Performance of Slow-Growing Chickens Fed with Tenebrio molitor Larval Meal as a Full Replacement for Soybean Meal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Composition of the Diets and Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
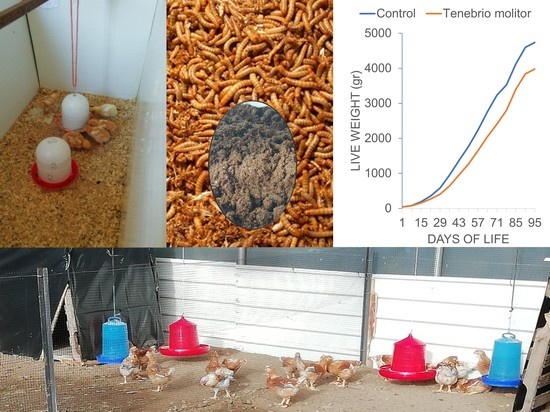
3.1. Productive Performance
| P | G | Indoor Stage | Outdoor Stage | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (0–29 d) | F2 (29–57) | F3 (57–95) | ||||||||||||||
| 0 w (0–1 d) | 1 w (1–8 d) | 2 w (8–15 d) | 3 w (15–22 d) | 4 w (22–29 d) | 5 w (29–36 d) | 6 w (36–43 d) | 7 w (43–50 d) | 8 w (50–57 d) | 9 w (57–64 d) | 10 w (64–71 d) | 11 w (71–78 d) | 12 w (78–85 d) | 13 w (85–92 d) | 14 w (92–95 d) | ||
| LW 1 | C | 39.9 ± 0.0 | 83.8 ± 2.6 | 191.5 ± 5.1 | 351.8 ± 11.7 | 583.6 ± 13.6 | 949.4 ± 17.2 | 1368.6 ± 31.7 | 1772.7 ± 35.0 | 2229.0 ± 45.3 | 2756.7 ± 51.6 | 3237.0 ± 53.2 | 3493.5 ± 66.5 | 4125.0 ± 70.0 | 4598.4 ± 73.5 | 4739.0 ± 73.5 |
| TM | 39.8 ± 0.1 | 78.3 ± 2.9 | 156.9 ± 4.4 | 268.7 ± 9.2 | 407.5 ± 14.8 | 643.6 ± 18.3 | 956.9 ± 23.8 | 1267.3 ± 25.5 | 1643.2 ± 49.2 | 2047.5 ± 59.5 | 2408.2 ± 68.9 | 2803.0 ± 78.2 | 3403.0 ± 97.7 | 3841.7 ± 111.7 | 3981.5 ± 124.4 | |
| Sig. | NS | NS | ** | ** | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | * | NS | * | NS | * | NS | |
| BWG | C | - | 6.3 ± 0.4 | 15.4 ± 0.6 | 22.9 ± 1.0 | 33.1 ± 1.3 | 52.3 ± 1.0 | 59.9 ± 3.4 | 57.7 ± 4.1 | 67.8 ± 2.2 | 75.4 ± 2.1 | 68.6 ± 2.1 | 36.6 ± 5.5 | 85.1 ± 2.6 | 67.6 ± 2.5 | 46.8 ± 3.5 |
| TM | - | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 11.2 ± 0.4 | 16.0 ± 0.9 | 19.8 ± 1.0 | 33.7 ± 1.1 | 44.8 ± 1.8 | 44.3 ± 2.3 | 59.1 ± 3.0 | 57.7 ± 2.5 | 51.5 ± 2.7 | 56.4 ± 3.0 | 85.7 ± 4.6 | 62.7 ± 4.0 | 46.6 ± 6.1 | |
| Sig. | - | NS | ** | ** | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| FI | C | - | 11.5 ± 0.9 | 28.1 ± 1.5 | 41.1 ± 1.2 | 70.7 ± 3.8 | 111.3 ± 2.0 | 134.9 ± 3.7 | 122.3 ± 3.7 | 167.2 ± 0.2 | 209.1 ± 1.8 | 233.4 ± 2.1 | 212.2 ± 0.3 | 260.8 ± 3.3 | 250.3 ± 1.1 | 234.8 ± 4.6 |
| TM | - | 9.0 ± 0.6 | 28.5 ± 1.4 | 40.1 ± 3.0 | 45.1 ± 2.7 | 76.4 ± 1.5 | 101.6 ± 3.5 | 97.6 ± 2.4 | 140.9 ± 2.0 | 169.6 ± 0.7 | 205.0 ± 2.9 | 207.8 ± 12.2 | 248.2 ± 1.2 | 241.5 ± 7.1 | 225.9 ± 17.1 | |
| Sig. | - | * | NS | NS | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | * | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| WI | C | - | 21.5 ± 0.6 | 47.9 ± 1.4 | 83.6 ± 2.7 | 133.4 ± 3.4 | 219.3 ± 9.7 | 231.3 ± 6.5 | 242.0 ± 7.4 | 298.0 ± 14.4 | 410.0 ± 15.7 | 410.3 ± 21.2 | 301.3 ± 19.4 | 409.8 ± 7.8 | 411.7 ± 18.5 | 404.0 ± 13.2 |
| TM | - | 14.7 ± 1.3 | 29.4 ± 1.0 | 55.2 ± 2.3 | 92.0 ± 5.1 | 113.0 ± 6.5 | 161.2 ± 5.0 | 165.9 ± 3.9 | 220.4 ± 3.2 | 287.6 ± 10.9 | 328.4 ± 2.3 | 266.4 ± 8.6 | 349.0 ± 10.6 | 330.1 ± 6.0 | 361.0 ± 20.8 | |
| Sig. | - | ** | ** | ** | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| FCR | C | - | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 2.8 ± 0.0 | 3.4 ± 0.0 | 5.1 ± 0.3 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 3.7 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.1 |
| TM | - | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.0 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 4.0 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 4.9 ± 0.3 | |
| Sig. | - | NS | ** | ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
3.2. Growth and Feed Intake Increases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allegretti, G.; Talamini, E.; Schmidt, V.; Bogorni, P.C.; Ortega, E. Insect as Feed: An Emergy Assessment of Insect Meal as a Sustainable Protein Source for the Brazilian Poultry Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, L.; Acuti, G.; Bani, P.; Dalle Zotte, A.; Danieli, P.P.; De Angelis, A.; Fortina, R.; Marino, R.; Parisi, G.; Piccolo, G.; et al. Insect and Fish By-Products as Sustainable Alternatives to Conventional Animal Proteins in Animal Nutrition. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 19, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olukosi, O.A.; Walker, R.L.; Houdijk, J.G.M. Evaluation of the Nutritive Value of Legume Alternatives to Soybean Meal for broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5778–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadd, S. Future Trends and Developments in Poultry Nutrition. In Poultry in the 21st Century: Avian Influenza and Beyond, Proceedings of the International Poultry Conference; Thieme, O., Pilling, D., Eds.; FAO Animal Production and Health Proceedings: Bangkok, Thailand, 2008; pp. 269–299. ISBN 978-92-5-107364-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Barroso, F.G.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Insect Meal as Renewable Source of Food for Animal Feeding: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiber, F.; Gelencsér, T.; Stamer, A.; Amsler, Z.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Früh, B.; Maurer, V. Insect and Legume-Based Protein Sources to Replace Soybean Cake in an Organic Broiler Diet: Effects on Growth Performance and Physical Meat Quality. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2015, 32, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selaledi, L.; Mbajiorgu, C.A.; Mabelebele, M. The Use of Yellow Mealworm (T. Molitor) as Alternative Source of Protein in Poultry Diets: A Review. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento-García, A.; Palacios, C.; González-Martín, I.; Revilla, I. Evaluation of the Production Performance and the Meat Quality of Chickens Reared in Organic System. As Affected by the Inclusion of Calliphora Sp. in the Diet. Animals 2021, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.H. Recent Advances in Role of Insects as Alternative Protein Source in Poultry Nutrition. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 1144–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nascimento Filho, M.A.; Pereira, R.T.; de Oliveira, A.B.S.; Suckeveris, D.; Burin Junior, A.M.; de Mastrangelo, T.A.; da Costa, D.V.; Menten, J.F.M. Cafeteria-Type Feeding of Chickens Indicates a Preference for Insect (Tenebrio molitor) Larvae Meal. Animals 2020, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Premalatha, M.; Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, S.A. Energy-Efficient Food Production to Reduce Global Warming and Ecodegradation: The Use of Edible Insects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4357–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, K.; Ognik, K.; Stcepniowska, A.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Zduńczyk, Z.; Kierończyk, B.; Benzertiha, A.; Józefiak, D.; Jankowski, J. Growth Performance, Immune Status and Intestinal Fermentative Processes of Young Turkeys Fed Diet with Additive of Full Fat Meals from Tenebrio molitor and Hermetia Illucens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 278, 114994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasato, I.; De Marco, M.; Rotolo, L.; Renna, M.; Lussiana, C.; Dabbou, S.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E.; Costa, P.; Gai, F.; et al. Effects of Dietary Tenebrio molitor Meal Inclusion in Free-Range Chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Huis, A.; van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security. FAO For. Pap. 2014, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Marono, S.; Piccolo, G.; Loponte, R.; Meo, C.D.; Attia, Y.A.; Nizza, A.; Bovera, F. In Vitro Crude Protein Digestibility of Tenebrio molitor and Hermetia Illucens Insect Meals and Its Correlation with Chemical Composition Traits. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 14, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Union Comission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1372 of 17 August 2021 Amending Annex IV of Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards a Feed Ban on Non-Ruminant Farmed Animals 2021; Euopean Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bovera, F.; Piccolo, G.; Gasco, L.; Marono, S.; Loponte, R.; Vassalotti, G.; Mastellone, V.; Lombardi, P.; Attia, Y.A.; Nizza, A. Yellow Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor, L.) as a Possible Alternative to Soybean Meal in Broiler Diets. Br. Poult. Sci. 2015, 56, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasato, I.; Gasco, L.; De Marco, M.; Renna, M.; Rotolo, L.; Dabbou, S.