Social Determinants of Association among Diabetes Mellitus, Visual Impairment and Hearing Loss in a Middle-Aged or Old Population: Artificial-Neural-Network Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (2014–2016)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Analysis
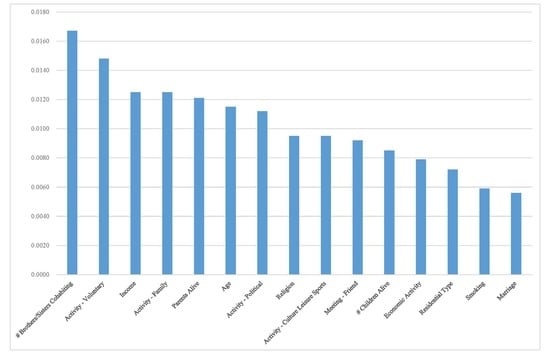
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. What is Already Known on the Topic
4.3. What This Study Adds
4.4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, R.R.; Flaxman, S.R.; Braithwaite, T.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J.H.; Leasher, J.; Limburg, H.; et al. Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e888–e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, B.O.; Neumann, K.J.; Saunders, J.E. The global burden of disabling hearing impairment: A call to action. Bull. World Health Organ. 2014, 92, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Korea. Year 2016 Statistics on Causes of Death in Korea; Statistics Korea: Sejong, Korea, 2017.
- Lee, K.S.; Park, J.H. Burden of disease in Korea during 2000-10. J. Public Health 2014, 36, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. A Conceptual Framework for Action on the Social Determinants of Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kahloun, R.; Jelliti, B.; Zaouali, S.; Attia, S.; Yahia, S.B.; Resnikoff, S.; Khairallah, M. Prevalence and causes of visual impairment in diabetic patients in Tunisia, North Africa. Eye 2014, 28, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Fine Olivarius, N.; Siersma, V.; Almind, G.J.; Nielsen, N.V. Prevalence and progression of visual impairment in patients newly diagnosed with clinical type 2 diabetes: A 6-year follow up study. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, E.M.; Mitchell, P.; Rochtchina, E.; Foran, S.; Golding, M.; Wang, J.J. Association between vision and hearing impairments and their combined effects on quality of life. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2006, 124, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneck, M.E.; Lott, L.A.; Haegerstrom-Portnoy, G.; Brabyn, J.A. Association between hearing and vision impairments in older adults. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2012, 32, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghupathi, V.; Raghupathi, W. Preventive healthcare: A neural network analysis of behavioral habits and chronic diseases. Healthcare 2017, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Luo, M.; Zheng, J.; Luo, J.; Zeng, R.; Feng, N.; Du, Q.; Fang, J. An artificial neural network prediction model of congenital heart disease based on risk factors: A hospital-based case-control study. Medicine 2017, 96, e6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizios, D.; Heijl, A.; Bengtsson, B. Trained artificial neural network for glaucoma diagnosis using visual field data: A comparison with conventional algorithms. J. Glaucoma 2007, 16, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadian, M.; Aliabadi, M.; Darvishi, E. Empirical estimation of the grades of hearing impairment among industrial workers based on new artificial neural networks and classical regression methods. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 19, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Micheline, K. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, 2ed ed.; Elsevier: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics Korea. The Results of Social Survey for Year 2009; Statistics Korea: Seoul, Korea, 2009.
- Lee, Y.K.; Jung, K.H.; Oh, Y.H.; Yeom, J.H.; Kim, H.A. Plans for Improving Leisure and Welfare Service Among the Old in Korea; Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs: Seoul, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S. Ways of Improving the Efficiency of Family Services for Diverse Families; Health & Social Welfare Forum: Seoul, Korea, 2017; pp. 78–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare in Korea. Plan for Ageing Society and Population; MHWK: Seoul, Korea, 2011.
