Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Comprehensive Regulation of Stropharia rugosoannulata Mycelia Exposed to Cadmium Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture and Treatment of Mycelia
2.2. Sample Preparation for LC−MS Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis
2.3. LC−MS Analysis
2.4. Data Preprocessing and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
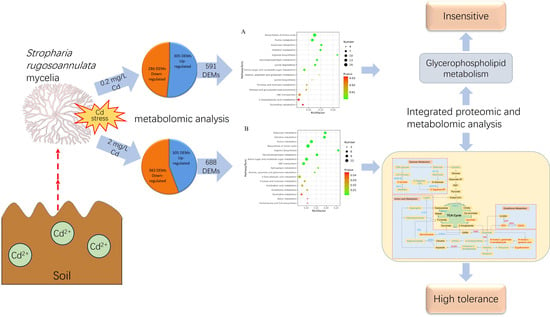
3. Results
3.1. Cd Induced Metabolic Response in S. rugosoannulata Mycelia
3.2. Identification of DEMs
3.3. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Metabolic Pathway Enrichment Analysis of the DEMs
3.4. Integrated Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses of S. rugosoannulata Mycelia in Response to Cd Stress
3.5. Pathway Analysis of the DEMs and DEPs
4. Discussion
4.1. Differential Response Mechanisms Are Activated in Mycelia under Different Levels of Cd Stress
4.2. Response Mechanism of Mycelia under Low-Cd Stress Based on Integrated Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses
4.3. Response Mechanism of Mycelia under High-Cd Stress Based on Integrated Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H. China’s soil plan needs strong support. Nature 2016, 536, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudka, S.; Miller, W.P. Permissible concentrations of arsenic and lead in soils based on risk assessment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1999, 133, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tong, Q.; He, C.; Fan, R. Investigation and research of cadmium pollution in soils. Sichuan Environ. 2004, 23, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; Tan, C.; Yu, X.; Sun, H.; Wan, D.; Yang, Y.; Cao, X. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation and analysis of the pollutant source of heavy metal in soils and sediments in xiangjiang changsha section. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2014, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Munir, S.; Sajjad, M.; Li, G. Urban park soil contamination by potentially harmful elements and human health risk in Peshawar City, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 165, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliardini, C.; Meyer, C.L.; Salis, P.; Saumitou-Laprade, P.; Verbruggen, N. CATION EXCHANGER1 Cosegregates with Cadmium Tolerance in the Metal Hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri and Plays a Role in Limiting Oxidative Stress in Arabidopsis spp. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yang, X.; He, Z.; Baligar, V.C. Morphological and Physiological Responses of Plants to Cadmium Toxicity: A Review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Castagna, A.; Ranieri, A.; di Toppi, L.S. Cadmium tolerance in Brassica juncea roots and shoots is affected by antioxidant status and phytochelatin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 57, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, A. Cadmium toxicity: Effects on human reproduction and fertility. Rev. Environ. Health 2019, 34, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, K.; Qin, W.; Tian, C.; Han, W. A review on heavy metals contamination in soil: Effects, sources, and remediation techniques. Soil Sediment Contam. 2019, 28, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O. A New Strategy for Heavy Metal Polluted Environments: A Review of Microbial Biosorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacky, J.; Cerny, J.; Santrucek, J.; Borovicka, J.; Leonhardt, T.; Kotrba, P. Cadmium hyperaccumulating mushroom Cystoderma carcharias has two metallothionein isoforms usable for cadmium and copper storage. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2021, 153, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Tan, Q.; Li, Y.; Lv, B.; Shang, X. Transcriptomic Analysis of Two Lentinula edodes Genotypes With Different Cadmium Accumulation Ability. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 558104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, H.W.; Wang, I.W.; Lin, S.Y.; Chang, Y.L. Transcriptome analysis of cadmium response in Ganoderma lucidum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 293, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, N.; Costa, P.; Massimino, M.L. In vitro uptake of cadmium by basidiomycetes Pleurotus ostreatus. Biotechnol. Lett. 1991, 13, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P.; Gabriel, J. Lignocellulose degradation by Pleurotus ostreatus in the presence of cadmium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 220, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, A.; Bajwa, R.; Shafique, U.; Anwar, J. Removal of heavy metals by adsorption on Pleurotus ostreatus. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Jiao, S.; Wu, K.; La, G.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of Cd and Cr removal and tolerance by macrofungus Pleurotus ostreatus HAU-2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 330, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashola, M.O.