Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Chronic Skin Wound Treatment
Abstract
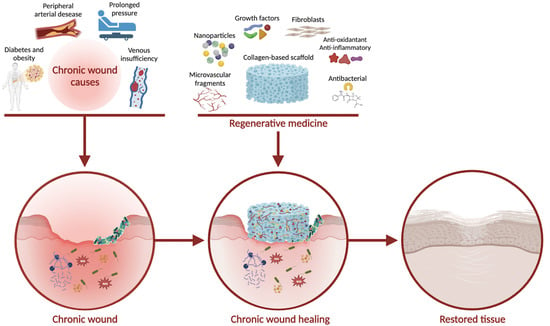
:1. Introduction
Acute and Chronic Wound Healing
2. Chronic Wounds Treatment
Tissue Engineering for Wound Healing
3. Scaffold Properties for Wound-Healing Treatment
3.1. Promoting Angiogenesis and Revascularization
3.2. Counteracting Inflammation
3.3. Counteracting Oxidative Stress
3.4. Counteracting Microbial Infections
3.5. Scaffoldings with Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
3.6. Promoting Cell Proliferation
3.7. Stimulating ECM Regeneration
3.8. Particular Case
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sardo, P.M.G.; Teixeira, J.P.F.; Machado, A.M.S.F.; Oliveira, B.F.; Alves, I.M. A Systematic Review of Prevalence and Incidence of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries in Hospital Emergency Services. J. Tissue Viability 2023, 32, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Ma, P.X. Conducting Polymers for Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1764–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.V.; Soulika, A.M. The Dynamics of the Skin’s Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound Healing: Cellular Mechanisms and Pathological Outcomes. Adv. Surg. Med. Spec. 2023, 10, 341–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, G.S.; Cooper, D.M.; Knighton, D.R.; Margolis, D.J.; Pecoraro, R.E.; Rodeheaver, G.; Robson, M.C. Definitions and Guidelines for Assessment of Wounds and Evaluation of Healing. Arch. Dermatol. 1994, 130, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Hansen, S.L. Management of Acute Wounds. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2007, 34, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velnar, T.; Bailey, T.; Smrkolj, V. The Wound Healing Process: An Overview of the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 1528–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonida, M.D.; Kumar, I. Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. In Bionanomaterials for Skin Regeneration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, L.M.; Phillips, T.J. Wound Healing and Treating Wounds: Differential Diagnosis and Evaluation of Chronic Wounds. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Nunan, R. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Repair in Acute and Chronic Wound Healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeo, M.; Lee, W.; Ito, M. Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a023267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Ceilley, R. Chronic Wound Healing: A Review of Current Management and Treatments. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adib, Y.; Bensussan, A.; Michel, L. Cutaneous Wound Healing: A Review about Innate Immune Response and Current Therapeutic Applications. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 5344085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Huang, B.S.; Horng, H.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Chen, Y.J. Wound Healing. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mohamedi, A.H.; Senkowsky, J.; Nair, A.; Tang, L. Imaging in Chronic Wound Diagnostics. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wound and Its Burden: Updated 2020 Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahim, K.; Saleha, S.; Zhu, X.; Huo, L.; Basit, A.; Franco, O.L. Bacterial Contribution in Chronicity of Wounds. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järbrink, K.; Ni, G.; Sönnergren, H.; Schmidtchen, A.; Pang, C.; Bajpai, R.; Car, J. Prevalence and Incidence of Chronic Wounds and Related Complications: A Protocol for a Systematic Review. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, M.; Järbrink, K.; Divakar, U.; Bajpai, R.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J. The Humanistic and Economic Burden of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review. Wound Repair. Regen. 2019, 27, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicke, C.; Bachinger, A.; Coerper, S.; Beckert, S.; Witte, M.B.; Königsrainer, A. Aging Influences Wound Healing in Patients with Chronic Lower Extremity Wounds Treated in a Specialized Wound Care Center. Wound Repair. Regen. 2009, 17, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinengo, L.; Olsson, M.; Bajpai, R.; Soljak, M.