Current Understanding of Hydrogel for Drug Release and Tissue Engineering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
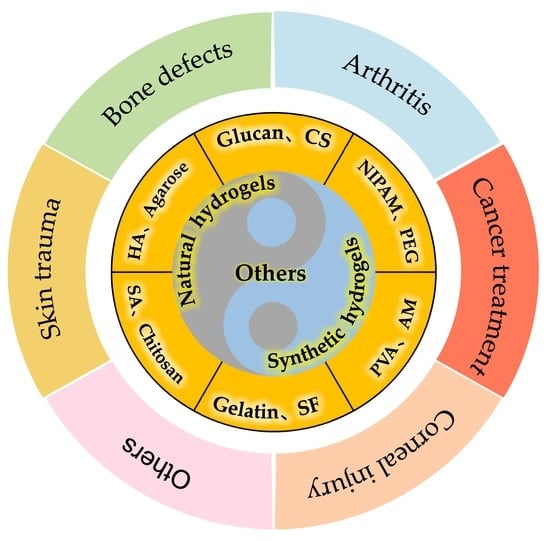
2. Classification of Hydrogels
2.1. Natural Hydrogels



2.2. Synthetic Hydrogels

3. Characterization Techniques for Hydrogels
4. Responsive Hydrogels
4.1. pH-Responsive Hydrogels
4.2. Temperature-Responsive Hydrogels
4.3. Electric Field-Responsive Hydrogels
4.4. Ion-Responsive Hydrogels
4.5. Magnetic Field-Responsive Hydrogels
4.6. Pressure-Responsive Hydrogels

4.7. Photo-Responsive Hydrogels
4.8. Biomolecule-Responsive Hydrogels
4.9. Redox-Responsive Hydrogels
4.10. Multi-Responsive Hydrogels

5. Application of Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering
5.1. Skin Trauma
5.2. Bone Defects
5.3. Arthritis
5.4. Cartilage Defects

5.5. Corneal Injury
5.6. Cancer Treatment
5.7. Cardiovascular System
5.8. Nervous System

5.9. Reproductive System
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freedman, B.R.; Kuttler, A.; Beckmann, N.; Nam, S.; Kent, D.; Schuleit, M.; Ramazani, F.; Accart, N.; Rock, A.; Li, J.Y.; et al. Enhanced tendon healing by a tough hydrogel with an adhesive side and high drug-loading capacity. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, G.W.; Henise, J.; Reid, R.; Santi, D.V. Hydrogel drug delivery system with predictable and tunable drug release and degradation rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, J.; Huang, H.H. Review on magnetic natural polymer constructed hydrogels as vehicles for drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2574–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, P.; Bisht, A.; Alexander, A.; Dave, V.; Sharma, S. Biomedical applications of hydrogels in drug delivery system: An update. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, K.Y. Hyaluronate-alginate hybrid hydrogels prepared with various linkers for chondrocyte encapsulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.G.; Lin, K.L. The application of biomaterials based on natural hydrogels in bone tissue engineering. J. China Biotech. 2020, 40, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Yuan, S.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Deng, S.; Xie, L.; Yang, Q. The Formation Mechanism of Hydrogels. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 13, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, W.; Han, E.J.; Ahn, G. Alginate-based nanomaterials: Fabrication techniques, properties, and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, H.; Akagi, Y.; Kayasuga-Kariya, Y.; Chung, U.; Sakai, T. “Nonswellable” hydrogel without mechanical hysteresis. Science 2014, 343, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, D.; Nah, J.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Advances in functionalizing fucoidans and alginates (bio) polymers by structural modifications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, Y.; Rehman, H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Ultratough, self-healing, and tissue-adhesive hydrogel for wound dressing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33523–33531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, M.; Chiellini, F.; Ottenbrite, R.M.; Chiellini, E. Chitosan-A versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 981–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.X.; Mao, J.J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, H.R.; Lv, L.; Ge, M.Z.; Li, S.H.; Huang, J.Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.Q.; et al. Recent progress of polysaccharide-based hydrogel interfaces for wound healing and tissue engineering. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.M.; Pan, Y.J.; Li, S.K.; Xing, L.; Du, S.K.; Yuan, G.L.; Li, J.L.; Zhou, T.L.; Xiong, D.S.; Tan, H.P.; et al. Doubly crosslinked biodegradable hydrogels based on gellan gum and chitosan for drug delivery and wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2204–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.X.; Shou, X.; Ni, D.; Kong, T.T.; Zhao, Y.J. Bio-inspired lubricant drug delivery particles for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17093–17102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prè, E.D.; Conti, G.; Sbarbati, A. Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Scaffolds and Multipotent Stromal Cells (MSCs) in Regenerative Medicine. Stem. Cell. Rev. 2016, 12, 664–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Maheriya, M.P. Hyaluronic acid as potential carrier in biomedical and drug delivery applications. Funct. Polysacch. Biomed. Appl. 2019, 213–265. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, Y.; Yoshida, C.; Hamada, K.; Kikkawa, Y.; Nomizu, M. Development of three-dimensional cell culture scaffolds using laminin peptide-conjugated agarose microgels. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 3765–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennink, W.E.; van Nostrum, C.F. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegappan, R.; Selvaprithiviraj, V.; Amirthalingam, S.; Jayakumar, R. Carrageenan based hydrogels for drug delivery, tissue engineering and wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wei, Z.H.; Xue, C.H. Recent advances in carrageenan-based delivery systems for bioactive ingredients: A review. Trends Food. Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Doroudian, M.; Ahadpour, A.; Azari, S. Injectable chitosan/κ-carrageenan hydrogel designed with au nanoparticles: A conductive scaffold for tissue engineering demands. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, L. Ultrastretchable and Self-Healing Double-Network Hydrogel for 3D Printing and Strain Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 26429–26437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.; Mehta, G.; Meena, R.; Siddhanta, A.K. Hydrogel-forming agar-graft-PVP and κ-carrageenan-graft-PVP blends: Rapid synthesis and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 3654–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huskisson, E. Glucosamine and Chondroitin for Osteoarthritis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2008, 36, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-A.; Varghese, S.; Sharma, B.; Strehin, L.; Fermanian, S.; Gorham, J.; Fairbrother, D.H.; Cascio, B.; Elisseeff, J.H. Multifunctional chondroitin sulphate for cartilage tissue–biomaterial integration. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawlee, S.; Sugandhi, A.; Balakrishnan, B.; Labarre, D.; Jayakrishnan, A. Oxidized chondroitin sulfate-cross-linked gelatin matrixes: A new class of hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, G.L.; Huang, H.L. Preparation and application of dextran and its derivatives as carriers. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Cao, X.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X. An interpenetrating HA/G/CS biomimic hydrogel via Diels–Alder click chemistry for cartilage tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Alhussain, H.; Zahid, A.A.; Rehman, S.R.U.; Ahmed, R.; Hasan, A. Crosslinking Strategies to Develop Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications in Nano Hydrogels; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 21–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, S.; Koski, C.; Vu, A.A. Additive manufacturing of natural biopolymers and composites for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Horizons 2020, 7, 2011–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.L.; Zhao, Z.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Huang, X.L.; Li, J.J.; Wei, Y.P. Tough, Antifreezing, and Conductive Hydrogel Based on Gelatin and Oxidized Dextran. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 2101382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Santiago, G.T.-D.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Chang, S.K.C. Isolation and characterization of collagen extracted from channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) skin. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, B.; Sun, L.Y.; Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Shang, Y.X.; Tan, H.; Zhao, Y.J.; Sun, L.Y. Recombinant human collagen hydrogels with hierarchically ordered microstructures for corneal stroma regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echalier, C.; Valot, L.; Martinez, J.; Mehdi, A.; Subra, G. Chemical cross-linking methods for cell encapsulation in hydrogels. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 20, 100536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altman, G.H.; Diaz, F.; Jakuba, C.; Calabro, T.; Horan, R.L.; Chen, J.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, X.; Sahoo, J.K.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Photo-crosslinked silk fibroin for 3D printing. Polymers 2020, 12, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.H.; Yan, L.; Liu, S.; Tan, Y.F.; Xiao, J.; Cao, Y.; Chen, K.; Xiao, W.Q.; Li, B.; Liao, X.L. Preparation of silk fibroin/hyaluronic acid hydrogels with enhanced mechanical performance by a combination of physical and enzymatic crosslinking. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2021, 32, 1635–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Xu, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Sericin hydrogels promote skin wound healing with effective regeneration of hair follicles and sebaceous glands after complete loss of epidermis and dermis. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 2859–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, F.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. Sericin for Resistance Switching Device with Multilevel Nonvolatile Memory. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5498–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Talukdar, S.; Kundu, S.C. Potential of 2D crosslinked sericin membranes with improved biostability for skin tissue engineering. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, M.; Donsi, F.; McClements, D.J. Protein-based delivery systems for the nanoencapsulation of food ingredients. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 920–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, C.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; Xu, L.M.; Wang, G.B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Photo-crosslinkable, injectable sericin hydrogel as 3D biomimetic extracellular matrix for minimally invasive repairing cartilage. Biomaterials 2018, 163, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Nazir, M.S.; Raza, M.R.; Wahjoedi, B.A.; Yussof, A.W. Autoclave and ultra-sonication treatments of oil palm empty fruit bunch fibers for cellulose extraction and its polypropylene composite properties. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 126, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyamurthy, P.; Jain, P.; Balasubramanya, R.H.; Vigneshwaran, N. Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanowhiskers from cotton fibres by controlled microbial hydrolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ParambathKanoth, B.; Claudino, M.; Johansson, M.; Berglund, L.A.; Zhou, Q. Biocomposites from natural rubber: Synergistic effects of functionalized cellulose nanocrystals as both reinforcing and cross-linking agents via free-radical thiol-ene chemistry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16303–16310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Xie, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, L.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Y. A novel method for amino starch preparation and its adsorption for Cu(II) and Cr(VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Mathew, N.; Nath, M.S. Starch modified alginate nanoparticles for drug delivery application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 173, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, R. Radiation initiated synthesis, characterization, and swelling behavior of poly (acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/starch grafted hydrogel. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhou, K.; Jiang, H.Y.; Zhang, S.K.; Zhang, B.J.; Guo, M.Y.; He, G. Poly (NIPAM-co-thienoviologen) for multi-responsive smart windows and thermo-controlled photodynamic antimicrobial therapy. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 18369–18376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhao, C.; Fu, X.; Zhang, W.J.; Kong, W.T.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.J. Ultrasound-responsive microfluidic microbubbles for combination tumor treatment. Adv. Ther. 2021, 4, 2100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X. Synergistic therapeutic effects of Schiff’s base cross-linked injectable hydrogels for local co-delivery of metformin and 5-fluorouracil in a mouse colon carcinoma model. Biomaterials 2016, 75, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, C.X.; Xiang, L.; Chen, Y.P. Advances in injectable and self-healing polysaccharide hydrogel based on the schiffbase reaction. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.T.; Gong, J.; Gu, X.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Dong, J.; Shen, X.Y. Fabrication and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan blend nanofibers produced by electrospinning method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, F. The influence of freeze-thawing conditions on swelling and long-term stability properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for controlled drug release. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 7369–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemikia, S.; Farhangpazhouh, F.; Parsa, M.; Hasan, M.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Hamidi, M. Fabrication of ciprofloxacin-loaded chitosan/polyethylene oxide/silica nanofibers for wound dressing application: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianfar, P.; Vitale, A.; DalleVacche, S.; Bongiovanni, R. Enhancing properties and water resistance of PEO-based electrospunnanofibrous membranes by photo-crosslinking. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 1879–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, R.H.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, C.H.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.S.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.L. Fabrication and properties of carboxymethyl chitosan/polyethylene oxide composite nonwoven mats by centrifugal spinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafi, N.M.; Rahman, N.A.; Rosdi, N.H. Citric acid cross-linking of highly porous carboxymethyl cellulose/poly(ethylene oxide) composite hydrogel films for controlled release applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 7, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifai, L.; Saleh, F.A. A review on acrylamide in food: Occurrence, toxicity, and mitigation strategies. Int. J. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennakesavan, G.; Mostakhdemin, M.; Dkhar, L.K.; Seyfoddin, A.; Fatihhi, S.J. Acrylic acid/acrylamide based hydrogels and its properties-A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 180, 109308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, T. Nanocomposite hydrogels: A unique organic inorganic network structure with extraordinary mechanical, optical, and swelling/de-swelling properties. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Q. A novel polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogel reinforced with natural chitosan nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 84, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, K.F.; Richter, A.; Ludwig, S.; Zimmermann, J.; Kressler, J.; Kuckling, D.; Adler, H.J. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels: FT-IR spectroscopic characterization of crosslinking reaction and work at transition point. Acta Polym. 2010, 50, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Chu, C.C. Synthesis and characterization of dextran-methacrylate hydrogels and structural study by SEM. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2015, 49, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurma, J.R.; Nand, A.V. Temperature and pH sensitive hydrogels composed of chitosan and poly(ethylene glycol). Polym. Bull. 2008, 59, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.K.; Ju, Y.K.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, K.Y. Controlled release of riboflavin and insulin through cross-linked poly(viny alcohol)/chitosan blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 44, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Samchenko, Y.; Ulberg, Z.; Korotych, O. Multipurpose smart hydrogel systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 168, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cai, L.J.; Zhang, D.G.; Shang, L.R.; Zhao, Y.J. Responsive janusstructural color hydrogel micromotors for label-free multiplex assays. Research 2021, 1, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrador, P.; Esteves, M.R.