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E.; Tarantola, M.; Bianchi, C.; et al. Effects of Yellow Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor) Inclusion in Diets for Female Broiler Chickens: Implications for Animal Health and Gut Histology. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 234, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasato, I.; Gasco, L.; De Marco, M.; Renna, M.; Rotolo, L.; Dabbou, S.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E.; Tarantola, M.; Sterpone, L.; et al. Yellow Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor) Inclusion in Diets for Male Broiler Chickens: Effects on Growth Performance, Gut Morphology, and Histological Findings. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vissers, L.S.M.; de Jong, I.C.; van Horne, P.L.M.; Saatkamp, H.W. Global Prospects of the Cost-Efficiency of Broiler Welfare in Middle-Segment Production Systems. Animals 2019, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allais, S.; Hennequet-Antier, C.; Berri, C.; Salles, L.; Demeure, O.; Le Bihan-Duval, E. Mapping of QTL for Chicken Body Weight, Carcass Composition, and Meat Quality Traits in a Slow-Growing Line. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Taddei, L.; Albiker, D.; Kreuzer, M.; Siegrist, M.; Messikommer, R.E.; Gangnat, I.D.M. Growth, Carcass, and Meat Quality of 2 Dual-Purpose Chickens and a Layer Hybrid Grown for 67 or 84 D Compared with Slow-Growing Broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, I.C.P.; Broch, J.; Eyng, C.; Silva, I.M.; Souza, C.; Avila, A.S.; Castilha, L.D.; Cirilo, E.H.; Tesser, G.L.S.; Nunes, R.V. Effects of Feeding Dried Brewers Grains to Slow-Growing Broiler Chickens. Livest. Sci. 2021, 250, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, Z.S.; Kheiri, F.; Faghani, M. Use of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) as a Protein Source on Growth Performance, Carcass Traits, Meat Quality and Intestinal Morphology of Japanese Quails (Coturnix Japonica). Vet. Anim. Sci. 2019, 8, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedgh-Gooya, S.; Torki, M.; Darbemamieh, M.; Khamisabadi, H.; Karimi Torshizi, M.A.; Abdolmohamadi, A. Yellow Mealworm, Tenebrio molitor (Col: Tenebrionidae), Larvae Powder as Dietary Protein Sources for Broiler Chickens: Effects on Growth Performance, Carcass Traits, Selected Intestinal Microbiota and Blood Parameters. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 105, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry; National Research Council, Ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-309-04892-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bovera, F.; Loponte, R.; Marono, S.; Piccolo, G.; Parisi, G.; Iaconisi, V.; Gasco, L.; Nizza, A. Use of Tenebrio molitor Larvae Meal as Protein Source in Broiler Diet: Effect on Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Carcass and Meat Traits. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nascimento Filho, M.A.; Pereira, R.T.; Oliveira, A.B.S.; Suckeveris, D.; Burin Junior, A.M.; Soares, C.A.P.; Menten, J.F.M. Nutritional Value of Tenebrio molitor Larvae Meal for Broiler Chickens: Metabolizable Energy and Standardized Ileal Amino Acid Digestibility. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2021, 30, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzertiha, A.; Kierończyk, B.; Ko\lodziejski, P.; Pruszyńska–Oszma\lek, E.; Rawski, M.; Józefiak, D.; Józefiak, A. Tenebrio molitor and Zophobas Morio Full-Fat Meals as Functional Feed Additives Affect Broiler Chickens’ Growth Performance and Immune System Traits. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza Oddon, S.; Biasato, I.; Imarisio, A.; Pipan, M.; Dekleva, D.; Colombino, E.; Capucchio, M.T.; Meneguz, M.; Bergagna, S.; Barbero, R.; et al. Black Soldier Fly and Yellow Mealworm Live Larvae for Broiler Chickens: Effects on Bird Performance and Health Status. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 105, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, D.-H.; Jeong, S.-B.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, H.-G.; Lee, K.-W. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Oil as an Alternative Fat Source in Broiler Nutrition. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3133–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atteh, J.O.; Ologbenla, F.D. Replacement of Fish Meal With Maggots In Broiler Diets: Effects On Performance And Nutrient Retention. Niger. J. Anim. Prod. 1993, 20, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamgbose, A. Utilization of Maggot-Meal in Cockerel Diets. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 69, 1056–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Awoniyi, T.A.M.; Aletor, V.A.; Aina, J.M. Performance of Broiler—Chickens Fed on Maggot Meal in Place of Fishmeal. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2003, 2, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindran, V.; Blair, R. Feed Resources for Poultry Production in Asia and the Pacific. III. Animal Protein Sources. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 1993, 49, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkowski, B. Feeding High Lupine Based Diets for Broiler Chickens: Effect of Soybean Meal Substitution with Yellow Lupine Meal at Various Time Points of Growth Cycle. Livest. Sci. 2018, 218, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Raw Matter | F1 (1–29 d) | F2 (29–57 d) | F3 (57–95 d) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | TM | C | TM | C | TM | |
| Corn | 37.0 | 10.0 | 48.0 | 9.0 | 31.0 | 18.0 |
| Wheat | 11.0 | 0.0 | 12.0 | 16.8 | 37.0 | 33.5 |
| Barley | 0.0 | 21.0 | 0.0 | 13.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Soybean meal | 29.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 0.0 | 12.0 | 0.0 |
| T. molitor meal | 0.0 | 22..3 | 0.0 | 13.0 | 0.0 | 9.2 |
| Sunflower | 19.0 | 0.0 | 16.0 | 9.0 | 16.0 | 9.0 |
| Oats | 0.0 | 42.7 | 0.0 | 35.0 | 0.0 | 26.3 |
| Vitamin-mineral premix | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Parameter | F1 (1–29 d) | F2 (29–57 d) | F3 (57–95 d) | T. molitor Meal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | TM | C | TM | C | TM | ||
| %Moisture | 7.6 | 7.9 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 8.6 | 8.5 | 6.6 |
| %Ash | 6.5 | 6.4 | 6.4 | 6.0 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 4.2 |
| %Crude fat | 12.3 | 9.9 | 9.5 | 9.1 | 10.7 | 9.7 | 21.2 |
| %Crude fiber | 6.1 | 7.9 | 5.0 | 8.5 | 6.1 | 6.9 | 8.3 |
| %Starch | 35.0 | 38.1 | 41.2 | 37.4 | 42.3 | 40.9 | 2.3 |
| %Crude protein | 19.7 | 19.3 | 15.6 | 15.5 | 14.8 | 14.2 | 54.9 |
| ME (Kcal/kgDM) | 2802.8 | 2898.9 | 2900.0 | 2900.7 | 2950.8 | 2964.7 | 5020.0 |
| Mean dietary Crude Protein (%) | 19.5 | 15.6 | 14.5 | 54.9 | |||
| Mean dietary ME (Kcal/kgDM) | 2850.8 | 2900.3 | 2957.8 | 5020.0 | |||
| %Ca | 1.24 | 1.94 | 1.21 | 1.63 | 1.20 | 1.49 | 3.6 |
| %P | 0.40 | 2.10 | 0.36 | 1.41 | 0.34 | 1.08 | 7.4 |
| %SFA | 1.6 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 5.0 |
| %MUFA | 3.0 | 3.7 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 8.4 |
| %PUFA | 7.8 | 4.1 | 6.0 | 4.7 | 7 | 5.4 | 7.9 |
| %n-3 PUFA | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.25 |
| %n-6 PUFA | 7.6 | 3.9 | 5.9 | 4.7 | 6.8 | 5.3 | 7.6 |
| %Trans FA (C18:1T + C18:2T + C13:3T) | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| 4-Hidroxiproline (mg/100 gDM) | 59.0 | 24.0 | 46.0 | 24.8 | 39.9 | 23.7 | 72.0 |
| Aspartic acid + Asparagine (g/100 gDM) | 2.54 | 1.83 | 1.92 | 0.84 | 1.20 | 0.86 | 4.5 |
