A Thermal-Responsive Zwitterionic Polymer Gel as a Filtrate Reducer for Water-Based Drilling Fluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of PAND
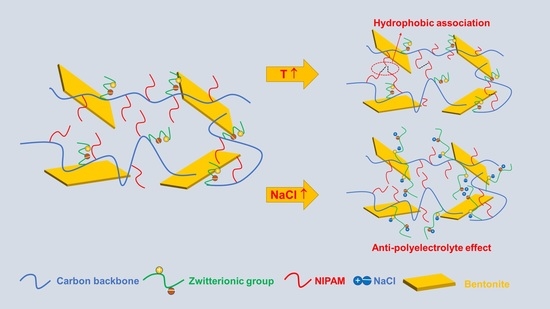
2.2. Salt Response Characteristics of the PAND Solution
2.3. Temperature Response Characteristics of the PAND Solution
2.4. Applied in Water-Based Drilling Fluid
2.4.1. Rheology and Filtration Performance
2.4.2. Filter Cake Quality
2.4.3. Colloidal Stability Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis and Characterization of P(AM-NIPAM-DMAPS) Copolymer
4.3. Characterization Methods of PAND
4.4. Preparation of PAND Solution
4.5. Rheological Properties of Polymer Solution
4.6. Pyrene Fluorescence Probe
4.7. The Mean Hydrodynamic Radius
4.8. Preparation of Water-Based Drilling Fluids
4.9. Rheological Properties of WDFs
4.10. Filtration Properties of WDFs
4.11. Zeta Potential
4.12. Microscopic Morphology of Filter Cake
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, H.; Lv, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Hydrophobic-associated polymer-based laponite nanolayered silicate composite as filtrate reducer for water-based drilling fluid at high temperature. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, L.; Cheng, G.; Xue, H.; Jiang, S. Engineering the polymer backbone to strengthen nonfouling sulfobetaine hydrogels. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14793–14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Lv, K.; Sun, J.; Lu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, J. Enhancement of thermal stability of drilling fluid using laponite nanoparticles under extreme temperature conditions. Mater. Lett. 2019, 248, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, P.; Pillai, P.; Leong, Y. Ageing and collapse of Bentonite gels—Effects of Mg(II), Ca(II) and Ba(II) ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdaman, E.; Osfouri, S.; Azin, R.; Niknam, K.; Roohi, A. Improving the rheology, lubricity, and differential sticking properties of water-based drilling muds at high temperatures using hydrophilic Gilsonite nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, M.H.; Lee, S.Y. Colloidal stability of bentonite clay considering surface charge properties as a function of pH and ionic strength. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Han, D.; Wei, L.; Lin, Q.; Fan, J. Synthesis and property evaluation of a salt- and alkali-resistant star-polymer. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2010, 37, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Ji, Y.; Ji, J.; Liu, J. Nano-Modified Polymer Gels as Temperature- and Salt-Resistant Fluid-Loss Additive for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Gels 2022, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wu, Q.; Li, M.; Ren, S.; Dong, L.; Zhang, X.; Lei, T.; Kojima, Y. Water-based bentonite drilling fluids modified by novel biopolymer for minimizing fluid loss and formation damage. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 507, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, W. Novel latex particles and aluminum complexes as potential shale stabilizers in water-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 135, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.; Leon, O.; Urdaneta, J.; Munoz-Bonilla, A.; Fernandez-Garcia, M. Modified Starch as a Filter Controller in Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Materials 2020, 13, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Zhang, F. Application of core-shell structural acrylic resin/nano-SiO2 composite in water based drilling fluid to plug shale pores. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 55, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Luo, P.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, J.; Kuang, X.; Wang, D. Application of a new family of organosilicon quadripolymer as a fluid loss additive for drilling fluid at high temperature. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Sun, J.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Lv, K.; Zhang, P. Synthesis of a Low-Molecular-Weight Filtrate Reducer and Its Mechanism for Improving High Temperature Resistance of Water-Based Drilling Fluid Gel System. Gels 2022, 8, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jiang, G.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Chang, X. Novel N, N-dimethylacrylamide copolymer containing multiple rigid comonomers as a filtrate reducer in water-based drilling fluids and mechanism study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Lv, K.; Dai, Z. A novel nano-lignin-based amphoteric copolymer as fluid-loss reducer in water-based drilling fluids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, G. Synthesis and aqueous solution properties of novel thermosensitive polyacrylamide derivatives. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, F.L.; Sylvia, R. The colloidal and rheological properties of bentonite suspensions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 82, 43–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Lv, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. A novel zwitterionic quaternary copolymer as a fluid-loss additive for water-based drilling fluids. