Neuroprotective Effect of Abelmoschus manihot Flower Extracts against the H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in PC12 Cells
Abstract
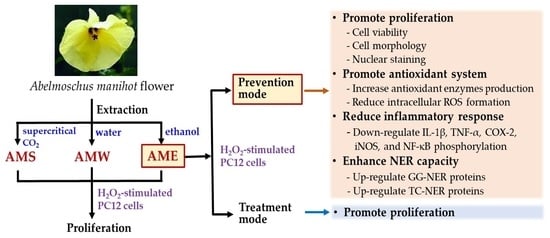
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of AMf Extracts
2.2. Cell Culture and Analyses
2.3. Assay of Cellular Oxidative System
2.3.1. Intracellular ROS Content of H2O2-Stimulated PC12 Cells
2.3.2. Antioxidant Enzymes Activity and Glutathione Content
2.4. Western Blot Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Extraction Yield and Chemical Composition Analysis of AMf Extracts
3.2. Cytotoxicity of AMf Extracts on PC12 Cells
3.3. Effects of AMf Extracts on Proliferation of H2O2-Stimulated PC12 Cells
3.4. Effect of AME Pretreatment on Cell Morphology and Nuclear Staining of H2O2-Stimulated PC12 Cells
3.5. Effect of AME Pretreatment on the Regulation of NER
3.6. Effect of AME Pretreatment on Antioxidant System
3.7. Effect of AME Pretreatment on Inflammatory Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaki, G.S.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Oxidative stress-induced signaling pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Neuromolecular Med. 2014, 16, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turunc Bayrakdar, E.; Uyanikgil, Y.; Kanit, L.; Koylu, E.; Yalcin, A. Nicotinamide treatment reduces the levels of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and PARP-1 activity in Aβ(1-42)-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, D.; Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Gao, J. Neuroprotection of andrographolide against microglia-mediated inflammatory injury and oxidative damage in PC12 neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 2619–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Dong, C.; Yin, J.; Shen, J.; Tian, J.; Li, C. Neuroprotective effect of fucoidan on H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 32, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wuliji, O.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.G.; Ghanbari, H.A. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24438–24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pei, J.P.; Fan, L.H.; Nan, K.; Li, J.; Dang, X.Q.; Wang, K.Z. HSYA alleviates secondary neuronal death through attenuating oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and neural apoptosis in SD rat spinal cord compression injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Guo, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhu, R.; Tian, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. Synthesis and neuroprotective effect of E-3,4-dihydroxy styryl aralkyl ketones derivatives against oxidative stress and inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3700–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffschir, F.; Daya-Grosjean, L.; Petit, P.X.; Nocentini, S.; Dutrillaux, B.; Sarasin, A.; Vuillaume, M. Low catalase activity in xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts and SV40-transformed human cell lines is directly related to decreased intracellular levels of the cofactor, NADPH. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 24, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, A.P.; Low, G.K.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Hande, M.P. Telomere attrition and genomic instability in xeroderma pigmentosum type-b deficient fibroblasts under oxidative stress. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.H.; Kang, T.H. DNA oxidation and excision repair pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie, A.; Shadifar, M.; Ataee, R. Polyphenolic antioxidants and neuronal regeneration. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Chugh, H.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Dhawan, U.; Chidambaram, S.B.; Chandra, R. Neuroinflammation mechanisms and phytotherapeutic intervention: A systematic review. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 3707–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; Yuan, X.