- Choi, Y.; Park, E.C.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, K.B.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, K.S. A change in social activity and depression among Koreans aged 45 years and more: Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (2006–2010). Int. Psychogeriatr. 2015, 27, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Korea. Korean Statistical Information Service; Statistics Korea: Sejong, Korea, 2018. Available online: http://kosis.kr/index/index.do (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Stephen, E.H. Bracing for Low Fertility and a Large Elderly Population in South Korea. Available online: http://www.keia.org/publications?pcat=421&%3Bauthors=All&%3Btitle=&%3Bitems_per_page=60 (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. A Framework for Growth and Social Cohesion in Korea; OECD: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. Social Expenditure Database; OECD: Paris, France, 2018; Available online: http://www.oecd.org/social/expenditure.htm (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Rabi, D.M.; Edwards, A.L.; Southern, D.A.; Svenson, L.W.; Sargious, P.M.; Norton, P.; Larsen, E.T.; Ghali, W.A. Association of socio-economic status with diabetes prevalence and utilization of diabetes care services. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2006, 6, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saydah, S.H.; Imperatore, G.; Beckles, G.L. Socioeconomic status and mortality: Contribution of health care access and psychological distress among U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Count | Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Association (in Y2016) | ||
| N-N-N † | 4629 | 75.64 |
| Y-N-N ‡ | 1157 | 18.91 |
| N-Y-N | 124 | 2.03 |
| N-N-Y | 93 | 1.52 |
| Y-Y-N | 65 | 1.06 |
| Y-N-Y | 40 | 0.65 |
| N-Y-Y | 9 | 0.15 |
| Y-Y-Y | 3 | 0.05 |
| Education (in Y2014 Hereafter) | ||
| Elementary or Below | 2742 | 44.80 |
| Junior High | 1056 | 17.25 |
| Senior High | 1707 | 27.89 |
| College or Above | 615 | 10.05 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 2578 | 42.12 |
| Female | 3542 | 57.88 |
| Marriage | ||
| Married | 4713 | 77.01 |
| Separated | 31 | 0.51 |
| Divorced | 127 | 2.08 |
| Widowed | 1209 | 19.75 |
| Unmarried | 40 | 0.65 |
| Religion | ||
| Non | 3422 | 55.92 |
| Protestant | 1106 | 18.07 |
| Catholic | 384 | 6.27 |
| Buddhist | 1169 | 19.10 |
| Won-Buddhist | 13 | 0.21 |
| Other | 26 | 0.42 |
| Residential Type | ||
| Apartment | 4093 | 66.88 |
| Other | 2027 | 33.12 |
| Region | ||
| Urban, Big | 2508 | 40.98 |
| Urban, Small | 1964 | 32.09 |
| Rural | 1648 | 26.93 |
| Parents Alive | ||
| Father and Mother | 267 | 4.36 |
| Father | 93 | 1.52 |
| Mother | 1029 | 16.81 |
| None | 4731 | 77.30 |
| Health Insurance | ||
| Medicare | 5792 | 94.64 |
| Medicaid | 328 | 5.36 |
| Economic Activity | ||
| Employed | 2395 | 39.13 |
| Unemployed | 3725 | 60.87 |
| Subjective Health | ||
| Very Good | 68 | 1.11 |
| Good | 1618 | 26.44 |
| Middle (Neither Good nor Poor) | 2747 | 44.89 |
| Poor | 1387 | 22.66 |
| Very Poor | 300 | 4.90 |
| Smoker | ||
| Non | 4245 | 69.36 |
| Former | 1080 | 17.65 |
| Current | 795 | 12.99 |
| Drinker | ||
| Non | 3163 | 51.68 |
| Former | 921 | 15.05 |
| Current | 2036 | 33.27 |
| Drug/Medicine Intake | ||
| Yes | 3856 | 63.01 |
| No | 2264 | 36.99 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | ||
| Yes | 1147 | 18.74 |
| No | 4973 | 81.26 |
| Visual Impairment | ||
| Yes | 202 | 3.30 |
| No | 5918 | 96.70 |
| Hearing Loss | ||
| Yes | 104 | 1.70 |
| No | 6016 | 98.30 |
| Mean | SD | Min | 25% | 50% | 75% | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 67.90 | 9.59 | 53 | 60 | 67 | 75 | 105 |
| Meeting with Friends | 3.57 | 2.54 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 10 |
| Activity: Religious | 2.14 | 0.71 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 |
| Activity: Friendship | 4.04 | 1.46 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 10 |
| Activity: Leisure | 3.01 | 0.41 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 10 |
