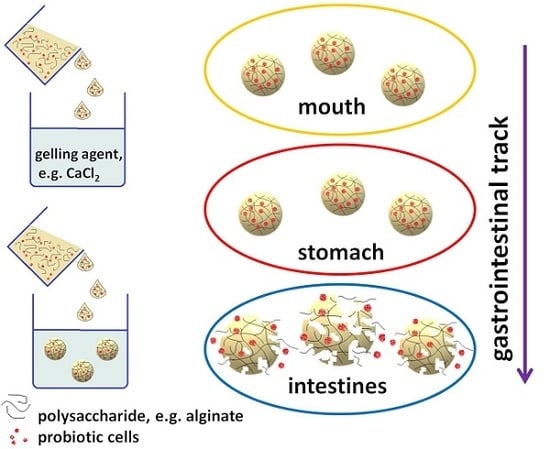
Application of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels as Probiotic Delivery Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Polysaccharide Hydrogels
2.1. Alginate-Based Hydrogels
2.2. Carrageenan-Based Hydrogels
2.3. Xanthan-Based Hydrogels
2.4. Pectin-Based Hydrogels
2.5. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Augustin, M.A.; Hemar, Y. Nano- and micro-structured assemblies for encapsulation of food ingredients. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC): A potential delivery system for bioactive food molecules. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, N.P.; Espinosa, Y.G.; Norton, I.T. Encapsulation systems for the delivery of hydrophilic nutraceuticals: Food application. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbassi, G.K.; Vandamme, T. Probiotic Encapsulation Technology: From Microencapsulation to Release into the Gut. Pharmaceutics 2012, 4, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.K.; Das, B.; Maji, R. Calcium alginate/gum Arabic beads containing glibenclamide: Development and in vitro characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO/WHO. Probiotics in Food. Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation; FAO Food and Nutrition Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2006; Volume 85, pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tuohy, K.M.; Probert, H.M.; Smejkal, C.W.; Gibson, G.R. Using probiotics and prebiotics to improve gut health. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Prebiotics: Present and future in food science and technology. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, H.-S.; Kuan, C.-Y.; Ewe, J.-A.; Fung, W.-Y.; Liong, M.-T. The Improvement of Hypertension by Probiotics: Effects on Cholesterol, Diabetes, Renin, and Phytoestrogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3755–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautava, S.; Kalliomäki, M.; Isolauri, E. Probiotics during pregnancy and breastfeeding might confer immunomodulatory protection against atopic disease in the infant. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.T. Roles of Probiotics and Prebiotics in Colon Cancer Prevention: Postulated Mechanisms and In-vivo Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón, F.; Perdigón, G.; de Moreno de LeBlanc, A. Modification in the diet can induce beneficial effects against breast cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govender, M.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; van Vuuren, S.; Pillay, V. A Review of the Advancements in Probiotic Delivery: Conventional vs. Non-conventional Formulations for Intestinal Flora Supplementation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varankovich, N.V.; Nickerson, M.T.; Korber, D.R. Probiotic-based strategies for therapeutic and prophylactic use against multiple gastrointestinal diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J. Designing biopolymer microgels to encapsulate, protect and deliver bioactive components: Physicochemical aspects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 240, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, M.K.; Giri, S.K. Probiotic functional foods: Survival of probiotics during processing and storage. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 9, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona-Hernandez, R.I.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Islas-Rubio, A.R.; de la Rosa, L.A.; Wall-Medrano, A. Structural stability and viability of microencapsulated probiotic bacteria: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.T.; Tzortzis, G.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Microencapsulation of probiotics for gastrointestinal delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Muhammad, N.; Jhun, B.H.; Yoo, J.W. Probiotic delivery systems: A brief overview. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 46, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros, J.M.; Scherer, T.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Edwards, A.D. A laminated polymer film formulation for enteric delivery of live vaccine and probiotic bacteria. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, H.K.; Pawar, D.D.; Shah, D.A.; Prajapati, V.D.; Jani, G.K.; Mulla, A.M.; Thakar, P.M. Development of Microencapsulation Delivery System for Long-Term Preservation of Probiotics as Biotherapeutics Agent. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 620719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, M.T.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Microencapsulation of Probiotic Bacteria into Alginate Hydrogels. In Hydrogels in Cell-Based Therapies, 1st ed.; Connon, C.J., Hamley, I.W., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2014; pp. 95–111. ISBN 978-1-84973-798-2. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, L.; Murphy, B.; McLoughlin, P.; Duggan, P.; Lawlor, P.G.; Hughes, H.; Gardiner, G.E. Prebiotics from Marine Macroalgae for Human and Animal Health Applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2038–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okolie, C.L.; Rajendran, S.R.C.K.