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J.; Järbrink, K. Prevalence of Chronic Wounds in the General Population: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Ann. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaniego-Ruiz, M.J.; Llatas, F.P.; Jiménez, O.S. Assessment of Chronic Wounds in Adults: An Integrative Review. Rev. Esc. Enferm. USP 2018, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Castaño, O.; Mateos-Timoneda, M.Á.; Engel, E.; Pérez-Amodio, S. Nanotechnology Approaches in Chronic Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, J.; Jing, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhu, D.; Bi, Y. Global Epidemiology of Diabetic Foot Ulceration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis †. Ann. Med. 2017, 49, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, V.; Moellmer, R.; Agrawal, D.K. Stem Cells and Angiogenesis: Implications and Limitations in Enhancing Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing. Cells 2022, 11, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyk, D.F. The Diabetic Foot: Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Treatment. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 31, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The Human Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, A.R.; Bernstein, J.M. Chronic Wound Infection: Facts and Controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 2010, 28, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswathanarayan, J.B.; Rao, P.; Hm, S.; Gs, S.; Rai, R.V. Biofilm-Associated Infections in Chronic Wounds and Their Management. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1370, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.J.; Barreto, R.T.; Barrois, B.M.; Gryson, L.G.; Meaume, S.; Monstrey, S.J. Update on the Role of Antiseptics in the Management of Chronic Wounds with Critical Colonisation and/or Biofilm. Int. Wound J. 2021, 18, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liang, H.; Clarke, E.; Jackson, C.; Xue, M. Inflammation in Chronic Wounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, S.R.; Carter, M.J.; Fife, C.E.; DaVanzo, J.; Haught, R.; Nusgart, M.; Cartwright, D. An Economic Evaluation of the Impact, Cost, and Medicare Policy Implications of Chronic Nonhealing Wounds. Value Health 2018, 21, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, C.; Searle, R. Wound Management for the 21st Century: Combining Effectiveness and Efficiency. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13 (Suppl. S2), 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.G.; Higham, C.; Broussard, K.; Phillips, T.J. Wound Healing and Treating Wounds: Chronic Wound Care and Management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M. Treatment Strategies for Infected Wounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.M.; Rothermel, A.T.; MacKay, D.R. Evidence-Based Medicine: Wound Management. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 201e–216e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.; Vacanti, J. Advances in Tissue Engineering. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 51, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, L.; Pu, T.; Porter, B.; Aziz, J.M.; La Pointe, C.; Asthana, A.; Orlando, G. Regenerative Medicine, Organ Bioengineering and Transplantation. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzic, A.; Pfenning, M.A.; Gores, G.J.; Harper, C.M. Regenerative Medicine Build-Out. Stem. Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, L.C.; Zuena, E.; Perez-Ramirez, B.; Kaplan, D.L. Guide to Collagen Characterization for Biomaterial Studies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 87B, 264–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Nourbakhsh, N.; Akbari Kenari, M.; Zare, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1986–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorushanova, A.; Delgado, L.M.; Wu, Z.; Shologu, N.; Kshirsagar, A.; Raghunath, R.; Mullen, A.M.; Bayon, Y.; Pandit, A.; Raghunath, M.; et al. The Collagen Suprafamily: From Biosynthesis to Advanced Biomaterial Development. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaparekar, P.S.; Anandasadagopan, S.K. In Vitro and in Vivo Effect of Novel GA-CSNPs Loaded Col-Fibrin Nanocomposite Scaffold on Diabetic Wound Healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2023, 111, 1074–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-González, P.U.; Lona-Ramos, M.C.; Gutiérrez-Verdín, L.D.; Luévano-Colmenero, G.H.; Tenorio-Rocha, F.; García-Contreras, R.; González-García, G.; Rosillo-De La Torre, A.; Delgado, J.; Castellano, L.E.; et al. Gel Dressing Based on Type I Collagen Modified with Oligourethane and Silica for Skin Wound Healing. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, S.; Wairkar, S. Collagen Fabricated Delivery Systems for Wound Healing: A New Roadmap. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 142, 213152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigogliuso, S.; Campora, S.; Notarbartolo, M.; Ghersi, G. Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Marine Organisms: Focus on the Future Perspectives for Pharmacological, Biomedical and Regenerative Medicine Applications of Marine Collagen. Molecules 2023, 28, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, T.A.T.; Almeida, M.C.; Avanzi, I.; Parisi, J.; Simon Sales, A.F.; Na, Y.; Renno, A. Collagen Membranes for Skin Wound Repair: A Systematic Review. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 36, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-López, A.; Morales-Peñaloza, A.; Martínez-Juárez, V.M.; Vargas-Torres, A.; Zeugolis, D.I.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Hydrolyzed Collagen—Sources and Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew-Steiner, S.S.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. Collagen in Wound Healing. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taupin, P.; Gandhi, A.; Saini, S. Integra® Dermal Regeneration Template: From Design to Clinical Use. Cureus 2023, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, M.L.; Goldstein, J.; Adams, M.; Steinberg, J.; Attinger, C. Functional Limb Salvage in the Diabetic Patient: The Use of a Collagen Bilayer Matrix and Risk Factors for Amputation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frueh, F.S.; Später, T.; Lindenblatt, N.; Calcagni, M.; Giovanoli, P.; Scheuer, C.; Menger, M.D.; Laschke, M.W. Adipose Tissue-Derived Microvascular Fragments Improve Vascularization, Lymphangiogenesis, and Integration of Dermal Skin Substitutes. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, M.; Rigogliuso, S.; Nicosia, A.; Campora, S.; Bruno, C.M.; Ghersi, G. 3D Collagen Hydrogel Promotes In Vitro Langerhans Islets Vascularization through Ad-MVFs Angiogenic Activity. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, K.S.; Vasconez, H.C. Wound Healing: Biologics, Skin Substitutes, Biomembranes and Scaffolds. Healthcare 2014, 2, 356–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, Y.M.; Falabella, A.F.; Eaglstein, W.H. Tissue-Engineered Skin: Current Status in Wound Healing. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2001, 2, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, A.A.; Vig, K.; Baganizi, D.R.; Sahu, R.; Dixit, S.; Dennis, V.; Singh, S.R.; Pillai, S.R. Future Prospects for Scaffolding Methods and Biomaterials in Skin Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Chen, B.; Yan, X.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Hou, X.; Dai, J. Promotion of Diabetic Wound Healing by Collagen Scaffold with Collagen-Binding Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in a Diabetic Rat Model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 8, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.; Liu, D.; He, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, X.; Chen, B.; Ouyang, W.; Dai, J.; Li, X. A Dual Functional Collagen Scaffold Coordinates Angiogenesis and Inflammation for Diabetic Wound Healing. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 6337–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Xu, Y.; Yan, X.; Lin, Y.; Tan, Q. Effect of Collagen Scaffold with Bcl-2-Modified Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on Diabetic Mice Wound Healing. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2020, 19, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Datta, P.; Das, H.; Jaiswal, S.; Ghosh, P.R.; Lahiri, D.; Kundu, B.; Nandi, S.K. Copper and Cobalt Doped Bioactive Glass-Fish Dermal Collagen Electrospun Mat Triggers Key Events of Diabetic Wound Healing in Full-Thickness Skin Defect Model. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 134, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akturk, O.; Kismet, K.; Yasti, A.C.; Kuru, S.; Duymus, M.E.; Kaya, F.; Caydere, M.; Hucumenoglu, S.; Keskin, D. Collagen/Gold Nanoparticle Nanocomposites: A Potential Skin Wound Healing Biomaterial. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 31, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti, D.; Hao, H.; Xia, L.; Tong, C.; Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; et al. Controlled Release of Thymosin Beta 4 Using a Collagen-Chitosan Sponge Scaffold Augments Cutaneous Wound Healing and Increases Angiogenesis in Diabetic Rats with Hindlimb Ischemia. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2015, 21, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, J.; Sanapalli, B.K.R.; Bano, M.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M.; Karri, V.V.S.R. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Pioglitazone Loaded Collagen/Chitosan Composite Scaffold for Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2019, 8, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.P.; Castaño, I.M.; Sridharan, R.; Kelly, D.; Lemoine, M.; Cavanagh, B.L.; Dunne, N.J.; McCarthy, H.O.; O’Brien, F.J. Collagen/GAG Scaffolds Activated by RALA-SiMMP-9 Complexes with Potential for Improved Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 111022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmartin, D.J.; Soon, A.; Thrasivoulou, C.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Jayasinghe, S.N.; Becker, D.L. Sustained Release of Cx43 Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotides from Coated Collagen Scaffolds Promotes Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Zhong, A.; Zhou, M.; Sun, Y.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Sustained Release of N-Acetylcysteine by Sandwich Structured Polycaprolactone/Collagen Scaffolds for Wound Healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2019, 107, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, M.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Fang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z. Multi-Layered Polyamide/Collagen Scaffolds with Topical Sustained Release of N-Acetylcysteine for Promoting Wound Healing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Luo, C.; Qian, B.; Liu, S.; Zeng, Y.; Hou, J.; Deng, B.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. N-Acetyl Cysteine-Loaded Graphene Oxide-Collagen Hybrid Membrane for Scarless Wound Healing. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5839–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, G.; Lonchin, S. Bioactive Functional Collagen-Oxidized Pullulan Scaffold Loaded with Polydatin for Treating Chronic Wounds. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 140, 213078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaii, M.; Oryan, S.; Javeri, A. Curcumin Nanoparticles Incorporated Collagen-Chitosan Scaffold Promotes Cutaneous Wound Healing through Regulation of TGF-Β1/Smad7 Gene Expression. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 98, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karri, V.V.S.R.; Kuppusamy, G.; Talluri, S.V.; Mannemala, S.S.; Kollipara, R.; Wadhwani, A.D.; Mulukutla, S.; Raju, K.R.S.; Malayandi, R. Curcumin Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Impregnated into Collagen-Alginate Scaffolds for Diabetic Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M.; Shahid, M.A. PVA, Licorice, and Collagen (PLC) Based Hybrid Bio-Nano Scaffold for Wound Healing Application. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2023, 34, 1217–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, S.; Ghorbani, M.; Mahmoodzadeh, F. Silver Sulfadiazine-Loaded Electrospun Ethyl Cellulose/Polylactic Acid/Collagen Nanofibrous Mats with Antibacterial Properties for Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, S.; Ramadass, S.K.; Madhan, B. Sol–Gel Processed Mupirocin Silica Microspheres Loaded Collagen Scaffold: A Synergistic Bio-Composite for Wound Healing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 52, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indrakumar, J.; Balan, P.; Murali, P.; Solaimuthu, A.; Vijayan, A.N.; Korrapati, P.S. Applications of Molybdenum Oxide Nanoparticles Impregnated Collagen Scaffolds in Wound Therapeutics. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 72, 126983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.A.; Salama, A.H. Norfloxacin-Loaded Collagen/Chitosan Scaffolds for Skin Reconstruction: Preparation, Evaluation and in-Vivo Wound Healing Assessment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 83, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahmar, A.; Rjab, M.; Sioud, F.; Selmi, M.; Salek, A.; Kilani-Jaziri, S.; Ghedira, L.C. Design of 3D Hybrid Plant Extract/Marine and Bovine Collagen Matrixes as Potential Dermal Scaffolds for Skin Wound Healing. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 8788061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.I.M.; Thangavelu, M.; Khalifa, A. Honey-Propolis-Engineered Collagen Peptides as Promising Wound-Healing Matrix in Mouse Model. Molecules 2022, 27, 7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhiraja, M.; Zafar, S.; Akhter, S.; Alrobaian, M.; Rashid, M.A.; Barkat, M.A.; Beg, S.; Ahmad, F.J. Mupirocin-Loaded Chitosan Microspheres Embedded in Piper Betle Extract Containing Collagen Scaffold Accelerate Wound Healing Activity. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, D.; Duraipandy, N.; Srivatsan, K.V.; Lakra, R.; Korapatti, P.S.; Jayavel, R.; Kiran, M.S. Fabrication of Hybrid Collagen Aerogels Reinforced with Wheat Grass Bioactives as Instructive Scaffolds for Collagen Turnover and Angiogenesis for Wound Healing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16939–16950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somchaichana, J.; Bunaprasert, T.; Patumraj, S. Acanthus Ebracteatus Vahl. Ethanol Extract Enhancement of the Efficacy of the Collagen Scaffold in Wound Closure: A Study in a Full-Thickness-Wound Mouse Model. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 754527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, F.; Campora, S.; Tirri, G.; Capuana, E.; Carfì Pavia, F.; Brucato, V.; Ghersi, G.; La Carrubba, V. Core-Shell PLA/Kef Hybrid Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering Applications Prepared by Direct Kefiran Coating on PLA Electrospun Fibers Optimized via Air-Plasma Treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 127, 112248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.O.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, J.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.M.; Chang, S.W.; Lee, H.S.; Choi, Y.S. Wound Healing Properties of a 3-D Scaffold Comprising Soluble Silkworm Gland Hydrolysate and Human Collagen. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, A.; Nanditha, C.K.; Vinod Kumar, G.S. ECM-Mimicking Nanofibrous Scaffold Enriched with Dual Growth Factor Carrying Nanoparticles for Diabetic Wound Healing. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 3085–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayi, A.C.; Haug, V.; Liu, Q.; Wu, M.; Karvar, M.; Aoki, S.; Ma, C.; Hamaguchi, R.; Endo, Y.; Orgill, D.P. Novel Application of Autologous Micrografts in a Collagen-Glycosaminoglycan Scaffold for Diabetic Wound Healing. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 035032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Nezhad-Mokhtari, P.; Ramazani, S. Aloe Vera-Loaded Nanofibrous Scaffold Based on Zein/Polycaprolactone/Collagen for Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.H.; Chen, K.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Li, S.J.; Huang, C.H. Lithospermi Radix Extract-Containing Bilayer Nanofiber Scaffold for Promoting Wound Healing in a Rat Model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, M.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Z.; Yue, H.; Shi, J.; Guan, F.; et al. Sodium Alginate/Collagen Hydrogel Loaded with Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Wound Healing and Skin Remodeling. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 383, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanapalli, B.K.R.; Chinna Gounder, K.; Ambhore, N.S.; Kuppuswamy, G.; Thaggikuppe Krishnamurthy, P.; Karri, V.V.S.R. Doxycycline Loaded Collagen-Chitosan Composite Scaffold for the Accelerated Healing of Diabetic Wounds. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 2021, e62184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, D.; Kiran, M.S. Fabrication of Juglone Functionalized Silver Nanoparticle Stabilized Collagen Scaffolds for Pro-Wound Healing Activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, R.B.; Kellar, R.S. An Acellular Tissue Engineered Biomimetic Wound Healing Device Created Using Collagen and Tropoelastin Accelerates Wound Healing. J. Tissue Viability 2022, 31, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, M.; Zimkowska, K.; Genoud, K.J.; Maughan, J.; Gutierrez Gonzalez, J.; Browne, S.; O’Brien, F.J. A Biomimetic, Bilayered Antimicrobial Collagen-Based Scaffold for Enhanced Healing of Complex Wound Conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 17444–17458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Gao, W.; Fu, X.; Shi, M.; Xie, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, F.; Chen, X. Enhanced Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats by Nanofibrous Scaffolds Mimicking the Basketweave Pattern of Collagen Fibrils in Native Skin. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Chang, S.H.; Chen, W.J.; Hung, K.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, S.J.; Hsieh, M.J.; Pang, J.H.S.; Juang, J.H. Augmentation of Diabetic Wound Healing and Enhancement of Collagen Content Using Nanofibrous Glucophage-Loaded Collagen/PLGA Scaffold Membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 439, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, K.A.; Liu, Z.J.; Xiao, M.; Chen, H.; Goldstein, L.J.; Buerk, D.G.; Nedeau, A.; Thom, S.R.; Velazquez, O.C. Diabetic Impairments in NO-Mediated Endothelial Progenitor Cell Mobilization and Homing Are Reversed by Hyperoxia and SDF-1α. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campora, S.; Ghersi, G. Recent Developments and Applications of Smart Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 2595–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dorrigan, A.; Saad, S.; Hare, D.J.; Cortie, M.B.; Valenzuela, S.M. In Vivo Study of Spherical Gold Nanoparticles: Inflammatory Effects and Distribution in Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renga, G.; Oikonomou, V.; Stincardini, C.; Pariano, M.; Borghi, M.; Costantini, C.; Bartoli, A.; Garaci, E.; Goldstein, A.L.; Romani, L. Thymosin Β4 Limits Inflammation through Autophagy. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, S.; Shukla, V.K.; Tripathi, K.; Srikrishna, S.; Singh, R.K. Targeting Connexin 43 in Diabetic Wound Healing: Future Perspectives. J. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 55, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suha, T.; Asli, M.; Aynur, S.; Yunus, K.; Ahmet, M.; Selim, D.; Esin, Y.; Ozgur, T.; Ari, N.S.; Süleyman, T. Effects of N-Acetylcysteine and Ethyl Pyruvate on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Experimental Electrical Burn Model. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayalakshmi, P.; Devika, P.T. Assessment of in vitro Antioxidant Activity Study of Polydatin. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kant, V.; Gopal, A.; Pathak, N.N.; Kumar, P.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Curcumin Accelerated the Cutaneous Wound Healing in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 20, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, M.A.; Gupta, K.; Mandal, M. Microbial Biofilm: Formation, Architecture, Antibiotic Resistance, and Control Strategies. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Antibacterial Biomaterials for Skin Wound Dressing. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matica, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Ostafe, V. Chitosan as a Wound Dressing Starting Material: Antimicrobial Properties and Mode of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizeq, B.R.; Younes, N.N.; Rasool, K.; Nasrallah, G.K. Synthesis, Bioapplications, and Toxicity Evaluation of Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | Composition | Use |
|---|---|---|
| OrCel® | Bilayered bovine collagen scaffold seeded with both keratinocytes and fibroblasts | Burns |
| Biobrane® | A porous nylon mesh with a silicone membrane including a porcine type I collagen dermal matrix | Chronic wounds, venous ulcers, partial thickness burns, dermabrasion |