| Activity: Family | 5.03 | 0.62 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 |
| Activity: Voluntary | 4.00 | 0.15 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 10 |
| Activity: Political | 4.00 | 0.07 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| # Children Alive | 2.94 | 1.43 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 |
| # Brothers/Sisters Cohabiting | 3.48 | 1.66 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 11 |
| Income (Monthly, $) | 1260.80 | 1642.64 | 0 | 300 | 684 | 1660 | 36,000 |
| BMI | 23.29 | 2.85 | 12 | 22 | 23 | 25 | 82 |
| Life Satisfaction: Economic | 53.68 | 19.77 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 70 | 100 |
| Life Satisfaction: Overall | 60.39 | 16.74 | 0 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 100 |
| Accuracy | RF-VI † | ANN-VI ‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multinomial Logistic Regression | 0.7507 | ||
| Decision Tree | 0.6294 | ||
| Naive Bayes | 0.1258 | ||
| Random Forest: 1000 Trees | 0.7533 | ||
| Support Vector Machine | 0.7542 | ||
| ANN Full | 0.7507 | ||
| ANN Excluding # Brothers/Sisters Cohabiting | 0.7340 | 0.0557 | 0.0167 |
| ANN Excluding Activity: Voluntary | 0.7359 | 0.0005 | 0.0148 |
| ANN Excluding Income | 0.7382 | 0.1046 | 0.0125 |
| ANN Excluding Activity: Family | 0.7382 | 0.0165 | 0.0125 |
| ANN Excluding Parents Alive | 0.7386 | 0.0145 | 0.0121 |
| ANN Excluding Age | 0.7392 | 0.1014 | 0.0115 |
| ANN Excluding Activity: Political | 0.7395 | 0.0002 | 0.0112 |
| ANN Excluding Religion | 0.7412 | 0.0357 | 0.0095 |
| ANN Excluding Activity: Culture Leisure Sports | 0.7412 | 0.0068 | 0.0095 |
| ANN Excluding Meeting: Friend | 0.7415 | 0.0559 | 0.0092 |
| ANN Excluding # Children Alive | 0.7422 | 0.0521 | 0.0085 |
| ANN Excluding Economic Activity | 0.7428 | 0.0151 | 0.0079 |
| ANN Excluding Residential Type | 0.7435 | 0.0161 | 0.0072 |
| ANN Excluding Smoking | 0.7448 | 0.0231 | 0.0059 |
| ANN Excluding Marriage | 0.7451 | 0.0193 | 0.0056 |
| ANN Excluding Health Insurance | 0.7454 | 0.0091 | 0.0053 |
| ANN Excluding Gender | 0.7461 | 0.0146 | 0.0046 |
| ANN Excluding Hearing Loss | 0.7461 | 0.0127 | 0.0046 |
| ANN Excluding Region | 0.7464 | 0.0286 | 0.0043 |
| ANN Excluding Subjective Health | 0.7474 | 0.0403 | 0.0033 |
| ANN Excluding Activity: Friend | 0.7474 | 0.0396 | 0.0033 |
| ANN Excluding Diabetes Mellitus | 0.7474 | 0.0205 | 0.0033 |
| ANN Excluding Education | 0.7477 | 0.0285 | 0.0030 |
| ANN Excluding Activity: Religious | 0.7480 | 0.0129 | 0.0027 |
| ANN Excluding Life Satisfaction: Economic | 0.7490 | 0.0601 | 0.0017 |
| ANN Excluding Life Satisfaction: Overall | 0.7490 | 0.0578 | 0.0017 |
| ANN Excluding Drug/Medicine Intake | 0.7497 | 0.0503 | 0.0010 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.-S.; Park, K.W. Social Determinants of Association among Diabetes Mellitus, Visual Impairment and Hearing Loss in a Middle-Aged or Old Population: Artificial-Neural-Network Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (2014–2016). Geriatrics 2019, 4, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics4010030
Lee K-S, Park KW. Social Determinants of Association among Diabetes Mellitus, Visual Impairment and Hearing Loss in a Middle-Aged or Old Population: Artificial-Neural-Network Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (2014–2016). Geriatrics. 2019; 4(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics4010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kwang-Sig, and Kun Woo Park. 2019. "Social Determinants of Association among Diabetes Mellitus, Visual Impairment and Hearing Loss in a Middle-Aged or Old Population: Artificial-Neural-Network Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (2014–2016)" Geriatrics 4, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics4010030
APA StyleLee, K. -S., & Park, K. W. (2019). Social Determinants of Association among Diabetes Mellitus, Visual Impairment and Hearing Loss in a Middle-Aged or Old Population: Artificial-Neural-Network Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (2014–2016). Geriatrics, 4(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics4010030