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Aryee, A.N.A.; Mason, B. Prospects of brown seaweed polysaccharides (BSP) as prebiotics and potential immunomodulators. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtuvia, V.; Maturana, N.; Acevedo, F.; Peña, C.; Díaz-Barrera, A. Bacterial alginate production: An overview of its biosynthesis and potential industrial production. World. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Tan, H. Alginate-Based Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine Applications. Materials 2013, 6, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draget, K.I.; Taylor, C. Chemical, physical and biological properties of alginates and their biomedical implications. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnsilawat, T.; Pongsawatmanit, R.; McClements, D.J. Characterization of β-lactoglobulin–sodium alginate interactions in aqueous solutions: A calorimetry, light scattering, electrophoretic mobility and solubility study. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyash, M.; Despang, F.; Ikonomidou, C.; Gelinsky, M. Swelling and Mechanical Properties of Alginate Hydrogels with Respect to Promotion of Neural Growth. Tissue Eng. Part C 2014, 20, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, S.K.; Kirar, N. Swelling and drug release behavior of calcium alginate/poly (sodium acrylate) hydrogel beads. Des. Monomers Polym. 2016, 19, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, C.; Li, J.; Mu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kong, M.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X. Construction of multilayer alginate hydrogel beads for oral delivery of probiotics cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokarram, R.R.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Najafi, M.B.H.; Shahidi, F. The influence of multi stage alginate coating on survivability of potential probiotic bacteria in simulated gastric and intestinal juice. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, M.; Feng, C.; Liu, W.F.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.J.; Chen, X.G. Preparation and property of layer-by-layer alginate hydrogel beads based on multi-phase emulsion technique. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 62, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumarasamy, P.; Allan-Wojtas, P.; Holley, R.A. Stability of Lactobacillus reuteri in Different Types of Microcapsules. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periayah, M.H.; Halim, A.S.; Saad, A.Z.M. Chitosan: A Promising Marine Polysaccharide for Biomedical Research. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2016, 10, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohail, A.; Turner, M.S.; Coombes, A.; Bostrom, T.; Bhandari, B. Survivability of probiotics encapsulated in alginate gel microbeads using a novel impinging aerosols method. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaeim, D.; Sarabi-Jamab, M.; Ghorani, B.; Kadkhodaee, R.; Tromp, R.H. Electrospray assisted fabrication of hydrogel microcapsules by single- and double-stage procedures for encapsulation of probiotics. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 102, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, M.; Bevilacqua, A.; Altieri, C.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R. Challenges for the Production of Probiotic Fruit Juices. Beverages 2015, 1, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nualkaekul, S.; Lenton, D.; Cook, M.T.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Charalampopoulos, D. Chitosan coated alginate beads for the survival of microencapsulated Lactobacillus plantarum in pomegranate juice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzzi, L.; Campaniello, D.; Speranza, B.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Bevilacqua, A. Thermal Treatments for Fruit and Vegetable Juices and Beverages: A Literature Overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 668–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.K.; Shah, N.P. Shah. Acid, Bile, and Heat Tolerance of Free and Microencapsulated Probiotic Bacteria. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khem, S.; Small, D.M.; May, B.K. The behaviour of whey protein isolate in protecting Lactobacillus plantarum. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbassi, G.K.; Vandamme, T.; Ennahar, S.; Marchioni, E. Microencapsulation of Lactobacillus plantarum spp in an alginate matrix coated with whey proteins. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 129, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Gagné-Bourque, F.; Dumont, M.-J.; Jabaji, S. Encapsulation of Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 cells and evaluation of their survival after freeze-drying, storage and under gastrointestinal conditions. J. Food Eng. 2016, 168, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, K.; Tucker, N.; Stanger, J.; Staiger, M.; Marshall, S.; Hall, B. Effects of the molecular format of collagen on characteristics of electrospun fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J.; Li, L. Microencapsulation of Lactobacillus salivarious Li01 for enhanced storage viability and targeted delivery to gut microbiota. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.A.; Grenha, A. Polysaccharide Nanoparticles for Protein and Peptide Delivery: Exploring Less-Known Materials. In Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 1st ed.; Donev, R., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 98, pp. 223–261. ISBN 978-0-12-802828-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kariduraganavar, M.Y.; Kittur, A.A.; Kamble, R.R. Polymer Synthesis and Processing. In Natural and Synthetic Biomedical Polymers, 1st ed.; Kumbar, S., Laurencin, C., Deng, M., Eds.; Elsevier Science BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–31. ISBN 978-0-12-396983-5. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Nicolai, T.; Benyahia, L.; Chassenieux, C. Synergistic effects of mixed salt on the gelation of κ-carrageenan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.; Ferreira, L.; Gil, A.M.; Trindade, T. Synthesis and swelling behavior of temperature responsive κ-carrageenan nanogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 355, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L.; McClements, D.J. Encapsulation of lactase (β-galactosidase) into κ-carrageenan-based hydrogel beads: Impact of environmental conditions on enzyme activity. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zou, L.; Chen, L.; Ahmed, Y.; Al Bishri, W.; Balamash, K.; McClements, D.J. Encapsulation of curcumin in polysaccharide-based hydrogel beads: Impact of bead type on lipid digestion and curcumin bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 58, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkova, Z.; Krastanov, A.; Murgov, I. Immobilized lactic acid bacteria for application as dairy starters and probiotic preparations. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.K.; Shah, N.P. Effect of Various Encapsulating Materials on the Stability of Probiotic Bacteria. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setijawati, D. Carrageenan from Eucheuma sp and concentration difference as encapsulation material toward Lactobacillus acidophilus viability at simulation GI Tract pH condition. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2014, 4, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lamboley, L.; Lacroix, C.; Champagne, C.P.; Vuillemard, J.C. Continuous mixed strain mesophilic lactic starter production in supplemented whey permeate medium using immobilized cell technology. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 56, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doleyres, Y.; Fliss, I.; Lacroix, C. Continuous Production of Mixed Lactic Starters Containing Probiotics Using Immobilized Cell Technology. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, L.; Garthoff, J.A.; Schaafsma, A.; Krul, L.; Schrijver, J.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Speijers, G.; Vandenplas, Y. Locust bean gum safety in neonates and young infants: An integrated review of the toxicological database and clinical evidence. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukoulis, C.; Behboudi-Jobbehdar, S.; Macnaughtan, W.; Parmenter, C.; Fisk, I.D. Stability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG incorporated in edible films: Impact of anionic biopolymers and whey protein concentrate. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonganurakkun, B.; Nodasaka, Y.; Sakairi, N.; Nishi, N. DNA-Based Gels for Oral Delivery of Probiotic Bacteria. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariffin, S.H.; Yeen, W.W.; Abidin, I.Z.; Abdul Wahab, R.M.; Ariffin, Z.Z.; Senafi, S. Cytotoxicity effect of degraded and undegraded kappa and iota carrageenan in human intestine and liver cell lines. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Sun, W.; Shan, X.; Jiang, H.; Cai, C.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Carrageenan-induced colitis is associated with decreased population of anti-inflammatory bacterium, Akkermansia muciniphila, in the gut microbiota of C57BL/6J mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 279, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheow, W.S.; Hadinoto, K. Biofilm-Like Lactobacillus rhamnosus Probiotics Encapsulated in Alginate and Carrageenan Microcapsules Exhibiting Enhanced Thermotolerance and Freeze-Drying Resistance. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3214–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, F.C.; Dorr, D.S.; Pawlicka, A.; Avellaneda, C.O. Microbial origin xanthan gum-based solid polymer electrolytes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, F.P.; Oliveira, A.M., Jr.; Nunes, T.P.; de Farias Silva, C.E.; de Souza Abud, A.K. Bioconversion of Agro-industrial Wastes into Xanthan Gum. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 49, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dário, A.F.; Hortêncio, L.M.A.; Sierakowski, M.R.; Neto, J.C.Q.; Petri, D.F.S. The effect of calcium salts on the viscosity and adsorption behavior of xanthan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, V.B.; Bentini, R.; Catalani, L.H.; Petri, D.F.S. Synthesis and swelling behavior of xanthan-based hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.Z.; Tang, S.M.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, R.G.; Li, Q.; Du, S.M.; You, Z.L. Injectable and release-controlled hydrogel based on xanthan gum and silk fibroin. J. Control. Release 2017, 259, e177–e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Deng, Y.M.; Ren, J.A.; Chen, G.P.; Wang, G.F.; Wang, F.; Wu, X.W. Novel in situ forming hydrogel based on xanthan and chitosan re-gelifying in liquids for local drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muadklay, J.; Charoenrein, S. Effects of hydrocolloids and freezing rates on freeze–thaw stability of tapioca starch gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroodi, S.G.; Rasco, B.A.; Lo, Y.M. Influence of Xanthan-Curdlan Hydrogel Complex on Freeze-Thaw Stability and Rheological Properties of Whey Protein Isolate Gel over Multiple Freeze-Thaw Cycle. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fareez, I.M.; Lim, S.M.; Mishra, R.K.; Ramasamy, K. Chitosan coated alginate–xanthan gum bead enhanced pH and thermotolerance of Lactobacillus plantarum LAB12. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argin, S.; Kofinas, P.; Lo, Y.M. The cell release kinetics and the swelling behavior of physically crosslinked xanthan-chitosan hydrogels in simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 40, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Liu, N.; Wan, H.; Shu, G.; Liao, N. Effect of complexation conditions on microcapsulation of Lactobacillus acidophilus in xanthan-chitosan polyelectrolyte complex gels. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2015, 14, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, T.; Song, Y.; Shu, G.; Chen, H. Effect of xanthan-chitosan-xanthan double layer encapsulation on survival of Bifidobacterium BB01 in simulated gastrointestinal conditions, bile salt solution and yogurt. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; He, Y.; Chen, L.; Song, Y.; Meng, J.; Chen, H. Microencapsulation of Lactobacillus Acidophilus by Xanthan-Chitosan and Its Stability in Yoghurt. Polymers 2017, 9, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.M.; Guido, L.F.; Cruz, J.M.; Barros, A.A. Determination of galacturonic acid content in pectin from fruit juices by liquid chromatographydiode array detection-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 8, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Fidalgo, A.; Delisi, R.; Ilharco, L.M.; Pagliaro, M. Pectin Production and Global Market. Agro Food Ind. Hi-Tech. 2016, 27, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ptichkina, N.M.; Markina, O.A.; Rumyantseva, G.N. Pectin extraction from pumpkin with the aid of microbial enzymes. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Mu, T.H.; Ma, M.M. Extraction, structure, and emulsifying properties of pectin from potato pulp. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, H.R.; Munarin, F.; Gentilini, R.; Visai, L.; Granja, P.L.; Tanzi, M.C.; Petrini, P. Injectable pectin hydrogels produced by internal gelation: pH dependence of gelling and rheological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Arnold, R.D.; Wicker, L. Pectin and charge modified pectin hydrogel beads as a colon-targeted drug delivery carrier. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 104, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Ko, S.; Lee, S. Use of Yuja (Citrus junos) Pectin as a Fat Replacer in Baked Foods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1837–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Polk, D.B.; Tomasula, P.M.; Yan, F.; Liu, L.S. Preserving viability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in vitro and in vivo by a new encapsulation system. J. Control. Release 2016, 230, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, K.; Yu, G.L.; Moller-Trane, R.; Koran, M.; Dosa, P.I.; McKenna, D.H.; Hubel, A. Combinations of Osmolytes, Including Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Sugar Alcohols Act in Concert During Cryopreservation to Improve Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Survival. Tissue Eng. Part C 2016, 22, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, B.M.; Stanton, C.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P. Survival of Probiotic Lactobacilli in Acidic Environments Is Enhanced in the Presence of Metabolizable Sugars. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3060–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bepeyeva, A.; de Barros, J.M.S.; Albadran, H.; Kakimov, A.K.; Kakimova, Z.K.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Encapsulation of Lactobacillus casei into Calcium Pectinate-Chitosan Beads for Enteric Delivery. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2954–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebara, C.; Chaves, K.S.; Ribeiro, M.C.E.; Souza, F.N.; Grosso, C.R.F.; Gigante, M.L. Viability of Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 in pectin–whey protein microparticles during exposure to simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, C.L.; de Valdez, G.F.; Gigante, M.L.; Grosso, C.R.F. Whey protein coating bead improves the survival of the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL 1505 to low pH. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 54, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotiko, A.; Sathivel, S. Development of a combined low-methoxyl-pectin and rice-bran extract delivery system to improve the viability of Lactobacillus plantarum under acid and bile conditions. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lišková, J.; Douglas, T.E.; Beranová, J.; Skwarczyńska, A.; Božič, M.; Samal, S.K.; Modrzejewska, Z.; Gorgieva, S.; Kokol, V.; Bačáková, L. Chitosan hydrogels enriched with polyphenols: Antibacterial activity, cell adhesion and growth and mineralization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 129, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A functional chitosan-based hydrogel as a wound dressing and drug delivery system in the treatment of wound healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonia, T.A.; Sharma, C.P. Chitosan and Its Derivatives for Drug Delivery Perspective. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2011, 243, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Biopolymer(s) | Probiotic Strains | Tested Conditions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate | B. breve | gastric fluids | [32] |
| Alginate, alginate–chitosan | L. rhamnosus, L. acidophilus | gastric fluids, bile salts | [37] |
| Alginate–chitosan | L. plantarum | gastric fluids, bile salts, pancreatic enzymes | [38] |
| Alginate, alginate–chitosan | L. plantarum | storage in pomegranate juice at fridge | [40] |
| Alginate | L. rhamnosus, B. longum, L. salivarius, L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, L. paracasei, B. lactis | gastric fluids and bile salts; heat treatment | [42] |
| Alginate, alginate–whey proteins | L. plantarum | gastric fluids, bile salts, pancreatic enzymes | [44] |
| Alginate–pea protein isolate | L. casei | storage at room temp., fridge and freezer | [45] |
| Alginate, alginate–gelatin | L. salivarious | wet storage; heat treatment; saliva, gastric fluids and bile salts | [47] |
| Biopolymer(s) | Probiotic Strains | Tested Conditions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| κ-carrageenan | L. delbrueckii, L. casei, L. lactis, S. thermophilus | freeze-drying; storage at room temp. and fridge | [54] |
| κ-carrageenan | L. rhamnosus, B. longum, L. salivarius, L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, L. paracasei, B. lactis, L. rhamnosus, B. bifidum | gastric fluids and bile salts | [55] |
| κ-carrageenan–ι-carrageenan | L. acidophilus | pH conditions of the gastrointestinal tract | [56] |
| κ-carrageenan–locust bean gum | L. rhamnosus | storage at room temp. and fridge | [60] |
| DNA–gelatin–κ-carrageenan | B. lactis, B. longum, B. bifidum, L. acidophilus | gastric fluids; storage at fridge | [61] |
| Biopolymer(s) | Probiotic Strains | Tested Conditions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xanthan–alginate, xanthan–alginate–chitosan | L. plantarum | gastric fluids and bile salts; heat treatment | [73] |
| Xanthan–chitosan | P. acidilactici | gastric and intestinal fluids; freeze-drying | [74] |
| Xanthan–chitosan, xanthan–chitosan–xanthan | B. bifidum | storage at room temp. and fridge in yogurt; gastric fluids and bile salts | [76] |
| Xanthan–chitosan, xanthan–chitosan–xanthan | L. acidophilus | storage in yogurt at room temp. and fridge | [77] |
| Biopolymer(s) | Probiotic Strains | Tested Conditions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pectin | L. rhamnosus | freeze-drying; stored at room temperature; gastric fluids, enzymes | [85] |
| Pectin, pectin–chitosan | L. casei | gastric and intestinal fluids | [88] |
| Pectin–whey protein | L. acidophilus | gastric and intestinal fluids | [89] |
| Pectin–whey protein | L. rhamnosus | gastric fluid | [90] |
| Pectin, pectin–rice bran extract | L. plantarum | acid and bile solutions | [91] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwiecień, I.; Kwiecień, M. Application of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels as Probiotic Delivery Systems. Gels 2018, 4, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020047
Kwiecień I, Kwiecień M. Application of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels as Probiotic Delivery Systems. Gels. 2018; 4(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwiecień, Iwona, and Michał Kwiecień. 2018. "Application of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels as Probiotic Delivery Systems" Gels 4, no. 2: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020047
APA StyleKwiecień, I., & Kwiecień, M. (2018). Application of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels as Probiotic Delivery Systems. Gels, 4(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4020047