Volume Transition and Phase Coexistence in Polyelectrolyte Gels Interacting with Amphiphiles and Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Aspects
2.1. Interactions in Mixtures of Opposite Charge
2.2. Role of Crosslinks
2.3. Electrostatic Gel Model
3. Volume Phase Transition (VPT)
3.1. Mechanisms
3.1.1. Spherical Macroions
3.1.2. Hysteresis
4. Phase Equilibrium in Gels
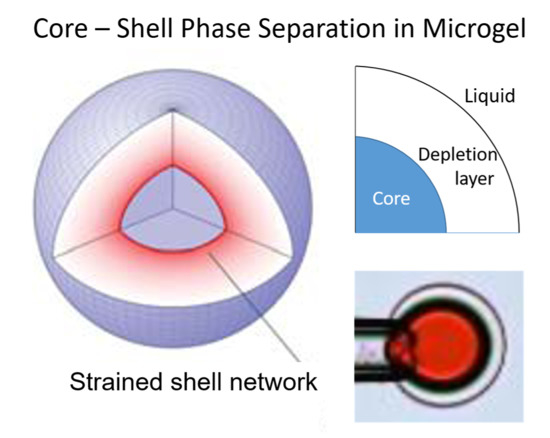
4.1. Shell Composition and Microstructure
4.2. Composition of Core
4.3. Theoretical Modeling of Core–Shell Phase Equilibrium
4.4. Core–Shell Equilibrium in Microgels
4.5. Salt-Free Systems: Cross-Linked Complex Salts
4.5.1. Variation of Surfactant/Polyion Charge Ratio
4.5.2. Variation of Osmotic Pressure
4.5.3. Variation of Micelle Charge
5. Volume Transition Kinetics
5.1. Deswelling Kinetics
5.2. Swelling Kinetics
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katchalsky, A. Rapid swelling and deswelling of reversible gels of polymeric acids by ionization. (A synthetic contractile system). Experientia 1949, 5, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katchalsky, A.; Zwick, M. Mechanochemistry and ion exchange. J. Polym. Sci. 1955, 16, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.L. Some Statistical Mechanical Models of Elastic Polyelectrolytes and Proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.L. Energetics and molecular mechanisms in muscle action. Part II—Statistical thermodynamical treatment of contractile systems. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1953, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T. Collapse of Gels and the Critical Endpoint. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1978, 40, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K. Responsive Gels: Volume Transitions I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 109. [Google Scholar]
- Matuso, E.S.; Tanaka, T. Kinetics of discontinous volume-phase transition of gels. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 89, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Hirotsu, S. Critical points of the volume phase transition in N-isopropylacrylamide gels. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 88, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Suzuki, A. Phase separation of weakly ionized polymer gels during shrinking phase transition. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 10338–10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frenken, J.W.M.; Marée, P.M.J.; Van Der Veen, J.F. Observation of surface-initiated melting. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 34, 7506–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dash, J.G. History of the search for continuous melting. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1999, 71, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuki, A. Paradox in phase transitions with volume change. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 2192–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekimoto, K. Temperature hysteresis and morphology of volume phase transition of gels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 4154–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomari, T.; Doi, M. Hysteresis and Incubation in the Dynamics of Volume Transition of Spherical Gels. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 8334–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Koga, S.; Imabayashi, R.; Maeda, H. Salt effects on the volume transition of ionic gel induced by the hydrophobic counterion binding. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 5852–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P. Interaction between polyelectrolyte gels and surfactants of opposite charge. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starodubtsev, S.G. Influence of topological structure of polyelectrolyte networks on their interaction with oppositely charged micelle-forming surfactants. Vysokomol. Soedin. Ser. B 1990, 32, 925–930. [Google Scholar]
- Khandurina, Y.V.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Zezin, A.B.; Kabanov, V.A. Interaction of cross-linked polyelectrolytes with oppositely charged surfactants. Polym. Sci. 1994, 36, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, P. Self-Assembly of Ionic Surfactant in Cross-Linked Polyelectrolyte Gel of Opposite Charge. A Physical Model for Highly Charged Systems. Langmuir 1998, 14, 2269–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P.; Schneider, S.; Lindman, B. Macroscopic phase separation in a polyelectrolyte gel interacting with oppositely charged surfactant: Correlation between anomalous deswelling and microstructure. Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2000, 115, 342–3466. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, P.; Schneider, S.; Lindman, B. Phase Separation in Polyelectrolyte Gels Interacting with Surfactants of Opposite Charge. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 9777–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Hansson, P. Phase Behavior of Salt-Free Polyelectrolyte Gel–Surfactant Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6064–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirotsu, S. Some exotic properties of polymer gels associated with the volume phase transition. Ferroelectronics 1997, 203, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Dreher, M.R. Locoregional drug delivery using image-guided intra-arterial drug eluting bead therapy. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, A.; Holden, R.R. DC Bead embolic drug-eluting bead: Clinical application in the locoregional treatment of tumours. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, T.; Ljunglöf, A.; Hagel, L.; Kula, M.-R.; Thömmes, J. Visualizing patterns of protein uptake to porous media using confocal scanning laser microscopy. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziennik, S.R.; Belcher, E.B.; Barker, G.A.; DeBergalis, M.J.; Fernandez, S.E.; Lenhoff, A.M. Nondiffusive mechanisms enhance protein uptake rates in ion exchange particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kizilay, E.; Kayitmazer, A.; Dubin, P.L. Complexation and coacervation of polyelectrolytes with oppositely charged colloids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thünemann, A.F.; Müller, M.; Dautzenberg, H.; Joanny, J.; Löwen, H. Polyelectrolyte complexes. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 166, 113–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, S.; Seijo, M.; Stoll, S. The many facets of polyelectrolytes and oppositely charged macroions complex formation. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, C.; Dubin, P.L.; Kayitmazer, A.; Turksen, S. Polyelectrolyte–protein complexes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10, 52–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kruif, K.G.; Weinbreck, F.; De Vries, R. Complex coacervation of proteins and anionic polysaccharides. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.; Stuart, M.C. Theory and simulations of macroion complexation. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piculell, L. Understanding and Exploiting the Phase Behavior of Mixtures of Oppositely Charged Polymers and Surfactants in Water. Langmuir 2013, 29, 10313–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, T.; Linse, P. Monte Carlo Simulations of Polyelectrolytes at Charged Micelles. 1. Effects of Chain Flexibility. Langmuir 1996, 12, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, T.; Linse, P. Monte Carlo Simulations of Polyelectrolytes at Charged Micelles. 2. Effects of Linear Charge Density. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 17873–17880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, T.; Linse, P. Monte Carlo Simulations of Polyelectrolytes at Charged Micelles. 3. Effects of Surfactant Tail Length. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 5506–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, A.; Piculell, L.; Cabane, B.; Ilekti, P. A New Approach to the Phase Behavior of Oppositely Charged Polymers and Surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 106, 1013–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, S.; Gustavsson, C.; Gudmundsson, C.; Linse, P.; Piculell, L. When Do Water-Insoluble Polyion−Surfactant Ion Complex Salts “Redissolve” by Added Excess Surfactant? Langmuir 2011, 27, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, C.; Moniri, E.; Pegado, L.; Wennerström, H. Electrostatic Attraction between DNA and a Cationic Surfactant Aggregate. The Screening Effect of Salt. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5999–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbart, W.M.; Bruinsma, R.F.; Pincus, P.A.; Parsegian, V.A. DNA-Inspired Electrostatics. Phys. Today 2000, 53, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granfeldt, M.K.; Joensson, B.; Woodward, C.E. A Monte Carlo simulation study of the interaction between charged colloids carrying adsorbed polyelectrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 4819–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, A.; Piculell, L.; Karlsson, L.; Cabane, B.; Jönsson, B. Phase Behavior of an Ionic Surfactant with Mixed Monovalent/Polymeric Counterions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 8119–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Kwak, J.C.T. Surfactant-polyelectrolyte interactions. 1. Binding of dodecyltrimethylammonium ions by sodium dextran sulfate and poly(styrenesulfonate) in aqueous solution in the presence of sodium chloride. J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 3866–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P. Self-Assembly of Ionic Surfactants in Polyelectrolyte Solutions: A Model for Mixtures of Opposite Charge. Langmuir 2001, 17, 4167–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tararyshkin, D.; Kramarenko, E.; Khokhlov, A. Two-phase structure of polyelectrolyte gel/surfactant complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 164905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magny, B.; Iliopoulos, I.; Zana, R.; Audebert, R. Mixed Micelles Formed by Cationic Surfactants and Anionic Hydrophobically Modified Polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 1994, 10, 3180–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemet, F.; Piculell, L. Interactions in aqueous mixtures of hydrophobically modified polyelectrolyte and oppsitely charged surfactant. Mixed micelle formation and associative phase separation. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 9201–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P.; Almgren, M. Interaction of alkyltrimethylammonium surfactants with polyacrylate and poly (styrensulfonate) in aqueous solution: Phase behavior and surfactant aggregation numbers. Langmuir 1994, 10, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalberg, K.; Lindman, B.; Bergfeldt, K. Phase behavior of systems of polyacrylate and cationic surfactants. Langmuir 1991, 7, 2893–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitar, S.; Goderis, B.; Hansson, P.; Kogej, K. Phase Diagram and Structures in Mixtures of Poly(styrenesulfonate anion) and Alkyltrimethylammonium Cations in Water: Significance of Specific Hydrophobic Interaction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 4634–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Ishizawa, M.; Gong, J.; Osada, Y. Molecular and supramolecular structures of complexes formed by polyelectrolyte-surfactant interactions: Effects of charge density and compositions. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Pol. Chem. 1999, 37, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Råsmark, P.J.; Elvingson, C.; Hansson, P. Single Microgel Particle Studies Demonstrate the Influence of Hydrophobic Interactions between Charged Micelles and Oppositely Charged Polyions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Liu, Z.; Suo, Z. Inhomogeneous swelling of a gel in equilibrium with a solvent and mechanical load. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 3282–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Hong, W.; Suo, Z. Inhomogeneous and anisotropic equilibrium state of a swollen hydrogel containing a hard core. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 051904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gernandt, J.; Frenning, G.; Richtering, W.; Hansson, P. A model describing the internal structure of core/shell hydrogels. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 10327–10338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-K.; Ågren, J. On two-phase coherent equilibrium in binary alloys. Acta Met. Mater. 1990, 38, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M. Gel dynamics. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 78, 052001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgecombe, S.; Linse, P. Monte Carlo Simulations of Cross-Linked Polyelectrolyte Gels with Oppositely Charged Macroions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3836–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jidheden, C.; Hansson, P. Single Microgels in Core–Shell Equilibrium: A Novel Method for Limited Volume Studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 10030–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P. Phase behavior of aqueous polyion–surfactant ion complex salts: A theoretical analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 332, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horkay, F.; Tasaki, I.; Basser, P.J. Effect of monovalent-divalent cation exchange on the swelling of polyacrylate hydrogels in physiological salt solutions. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, P.; Bysell, H.; Månsson, R.; Malmsten, M. Peptide–Microgel Interactions in the Strong Coupling Regime. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 10964–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokufuta, E.; Nakaizumi, S.; Ito, S.; Tanaka, T. Uptake of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate by poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel and effect of surfactant uptake on the volume-phase transition. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, P.; Hansson, P. Ion-Exchange Controls the Kinetics of Deswelling of Polyelectrolyte Microgels in Solutions of Oppositely Charged Surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 23843–23856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhlov, A.R.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Makhaeva, E.E.; Starodubtzev, S.G. Collapse of polyelectrolyte networks induced by their interaction with an oppositely charged surfactant. Theory. Makromol. Chem. Theory Simul. 1992, 1, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhlov, A.R.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Makhaeva, E.E.; Starodubtsev, S.G. Collapse of polyelectrolyte networks induced by their interaction with oppositely charged surfactants. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 4779–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernandt, J.; Hansson, P. Hysteresis in the Surfactant-Induced Volume Transition of Hydrogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tikriti, Y.; Hansson, P. Drug-Eluting Polyacrylate Microgels: Loading and Release of Amitriptyline. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schosseler, F.; Moussaid, A.; Munch, J.P.; Candau, S.J. Weakly charged polyelectrolyte gels: Temperature and salt effects on the statics and the dynamics. J. Phys. II Fr. 1991, 1, 1197–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, K.B.; Dormidontova, E.E.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Vilgis, T.A. Microphase Separation Transition for Polyelectrolyte Gels in Poor Solvents. J. Phys. II Fr. 1997, 7, 627–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernandt, J.; Hansson, P. Core–shell separation of a hydrogel in a large solution of proteins. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10905–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekimoto, K.; Kawasaki, K. Elastic instabilities and phase coexistence of gels. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 1989, 154, 384–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernandt, J.; Hansson, P. Surfactant-induced core/shell phase equilibrium in hydrogels. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 64902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göransson, A.; Hansson, P. Shrinking Kinetics of Polyacrylate Gels in Surfactant Solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 9203–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, P.; Hansson, P. Deswelling kinetics of polyacrylate gels in solutions of cetyltrimethylammunium bromide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 9770–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Malmsten, M. Visualizing the Interaction between Poly-l-lysine and Poly(acrylic acid) Microgels Using Microscopy Techniques: Effect of Electrostatics and Peptide Size. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5476–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Hansson, P. Binding of Lysozyme to Spherical Poly(styrenesulfonate) Gels. Gels 2018, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, C.; Hansson, P.; Malmsten, M. Mechanism of Lysozyme Uptake in Poly(acrylic acid) Microgels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6183–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Koga, S. Elastic Relaxations of Ionic Gel Associated with Hydrophobic Counterion. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 11893–11897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, V.A.; Zezin, A.B.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Khandurina, Y.V.; Novoskoltseva, O. Absorption of ionic amphiphils by oppositely charged polyelectrolyte gels. Macromol. Symp. 1998, 126, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabanova, V.B.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Zezin, A.B.; Kabanov, V.A. Interaction of cross-linked sodium polyacrylate with proteins. Polym. Sci. 1995, 37, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Khandurina, Y.V.; Alexeev, V.L.; Evmenenko, G.A.; Dembo, A.T.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Zezin, A.B. On the structure of polyacrylate-surfactant complexes. J. Phys. II Fr. 1995, 5, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandurina, Y.V.; Dembo, A.T.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Zezin, A.B.; Kabanov, V.A. Structure of polycomplexes composed of cross-linked sodium polyacrylate and cationic micelle-forming surfactants. Polym. Sci. 1994, 36, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Skobeleva, V.V.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Zezin, A.B.; Kabanov, V.A. Collapse of swollen gel network and phase transition in a weakly cross-linked polyelectrolyte gel upon its interaction with oppositely charged proteins. Dokl. Phys. Chem. 1996, 347, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zezin, A.B.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Kabanov, V.A. Interaction of Linear Polyelectrolytes with Oppositely Charged Lightly Cross-Linked Networks. Macromol. Symp. 1998, 126, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, V.A.; Skobeleva, V.B.; Rogacheva, V.B.; Zezin, A.B. Sorption of Proteins by Slightly Cross-Linked Polyelectrolyte Hydrogels: Kinetics and Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Yeh, F.; Sokolov, E.L.; Starodoubtsev, S.G.; Khokhlov, A.R. Interaction of Slightly Cross-Linked Gels of Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) with Surfactants. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 8447–8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembo, A.T.; Yakunin, A.N.; Zaitsev, V.S.; Mironov, A.V.; Starodoubtsev, S.G.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Chu, B. Regular microstructures in gel-surfactant complexes: Influence of water content and comparison with the surfactant structure in water. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1996, 34, 2893–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, E.L.; Yeh, F.; Khokhlov, A.; Chu, B. Nanoscale Supramolecular Ordering in Gel−Surfactant Complexes: Sodium Alkyl Sulfates in Poly(diallyldimethylammonium Chloride). Langmuir 1996, 12, 6229–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.; Sokolov, E.L.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Chu, B. Nanoscale Supramolecular Structures in the Gels of Poly(Diallyldimethylammonium Chloride) Interacting with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 6615–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.; Sokolov, E.L.; Walter, T.; Chu, B. Structure Studies of Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride-co-acrylamide) Gels/Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Complex. Langmuir 1998, 14, 4350–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Burger, C.; Yeh, F.; Chu, B. Charge Density Effect of Polyelectrolyte Chains on the Nanostructures of Polyelectrolyte−Surfactant Complexes. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 8157–8163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yeh, F.; Burger, C.; Chu, B. Nanostructures of polyelectrolyte gel-surfactant complexes. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbaugh, H.S.; Lindman, B. Swelling and Structural Changes of Oppositely Charged Polyelectrolyte Gel−Mixed Surfactant Complexes. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1522–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P. Surfactant Self-Assembly in Polyelectrolyte Gels: Aggregation Numbers and Their Relation to the Gel Collapse and the Appearance of Ordered Structures in the NaPA/C12TAB System. Langmuir 1998, 14, 4059–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, P.; Unga, J.; Hansson, P. Effect of Salt and Surfactant Concentration on the Structure of Polyacrylate Gel/Surfactant Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 10959–10964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Koga, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Annaka, M. Nanostructures of polyelectrolyte gel-surfactant complexes in uniaxially stretched networks. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 021504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, A.; Topgaard, D.; Piculell, L.; Söderman, O. Molecular Self-Diffusion in Micellar and Discrete Cubic Phases of an Ionic Surfactant with Mixed Monovalent/Polymeric Counterions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 13241–13250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, A.; Norrman, J.; Piculell, L. Phase behavior of polyion-surfactant ion complex salts: Effects of surfactant chain length and polyion length. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 10332–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrman, J.; Lynch, I.; Piculell, L. Phase Behavior of Aqueous Polyion-Surfactant Ion Complex Salts: Effects of Polyion Charge Density. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 8402–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrman, J.; Piculell, L. Phase Behavior of Cetyltrimethylammonium Surfactants with Oligo Carboxylate Counterions Mixed with Water and Decanol: Attraction between Charged Planes or Spheres with Oligomeric Counterions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13364–13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janiak, J.; Schillén, K.; Piculell, L.; Olofsson, G. The aqueous phase behavior of polyion–surfactant ion complex salts mixed with nonionic surfactants. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3126–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalberg, K.; Lindman, B.; Karlstroem, G. Phase diagram of a system of cationic surfactant and anionic polyelectrolyte: Tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide-hyaluronan-water. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 4289–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xiao, X.; Chou, T.-M.; Libera, M. Counterion Exchange in Peptide-Complexed Core–Shell Microgels. Langmuir 2019, 35, 9521–9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Råsmark, P.J.; Andersson, M.; Lindgren, J.; Elvingson, C. Differences in Binding of a Cationic Surfactant to Cross-Linked Sodium Poly(Acrylate) and Sodium Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) Studied by Raman Spectroscopy. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P. Surfactant Self-Assembly in Oppositely Charged Polymer Networks. Theory. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 12903–12915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, P.; Hansson, P. Regular and irregular deswelling of polyacrylate and hyaluronate gels induced by oppositely charged surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnfelt, E.; Gernandt, J.; Al-Tikriti, Y.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernäs, H.; Hansson, P. Single bead investigation of a clinical drug delivery system—A novel release mechanism. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnfelt, E.; Sjögren, E.; Hansson, P.; Lennernäs, H. In Vitro Release Mechanisms of Doxorubicin From a Clinical Bead Drug-Delivery System. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 3387–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bysell, H.; Hansson, P.; Malmsten, M. Transport of poly-l-lysine into oppositely charged poly(acrylic acid) microgels and its effect on gel deswelling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Hansson, P.; Malmsten, M. Effect of Charge Density on the Interaction between Cationic Peptides and Oppositely Charged Microgels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7207–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bysell, H.; Hansson, P.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Effect of Hydrophobicity on the Interaction between Antimicrobial Peptides and Poly(acrylic acid) Microgels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bysell, H.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Binding and Release of Consensus Peptides by Poly(acrylic acid) Microgels. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2162–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, G.; Ubiera, A.R.; Pabst, T.M. Protein Mass Transfer Kinetics in Ion Exchange Media: Measurements and Interpretations. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2005, 28, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, M.; Fusco, S.; Lewis, A.L.; Netti, P.A. New Insights into the Mechanisms of the Interactions Between Doxorubicin and the Ion-Exchange Hydrogel DC Bead™ for Use in Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE). J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



























© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hansson, P. Volume Transition and Phase Coexistence in Polyelectrolyte Gels Interacting with Amphiphiles and Proteins. Gels 2020, 6, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6030024
Hansson P. Volume Transition and Phase Coexistence in Polyelectrolyte Gels Interacting with Amphiphiles and Proteins. Gels. 2020; 6(3):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleHansson, Per. 2020. "Volume Transition and Phase Coexistence in Polyelectrolyte Gels Interacting with Amphiphiles and Proteins" Gels 6, no. 3: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6030024
APA StyleHansson, P. (2020). Volume Transition and Phase Coexistence in Polyelectrolyte Gels Interacting with Amphiphiles and Proteins. Gels, 6(3), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6030024