| Apligraf® | Bilayered construct composed of an upper part with keratinocytes embedded on a bovine collagen type I gel and a lower part with fibroblasts included into a dermal matrix | Burns, and pressure, venous, and diabetic ulcers |
| Application | Scaffold | Functionalization | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Promoting angiogenesis and revascularization | Collagen scaffold | CBD-VEGF fusion protein | [57] |
| Collagen scaffold | CBD-VEGF and CBD-SDF-1α fusion proteins | [58] | |
| Collagen scaffold | Bcl-2-ADSCs | [59] | |
| Fish collagen and bioactive glass microfibrous mat | Copper/cobalt ion | [60] | |
| Counteracting inflammation | Crosslinked collagen scaffolds | Gold nanoparticles | [61] |
| Collagen/chitosan scaffold | Thymosin beta 4 | [62] | |
| Collagen/chitosan scaffold | Pioglitazone | [63] | |
| Collagen/GAG scaffold | siMMP-9 | [64] | |
| Collagen scaffold | Antisense oligonucleotides against Cx43 | [65] | |
| Counteracting oxidative stress | Collagen–polycaprolactone sandwich scaffold | N-acetylcysteine | [66] |
| Collagen–polyamide sandwich scaffold | N-acetylcysteine | [67] | |
| Graphene oxide–collagen hybrid membrane | N-acetylcysteine | [68] | |
| Collagen scaffold | Polydatin | [69] | |
| Collagen/chitosan scaffolds | Curcumin-conjugated nanoparticles | [70] | |
| Alginate/collagen scaffolds | Curcumin-conjugated chitosan nanoparticles | [71] | |
| Counteracting microbial infections | PVA (Polyvinyl alcohol) and collagen scaffold | Licorice extracts | [72] |
| collagen, ethyl cellulose (EC), and poly-lactic acid (PLA) scaffold | Silver Sulfadiazine | [73] | |
| Collagen scaffold | Mupirocin-loaded silica microspheres | [74] | |
| Collagen scaffold | Molybdenum trioxide nanoparticles | [75] | |
| Collagen/chitosan scaffold | Norfloxacin | [76] | |
| Combination of antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties | Scaffolds made of a mix of bovine and marine collagen | Pistacia lentiscus and/or Calendula officinalis | [77] |
| Honey-propolis wax | Collagen hydrolysates | [78] | |
| Collagen Scaffold | Mupirocin-Loaded Chitosan Microspheres and Piper Betle Extract | [79] | |
| Collagen aerogel | Wheatgrass | [80] | |
| Collagen scaffold | Acanthus ebracteatus vahl extract | [81] | |
| Promoting cell proliferation | PLA scaffold | Plasma pretreatment and kefiran coating | [82] |
| Collagen scaffold | Silkworm gland hydrolysate (SSGH) | [83] | |
| Collagen/PLGA/chitosan scaffold | VEGF and bFGF | [84] | |
| Collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffold | Autologous micrografts | [85] | |
| Zein/PCL (zein/poly-ε-caprolactone) and Collagen | ZnO nanoparticles and Aloe vera extracts | [86] | |
| Gelatin and collagen electrospinned onto a chitosan scaffold | Lithosperm radix (LR) extract | [87] | |
| Sodium alginate and collagen type-I hydrogel | Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) | [88] | |
| Stimulating ECM regeneration | Collagen/chitosan scaffold | Doxycycline | [89] |
| Collagen scaffold | Silver nanoparticles conjugated with juglone | [90] | |
| Collagen type-I and tropoelastin scaffold | Not functionalized | [91] | |
| Bilayered collagen/chitosan—collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffold | Not functionalized | [92] | |
| Collagen type-I and type-III crossed-fiber scaffold | Not functionalized | [93] | |
| Particular case | Collagen/PLGA (poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold | Glucophage (metformin) | [94] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Monica, F.; Campora, S.; Ghersi, G. Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Chronic Skin Wound Treatment. Gels 2024, 10, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10020137
La Monica F, Campora S, Ghersi G. Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Chronic Skin Wound Treatment. Gels. 2024; 10(2):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10020137
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Monica, Francesco, Simona Campora, and Giulio Ghersi. 2024. "Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Chronic Skin Wound Treatment" Gels 10, no. 2: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10020137
APA StyleLa Monica, F., Campora, S., & Ghersi, G. (2024). Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Chronic Skin Wound Treatment. Gels, 10(2), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10020137