Transfer of Pollutants from Macrocystis pyrifera to Tetrapygus niger in a Highly Impacted Coastal Zone of Chile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feeding Experiment
2.2. Analysis of PAHs in Algal and Animal Tissues
2.3. Sampling and Analysis for Heavy Metals
2.4. Ecotoxicological Indices and Factors
2.5. Statistical Analysis
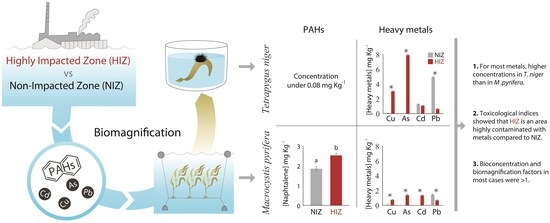
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. BCF and Transfer of PAHs in M. pyrifera and T. niger
4.2. BCF and Transfer of Heavy Metals in M. pyrifera and T. niger
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Oost, R.; Heida, H.; Opperhuizen, A. Polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in sediments, plankton, mollusks, crustaceans, and eel in a freshwater lake: Implications of using reference chemicals and indicator organisms in bioaccumulation studies. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1988, 17, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.H.; Colin, H.; Sibly, R.M.; Hopkin, S.P.; Peakall, D.B. Principles of Ecotoxicology, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Nagarajan, K.; Loh, K.C. Biodegradation of aromatic compounds: Current status and opportunities for biomolecular approaches. App. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 85, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscoso, F.; Deive, F.J.; Longo, M.A.; Sanromán, M.A. Technoeconomic assessment of phenanthrene degradation by Pseudomonas stutzeri CECT 930 in a batch bioreactor. Biores. Tech. 2012, 104, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Wu, X.; Massey Simonich, S.L.; Kang, H.; Xie, Z. Volatilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) over the North Pacific and adjacent Artic Ocean: The impact of offshore oil drilling. Environ. Poll. 2021, 268 Pt B, 115963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcke, W. Global patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil. Geoderma 2007, 141, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, S. Global atmospheric emission inventory of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) for 2004. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, L.; Rieth, S.H.; Cogliano, V.J.; Foureman, G.L.; Hertzberg, R.; Hofmann, E.L.; Schoeny, R.S. Health assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures: Current practices and future directions. Polyc. Arom. Comp. 2002, 22, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J.; Saco-Álvarez, L.; Nieto, Ó.; Beiras, R. Ecotoxicological evaluation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using marine invertebrate embryo–larval bioassays. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2008, 57, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Jahan, S.A.; Kabir, E.; Brown, R.J. A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.; Rogers, E.; Altin, D.; Salaberria, I.; Booth, A.M. Sorption of PAHs to microplastic and their bioavailability and toxicity to marine copepods under co-exposure conditions. Environ. Poll. 2020, 258, 113844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, H.A. Assessment and management of heavy metal pollution in the marine environment of the Arabian Gulf: A review. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2013, 72, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, T.M.; Marr, I.L.; Tariq, N. Heavy metals in marine pollution perspective—A mini review. J. Appl. Sci. 2004, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. Exp. Suppl. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamelink, J.; Landrum, P.F.; Bergman, H.; Benson, W.H. Bioavailability: Physical, Chemical, and Biological Interactions, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; p. 239. [Google Scholar]
- Meynard, A.; Espinoza-González, C.; Núñez, A.; Castañeda, F.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Synergistic, antagonistic, and additive effects of heavy metals (copper and cadmium) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) under binary and tertiary combinations in key habitat-forming kelp species of Chile. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2021, 28, 18300–18307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza-González, C.; Meynard, A.; Núñez, A.; Castañeda, F.; Oyarzo-Miranda, C.; Latorre-Padilla, N.; Rivas, J.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Assessment of the independent and combined effects of copper and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on gametogenesis and sporophyte development of the kelp Lessonia spicata (Phaeophyceae, Ochrophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.W.; Magos, L.; Suzuki, T. Toxicology of Metals, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; 1224p. [Google Scholar]
