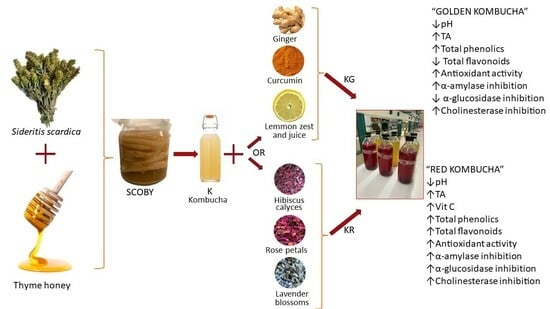
Evaluating the Effect of Adding Selected Herbs, Spices, and Fruits to Fermented Olympus Mountain Tea (Sideritis scardica) Kombucha Sweetened with Thyme Honey: Assessment of Physicochemical and Functional Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Beverages
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Analysis of Color
2.5. Determination of Active and Titratable Acidities
2.6. Determination of Sugars, Ethanol, Organic Acids, and Minerals
2.7. Vitamin C
2.8. Content of Total Phenolics
2.9. Content of Total Flavonoids
2.10. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.11. α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibition Assays
2.11.1. α-Glucosidase Inhibition Assay
2.11.2. α-Amylase Inhibition Assay
2.12. Anticholinesterase Assays: Ache and Bche Inhibition
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Macroscopic Changes Due to the Addition of Herbs, Spices, and Fruits: Color Changes
3.2. PH and TA
3.3. Changes in Sugars, Ethanol, Organic Acids, Minerals, and Vitamin C
3.3.1. Sugars
3.3.2. Acids
3.3.3. Ethanol
3.3.4. Minerals
3.3.5. Vitamin C
3.4. Changes in Total Phenolic Compounds, Flavonoids, and Phenolic Profile
3.5. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity
3.6. α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibition Assays
3.7. Cholinesterase Inhibition Assays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watawana, M.I.; Jayawardena, N.; Waisundara, V.Y. Enhancement of the Functional Properties of Coffee Through Fermentation by “Tea Fungus” (Kombucha). J. Food Process Preserv. 2015, 39, 2596–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, H.; Hashemi Gahruie, H.; Golmakani, M.-T.; Eskandari, M.H.; Movahedi, M. Effect of Medicinal Plant Type and Concentration on Physicochemical, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Sensorial Properties of Kombucha. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, S.Y. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Compounds in Selected Herbs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5165–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, M.; Adelberg, J.; Chen, F.; Rieck, J. Antioxidant Capacity of Fresh and Dried Rhizomes from Four Clones of Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Grown in Vitro. Ind. Crops Prod. 2007, 25, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinneburg, I.; Damien Dorman, H.J.; Hiltunen, R. Antioxidant Activities of Extracts from Selected Culinary Herbs and Spices. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Nayaka, H.; Dharmesh, S.M.; Salimath, P.V. Free and Bound Phenolic Antioxidants in Amla (Emblica officinalis) and Turmeric (Curcuma longa). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Esa, N.; Hern, F.S.; Ismail, A.; Yee, C.L. Antioxidant Activity in Different Parts of Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) Extracts and Potential Exploitation of the Seeds. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoh, I.F.; Ekaidem, I.S.; Etim, O.E.; Akpan, H.D.; Akpan, E.J.; Fakoya, A. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Dried Flower Extracts of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. On Rats Treated with Carbon Tetrachloride. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-H.; Chyau, C.-C.; Chan, K.-C.; Chan, T.-H.; Wang, C.-J.; Huang, C.-N. Hibiscus sabdariffa Polyphenolic Extract Inhibits Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia, and Glycation-Oxidative Stress While Improving Insulin Resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9901–9909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderJagt, T.J.; Ghattas, R.; VanderJagt, D.J.; Crossey, M.; Glew, R.H. Comparison of the Total Antioxidant Content of 30 Widely Used Medicinal Plants of New Mexico. Life Sci. 2002, 70, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.-M.; Hwang, J.-K. Investigations of Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities of Piper Cubeba, Physalis Angulata and Rosa Hybrida. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesini, C.; Perez, C. Screening of Plants Used in Argentine Folk Medicine for Antimicrobial Activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1993, 39, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, C.; Anesini, C. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Argentine Folk Medicinal Plants against Salmonella typhi. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 44, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, N.; Piacente, S.; Pizza, C.; Burke, A.; Khan, A.I.; Hayt, A.J. The Anti-HIV Activity and Mechanisms of Action of Pure Compounds Isolated from Rosa damascena. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 229, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurzynska-Wierdak, R.; Zawislak, G. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia Mill.) Aboveground Parts. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2016, 15, 225–241. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.A.; Song, C.W.; Koh, W.S.; Yon, G.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Ryu, S.