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Babalola, O.O. Heavy Metal Pollution from Gold Mines: Environmental Effects and Bacterial Strategies for Resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibuike, G.U.; Obiora, S.C. Heavy metal polluted soils: Effect on plants and bioremediation methods. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2014, 2014, 752708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, S.; Sharma, A. Microbial Bioremediation of Heavy Metals: Emerging Trends and Recent Advances. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 15, 164–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Nayak, A.; Agarwal, S. Bioadsorbents for remediation of heavy metals: Current status and their future prospects. Environ. Eng. Res. 2015, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, G.M. Interactions of fungi with toxic metals. New Phytol. 1993, 124, 25–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P. Interactions of heavy metals with white-rot fungi. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 32, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimala, R.; Das, N. Mechanism of Cd(II) adsorption by macrofungus Pleurotus platypus. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.B.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Shi, D.; Bian, Y.B.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Huang, W. Purification and Characterization of a Cadmium-Binding Protein from Lentinula edodes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.B.; Huang, W.; Bian, Y.B.; Feng, X.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Shi, D.F.; Qiao, X.; Liu, Y. Remediation and Mechanisms of Cadmium Biosorption by a Cadmium-Binding Protein from Lentinula edodes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11373–11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujs, S.; Gazdag, Z.; Poljsak, B.; Stibilj, V.; Milacic, R.; Pesti, M.; Raspor, P.; Batic, M. The oxidative stress response of the yeast Candida intermedia to copper, zinc, and selenium exposure. J. Basic Microbiol. 2005, 45, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, K.; Ma, H.; Li, L.; Tan, H.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. Mechanisms into the removal and translocation of cadmium by Oudemansiella radicata in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6388–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Song, P.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, C.; Zha, L. Integrated physiologic and proteomic analysis of Stropharia rugosoannulata mycelia in response to Cd stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ge, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Jia, Y. Proteomics integrated with metabolomics: Analysis of the internal causes of nutrient changes in alfalfa at different growth stages. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature 2008, 455, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassel, G.W.; Gaudinier, A.; Brady, S.M.; Hennig, L.; Rhee, S.Y.; De Smet, I. Systems analysis of plant functional, transcriptional, physical interaction, and metabolic networks. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3859–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shohag, M.J.I.; Yang, Q.; Chen, S.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Proteomics and Metabolomics of Metal Hypeaccumulating Plant Sedum alfredii Hance. In Proceedings of the 16th International Phytotechnology Conference, Changsha, China, 23–27 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Taamalli, M.; Gevi, F.; Timperio, A.M.; Zolla, L.; Ghnaya, T. Cadmium stress responses in Brassica juncea: Hints from proteomics and metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 4979–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xing, L.; Song, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Lu, Q.; Hu, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Large-scale metabolome analysis reveals dynamic changes of metabolites during foxtail millet grain filling. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieffer, P.; Planchon, S.; Oufir, M.; Ziebel, J.; Dommes, J.; Hoffmann, L.; Hausman, J.F.; Renaut, J. Combining proteomics and metabolite analyses to unravel cadmium stress-response in poplar leaves. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngu, M.; Moya, E.; Magan, N. Tolerance and uptake of cadmium\arsenic and lead by Fusarium pathogens of cereals. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1998, 42, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H. Differentiation of quantitative characters of Vicia faba contaminated with heavy meatals. Acta Ecol. Sinca 1997, 17, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C. Environmental Biology, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Wu, C. Heat preadaptation improved the ability of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii to salt stress: A combined physiological and transcriptomic analysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsh, G.S.; Hernández, S.B.; Cota, I.; Ducret, A.; Aussel, L.; Casadesús, J. Adaptation and Preadaptation of Salmonella enterica to Bile. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002459. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, Y.B.; Swati, S.; Sameer, S.; Kumar, S.N.; Ashutosh, M. Whole transcriptome expression profiling and biological network analysis of chickpea during heavy metal stress. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.; Xu, J.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Deng, P.; Yang, L.; Tan, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; et al. Cadmium perturbed metabolomic signature in pancreatic beta cells correlates with disturbed metabolite profile in human urine. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R.; Finka, A.; Goloubinoff, P. How do plants feel the heat? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, S.; Gervais, P.; Young, M.; Winckler, P.; Dumont, J.; Davey, H.M. Surviving the heat: Heterogeneity of response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae provides insight into thermal damage to the membrane. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2982–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wu, J.; Ji, R.; Sun, Y.; Guo, H. Response of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) to perfluorooctanoic acid in photosynthesis and metabolomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoden, J.B.; Holden, H.M. The molecular architecture of galactose mutarotase/UDP-galactose 4-epimerase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21900–21907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Yang, Z.; Qu, J.; Xun, H.; Dou, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, L. Phenotypic, transcriptional, physiological and metabolic responses to carbon nanodot exposure in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.). Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 2672–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, A.; Yabuta, Y.; Shigeoka, S. Galactinol and raffinose constitute a novel function to protect plants from oxidative damage. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Feng, M.; Wang, J.; Cang, J.; Li, S.; Bao, Y.; Wang, X. Research progress of sugar metabolism of plants under cold stress. J. Northeast. Agric. Univ. 2015, 46, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Zuo, S.; Cao, X.; Tong, H.; Wei, S. Effect of Exogenous Sugar on the Sugar Metabolism in Triticale Seedling under Salt Stress. J. Triticeae Crops 2017, 37, 548–553. [Google Scholar]
- Nagele, T.; Stutz, S.; Hormiller, I.I.; Heyer, A.G. Identification of a metabolic bottleneck for cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2012, 72, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Gu, X.; Du, W.; Wei, H.; Ji, R.; Zhao, L. Metabolomics Reveals the “Invisible” Responses of Spinach Plants Exposed to CeO(2) Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6007–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Thielen, I.; Barnett, A.; Loveday, S.M.; Singh, H. epsilon-Polylysine and beta-cyclodextrin assembling as delivery systems for gastric protection of proteins and possibility to enhance intestinal permeation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 546, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhan, Y.; He, L. Graphene oxide/poly-L-lysine assembled layer for adhesion and electrochemical impedance detection of leukemia K562 cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fait, A.; Fromm, H.; Walter, D.; Galili, G.; Fernie, A.R. Highway or byway: The metabolic role of the GABA shunt in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, D.; Breitenstein, B.; Kleinwachter, M.; Selmar, D. Stress metabolism in green coffee beans (Coffea arabica L.): Expression of dehydrins and accumulation of GABA during drying. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, H.; Ando, A.; Saito, T. The Contents of γ-Amino Butyric Acid in Eggplant and its Accumulation with Heat Treatment. Nippon. Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi 2013, 60, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatierra, A.; Pimentel, P.; Almada, R.; Hinrichsen, P. Exogenous GABA application transiently improves the tolerance to root hypoxia on a sensitive genotype of Prunus rootstock. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 125, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcay, N.; Bor, M.; Karabudak, T.; Ozdemir, F.; Turkan, I. Contribution of Gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) to salt stress responses of Nicotiana sylvestris CMSII mutant and wild type plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.T.; Kao, C.H. Changes in protein and amino acid contents in two cultivars of rice seedlings with different apparent tolerance to cadmium. Plant Growth Regul. 2003, 40, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.B.; Chen, F.; Wei, K.; Zhang, G.P. Effect of cadmium on free amino acid, glutathione and ascorbic acid concentrations in two barley genotypes (Hordeum vulgare L.) differing in cadmium tolerance. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Xiao, H.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yang, D. Effects of cadmium stress on growth and amino acid metabolism in two Compositae plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 158, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozefczak, M.; Remans, T.; Vangronsveld, J.; Cuypers, A. Glutathione is a key player in metal-induced oxidative stress defenses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3145–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, L.; Tian, S.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Zhou, W.; Lin, X. Cadmium-induced nitric oxide burst enhances Cd tolerance at early stage in roots of a hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii partially by altering glutathione metabolism. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocsi, I.; Prade, R.A.; Penninckx, M.J. Glutathione, altruistic metabolite in fungi. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2004, 49, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Lin, Z. Anti-aging Effect of Ganoderma (Lingzhi) with Health and Fitness. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1182, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Urano, K.; Maruyama, K.; Ogata, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Takeda, M.; Sakurai, N.; Suzuki, H.; Saito, K.; Shibata, D.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Characterization of the ABA-regulated global responses to dehydration in Arabidopsis by metabolomics. Plant J. 2009, 57, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner-Giner, M.A.; Llosa, M.J.; Carrasco, J.L.; Perez-Amador, M.A.; Navarro, L.; Ancillo, G. Differential gene expression analysis provides new insights into the molecular basis of iron deficiency stress response in the citrus rootstock Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.B.; Smith, A.P.; Howden, R.; Dietrich, W.M.; Bugg, S.; O’Connell, M.J.; Goldsbrough, P.B.; Cobbett, C.S. Phytochelatin synthase genes from Arabidopsis and the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, S.; Kim, E.J.; Neumann, D.; Schroeder, J.I. Tolerance to toxic metals by a gene family of phytochelatin synthases from plants and yeast. Embo J. 1999, 18, 3325–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Ding, H.; Wang, G.; Kang, J.; Pang, H.; Lv, J. Sulfur decreases cadmium translocation and enhances cadmium tolerance by promoting sulfur assimilation and glutathione metabolism in Brassica chinensis L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, L.; Kang, J.; Pang, H.; Li, Q.; Du, X.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Lv, J. Sulfur Protects Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) Seedlings against Cadmium Stress by Regulating Ascorbate-Glutathione Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Pathway Name | Proteomics | Metabolomics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway ID | p Value | Pathway ID | p Value | |
| Treatment with 0.2 mg/L Cd | ||||
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | ko00564 | 0.0094522 | sce00564 | 0.00048 |
| Treatment with 2 mg/L Cd | ||||
| Galactose metabolism | ko00052 | 0.016538 | sce00052 | 4.73 × 10−6 |
| Arginine biosynthesis | ko00220 | 0.039474 | sce00220 | 3.5 × 10−5 |
| Alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism | ko00250 | 0.034689 | sce00250 | 0.007973 |
| Histidine metabolism | ko00340 | 0.023705 | sce00340 | 5.71 × 10−6 |
| Glutathione metabolism | ko00480 | 0.00018 | sce00480 | 0.023039 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | ko00590 | 0.033405 | sce00590 | 0.020527 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Q.; Chen, M.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zha, L.; Kakumyan, P.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y. Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Comprehensive Regulation of Stropharia rugosoannulata Mycelia Exposed to Cadmium Stress. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020134
Dong Q, Chen M, Yu C, Zhang Y, Zha L, Kakumyan P, Yang H, Zhao Y. Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Comprehensive Regulation of Stropharia rugosoannulata Mycelia Exposed to Cadmium Stress. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(2):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020134
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Qin, Mingjie Chen, Changxia Yu, Yaru Zhang, Lei Zha, Pattana Kakumyan, Huanling Yang, and Yan Zhao. 2024. "Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Comprehensive Regulation of Stropharia rugosoannulata Mycelia Exposed to Cadmium Stress" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 2: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020134
APA StyleDong, Q., Chen, M., Yu, C., Zhang, Y., Zha, L., Kakumyan, P., Yang, H., & Zhao, Y. (2024). Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Comprehensive Regulation of Stropharia rugosoannulata Mycelia Exposed to Cadmium Stress. Journal of Fungi, 10(2), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020134