- Mattia, G.D.; Bravi, M.C.; Laurenti, O.; Luca, O.D.; Palmeri, A.; Sabatucci, A.; Gino Mendico, M.D.; Ghiselli, A. Impairment of cell and plasma redox state in subjects professionally exposed to chromium. Am. J. Indu. Med. 2004, 46, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, L.; Mella, D.; Moenne, A.; Correa, J.A. Differential responses to copper-induced oxidative stress in the marine macroalgae Lessonia nigrescens and Scytosiphon lomentaria (Phaeophyceae). Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 94, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovazzano, C.; Serrano, C.; Correa, J.A.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Comparative analysis of peroxiredoxin activation in the brown macroalgae Scytosiphon gracilis and Lessonia nigrescens (Phaeophyceae) under copper stress. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 149, 378–388. [Google Scholar]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyarzo-Miranda, C.; Latorre, N.; Meynard, A.; Rivas, J.; Bulboa, C.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Coastal pollution from the industrial park Quintero Bay of central Chile: Effects on abundance, morphology, and development of the kelp Lessonia spicata (Phaeophyceae). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervé, D.; Schönsteiner, J.; Cavada, S.M.; Mewes, I. Empresas, medio ambiente y derechos humanos: La zona industrial de Quintero-Puchuncaví. In Informe Anual sobre Derechos Humanos en Chile; Instituto Nacional de Derechos Humanos: Providencia, Chile, 2012; pp. 131–162. [Google Scholar]
- FIC ALGAS. Cultivo del Alga Parda Macrocystis pyrifera en la Zona de Quintero y Puchuncaví: Evaluación de la Productividad y Potencial Uso para Biorremediación de Metales Pesados y Compuestos Orgánicos. 2017; N° 30397482-0. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344238463_Cultivo_del_alga_parda_Macrocystis_pyrifera_en_la_zona_de_Quintero_y_Puchuncavi_Evaluacion_de_la_productividad_y_potencial_uso_para_biorremediacion_de_metales_pesados_y_compuestos_organicos (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Latorre-Padilla, N.; Meynard, A.; Oyarzun, F.X.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Ingestion of contaminated kelps by the herbivore Tetrapygus niger: Negative effects on food intake, growth, fertility, and early development. Mar. Poll. Bul. 2021, 167, 112365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, R.; Pelosi, S.; Trotta, P.; Sansone, G. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aquatic organisms. Marin. Chem. 1997, 56, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.R.; Pruski, A.M.; Dixon, L.R.; Jha, A.N. Marine invertebrate eco-genotoxicology: A methodological overview. Mutagenesis 2002, 17, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Xue, B.; Wang, S. Factors affecting annual occurrence, bioaccumulation, and biomagnification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in plankton food webs of subtropical eutrophic lakes. Water Res. 2018, 132, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.X.; Zheng, X.; Luo, X.; Mai, B. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments and marine organisms: Implications of anthropogenic effects on the coastal environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, R.H.; Tang, A.K.; Xu, L.Q.; Wang, J.Y. Study on the pollution characteristics of heavy metals in seawater of Jinzhou Bay. Proc. Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meador, J.O.; Stein, J.E.; Reichert, W.L.; Varanasi, U. Bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by marine organisms. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1st ed.; Pim de Voogt, H.B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 143, pp. 79–165. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, D.T. Perspective on ecotoxicology of PAHs to fish. Hum. Ecol. Risk. Assess. 2007, 13, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinodhini, R.; Narayanan, M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in organs of freshwater fish Cyprinus carpio (Common carp). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 5, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contreras, L.; Moenne, A.; Correa, J.A. Antioxidant responses in Scytosiphon lomentaria (Phaeophyceae) inhabiting copper-enriched coastal environments. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, A.P.; Hu, Z.L.; Wong, Y.S.; Tam, F.Y. Bioconcentration and metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by algae. Plant. Sci. 2005, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, L.K.; Edwards, M.S. Bioaccumulation of copper and zinc by the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera. Algae 2011, 26, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yozukmaz, A.; Yabanli, M.; Sel, F. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in Enteromorpha intestinalis, (L.) Nees, a macrophytic algae: The example of Kadin Creek (Western Anatolia). Braz. Arch. Biol. Tech. 2018, 61, e18160777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.H.; Vasquez, J.A.; Buschmann, A.H. Global ecology of the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera: From ecotypes to ecosystems. Ocean. Mar. Biol. 2007, 45, 39–88. [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Soto, A.; Palacios, A.; Macaya, E.C.; Gómez, I.; Huovinen, P.; Pérez-Matus, A.; Young, M.; Golding, N.; Toro, M.; Yaqub, M.; et al. A high-resolution global map of giant kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera) forests and intertidial green algae (Ulvophyceae) with Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiel, D.R.; Foster, M.S. The Biology and Ecology of Giant Kelp Forests, 1st ed.; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2015; 416p. [Google Scholar]