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, K.H. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Zingiber officinale Roscoe Constituent 12-Dehydrogingerdione in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Raw 264.7 Cells. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nile, S.H.; Park, S.W. Chromatographic Analysis, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activities of Ginger Extracts and Its Reference Compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 70, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Viennois, E.; Prasad, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.K.; Xiao, B.; Xu, C.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. Edible Ginger-Derived Nanoparticles: A Novel Therapeutic Approach for the Prevention and Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colitis-Associated Cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 101, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijendra Kumar, N.; Murthy, P.S.; Manjunatha, J.R.; Bettadaiah, B.K. Synthesis and Quorum Sensing Inhibitory Activity of Key Phenolic Compounds of Ginger and Their Derivatives. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citronberg, J.; Bostick, R.; Ahearn, T.; Turgeon, D.K.; Ruffin, M.T.; Djuric, Z.; Sen, A.; Brenner, D.E.; Zick, S.M. Effects of Ginger Supplementation on Cell-Cycle Biomarkers in the Normal-Appearing Colonic Mucosa of Patients at Increased Risk for Colorectal Cancer: Results from a Pilot, Randomized, and Controlled Trial. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-C.; Chang, K.-S.; Lin, C.-C. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Capacity of Fresh Ginger Is Attributed Mainly to 10-Gingerol. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, A.J.; Thome, G.R.; Morsch, V.M.; Stefanello, N.; da Costa, P.; Cardoso, A.; Goularte, J.F.; Belló-Klein, A.; Akindahunsi, A.A.; Oboh, G. Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Ginger and Turmeric Rhizomes on Ectonucleotidases, Adenosine Deaminase and Acetylcholinesterase Activities in Synaptosomes from the Cerebral Cortex of Hypertensive Rats. J. Appl. Biomed. 2016, 14, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, S.; Kwon, G.T.; Lee, E.; Jang, W.J.; Yang, H.; Kim, J.H.; Thimmegowda, N.R.; Chung, M.-Y.; Kwon, J.Y.; Yang, S.; et al. Gingerenone A, a Polyphenol Present in Ginger, Suppresses Obesity and Adipose Tissue Inflammation in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-K.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Korinek, M.; Hung, P.-H.; El-Shazly, M.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Wu, Y.-C.; Hsieh, T.-J.; Chang, F.-R. 6-Paradol and 6-Shogaol, the Pungent Compounds of Ginger, Promote Glucose Utilization in Adipocytes and Myotubes, and 6-Paradol Reduces Blood Glucose in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstab, J.; Krüger, D.; Stark, T.; Hofmann, T.; Demir, I.E.; Ceyhan, G.O.; Feistel, B.; Schemann, M.; Niesler, B. Ginger and Its Pungent Constituents Non-Competitively Inhibit Activation of Human Recombinant and Native 5-HT3 Receptors of Enteric Neurons. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 439–447, e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, E.A.; Siviski, M.E.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Hoonjan, B.; Emala, C.W. Effects of Ginger and Its Constituents on Airway Smooth Muscle Relaxation and Calcium Regulation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qassabi, J.S.A.; Weli, A.M.; Hossain, M.A. Comparison of Total Phenols Content and Antioxidant Potential of Peel Extracts of Local and Imported Lemons Samples. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 8, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diankov, S.; Karsheva, M.; Hinkov, I. Extraction of Natural Antioxidants from Lemon Peels. Kinetics and Antioxidant Capacity. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2011, 46, 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, C.; Kapoor, H.C. Anti-oxidant Activity and Total Phenolic Content of Some Asian Vegetables. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraris Kartelias, I.; Karantonis, H.C.; Giaouris, E.; Panagiotakopoulos, I.; Nasopoulou, C. Kombucha Fermentation of Olympus Mountain Tea (Sideritis scardica) Sweetened with Thyme Honey: Physicochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Functional Properties. Foods 2023, 12, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Li, R.-Y.; Chen, J.-X.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.-Q.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Yin, J.-F. Zijuan Tea- Based Kombucha: Physicochemical, Sensorial, and Antioxidant Profile. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chatzinotas, A.; Chakraborty, W.; Bhattacharya, D.; Gachhui, R. Kombucha Tea Fermentation: Microbial and Biochemical Dynamics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 220, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, K.L.; Kaur, G. Spectrophotometric Determination of L-Ascorbic Acid in Vegetables and Fruits. Analyst 1981, 106, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of Total Phenols and Other Oxidation Substrates and Antioxidants by Means of Folin-Ciocalteu Reagent. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 299, pp. 152–178. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, K.R. Flavones, Flavonols and Their Glycosides. In Methods in Plant Biochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 197–235. ISBN 1059-7522. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.-I.; Apostolidis, E.; Kim, Y.-C.; Shetty, K. Health Benefits of Traditional Corn, Beans, and Pumpkin: In Vitro Studies for Hyperglycemia and Hypertension Management. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Dai, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yin, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, J. Kombucha Fermentation Enhances the Health-Promoting Properties of Soymilk Beverage. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 62, 103549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-W.; Huang, M.-Z.; Jin, Y.-S.; Sun, L.-N.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.-S. Phenolics from Bidens Bipinnata and Their Amylase Inhibitory Properties. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A New and Rapid Colorimetric Determination of Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da-Costa-Rocha, I.; Bonnlaender, B.; Sievers, H.; Pischel, I.; Heinrich, M. Hibiscus sabdariffa L.—A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 424–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummer, B.A. Kombucha Brewing under the Food and Drug Administration Model Food Code: Risk Analysis and Processing Guidance. J. Environ. Health 2013, 76, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.; Ikram, E.H.K.; Nazri, H.S.M. Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) Seeds Nutritional Composition Protein Quality and Health Benefits. Food 2008, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Herranz-López, M.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Pérez-Sanchez, A.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Menéndez, J.A.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Joven, J.; Micol, V. Synergism of Plant-Derived Polyphenols in Adipogenesis: Perspectives and Implications. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Rodrigues, M.M.; Balaban, M.O.; Marshall, M.R.; Rouseff, R.L. Hot and Cold Water Infusion Aroma Profilesof Hibiscus sabdariffa: Fresh Compared with Dried. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C212–C217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Rodrigues, M.M.; Plaza, M.L.; Azeredo, A.; Balaban, M.O.; Marshall, M.R. Physicochemical and Phytochemical Properties of Cold and Hot Water Extraction from Hibiscus sabdariffa. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C428–C435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Debón, R.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Aragones, G.; Rodriguez-Medina, I.; Rull, A.; Micol, V.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Camps, J.; Joven, J. The Aqueous Extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa Calices Modulates the Production of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in Humans. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Medina, I.C.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Molina, V.M.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Joven, J.; Menéndez, J.A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Direct Characterization of Aqueous Extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa Using HPLC with Diode Array Detection Coupled to ESI and Ion Trap MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 3441–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, D.L.; Chen, C.-Y.O.; Saltzman, E.; Blumberg, J.B. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Tea (Tisane) Lowers Blood Pressure in Prehypertensive and Mildly Hypertensive Adults. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinokur, Y.; Rodov, V.; Reznick, N.; Goldman, G.; Horev, B.; Umiel, N.; Friedman, H. Rose Petal Tea as an Antioxidant-Rich Beverage: Cultivar Effects. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, S42–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, R.; Olech, M.; Pecio, L.; Oleszek, W.; Los, R.; Malm, A.; Rzymowska, J. Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial Properties and Chemical Composition of Rose Petals. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Morimitsu, Y.; Osawa, T. Isolation of C-Glucosylflavone from Lemon Peel and Antioxidative Activity of Flavonoid Compounds in Lemon Fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 4619–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, S.O.; Babalola, A.O.; Aworh, O.C. Compositional Attributes of the Calyces of Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.). J. Food Technol. Afr. 2001, 6, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădulescu, L.; Bordean, D.-M.; Hădărugă, N.G.; Megyesi, C.I.; Rinovetz, A.E. Nutritional Data Evaluation Study on Rose Petals, Ginger Root and Lemon. J. Agroaliment. Proc. Technol. 2021, 27, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq, Z.; Tahir Nadeem, M.; Arshad, M.U.; Saeed, F.; Ahmed, M.H.; Bader Ul Ain, H.; Javed, A.; Anjum, F.M.; Hussain, S. Exploring the Biochemical and Antioxidant Potential of Ginger (Adric) and Turmeric (Haldi). Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Kaur, N.; Singh, H.; Sangha, M.K. Compositional Differences in Peel and Juice of Cracked and Normal Fruits of Lemon (Citrus limon Burm.). J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 24, 861–872. [Google Scholar]
