P.; Von Tungeln, L.S.; Schoket, B.; Camara, J.E.; Ghei, M.; Rothman, N.; Sinha, R.; Poirier, M.C. Highly sensitive chemiluminescence immunoassay for benzo[a]pyrene-DNA adducts: Validation by comparison with other methods, and use in human biomonitoring. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, M.C. Chemical-induced DNA damage and human cancer risk. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanat, J.L.; Turesky, R.J.; Gremaud, E.; Trudel, L.J.; Stadler, R.H. Determination of 8-oxoguanine in DNA by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and HPLC-electrochemical detection: Overestimation of the background level of the oxidized base by the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry assay. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1995, 8, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turesky, R.J.; Vouros, P. Formation and analysis of heterocyclic aromatic amine-DNA adducts in vitro and in vivo. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 802, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretyakova, N.; Villalta, P.W.; Kotapati, S. Mass spectrometry of structurally modified DNA. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2395–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalta, P.W.; Hochalter, J.B.; Hecht, S.S. Ultrasensitive High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Analysis of a DNA Adduct of the Carcinogen Benzo[a]pyrene in Human Lung. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12735–12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Villalta, P.W.; Turesky, R.J. Data-Independent Mass Spectrometry Approach for Screening and Identification of DNA Adducts. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11728–11736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessette, E.E.; Goodenough, A.K.; Langouet, S.; Yasa, I.; Kozekov, I.D.; Spivack, S.D.; Turesky, R.J. Screening for DNA adducts by data-dependent constant neutral loss-triple stage mass spectrometry with a linear quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbo, S.; Hecht, S.S.; Upadhyaya, P.; Villalta, P.W. Application of a high-resolution mass-spectrometry-based DNA adductomics approach for identification of DNA adducts in complex mixtures. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalta, P.W.; Balbo, S. The Future of DNA Adductomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zarth, A.T.; Carlson, E.S.; Villalta, P.W.; Upadhyaya, P.; Stepanov, I.; Hecht, S.S. Methyl DNA Phosphate Adduct Formation in Rats Treated Chronically with 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone and Enantiomers of Its Metabolite 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Zarth, A.T.; Carlson, E.S.; Villalta, P.W.; Stepanov, I.; Hecht, S.S. Pyridylhydroxybutyl and pyridyloxobutyl DNA phosphate adduct formation in rats treated chronically with enantiomers of the tobacco-specific nitrosamine metabolite 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.M.; Vouros, P. Application of capillary liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometric methods to the rapid screening of adducts formed by the reaction of N-acetoxy-N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene with calf thymus DNA. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1994, 7, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaly, R.A.; Matsui, S.; Hanaoka, T.; Matsuda, T. Application of the adductome approach to assess intertissue DNA damage variations in human lung and esophagus. Mutat. Res. 2007, 625, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbo, S.; Turesky, R.J.; Villalta, P.W. DNA adductomics. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.H.; Johnson, F.B.; Whiting, J.; Roller, P.P. Formaldehyde fixation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1985, 33, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, E.A.; Frey, B.L.; Smith, L.M.; Auble, D.T. Formaldehyde crosslinking: A tool for the study of chromatin complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26404–26411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy-Darling, J.; Smith, L.M. Measuring the formaldehyde Protein-DNA cross-link reversal rate. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5678–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boenisch, T. Effect of heat-induced antigen retrieval following inconsistent formalin fixation. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2005, 13, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graw, S.; Meier, R.; Minn, K.; Bloomer, C.; Godwin, A.K.; Fridley, B.; Vlad, A.; Beyerlein, P.; Chien, J. Robust gene expression and mutation analyses of RNA-sequencing of formalin-fixed diagnostic tumor samples. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ludgate, J.L.; Wright, J.; Stockwell, P.A.; Morison, I.M.; Eccles, M.R.; Chatterjee, A. A streamlined method for analysing genome-wide DNA methylation patterns from low amounts of FFPE DNA. BMC Med. Genom. 2017, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robbe, P.; Popitsch, N.; Knight, S.J.L.; Antoniou, P.; Becq, J.; He, M.; Kanapin, A.; Samsonova, A.; Vavoulis, D.V.; Ross, M.T.; et al. Clinical whole-genome sequencing from routine formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens: Pilot study for the 100,000 Genomes Project. Genet. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, S.; Vizoso, M.; Martinez-Cardus, A.; Gomez, A.; Matias-Guiu, X.; Chiavenna, S.M.; Fernandez, A.G.; Esteller, M. Validation of DNA methylation profiling in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples using the Infinium HumanMethylation450 Microarray. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Jiang, X.; Feng, S.; Tian, R.; Ye, M.; Zou, H. Development of efficient protein extraction methods for shotgun proteome analysis of formalin-fixed tissues. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprung, R.W.; Brock, J.W.C.; Tanksley, J.P.; Li, M.; Washington, M.K.; Slebos, R.J.C.; Liebler, D.C. Equivalence of Protein Inventories Obtained from Formalin-fixed Paraffin-embedded and Frozen Tissue in Multidimensional Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Shotgun Proteomic Analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 1988–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giusti, L.; Lucacchini, A. Proteomic studies of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2013, 10, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.D.; Breitkopf, S.B.; Yuan, M.; Goldsmith, J.; Spentzos, D.; Asara, J.M. Metabolomic profiling from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor tissue using targeted LC/MS/MS: Application in sarcoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojakowska, A.; Chekan, M.; Marczak, L.; Polanski, K.; Lange, D.; Pietrowska, M.; Widlak, P. Detection of metabolites discriminating subtypes of thyroid cancer: Molecular profiling of FFPE samples using the GC/MS approach. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 417, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, E.; Brown, J. Effects of Fixation on Tissues. In Prostate Cancer Methods and Protocols; Russell, P., Jackson, P., Kingsley, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 81, pp. 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Chung, J.Y.; Ylaya, K.; Williams, R.L.; Guerrero, N.; Nakatsuka, N.; Badie, C.; Hewitt, S.M. Factors influencing the degradation of archival formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, B.H.; Yao, L.; Jelakovic, B.; Nikolic, J.; Dickman, K.G.; Grollman, A.P.; Rosenquist, T.A.; Turesky, R.J. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue as a source for quantitation of carcinogen DNA adducts: Aristolochic acid as a prototype carcinogen. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, M.M.; King, L.C.; Adams, L.D.; John, K.; Sirajuddin, P.; Olivero, O.A.; Manchester, D.K.; Sram, R.J.; DeMarini, D.M.; Poirier, M.C. Assessment of multiple types of DNA damage in human placentas from smoking and nonsmoking women in the Czech Republic. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2011, 52, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Gijssel, H.E.; Divi, R.L.; Olivero, O.A.; Roth, M.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Dawsey, S.M.; Albert, P.S.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R.; Dong, Z.W.; et al. Semiquantitation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts in human esophagus by immunohistochemistry and the automated cellular imaging system. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2002, 11, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Turesky, R.J.; Freeman, J.P.; Holland, R.D.; Nestorick, D.M.; Miller, D.W.; Ratnasinghe, D.L.; Kadlubar, F.F. Identification of aminobiphenyl derivatives in commercial hair dyes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curigliano, G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Flamini, G.; Alcini, A.; Ratto, C.; Giustacchini, M.; Alcini, E.; Cittadini, A.; Santella, R.M. Immunohistochemical quantitation of 4-aminobiphenyl-DNA adducts and p53 nuclear overexpression in T1 bladder cancer of smokers and nonsmokers. Carcinogenesis 1996, 17, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santella, R.M.; Gammon, M.D.; Zhang, Y.J.; Motykiewicz, G.; Young, T.L.; Hayes, S.C.; Terry, M.B.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Brinton, L.A.; Bose, S.; et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts in breast tumor tissue. Cancer Lett. 2000, 154, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motykiewicz, G.; Malusecka, E.; Michalska, J.; Kalinowska, E.; Wloch, J.; Butkiewicz, D.; Mazurek, A.; Lange, D.; Perera, F.P.; Santella, R.M. Immunoperoxidase detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts in breast tissue sections. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2001, 25, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hecht, S.S. Progress and challenges in selected areas of tobacco carcinogenesis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, M.C.; Santella, R.; Weinstein, I.B.; Grunberger, D.; Yuspa, S.H. Quantitation of benzo(a)pyrene-deoxyguanosine adducts by radioimmunoassay. Cancer Res. 1980, 40, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weston, A.; Manchester, D.K.; Poirier, M.C.; Choi, J.S.; Trivers, G.E.; Mann, D.L.; Harris, C.C. Derivative fluorescence spectral analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts in human placenta. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1989, 2, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gijssel, H.E.; Schild, L.J.; Watt, D.L.; Roth, M.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Dawsey, S.M.; Albert, P.S.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R.; Dong, Z.W.; et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts determined by semiquantitative immunohistochemistry in human esophageal biopsies taken in 1985. Mutat. Res. 2004, 547, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, K.; Ragavan, N.; Pratt, M.M.; Singh, P.B.; Al-Buheissi, S.; Matanhelia, S.S.; Phillips, D.H.; Poirier, M.C.; Martin, F.L. Quantification of phase I/II metabolizing enzyme gene expression and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adduct levels in human prostate. Prostate 2009, 69, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pratt, M.M.; Sirajuddin, P.; Poirier, M.C.; Schiffman, M.; Glass, A.G.; Scott, D.R.; Rush, B.B.; Olivero, O.A.; Castle, P.E. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts in cervix of women infected with carcinogenic human papillomavirus types: An immunohistochemistry study. Mutat. Res. 2007, 624, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rundle, A.; Tang, D.L.; Mooney, L.; Grumet, S.; Perera, F. The interaction between alcohol consumption and GSTM1 genotype on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adduct levels in breast tissue. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2003, 12, 911–914. [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch, H.; Hietanen, E. The role of individual susceptibility in cancer burden related to environmental exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104 (Suppl. 3), 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Divi, R.L.; Dragan, Y.P.; Pitot, H.C.; Poirier, M.C. Immunohistochemical localization and semi-quantitation of hepatic tamoxifen-DNA adducts in rats exposed orally to tamoxifen. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felton, J.S.; Jagerstad, I.M.; Knize, M.G.; Skog, K.; Wakabayashi, K. Contents in Foods, Beverages and Tobacco. In Food Borne Carcinogens: Heterocyclic Amines; Nagao, M., Sugimura, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 31–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shirai, T.; Takahashi, S.; Cui, L.; Yamada, Y.; Tada, M.; Kadlubar, F.F.; Ito, N. Use of polyclonal antibodies against carcinogen-DNA adducts in analysis of carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Lett. 1998, 102–103, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Tamano, S.; Hirose, M.; Kimoto, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Sakakibara, M.; Tada, M.; Kadlubar, F.F.; Ito, N.; Shirai, T. Immunohistochemical demonstration of carcinogen-DNA adducts in tissues of rats given 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP): Detection in paraffin-embedded sections and tissue distribution. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4307–4313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chang, P.; Bondy, M.L.; Sahin, A.A.; Singletary, S.E.; Takahashi, S.; Shirai, T.; Li, D. Detection of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]-pyridine-DNA adducts in normal breast tissues and risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2003, 12, 830–837. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Liu, J.J.; Rundle, A.; Neslund-Dudas, C.; Savera, A.T.; Bock, C.H.; Nock, N.L.; Yang, J.J.; Rybicki, B.A. Grilled meat consumption and PhIP-DNA adducts in prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2007, 16, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Turesky, R.J.; Tao, Y.; Langouet, S.A.; Nauwelaers, G.C.; Yuan, J.M.; Yee, D.; Yu, M.C. DNA adducts of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine and 4-aminobiphenyl are infrequently detected in human mammary tissue by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Guo, J.; Yun, B.H.; Villalta, P.W.; Krishna, S.; Tejpaul, R.; Murugan, P.; Weight, C.J.; Turesky, R.J. Biomonitoring DNA Adducts of Cooked Meat Carcinogens in Human Prostate by Nano Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Identification of 2-Amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine DNA Adduct. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12508–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoshiba, K.; Koinuma, M.; Yokohori, N.; Nagai, A. Immunohistochemical evaluation of oxidative stress in murine lungs after cigarette smoke exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewer, A.; Phillips, D.H. Effect of tissue fixation on recovery of DNA adducts in the 32P-postlabelling assay. IARC Sci. Publ. 1993, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, B.H.; Rosenquist, T.A.; Nikolic, J.; Dragicevic, D.; Tomic, K.; Jelakovic, B.; Dickman, K.G.; Grollman, A.P.; Turesky, R.J. Human Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues: an untapped specimen for biomonitoring of carcinogen DNA adducts by mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Yun, B.H.; Upadhyaya, P.; Yao, L.; Krishnamachari, S.; Rosenquist, T.A.; Grollman, A.P.; Turesky, R.J. Multiclass carcinogenic DNA adduct quantification in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues by ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4780–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goelz, S.E.; Hamilton, S.R.; Vogelstein, B. Purification of DNA from formaldehyde fixed and paraffin embedded human tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 130, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Smokeless Tobacco and Some Tobacco-Specific N-Nitrosamines. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2007, 89, 1–152. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, B.H.; Xiao, S.; Yao, L.; Krishnamachari, S.; Rosenquist, T.A.; Dickman, K.G.; Grollman, A.P.; Murugan, P.; Weight, C.J.; Turesky, R.J. A rapid throughput method to extract DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues for biomonitoring carcinogenic DNA adducts. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stornetta, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Cimino, G.D.; Henderson, P.T.; Sturla, S.J. DNA adducts from anticancer drugs as candidate predictive markers for precision medicine. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 388–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Feng, Y.L. A nontargeted screening method for covalent DNA adducts and DNA modification selectivity using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 159, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratton, M.R.; Campbell, P.J.; Futreal, P.A. The cancer genome. Nature 2009, 458, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Detection Methods | DNA Adducts Detected | Tissues | LOD (Per 108 Nucleotides) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IHC | 4-ABP-DNA | Human bladder | NR a | [83] |
| PAH-DNA | Human breast | NR a | [84,85,92] | |
| Human esophagus | NR a | [81,89] | ||
| Human prostate | 8 | [90] | ||
| Human cervix | 20 | [91] | ||
| Human vulva | 8 | [47] | ||
| Human placenta | 20 | [80] | ||
| DMAB-DNA | Rat multiple tissues | NR a | [96] | |
| PhIP-DNA | Human prostate tissue transplanted to mice | NR b | [96] | |
| Rat multiple tissues | NR b | [97] | ||
| 8-OHdG | Mouse pulmonary epithelial cells | NR a | [102] | |
| Tamoxifen-DNA | Rat hepatocytes | 10 | [94] | |
| 32P-postlabeling | B[a]P-DNA, 2-AAF-DNA | Rat multiple tissues | NR c | [103] |
| LC-MS3 | dA-AL-I | Mouse liver and kidney, human kidney | 0.1 | [79,104] |
| dG-C8-4-ABP/PhIP, dG-N2-BPDE, O6-Me-dG and O6-POB-dG | Rodent multiple tissues | 0.2–0.5 | [105] | |
| LC-HR-MS2 | dG-C8-PhIP | Human prostate | 0.13 | [101] |
| dG-C8-4-ABP | Human bladder | 0.2 | [55] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, B.H.; Guo, J.; Turesky, R.J. Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues—An Untapped Biospecimen for Biomonitoring DNA Adducts by Mass Spectrometry. Toxics 2018, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020030
Yun BH, Guo J, Turesky RJ. Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues—An Untapped Biospecimen for Biomonitoring DNA Adducts by Mass Spectrometry. Toxics. 2018; 6(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Byeong Hwa, Jingshu Guo, and Robert J. Turesky. 2018. "Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues—An Untapped Biospecimen for Biomonitoring DNA Adducts by Mass Spectrometry" Toxics 6, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020030
APA StyleYun, B. H., Guo, J., & Turesky, R. J. (2018). Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues—An Untapped Biospecimen for Biomonitoring DNA Adducts by Mass Spectrometry. Toxics, 6(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020030