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Antiepileptic effects of protein-rich extract from Bombyx batryticatus on mice and its protective effects against H2O2-induced oxidative damage in PC12 cells via regulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7897584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Srivastava, P.; Seth, A.; Tripathi, P.N.; Banerjee, A.G.; Shrivastava, S.K. Comprehensive review of mechanisms of pathogenesis involved in Alzheimer’s disease and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 174, 53–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Ma, Q.; Matsabisa, M.G.; Chabalala, H.; Braga, F.C.; Tang, M. Panax notoginseng for cerebral ischemia: A systematic review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 1331–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubiang-Yalambing, L.; Arcot, J.; Greenfield, H.; Holford, P. Aibika (Abelmoschus manihot L.): Genetic variation, morphology and relationships to micronutrient composition. Food Chem. 2016, 193, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Dusabimana, T.; Kim, S.R.; Je, J.; Jeong, K.; Kang, M.C.; Cho, K.M.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.W. Supplementation of Abelmoschus manihot ameliorates diabetic nephropathy and hepatic steatosis by activating autophagy in mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luan, F.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Lv, H.; Liu, D.; Gan, Z.; Zeng, N. Traditional uses, chemical constituents, biological properties, clinical settings, and toxicities of Abelmoschus manihot L.: A comprehensive review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Sun, W.; Wan, Y.G.; Che, X.Y.; Pu, H.P.; Yin, X.J.; Chen, H.L.; Meng, X.J.; Huang, Y.R.; Shi, X.M. Huangkui capsule, an extract from Abelmoschus manihot (L.) medic, ameliorates adriamycin-induced renal inflammation and glomerular injury via inhibiting p38MAPK signaling pathway activity in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, W.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Han, L.; Liu, E.; Wang, T. Antioxidative flavonol glycosides from the flowers of Abelmouschus manihot. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 67, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Qian, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, A.; Zhong, S.; Qiao, L.; Qian, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, R.; Li, R.; et al. Bioactive compounds from Abelmoschus manihot L. alleviate the progression of multiple myeloma in mouse model and improve bone marrow microenvironment. Onco. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourdy, G.; Walter, A. Maternity and medicinal plants in Vanuatu. I. The cycle of reproduction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1992, 37, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puel, C.; Mathey, J.; Kati-Coulibaly, S.; Davicco, M.J.; Lebecque, P.; Chanteranne, B.; Horcajada, M.N.; Coxam, V. Preventive effect of Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medik. on bone loss in the ovariectomised rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 99, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Houng, J.Y.; Peng, W.H.; Yeh, T.W.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Chang, T.H.; Hung, W.C.; Yu, T.H. Effects of Abelmoschus manihot flower extract on enhancing sexual arousal and reproductive performance in zebrafish. Molecules 2022, 27, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Sun, X.; Chen, X. Treatment of chronic kidney disease using a traditional Chinese medicine, Flos Abelmoschus manihot (Linnaeus) Medicus (Malvaceae). Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 43, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Tang, H.; Wu, L.; Ge, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Gu, H.F. Chemical constituents, clinical efficacy and molecular mechanisms of the ethanol extract of Abelmoschus manihot flowers in treatment of kidney diseases. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Fan, L.; Dong, L.Y.; Cen, D.Y.; Jiang, Q.; Fang, M. Protection effects of the total flavone from Abelmoschus manihot L. medic on acute incompletely cerebral ischemia in rats. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 8, 167–169. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.P.; Qin, S.; Dong, L.Y.; Zhou, J.N. Inhibitory effect of total flavone of Abelmoschus manihot L. Medic on NMDA receptor-mediated current in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 55, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Clementi, M.E.; Lazzarino, G.; Sampaolese, B.; Brancato, A.; Tringali, G. DHA protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress and apoptotic signals through the activation of the NFE2L2/HO-1 axis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Qin, D.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, L.; Fu, H. Neuroprotective effects of deuterium-depleted water (DDW) against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in differentiated PC12 cells through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.D.; Hsu, H.