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Ji, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Shi, S. Temperature- and Salt-Resistant Micro-Crosslinked Polyampholyte Gel as Fluid-Loss Additive for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Gels 2022, 8, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranka, M.; Brown, P.; Hatton, T.A. Responsive Stabilization of Nanoparticles for Extreme Salinity and High-Temperature Reservoir Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19651–19658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; He, Y.; Cui, W.; Yang, L.; Ye, C. A saturated saltwater drilling fluid based on salt-responsive polyampholytes. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chang, X.; Lv, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, J. Salt-responsive zwitterionic copolymer as tackifier in brine drilling fluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chang, X.; Zhang, F.; Bai, Y.; Lv, K.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, B. Salt-Responsive Zwitterionic Polymer Brush Based on Modified Silica Nanoparticles as a Fluid-Loss Additive in Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Sundaram, H.S.; Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Applications of zwitterionic polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 118, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jiang, G.; Peng, S.; He, Y.; Wang, J. Amphoteric Polymer as an Anti-calcium Contamination Fluid-Loss Additive in Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 7221–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourdet, D.; L’Alloret, F.; Audebert, R. Reversible thermothickening of aqueous polymer solutions. Polymer 1994, 35, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourdet, D.; L’Alloret, F.; Audebert, R. Synthesis of thermoassociative copolymers. Polymer 1997, 38, 2535–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourdet, D.; Gadgil, J.; Podhajecka, K.; Badiger, M.V.; Brûlet, A.; Wadgaonkar, P.P. Thermoreversible Behavior of Associating Polymer Solutions: Thermothinning versus Thermothickening. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8512–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Lv, K.; Liu, J.; Xiu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, J. Synthesis of hydrophobic associative polymers to improve the rheological and filtration performance of drilling fluids under high temperature and high salinity conditions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 209, 109808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, R.; Kodama, K.; Ueki, T.; Kokubo, H.; Imabayashi, S.; Watanabe, M. LCST-type liquid-liquid phase separation behaviour of poly(ethylene oxide) derivatives in an ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2008, 40, 4939–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhuang, B.; Yu, J. Functional Zwitterionic Polymers on Surface: Structures and Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2020, 15, 2060–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Gong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Xu, W.; Wang, L. Structures, properties, and applications of zwitterionic polymers. Chem. Phys. Mater. 2022, 1, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Tchameni, A.P.; Luo, M.; Wen, J. A novel thermo-associating polymer as rheological control additive for bentonite drilling fluid in deep offshore drilling. Mater. Lett. 2021, 284, 128914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wickramasinghe, R.; Qian, X. Effects of salt on the lower critical solution temperature of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide). J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 16594–16604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Qiu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Huang, W. Hydrophobic associated polymer based silica nanoparticles composite with core–shell structure as a filtrate reducer for drilling fluid at utra-high temperature. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 129, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, G.; Nichifor, M.; Picton, L.; About-Jaudet, E.; Le Cerf, D. Preparation and characterization of anionic pullulan thermoassociative nanoparticles for drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.; Fernandez, L. Dehydration and rehydration processes of cement paste exposed to high temperature environments. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 3015–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, K.; Du, H.; Sun, J.; Huang, X.; Shen, H. A Thermal-Responsive Zwitterionic Polymer Gel as a Filtrate Reducer for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Gels 2022, 8, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8120832
Lv K, Du H, Sun J, Huang X, Shen H. A Thermal-Responsive Zwitterionic Polymer Gel as a Filtrate Reducer for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Gels. 2022; 8(12):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8120832
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Kaihe, Hongyan Du, Jinsheng Sun, Xianbin Huang, and Haokun Shen. 2022. "A Thermal-Responsive Zwitterionic Polymer Gel as a Filtrate Reducer for Water-Based Drilling Fluids" Gels 8, no. 12: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8120832
APA StyleLv, K., Du, H., Sun, J., Huang, X., & Shen, H. (2022). A Thermal-Responsive Zwitterionic Polymer Gel as a Filtrate Reducer for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Gels, 8(12), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8120832