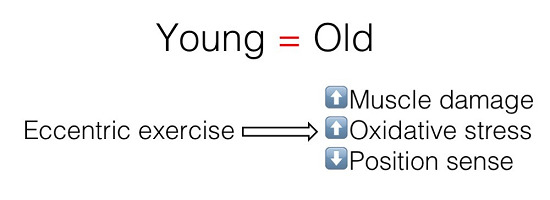
The Effects of Resistance Exercise on Muscle Damage, Position Sense, and Blood Redox Status in Young and Elderly Individuals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Assessment of 1 Repetition Maximum (1RM)
4.3. Research Design
4.4. Resistance Exercise Protocol
4.5. Muscle Damage Indices
4.6. Position Sense
4.7. Blood Collection
4.8. Assays
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nair, K.S. Aging muscle. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I. Influence of sarcopenia on the development of physical disability: The cardiovascular health study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metter, E.J.; Talbot, L.A.; Schrager, M.; Conwit, R. Skeletal muscle strength as a predictor of all-cause mortality in healthy men. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2002, 57, B359–B365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaStayo, P.; McDonagh, P.; Lipovic, D.; Napoles, P.; Bartholomew, A.; Esser, K.; Lindstedt, S. Elderly patients and high force resistance exercise—A descriptive report: Can an anabolic, muscle growth response occur without muscle damage or inflammation? J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2007, 30, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, A.; Bull, F.; Chey, T.; Craig, C.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Sallis, J.F.; Bowles, H.R.; Hagstromer, M.; Sjostrom, M.; Pratt, M.; et al. The international prevalence study on physical activity: Results from 20 countries. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2009, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, J.; Norman, R.; Lambert, E.V.; Groenewald, P.; Schneider, M.; Bull, F.; Bradshaw, D.; South African Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating Group. Estimating the burden of disease attributable to physical inactivity in south africa in 2000. S. Afr. Med. J. 2007, 97, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paschalis, V.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Theodorou, A.A.; Panayiotou, G.; Fatouros, I.G.; Koutedakis, Y.; Jamurtas, A.Z. A weekly bout of eccentric exercise is sufficient to induce health-promoting effects. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppeler, H. Exercise-induced ultrastructural changes in skeletal muscle. Int. J. Sports Med. 1986, 7, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavender, A.P.; Nosaka, K. Comparison between old and young men for changes in makers of muscle damage following voluntary eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2006, 31, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosaka, K.; Newton, M.; Sacco, P. Delayed-onset muscle soreness does not reflect the magnitude of eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2002, 12, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschalis, V.; Koutedakis, Y.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Mougios, V.; Baltzopoulos, V. Equal volumes of high and low intensity of eccentric exercise in relation to muscle damage and performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R.B. Initial events in exercise-induced muscular injury. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1990, 22, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paschalis, V.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Giakas, G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Owolabi, E.O.; Koutedakis, Y. Position sense and reaction angle after eccentric exercise: The repeated bout effect. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 103, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerakkody, N.S.; Percival, P.; Hickey, M.W.; Morgan, D.L.; Gregory, J.E.; Canny, B.J.; Proske, U. Effects of local pressure and vibration on muscle pain from eccentric exercise and hypertonic saline. Pain 2003, 105, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalis, V.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Giakas, G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Pappas, A.; Koutedakis, Y. The effect of eccentric exercise on position sense and joint reaction angle of the lower limbs. Muscle Nerve 2007, 35, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschalis, V.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Theodorou, A.A.; Giakas, G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Koutedakis, Y. Eccentric exercise affects the upper limbs more than the lower limbs in position sense and reaction angle. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.A.; Morgan, D.L.; Proske, U. Effects of repeated eccentric contractions on structure and mechanical properties of toad sartorius muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, C792–C800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, M.G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Paschalis, V.; Fatouros, I.G.; Koutedakis, Y.; Kouretas, D. The effect of muscle-damaging exercise on blood and skeletal muscle oxidative stress: Magnitude and time-course considerations. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 579–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, M.G.; Kyparos, A.; Dipla, K.; Zafeiridis, A.; Sambanis, M.; Grivas, G.V.; Paschalis, V.; Theodorou, A.A.; Papadopoulos, S.; Spanou, C.; et al. Exercise as a model to study redox homeostasis in blood: The effect of protocol and sampling point. Biomarkers 2012, 17, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, M.G.; Paschalis, V.; Giakas, G.; Fatouros, I.G.; Koutedakis, Y.; Kouretas, D.; Jamurtas, A.Z. Decreased blood oxidative stress after repeated muscle-damaging exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, A.A.