- Manuha, M.I.; Paranagama, P.A.; Nageeb, B.M. Quantitative Analysis of Vitamin C in Lime and Lemon in Vitro: Verification of Vitamin C on the Impairment of Obesity. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Res. Eng. 2019, 5, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashidoko, Y. The Phytochemistry of Rosa Rugosa. Phytochemistry 1996, 43, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochir, S.; Park, B.; Nishizawa, M.; Kanazawa, T.; Funaki, M.; Yamagishi, T. Simultaneous Determination of Hydrolysable Tannins in the Petals of Rosa rugosa and Allied Plants. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 64, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamijo, M.; Kanazawa, T.; Funaki, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Yamagishi, T. Effects of Rosa rugosa Petals on Intestinal Bacteria. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, E.N.; Meyer, A.S. The Problems of Using One-Dimensional Methods to Evaluate Multifunctional Food and Biological Antioxidants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1925–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon-Aguilar, F.J.; Zamilpa, A.; Perez-Garcia, M.D.; Almanza-Perez, J.C.; Romero-Nuñez, E.; Campos-Sepulveda, E.A.; Vazquez-Carrillo, L.I.; Roman-Ramos, R. Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa on Obesity in MSG Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Alonso, J.; Zamilpa, A.; Aguilar, F.A.; Herrera-Ruiz, M.; Tortoriello, J.; Jimenez-Ferrer, E. Pharmacological Characterization of the Diuretic Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn (Malvaceae) Extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, A.; Knapp, H.; Winterhalter, P. Separation and Purification of Anthocyanins by High-Speed Countercurrent Chromatography and Screening for Antioxidant Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitas, J.; Malbaša, R.; Jokić, A.; Lončar, E.; Milanović, S. ANN and RSM Modelling of Antioxidant Characteristics of Kombucha Fermented Milk Beverages with Peppermint. Mljekarstvo Časopis Za Unaprjeđenje Proizv. I Prerade Mlijeka 2018, 68, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratil, P.; Klejdus, B.; Kubáň, V. Determination of Phenolic Compounds and Their Antioxidant Activity in Fruits and Cereals. Talanta 2007, 71, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirunpanich, V.; Utaipat, A.; Morales, N.P.; Bunyapraphatsara, N.; Sato, H.; Herunsalee, A.; Suthisisang, C. Antioxidant Effects of Aqueous Extracts from Dried Calyx of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. (Roselle) in Vitro Using Rat Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G.; Arranz, S.; Serrano, J.; Goñi, I. Dietary Fiber Content and Associated Antioxidant Compounds in Roselle Flower (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) Beverage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7886–7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.-H.; Kao, E.-S.; Chu, C.-Y.; Chou, F.-P.; Lin Wu, H.-W.; Wang, C.-J. Protective Effects of Dried Flower Extracts of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. against Oxidative Stress in Rat Primary Hepatocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1997, 35, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olalye, M.T.; Rocha, J.B.T. Commonly Used Tropical Medicinal Plants Exhibt Distinct in Vitro Antioxidant Activities against Hepatotoxins in Rat Liver. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 58, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, V.S. Ginger—Chemistry, Technology, and Quality Evaluation: Part 2. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1983, 17, 189–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, V.S. Ginger—Chemistry, Technology, and Quality Evaluation: Part 1. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1983, 17, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custódio, L.; Patarra, J.; Alberício, F.; Neng, N.R.; Nogueira, J.M.F.; Romano, A. In Vitro Antioxidant and Inhibitory Activity of Water Decoctions of Carob Tree (Ceratonia siliqua L.) on Cholinesterases, α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, R.; Cristians, S.; Escandón-Rivera, S.; Juárez-Reyes, K.; Rivero-Cruz, I. Mexican Antidiabetic Herbs: Valuable Sources of Inhibitors of α-Glucosidases. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Xiao, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, B.; Li, X.; Kong, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. An Overview of Plant Phenolic Compounds and Their Importance in Human Nutrition and Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Molecules 2016, 21, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagappan, H.; Pee, P.P.; Kee, S.H.Y.; Ow, J.T.; Yan, S.W.; Chew, L.Y.; Kong, K.W. Malaysian Brown Seaweeds Sargassum Siliquosum and Sargassum Polycystum: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Oxidation, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE), α-Amylase, and α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activities. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, D.M.; Porzel, A.; Frolov, A.; El Seedi, H.R.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Farag, M.A. Comparative Analysis of Hibiscus sabdariffa (Roselle) Hot and Cold Extracts in Respect to Their Potential for α-Glucosidase Inhibition. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholamhoseinian, A.; Fallah, H.; Sharifi far, F. Inhibitory Effect of Methanol Extract of Rosa damascena Mill. Flowers on α-Glucosidase Activity and Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Normal and Diabetic Rats. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranilla, L.G.; Kwon, Y.-I.; Apostolidis, E.; Shetty, K. Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Activity and in Vitro Inhibitory Potential against Key Enzymes Relevant for Hyperglycemia and Hypertension of Commonly Used Medicinal Plants, Herbs and Spices in Latin America. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4676–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bei, Q.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. Improving Phenolic Compositions and Bioactivity of Oats by Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Microbial Fermentation. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adisakwattana, S.; Ruengsamran, T.; Kampa, P.; Sompong, W. In Vitro Inhibitory Effects of Plant-Based Foods and Their Combinations on Intestinal α-Glucosidase and Pancreatic α-Amylase. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Hida, H.; Yamada, Y. Chemistry, Physiological Properties, and Microbial Production of Hydroxycitric Acid. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansawasdi, C.; Kawabata, J.; Kasai, T. α-Amylase Inhibitors from Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn.) Tea. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Beecher, G.R.; Holden, J.M.; Haytowitz, D.B.; Gebhardt, S.E.; Prior, R.L. Lipophilic and Hydrophilic Antioxidant Capacities of Common Foods in the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4026–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oboh, G.; Adewuni, T.M.; Ademiluyi, A.O.; Olasehinde, T.A.; Ademosun, A.O. Phenolic Constituents and Inhibitory Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. (Sorrel) Calyx on Cholinergic, Monoaminergic, and Purinergic Enzyme Activities. J. Diet. Suppl. 2018, 15, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, A.; Ballard, C.; Bullock, R.; Darreh-Shori, T.; Somogyi, M. A Review of Butyrylcholinesterase as a Therapeutic Target in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2013, 15, 26731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseiro, L.B.; Rauter, A.P.; Serralheiro, M.L.M. Polyphenols as Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Structural Specificity and Impact on Human Disease. Nutr. Aging 2012, 1, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olech, M.; Nowak, R.; Załuski, D.; Kapusta, I.; Amarowicz, R.; Oleszek, W. Hyaluronidase, Acetylcholinesterase Inhibiting Potential, Antioxidant Activity, and LC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Polyphenolics of Rose (Rosa rugosa Thunb.) Teas and Tinctures. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S16–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, B.T.; Thu, D.K.; Thu, N.T.K.; Hai, N.T. Antioxidant and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activities of Ginger Root (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) Extract. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2017, 14, 20160116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.; Subramanian, S. In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Alzheimer Effects of Dry Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) Extract. Indian. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 52, 606–612. [Google Scholar]
- Oboh, G.; Ademiluyi, A.O.; Akinyemi, A.J. Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase Activities and Some Pro-Oxidant Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Rat Brain by Two Varieties of Ginger (Zingiber officinale). Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuya, T.; Baptista, L.; Celmar Costa França, T. A Molecular Dynamics Study of Components of the Ginger (Zingiber officinale) Extract inside Human Acetylcholinesterase: Implications for Alzheimer Disease. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 3843–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuya, T.; França, T.C.C. A Molecular Modeling Study of Components of the Ginger (Zingiber officinale) Extract inside Human Butyrylcholinesterase: Implications for Alzheimer Disease. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Reza, A.S.