- Jara-Yañez, R.; Meynard, A.; Acosta, G.; Latorre-Padilla, N.; Oyarzo-Miranda, C.; Castañeda, F.; Piña, F.; Rivas, J.; Bulboa, C.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Negative consequences on the growth, morphometry, and community structure of the kelp Macrocystis pyrifera (Phaeophyceae, Ochrophyta) by short pollution pulse of heavy metal and PAHs. Toxics 2021, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobday, A.J. Abundance and dispersal of drifting kelp Macrocystis pyrifera rafts in the Southern California Bight. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 195, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothäusler, E.; Gómez, I.; Hinojosa, I.A.; Karsten, U.; Tala, F.; Thiel, M. Effect of temperature and grazing on growth and reproduction of floating Macrocystis spp. (Phaeophyceae) along a latitudinal gradient. J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, S. Consumption of drift kelp by intertidal populations of the sea urchin Tetrapygus niger on the central Chilean coast: Possible consequences at different ecological levels. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 251, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, M.; Koch, P. Correlation between allochthonous subsidy input and isotopic variability in the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera in central California, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 409, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perreault, M.C.; Borgeaud, I.A.; Gaymer, C.F. Impact of grazing by the sea urchin Tetrapygus niger on the kelp Lessonia trabeculata in Northen Chile. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 453, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, S.; Stotz, W. Ciclo reproductivo de Tetrapygus niger (Molina 1782) (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) en dos localidades de la IV Región, Coquimbo, Chile. Rev. Chil. de Hist. Nat. 1993, 66, 155–169. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, A.C.; Camacho, C.; Eljarrat, E.; Peris, A.; Aminot, Y.; Readman, J.W.; Boti, V.; Nannou, C.; Marques, A.; Nunes, M.L.; et al. Bioaccumulation of persistent and emerging pollutants in wild sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmani-Ghabeshi, S.; Palomo-Marín, M.R.; Bernalte, E.; Rueda-Holgado, F.; Miró-Rodríguez, C.; Cereceda-Balic, F.; Fadic, X.; Vidal, V.; Funes, M.; Pinilla-Gil, E. Spatial gradient of human health risk from exposure to trace elements and radioactive pollutants in soils at the Puchuncaví-Ventanas industrial complex, Chile. Environ. Poll. 2016, 218, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahamondes, P.; Serey, I.; Cubillos, J.; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente. Informe Final, Sistematización de Calidad de Agua, Sedimentos, Objetivos de Valoración Ambiental y Fuente de Emisión, como Insumos para la Elaboración de una Norma Secundaria de Calidad de Aguas en la Bahía de Quintero; Centro de Ecología Aplicada Ltda.: La Reina, Chile, 2020; N° 608897-34-LE19. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, N.; Okamura, H. Effects of heavy metals on sea urchin embryo development. 1. Tracing the cause by the effects. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Okamura, H. Effects of heavy metals on sea urchin embryo development. Part 2. Interactive toxic effects of heavy metals in synthetic mine effluents. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usero, J.; Morillo, J.; Garcia, I. Heavy metal concentrations in molluscs from the Atlantic coast of southern Spain. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabee, A.M.; Al-Fatlawy, Y.F.; Najim Abd Own, A.; Nameer, M. Using pollution load index (PLI) and geoaccumulation index (I-Geo) for the assessment of heavy metals pollution in Tigris river sediment in Baghdad region. J. Al-Nahrain Uni. 2011, 14, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.P.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meersunters 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.X. Chapter 4. Bioaccumulation and biomonitoring. In Marine Ecotoxicology, 1st ed.; Blasco, J., Chapman, P.M., Campana, O., Mariam, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ciesielski, T.; Pastukhov, M.V.; Fodor, P.; Bertenyi, Z.; Namieśnik, J.; Szefer, P. Relationships and bioaccumulation of chemical elements in the Baikal seal (Phoca sibirica). Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Bazzi, A.O. Heavy metals in seawater, sediments, and marine organisms in the Gulf of Chabahar, Moan Sea. J. Ocean. Mar. Sci. 2014, 5, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, S.; Sadikoglu, M. Study of heavy metal pollution in seawater of Kepez harbor of Canakkale (Turkey). Environ. Monitor. Asses. 