| Glutamic acid + Glutamine (g/100 gDM) | 5.22 | 4.13 | 4.45 | 2.83 | 4.12 | 2.86 | 6.4 |
| Alanine (g/100 gDM) | 0.91 | 1.40 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 5.0 |
| Arginine (g/100 gDM) | 1.28 | 0.91 | 1.21 | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 2.74 |
| Cysteine (g/100 gDM) | <20 | <20 | <20 | <20 | <20 | <20 | <20 |
| Cystine (g/100 gDM) | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.30 |
| Phenylalanine (g/100 gDM) | 0.81 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 2.17 |
| Glycine (g/100 gDM) | 1.02 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 0.45 | 0.40 | 0.67 | 2.72 |
| Histidine (g/100 gDM) | 0.76 | 0.57 | 0.65 | 0.95 | 0.76 | 0.48 | 1.51 |
| Isoleucine (g/100 gDM) | 0.68 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 2.39 |
| Leucine (g/100 gDM) | 1.18 | 0.94 | 1.09 | 1.04 | 0.94 | 0.76 | 4.9 |
| Lysine (g/100 gDM) | 1.44 | 1.23 | 1.28 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 0.69 | 2.80 |
| Methionine (g/100 gDM) | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.47 |
| Proline (g/100 gDM) | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.45 | 1.03 | 1.03 | 1.16 | 2.74 |
| Serine (g/100 gDM) | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.59 | 2.25 |
| Tyrosine (g/100 gDM) | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.46 | 0.81 | 0.34 | 0.80 | 4.1 |
| Threonine (g/100 gDM) | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.65 | 1.89 |
| Tryptophan (g/100 gDM) | <20 | <20 | <20 | <20 | <20 | <20 | <20 |
| Valine (g/100 gDM) | 0.65 | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.46 | 0.41 | 4.7 |
| Hydrolyze protein (g/100 gDM) | 20.22 | 16.83 | 17.80 | 13.94 | 14.56 | 12.87 | 52 |
| Parameter | F1 (1–29 d) | F2 (29–57 d) | F3 (57–95 d) | Total (1–95 d) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | TM | Sig. | C | TM | Sig. | C | TM | Sig. | C | TM | Sig. | |
| LW 1 | 583.6 ± 13.6 | 407.5 ± 14.8 | ** | 2229.0 ± 45.3 | 1643.3 ± 49.2 | NS | 4739.0 ± 73.5 | 3981.5 ± 124.4 | NS | 4739.0 ± 73.5 | 3981.5 ± 124.4 | NS |
| BWG | 19.4 ± 0.5 | 13.1 ± 0.5 | ** | 60.2 ± 1.9 | 44.3 ± 2.1 | * | 66.0 ± 1.4 | 63.8 ± 1.2 | NS | 49.99 ± 0.78 | 43.8 ± 1.2 | ** |
| FI | 1059.4 ± 41.6 | 858.8 ± 47.0 | ** | 3749.9 ± 71.7 | 2915.7 ± 78.6 | NS | 8865.0 ± 41.1 | 8182.8 ± 193.8 | NS | 13,674.30 ± 198.56 | 11,957.4 ± 282.6 | * |
| WI | 2004.3 ± 48.8 | 1339.4 ± 43.5 | ** | 6934.2 ± 178.1 | 4623.6 ± 118.5 | NS | 14,813.5 ± 618.5 | 12,014.1 ± 54.1 | NS | 23,751.88 ± 601.13 | 17,977.1 ± 427.6 | ** |
| FCR | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.1 | ** | 2.3 ± 0.0 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | NS | 3.5 ± 0.0 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | NS | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nieto, J.; Plaza, J.; Lara, J.; Abecia, J.-A.; Revilla, I.; Palacios, C. Performance of Slow-Growing Chickens Fed with Tenebrio molitor Larval Meal as a Full Replacement for Soybean Meal. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030131
Nieto J, Plaza J, Lara J, Abecia J-A, Revilla I, Palacios C. Performance of Slow-Growing Chickens Fed with Tenebrio molitor Larval Meal as a Full Replacement for Soybean Meal. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(3):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030131
Chicago/Turabian StyleNieto, Jaime, Javier Plaza, Javier Lara, José-Alfonso Abecia, Isabel Revilla, and Carlos Palacios. 2022. "Performance of Slow-Growing Chickens Fed with Tenebrio molitor Larval Meal as a Full Replacement for Soybean Meal" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 3: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030131
APA StyleNieto, J., Plaza, J., Lara, J., Abecia, J.-A., Revilla, I., & Palacios, C. (2022). Performance of Slow-Growing Chickens Fed with Tenebrio molitor Larval Meal as a Full Replacement for Soybean Meal. Veterinary Sciences, 9(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030131