Temperature Dependence of Electrophoretic Mobility and Hydrodynamic Radius of Microgels of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
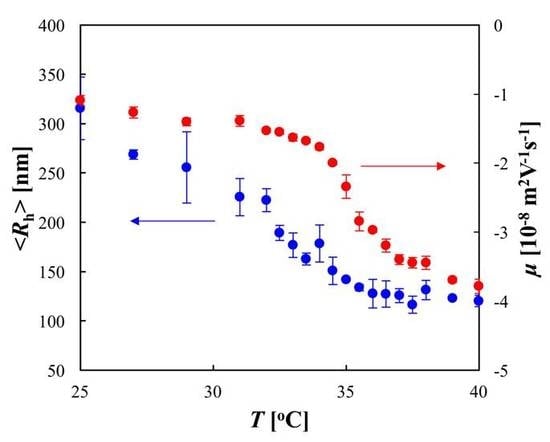
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Microgels
4.2. SLS, DLS, and ELS Measurements
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saunders, B.R.; Vincent, B. Microgel particles as model colloids: Theory, properties and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 80, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, J.B.; Vine, G.J.; Snowden, M.J. Microgel application and commercial consideration. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 625–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, B.R.; Laajam, N.; Daly, E.; Teow, S.; Hu, X.; Stepto, R. Microgels: From responsive polymer colloids to biomaterials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. PNIPAM microgels for biomedical applications: From dispersed particles to 3D assemblies. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 6375–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R. Temperature-sensitive aqueous microgels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R.H.; Chibante, P. Preparation of aqueous latices with N-isopropylacrylamide. Colloid Surf. 1986, 20, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R.H.; Pelton, H.M.; Morphesis, A.; Rowell, R.L. Particle sizes and electrophoretic mobilities of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) latex. Langmuir 1989, 5, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.; Saunders, B.R. Temperature-dependent electrophoretic mobility and hydrodynamic radius measurements of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particles: Structural insights. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 3187–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramusson, M.; Vincent, B.; Marston, N. The electrophoresis of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2000, 278, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Salinas, M.J.; Romero-Cano, M.S.; de las Nieves, F.J. Electrokinetic characterization of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particles: Effect of electrolyte concentration and temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 241, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-León, T.; Ortega-Vinuesa, J.L.; Bastos-González, D.; Elaïssari, A. Cationic and anionic poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) based submicron gel particles: Electrokinetic properties and colloidal stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4629–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Martín, B.; Romero-Cano, M.S.; Fernández-Nieves, A.; Fernández-Barbero, A. Thermal control over the electrophoresis of soft colloidal particles. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3586–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncho-Jordá, A. Effective charge of ionic microgel particles in the swollen and collapsed states: The role of the steric microgel-ion repulsion. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 064906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adroher-Benítez, I.; Ahualli, S.; Bastos-González, D.; Ramos, J.; Forcada, J.; Moncho-Jordá, A. The effect of electrosteric interactions on the effective chare of thermresponsive ionic microgels: Theory and experiments. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 2038–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mozuelos, P. Effective electrostatic interactions among charged thermo-responsive microgels immersed in a simple electrolyte. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 054902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braibanti, M.; Haro-Pérez, C.; Quesada-Pérez, M.; Rojas-Ochoa, L.F.; Trappe, V. Impact of volume transition on the net charge of poly-N-isopropyl acrylamide microgels. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 032601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmqvist, P.; Mohanty, P.S.; Nägele, G.; Schurtenberger, P.; Heinen, M. Structure and dynamics of loosely cross-linked ionic microgel dispersions in the fluid regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 048302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K.; Nakayama, A.; Kokufuta, E. Electrophoretic behavior of ampholytic polymers and nanogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 8223–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokufuta, E.; Sato, S.; Kokufuta, M.K. Electrophoretic behavior of microgel-immobilized polyions. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15442–15449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.J. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981; pp. 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, J.J.; Fujita, H. Electrophoresis of charged polymer molecules with partial free drainage. Proc. Akad. Amst. 1955, 58, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima, H. Electrophoretic mobility of soft particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 163, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, H. On the general expression for the electrophoretic mobility of a soft particle. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 228, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Pelton, R.H.; Hamielec, A.E.; Woods, D.R.; McPee, W. The kinetics of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel latex formation. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1994, 272, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, H. Electrokinetics of soft particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2007, 285, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, H. Electrophoresis and electrostatic interaction of soft particles. Butsuri 2013, 68, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, D.L.; Sangani, A.S. Particle pressure and marginal stability limits for a homogeneous monodispersed gas-fluidized bed: Kinetic theory and numerical simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 400, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekko, K.; Noguchi, H. Potentiometric studies of hydrophobic effect on ion binding of ionic dextran derivatives. Biopolymers 1975, 14, 2555–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehler, E.L.; Fuxreiter, M.; Simon, I.; Garcia-Moreno, E.B. The role of hydrophobic microenvironments in modulating pKa shifts in proteins. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2002, 48, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieger, M.; Richtering, W.; Pederson, J.S.; Lindner, P. Small-angle neutron scattering study of structural changes in temperature sensitive microgel colloids. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 6197–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Richtering, W. Influence of polymerization conditions on the structure of temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.F.; Schätzel, K.; Vincent, B. The determination of very small electrophoretic mobilities in polar and nonpolar colloidal dispersions using phase analysis light scattering. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 143, 532–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| (109 g/mol) | (102 nm) | (102 nm) | (102 nm) | (102 nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.2 | 2.8 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 3.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maki, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Nagai, D. Temperature Dependence of Electrophoretic Mobility and Hydrodynamic Radius of Microgels of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Gels 2018, 4, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020037
Maki Y, Sugawara K, Nagai D. Temperature Dependence of Electrophoretic Mobility and Hydrodynamic Radius of Microgels of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Gels. 2018; 4(2):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaki, Yasuyuki, Kentaro Sugawara, and Daisuke Nagai. 2018. "Temperature Dependence of Electrophoretic Mobility and Hydrodynamic Radius of Microgels of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)" Gels 4, no. 2: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020037
APA StyleMaki, Y., Sugawara, K., & Nagai, D. (2018). Temperature Dependence of Electrophoretic Mobility and Hydrodynamic Radius of Microgels of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Gels, 4(2), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020037