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Wang, Y.T.; Huang, S.H.; Chen, H.J.; Wang, C.P.; Wang, S.W.; Chang, C.C.; Houng, J.Y. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative activities of extracts from different parts of farmed and wild Glossogyne tenuifolia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 57, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Chang, C.C.; Houng, J.Y.; Chang, T.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Chang, L.S. Suppressive effects of Siegesbeckia orientalis ethanolic extract on proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through promoting oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammatory responses. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Liang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, B. Simultaneous determination of seven active flavonols in the flowers of Abelmoschus manihot by HPLC. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2009, 47, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, K.; Fu, Q.; Wang, L.; Gao, M.; Xia, Z.; Gao, D. Extraction and determination of bioactive flavonoids from Abelmoschus manihot (Linn.) Medicus flowers using deep eutectic solvents coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Yang, J. Profiles and neuroprotective effects of Lycium ruthenicum polyphenols against oxidative stress-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, M.W.; Yang, W.; Wan, L.J.; Yan, H.L.; Li, J.C.; Tang, S.Y.; Wang, Y.Q. Naringenin induces neuroprotection against homocysteine-induced PC12 cells via the upregulation of superoxide dismutase 1 expression by decreasing miR-224-3p expression. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Munir, S.; Badshah, S.L.; Khan, N.; Ghani, L.; Poulson, B.G.; Emwas, A.H.; Jaremko, M. Important flavonoids and their role as a therapeutic agent. Molecules 2020, 25, 5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.T.; Ke, X.; Meng, G.L.; Liu, G.J.; Wu, H.Y.; Gong, J.H.; Qian, X.D.; Cheng, J.L.; Hong, H. Telmisartan attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in differentiated PC12 cells. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, C.; Huang, M. Nischarin attenuates apoptosis induced by oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; An, X.F.; Teng, S.C.; Liu, J.S.; Shang, W.B.; Zhang, A.H.; Yuan, Y.G.; Yu, J.Y. Pretreatment with the total flavone glycosides of Flos Abelmoschus manihot and hyperoside prevents glomerular podocyte apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Pan, W.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Z.; Lv, D.; Jiang, M. Total flavones of Abelmoschus manihot enhances angiogenic ability both in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69768–69778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; He, W.; Xia, P.; Sun, W.; Shi, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Zhu, J.; et al. Total extracts of Abelmoschus manihot L. attenuates adriamycin-induced renal tubule injury via suppression of ROS-ERK1/2-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jia, Y.; Qiu, Y. Ethyl acetate fraction of Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic flowers exerts inhibitory effects against oxidative stress in H2O2-induced HepG2 cells and D-galactose-induced aging mice. J. Med. Food 2021, 24, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lans, H.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.J.; Vermeulen, W.; Marteijn, J.A. The DNA damage response to transcription stress. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 766–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakabe, M.; Onishi, Y.; Tada, H.; Kurihara, F.; Kusao, K.; Furukawa, M.; Iwai, S.; Yokoi, M.; Sakai, W.; Sugasawa, K. Mechanism and regulation of DNA damage recognition in nucleotide excision repair. Genes Environ. 2019, 41, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Iwamoto, T.; Yoshioka, A.; Kuniyasu, H.; Kishimoto, T.; Mori, T. Neurons and astrocytes exhibit lower activities of global genome nucleotide excision repair than do fibroblasts. DNA Repair 2007, 6, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langie, S.A.; Knaapen, A.M.; Houben, J.M.; van Kempen, F.C.; de Hoon, J.P.; Gottschalk, R.W.; Godschalk, R.W.; van Schooten, F.J. The role of glutathione in the regulation of nucleotide excision repair during oxidative stress. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.D.; Araújo, S.J.; Ariza, R.R.; Batty, D.P.; Biggerstaff, M.; Evans, E.; Gaillard, P.H.; Gunz, D.; Köberle, B.; Kuraoka, I.; et al. DNA damage recognition and nucleotide excision repair in mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2000, 65, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, U.; Dybdahl, M.; Frentz, G.; Nexo, B.A. DNA repair capacity: Inconsistency between effect of over-expression of five NER genes and the correlation to mRNA levels in primary lymphocytes. Mutat. Res. 2000, 461, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; He, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Yu, Z.; Qi, T.; Xu, S.; Xu, Z.; Fang, L. Huangkui capsule attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and macrophage sctivation by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 6626483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.M.; Shen, S.M.; Wan, Y.G.; Sun, W.; Chen, H.L.; Huang, M.M.; Yang, J.J.; Wu, W.; Tang, H.T.; Tang, R.M. Huangkui capsule attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy rats through regulating oxidative stress and p38MAPK/Akt pathways, compared to α-lipoic acid. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 173, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ai, P.F.; Song, J.J.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.W. Total flavonoid extract from Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic flowers attenuates d-galactose-induced oxidative stress in mouse liver through the Nrf2 pathway. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, G.; Liu, Q.; Hua, W.; Huang, Z.; Wang, D. Hepatoprotective evaluation of the total flavonoids extracted from flowers of Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.Y.; Ai, G.; Zhang, X.J.; Xu, H.J.; Huang, Z.M. Investigations of the total flavonoids extracted from flowers of Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic against α-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic liver injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 172, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| 1∘ Ab | 2∘ Ab | Molecular Weight (kDa) |
|---|---|---|
| Catalase | Rabbit | 60 |
| GPx 1/2 | Rabbit | 24 |
| SOD-1 | Mouse | 16 |
| p-NF-κB | Rabbit | 65 |
| iNOS | Rabbit | 130 |
| COX-2 | Rabbit | 75 |
| TNF-α | Rabbit | 25 |
| IL-1β | Rabbit | 17 |
| XPE | Rabbit | 127 |
| XPC | Rabbit | 106 |
| RPA | Rabbit | 37 |
| XPA | Rabbit | 31 |
| XPF | Rabbit | 104 |
| ERCC | Rabbit | 36 |
| XPG | Rabbit | 133 |
| PCNA | Rabbit | 36 |
| β-actin | Mouse | 48 |
| Extract | AME | AMW | AMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction yield (w/w %) | 25.2 | 16.4 | 1.0 |
| TPC (mg/g extract) | 120.8 ± 0.8 A | 61.5 ± 1.4 B | 47.3 ± 0.8 C |
| TFC (mg/g extract) | 57.0 ± 1.0 A | 28.9 ± 1.7 B | 30.9 ± 1.4 B |
| Rutin (1) | 10.0 ± 0.4 Ac | 6.8 ± 0.2 Bc | 5.0 ± 0.2 Cc |
| Hyperoside (2) | 37.8 ± 2.1 Ba | 18.9 ± 1.2 Ca | 42.4 ± 2.2 Aa |
| Isoquercitrin (3) | 20.6 ± 1.7 Ab | 10.9 ± 1.3 Bb | 17.9 ± 1.0 Ab |
| Myricetin (4) | 36.9 ± 1.4 Aa | 17.5 ± 0.5 Ba | 19.2 ± 1.1 Bb |
| Quercetin (5) | 2.6 ± 0.1 Bd | 1.1 ± 0.1 Cd | 4.1 ± 0.3 Ac |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Hsuan, C.-F.; Chang, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Yu, T.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Houng, J.-Y. Neuroprotective Effect of Abelmoschus manihot Flower Extracts against the H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in PC12 Cells. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100596
Wang S-W, Chang C-C, Hsuan C-F, Chang T-H, Chen Y-L, Wang Y-Y, Yu T-H, Wu C-C, Houng J-Y. Neuroprotective Effect of Abelmoschus manihot Flower Extracts against the H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in PC12 Cells. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(10):596. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100596
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shih-Wei, Chi-Chang Chang, Chin-Feng Hsuan, Tzu-Hsien Chang, Ya-Ling Chen, Yun-Ya Wang, Teng-Hung Yu, Cheng-Ching Wu, and Jer-Yiing Houng. 2022. "Neuroprotective Effect of Abelmoschus manihot Flower Extracts against the H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in PC12 Cells" Bioengineering 9, no. 10: 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100596
APA StyleWang, S. -W., Chang, C. -C., Hsuan, C. -F., Chang, T. -H., Chen, Y. -L., Wang, Y. -Y., Yu, T. -H., Wu, C. -C., & Houng, J. -Y. (2022). Neuroprotective Effect of Abelmoschus manihot Flower Extracts against the H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in PC12 Cells. Bioengineering, 9(10), 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100596