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Akhter, S.; Rahman, M.R.; Nasrin, M.S.; Uddin, M.J.; Sadik, G.; Khurshid Alam, A.H.M. In Vitro Antioxidant and Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activities of Elatostema papillosum Leaves and Correlation with Their Phytochemical Profiles: A Study Relevant to the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amessis-Ouchemoukh, N.; Madani, K.; Falé, P.L.V.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Araújo, M.E.M. Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolic Contents of Some Mediterranean Medicinal Plants and Their Potential Role in the Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-1 and Acetylcholinesterase Activities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 53, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Szwajgier, D.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A. Honey as the Potential Natural Source of Cholinesterase Inhibitors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Plant Foods Human. Nutr. 2020, 75, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.J.; Oh, C.-S.; Park, Y.-D.; Eom, S.H.; Kim, D.-O.; Kim, U.-J.; Cho, Y.-S. Physiological Components of Kiwifruits with in Vitro Antioxidant and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activities. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, M.A.; Dimakopoulou, A.; Linardaki, Z.I.; Cordopatis, P.; Klimis-Zacas, D.; Margarity, M.; Lamari, F.N. Effect of a Polyphenol-Rich Wild Blueberry Extract on Cognitive Performance of Mice, Brain Antioxidant Markers and Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 198, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwajgier, D.; Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A.; Gajowniczek-Ałasa, D. Honeys as Possible Sources of Cholinesterase Inhibitors. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, H.; Ouchemoukh, S.; Amessis-Ouchemoukh, N.; Debbache, N.; Pacheco, R.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Araujo, M.E. Biological Properties of Phenolic Compound Extracts in Selected Algerian Honeys—The Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase and α-Glucosidase Activities. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, Y.; Mohd Fadzelly, A.B. Antioxidative and acetylcholinesterase inhibitor potential of selected honey of Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar]









| Replication | K | KG | KR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | AG | AR |
| 2 | B | BG | BR |
| 3 | C | BG | CR |
| Chromatic Parameter | K | KR | KG |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | 66.5 ± 0.1 a | 41.8 ± 0.3 b | 67.3 ± 0.1 c |
| a | −4.1 ± 0.2 d | 39.1 ± 0.4 c | −4.8 ± 0.1 d |
| b | 22.0 ± 0.3 e | 23.7 ± 0.1 f | 23.5 ± 0.1 g |
| Sample | pH | TA (Acetic Acid g/L) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 3.06 ± 0.02 | 4.45 ± 0.02 |
| AG | 3.00 ± 0.01 | 4.68 ± 0.01 |
| AR | 2.96 ± 0.01 | 4.71 ± 0.02 |
| B | 3.02 ± 0.01 | 4.69 ± 0.04 |
| BG | 2.96 ± 0.02 | 4.86 ± 0.02 |
| BR | 2.94 ± 0.01 | 5.10 ± 0.04 |
| C | 2.96 ± 0.03 | 4.24 ± 0.05 |
| CG | 2.87 ± 0.01 | 4.35 ± 0.02 |
| CR | 2.85 ± 0.01 | 4.42 ± 0.01 |
| Sample | Glucose (g/L) | Fructose (g/L) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 20.4 ± 0.7 | 17.1 ± 0.8 |
| AG | 19.8 ± 0.9 | 16.5 ± 0.9 |
| AR | 20.1 ± 0.6 | 16.8 ± 0.9 |
| B | 20.1 ± 0.8 | 18.6 ± 1 |
| BG | 20.1 ± 0.6 | 18.3 ± 0.9 |
| BR | 20.1 ± 0.7 | 18.6 ± 0.8 |
| C | 18.6 ± 0.7 | 21 ± 0.9 |
| CG | 18 ± 0.9 | 19.5 ± 0.9 |
| CR | 18.3 ± 0.8 | 19.4 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geraris Kartelias, I.; Panagiotakopoulos, I.; Nasopoulou, C.; Karantonis, H.C. Evaluating the Effect of Adding Selected Herbs, Spices, and Fruits to Fermented Olympus Mountain Tea (Sideritis scardica) Kombucha Sweetened with Thyme Honey: Assessment of Physicochemical and Functional Properties. Beverages 2024, 10, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10010009
Geraris Kartelias I, Panagiotakopoulos I, Nasopoulou C, Karantonis HC. Evaluating the Effect of Adding Selected Herbs, Spices, and Fruits to Fermented Olympus Mountain Tea (Sideritis scardica) Kombucha Sweetened with Thyme Honey: Assessment of Physicochemical and Functional Properties. Beverages. 2024; 10(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeraris Kartelias, Ioannis, Ioannis Panagiotakopoulos, Constantina Nasopoulou, and Haralabos Christos Karantonis. 2024. "Evaluating the Effect of Adding Selected Herbs, Spices, and Fruits to Fermented Olympus Mountain Tea (Sideritis scardica) Kombucha Sweetened with Thyme Honey: Assessment of Physicochemical and Functional Properties" Beverages 10, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10010009
APA StyleGeraris Kartelias, I., Panagiotakopoulos, I., Nasopoulou, C., & Karantonis, H. C. (2024). Evaluating the Effect of Adding Selected Herbs, Spices, and Fruits to Fermented Olympus Mountain Tea (Sideritis scardica) Kombucha Sweetened with Thyme Honey: Assessment of Physicochemical and Functional Properties. Beverages, 10(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10010009