2010, 173, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qari, H.A.; Hassan, I.A. Bioaccumulation of PAHs in Padina boryana alga collected from a contaminated site on the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Sakuraba, S.; Matubayasi, N. Interaction of naphtalene derivatives with lipids in membranes studied by the H-nuclear overhauser effect and molecular dynamics simulation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 14049–14060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerniglia, C.E. Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Biodegradation 1992, 3, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.T.; Koch, J.R.; Kallio, R.E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. I. Enzymic formation of catechol from benzene. Biochemistry 1968, 7, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eibes, G.; Cajthaml, T.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G.; Lema, J.M. Enzymatic degradation of anthracene, dibezonthiophene and pyrene by manganese peroxidase in media containing acetone. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirso, U.; Irha, N. Role of algae in fate of carcinogenic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 41, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-C.; Zhao, H.-M. Uptake and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by marine seaweed. J. Coast. Res. 2007, SI50, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.W.; Yuan, D.X.; Lin, Q.M.; Yang, T.L. Accumulation and biodegradation of phenanthrene and fluoranthene by the algae enriched from a mangrove aquatic ecosystem. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2008, 56, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.K.; Kaushik, C.P. Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. J. Hazard. Mat. 2009, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhler, D.R.; Williams, D.E. Enzymes involved in metabolism of PAH by fishes and other aquatic animals: Part I, oxidative enzymes (or phase I enzymes). In Metabolism of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Aquatic Environment, 1st ed.; Varanasi, U., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989; pp. 151–184. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayavel, K.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Fluctuations of biochemicals constituents and marker enzymes as a consequences of naphthalene toxicity in the edible estuarine crab Scylla serrata. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 63, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, S.; Köhler, A. Gonadal lesions of female sea urchin (Psammechinus miliaris) after exposure to the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon phenanthrene. Mar. Environ. Res. 2009, 68, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lister, K.N.; Lamare, M.D.; Burritt, D.J. Maternal antioxidant provisioning mitigates pollutant-induced oxidative damage in embryos of the temperate sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falk-Petersen, I.B.; Sæthre, L.J.; Lõnning, S. Toxic effect of naphthalene and methylnaphthalenes on marine plankton organisms. Sarsia 1982, 67, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæthre, L.J.; Falk-Petersen, I.B.; Sydnes, L.K.; Lõnning, S.; Naley, A.M. Toxicity and chemical reactivity of naphthalene and methylnaphthalenes. Aquat. Toxicol. 1984, 5, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.M.; Mercon, J.; Passos, L.S.; Coppo, G.C.; Lopes, T.O.M.; Cabral, D.S.; Scherer, R.; Chippari-Gomes, A.R. Effects of the water-soluble fraction of diesel oil (WSD) on the fertilization and development of a sea urchin (Echinometra lucunter). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, M.C.; Vines, C.A.; Wikramanayake, A.H.; Cherr, G.N. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons disrupt axial development in sea urchin embryos through a beta-catenin dependent pathway. Toxicology 2003, 186, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xiong, D. Bioaccumulation and subacute toxicity of mechanically and chemically dispersed heavy fuel oil in sea urchin (Glyptocidaris crenulari). Sci. Mar. 2015, 79, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, A.; Gong, J.; Zheng, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) distribution in surface sediments from Yazhou Bay of Sanya South China, and their source and risk assessment. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2021, 161, 111800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Jin, H.; Ji, Z.; Li, D.; Kaw, H.Y.; Chen, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, T. PAEs and PAHs in the surface sediments on the East China Sea: Occurrence, distribution and influence factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Laxen, D.P.H. Lead Pollution. Causes and Control; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1981; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, C.; Settle, D.; Glover, B. Analysis of lead in polluted coastal seawater. Mar. Chem. 1976, 4, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, M.T.S.; Leal, M.F.C. Antagonistic interaction of Pb and Cd on Cu uptake, growth inhibition and chelator release in the marine algae Emiliania huxleyi. Mar. Chem. 2001, 75, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, S.R.; Negrete, J.M.; Rios, J.A.; Hadad, H.R.; Maine, M.A. Hg, Cu, Pb, Cd, and Zn accumulation in macrophytes growing in tropical wetlands. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnham, G.W.; Codd, G.A.; Gadd, G.M. Kinetics of uptake and intracellular location of cobalt, manganese and zinc in the estuarine green alga Chlorella salina. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 37, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, L.; Moenne, A.; Gaillard, F.; Potin, P.; Correa, J.A. Proteomic analysis and identification of copper stress-regulated proteins in the marine alga Scytosiphon gracilis (Phaeophyceae). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 96, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordet, C.; Contreras-Porcia, L.; Lovazzano, C.; Goulitquer, S.; Andrade, S.; Potin, P.; Correa, J.A. Physiological plasticity of Dictyota kunthii (Phaeophyceae) to copper excess. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 150, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, O.D.; Gutiérrez, Á.J.; González-Weller, D.; Lozano, G.; Melón, E.G.; Rubio, C.; Hardisson, A. Accumulation of toxic metals (Pb and Cd) in the sea urchin Diadema aff. antillarum Philippi, 1845, in an oceanic island (Tenerife, Canary Islands). Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Warnau, M.; Teyssié, J.L.; Fowler, S.W. Cadmium bioconcentration in the echinoid Paracentrotus lividus: Influence of the cadmium concentration in seawater. Mar. Environ. Res. 1997, 43, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnau, M.; Biondo, R.; Temara, A.; Bouquegneau, J.M.; Jangoux, M.; Dubois, P. Distribution of heavy metals in the echinoid Paracentrotus lividus from the Mediterranean Posidonia oceanica ecosystem: Seasonal and geographical variations. J. Sea Res. 1998, 39, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.F.; Stauber, J.L.; Lim, R.P.; Petocz, P. Toxicity of metal mixtures to a tropical freshwater alga (Chlorella sp.): The effect of interactions between copper, cadmium, and zinc on metal cell binding and uptake. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 2412–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, S.; Medina, M.H.; Moffett, J.W.; Correa, J.A. Cadmium-copper antagonism in seaweeds inhabiting coastal areas affected by copper mine waste disposals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4382–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, N.E.; Rouchon, A.M. A dose-dependent relationship between copper burden in female urchin gonads and developmental impairment of their offspring. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 136, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, S.J.; Cáceres, C.; Ojeda, F.P. Feeding and nutritional ecology of the edible sea urchin Loxechinus albus in the northern Chilean coast. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2008, 81, 575–584. [Google Scholar]
- Iordache, S.; Dunea, D.; Radulescu, C.; Culama, I.; Ianache, R.; Predescu, M. Investigation of heavy metals content in Airborne Particles from Ploiesti, Romania. Rev. Chim. Buchar. 2017, 68, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Index | Treatment | Water Column | M. pyrifera Tissue | T. niger Gonad |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPI | NIZ | 6.6 × 10−4 | 0.49 | 1.60 |
| HIZ | 80.4 × 10−4 | 0.99 | 2.07 | |
| PLI | NIZ | 0.015 | ||
| HIZ | 10.896 |
| Factor | Treatment | Species | Cu | As | Cd | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCF | NIZ | M. pyrifera | N.D. | N.D. | 80.0 | 1152 |
| HIZ | 34.2 | 3.4 | 4214 | 475.3 | ||
| TTF | NIZ | T. niger | N.D. | N.D. | 33.0 | 3.4 |
| HIZ | 4.1 | 5.7 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latorre-Padilla, N.; Meynard, A.; Rivas, J.; Contreras-Porcia, L. Transfer of Pollutants from Macrocystis pyrifera to Tetrapygus niger in a Highly Impacted Coastal Zone of Chile. Toxics 2021, 9, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9100244
Latorre-Padilla N, Meynard A, Rivas J, Contreras-Porcia L. Transfer of Pollutants from Macrocystis pyrifera to Tetrapygus niger in a Highly Impacted Coastal Zone of Chile. Toxics. 2021; 9(10):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9100244
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatorre-Padilla, Nicolás, Andrés Meynard, Jorge Rivas, and Loretto Contreras-Porcia. 2021. "Transfer of Pollutants from Macrocystis pyrifera to Tetrapygus niger in a Highly Impacted Coastal Zone of Chile" Toxics 9, no. 10: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9100244
APA StyleLatorre-Padilla, N., Meynard, A., Rivas, J., & Contreras-Porcia, L. (2021). Transfer of Pollutants from Macrocystis pyrifera to Tetrapygus niger in a Highly Impacted Coastal Zone of Chile. Toxics, 9(10), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9100244