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Paschalis, V.; Koutsias, S.; Panayiotou, G.; Fatouros, I.G.; Koutedakis, Y.; Jamurtas, A.Z. No effect of antioxidant supplementation on muscle performance and blood redox status adaptations to eccentric training. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorou, A.A.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Paschalis, V.; Sakellariou, G.K.; Fatouros, I.G.; Koutedakis, Y.; Jamurtas, A.Z. Comparison between glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient and normal individuals after eccentric exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roth, S.M.; Martel, G.F.; Ivey, F.M.; Lemmer, J.T.; Tracy, B.L.; Hurlbut, D.E.; Metter, E.J.; Hurley, B.F.; Rogers, M.A. Ultrastructural muscle damage in young vs. Older men after high-volume, heavy-resistance strength training. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 86, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavender, A.P.; Nosaka, K. Changes in markers of muscle damage of middle-aged and young men following eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2008, 11, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedrick, M.E.; Clarkson, P.M. The effects of eccentric exercise on motor performance in young and older women. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1990, 60, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, T.G.; Fielding, R.A.; O'Reilly, K.P.; Meredith, C.N.; Lee, H.Y.; Evans, W.J. Plasma creatine kinase activity and exercise-induced muscle damage in older men. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1991, 23, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploutz-Snyder, L.L.; Giamis, E.L.; Formikell, M.; Rosenbaum, A.E. Resistance training reduces susceptibility to eccentric exercise-induced muscle dysfunction in older women. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, B384–B390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proske, U.; Allen, T.J. Damage to skeletal muscle from eccentric exercise. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2005, 33, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockett, C.; Warren, N.; Gregory, J.E.; Morgan, D.L.; Proske, U. A comparison of the effects of concentric versus eccentric exercise on force and position sense at the human elbow joint. Brain Res. 1997, 771, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.M.; McEneny, J.; Mathieu-Costello, O.; Henry, R.R.; James, P.E.; McCord, J.M.; Pietri, S.; Young, I.S.; Richardson, R.S. Sedentary aging increases resting and exercise-induced intramuscular free radical formation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, M.; Mortensen, S.P.; Cabo, H.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Vina, J.; Hellsten, Y. Roles of sedentary aging and lifelong physical activity in exchange of glutathione across exercising human skeletal muscle. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, C.B.; Robertson, R.J.; Goss, F.L.; Timmer, J.M.; Nagle, E.F.; Evans, R.W. The effect of acute resistance exercise on serum malondialdehyde in resistance-trained and untrained collegiate men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sacheck, J.M.; Decker, E.A.; Clarkson, P.M. The effect of diet on vitamin e intake and oxidative stress in response to acute exercise in female athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 83, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, C.L.; Morgan, P.E.; Davies, M.J. Quantification of protein modification by oxidants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 965–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushworth, G.F.; Megson, I.L. Existing and potential therapeutic uses for n-acetylcysteine: The need for conversion to intracellular glutathione for antioxidant benefits. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, S.J.; Booth, F.W. Sedentary death syndrome. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 29, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbat-Artigas, S.; Rolland, Y.; Cesari, M.; Abellan van Kan, G.; Vellas, B.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M. Clinical relevance of different muscle strength indexes and functional impairment in women aged 75 years and older. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, M.J.; Spinks, W.L. Exercise, mobility and aging. Sports Med. 2000, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, Y.N.; Murthy, S.V.; Krishna, D.R.; Prabhakar, M.C. Role of free radicals and antioxidants in tuberculosis patients. Indian J. Tuberc. 2004, 51, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Veskoukis, A.S.; Kyparos, A.; Paschalis, V.; Nikolaidis, M.G. Spectrophotometric assays for measuring redox biomarkers in blood. Biomarkers 2016, 21, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaidis, M.G. The Effects of Resistance Exercise on Muscle Damage, Position Sense, and Blood Redox Status in Young and Elderly Individuals. Geriatrics 2017, 2, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics2030020
Nikolaidis MG. The Effects of Resistance Exercise on Muscle Damage, Position Sense, and Blood Redox Status in Young and Elderly Individuals. Geriatrics. 2017; 2(3):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics2030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaidis, Michalis G. 2017. "The Effects of Resistance Exercise on Muscle Damage, Position Sense, and Blood Redox Status in Young and Elderly Individuals" Geriatrics 2, no. 3: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics2030020
APA StyleNikolaidis, M. G. (2017). The Effects of Resistance Exercise on Muscle Damage, Position Sense, and Blood Redox Status in Young and Elderly Individuals. Geriatrics, 2(3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics2030020