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F. Stimuli-responsive nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, K.; Chandran, S.V.; Balagangadharan, K.; Selvamurugan, N. Temperature-and pH-responsive chitosan-based injectable hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahkam, M.; Poorgholy, N.; Vakhshouri, L. Synthesis and characterization of novel ph-sensitive hydrogels containing ibuprofen pendents for colon-specific drug delivery. Macromol. Res. 2009, 17, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, S.; Nazari, N.; Rakhshaei, R.; Namazi, H. Cu-crosslinked carboxymethylcellulose/naproxen/graphene quantum dot nanocomposite hydrogel beads for naproxen oral delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glajch, J.L.; Kirkland, J.J.; Köhler, J. Effect of column degradation on the reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of peptides and proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 1987, 384, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, X.; Chen, R.; Yang, W. Synthesis of pH-responsive hydrogel thin films grafted on PCL substrates for protein delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7673–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.G.; Wang, J.; Tan, H.; Kong, T.T. Enzyme-functionalized structural color hydrogel particles for urea detection and elimination. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, L.E.; West, J.L. Thermally responsive polymer-nanoparticle composites for biomedical applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.; Cosgrove, T. Dynamic Light Scattering Studies of Poly(ethylene oxide) Adsorbed on Laponite: Layer Conformation and Its Effect on Particle Stability. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10382–10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.; Cosgrove, T. A Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Study of Adsorbed Poly(ethylene oxide) on Laponite. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwenburgh, S.C.G.; Jansen, J.A.; Mikos, A.G. Functionalization of oligo(poly(ethylene glycol)fumarate) hydrogels with finely dispersed calcium phosphate nanocrystals for bone-substituting purposes. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 1547–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Sun, D.; Sun, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chang, F.; Chen, X. Thermogel-mediated sustained drug delivery for in situ malignancy chemotherapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiancich, C.; Danhier, P.; Préat, V.; Danhier, F. Anticancer drug-loaded hydrogels as drug delivery systems for the local treatment of glioblastoma. J. Control. Release 2016, 243, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Pizano, M.D.; Vélaz, I.; Peñas, F.J.; Zavala-Rivera, P.; Rosas-Durazo, A.J.; Maldonado-Arce, A.D.; Martínez-Barbosa, M.E. Effect of freeze-thawing conditions for preparation of chitosan-poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels and drug release studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Valenberg, F.J.P.; Strauss-Ayali, D.; Agmon-Gerstein, Y.; Friedman, A.; Arentsen, H.C.; Witjes, J.A.; Oosterwijk, E. 1048 Assessment of the efficacy of repeated instillations of TC-gel mixed with MMC in an invasive rat bladder cancer model. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2016, 15, e1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, Y.; Kishi, R.; Hasebe, M. Anomalous chemomechanical characteristics of electro-activated polyelectrolyte gels. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Lett. 1987, 25, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Yue, L.; Qiao, K.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Quan, H. Dual stimulus responsive drug release under the interaction of pH value and pulsatile electric field for a bacterial cellulose/sodium alginate/multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrid hydrogel. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 41820–41829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradee, N.; Sirivat, A. Encapsulation of Folic Acid in Zeolite Y for Controlled Release via Electric Field. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 13, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, Y.; Okuzaki, H.; Hori, H. A polymer gel with electrically driven motility. Nature 1992, 355, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlen, R.P.; Kent, C.E.; Shafer, S.N. Electrolytically Activated Contractile Polymer. Nature 1965, 206, 1149–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschou, E.A.; Peteu, S.F.; Bachas, L.G.; Madou, M.J.; Daunert, S. Artificial Muscle Material with Fast Electroactuation under Neutral pH Conditions. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2499–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Shakushiro, K.; Sako, K. Ion-responsive drug delivery systems. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.W.; Song, W.L.; Wang, S.T. Tunable multi-stage wettability and adhesion force on polymer brushes triggered by temperature and pH. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Y.L.; Liu, X.Z.; Shen, P.; Zheng, Y.G.; Lan, X.R.; Lu, C.B.; Wang, J.Z. Current understanding of metal ions in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Lv, F.; Cao, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z. Multistimuli-Responsive, Moldable Supramolecular Hydrogels Cross-Linked by Ultrafast Complexation of Metal Ions and Biopolymers. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 8055–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hu, S.; Liu, K.; Liu, D.; Chen, S. Study on controlled drug permeation of magnetic-sensitive ferrogels: Effect of Fe3O4 and PVA. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hu, S.; Liu, T.; Liu, D.; Chen, S. Magnetic-sensitive behavior of intelligent ferrogels for controlled release of drug. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5974–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.S.; Yin, Y.D. Magnetically responsive nanostructures with tunable optical properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6315–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.M.; Bottom, C.E.; Liang, Z.; Puleo, D.A.; Hilt, J.Z. Magnetic Nanocomposite Sol-Gel Systems for Remote Controlled Drug Release. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2011, 1, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Liu, G.; Xu, M.; Feng, C. A redox-responsive supramolecular hydrogel for controllable dye release. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, L.; Bock, M.; Glockl, G.; Garbacz, G.; Weitschies, W. Development of a pressure-sensitive glyceryl tristearate capsule filled with a drug-containing hydrogel. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K.; Cussler, E.L.; Marchetti, M.; McHugh, M.A. Pressure-dependent phase transitions in hydrogels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1990, 45, 766–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, A.; Kaushik, A.; Jayant, R.D.; Vashist, A.; Ghosal, A.; Nair, M. Hydrogels: Stimuli responsive to on-demand drug delivery systems. Adv. Pers. Nanother. 2017, 8, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.Y.; Peters, M.C.; Anderson, K.W.; Mooney, D.J. Controlled growth factor release from synthetic extracellular matrices. Nature 2000, 408, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Yoon, S.G.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S.I. Electrical behavior of polymer hydrogel composed of poly(vinyl alcohol)–hyaluronic acid in solution. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinifar, T.; Sheybani, S.; Abdouss, M.; HassaniNajafabadi, S.A.; ShafieeArdestani, M. Pressure responsive nanogel base on Alginate-Cyclodextrin with enhanced apoptosis mechanism for colon cancer delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 106, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.F.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.J. Graphene hybrid colloidal crystal arrays with photo-controllable structural colors. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 10846–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehls, E.M.; Rosales, A.M.; Anseth, K.S. Enhanced user-control of small molecule drug release from a poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel via azobenzene/cyclodextrin complex tethers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y. A polydopaminenanoparticle-knotted poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogel for on-demand drug delivery and chemo-photothermaltherapy. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Yoshida, R.; Kataoka, K. Glucose-Responsive Polymer Gel Bearing Phenylborate Derivative as a Glucose-Sensing Moiety Operating at the Physiological pH. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhao, X.; Ye, L. Synthesis of cationic chitosan hydrogel with long chain alkyl and its controlled glucose-responsive drug delivery behavior. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 96230–96241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Sheng, C.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J. Progress in enzyme responsive peptide hydrogel and its applications. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 43, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatovic, D.; Nobis, M.; Son, J.; Anderson, K.I.; Ulijn, R.V. MMP-9 triggered self-assembly of doxorubicin nanofiber depots halts tumor growth. Biomaterials 2016, 98, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, G.; Li, R.; Guan, M.; Wang, X.; Zou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shu, C.; Hong, H.; et al. Biodegradable, hydrogen peroxide, and glutathione dual responsive nanoparticles for potential programmable paclitaxel release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7373–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, C.Q.; Deng, D.W.; Gu, Y.Q.; Wang, H.; Zhong, Q.F. Multiple stimuli-responsive mxene-based hydrogel as intelligent drug delivery carriers for deep chronic wound healing. Small 2022, 18, 2104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshyar, Z.; Bardajee, G.R. A novel dual thermo-and pH-responsive silver nanocomposite hydrogel as a drug delivery system. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 14, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Song, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Z. Mechanically strong dual responsive nanocomposite double network hydrogel for controlled drug release of asprin. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 82, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinia, G.R.; Rahmani, Z.; Karami, S.; Pourjavadi, A. Magnetic/pH-sensitiveκ-carrageenan/sodium alginate hydrogel nanocomposite beads: Preparation, swelling behavior, and drug delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 1891–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yi, J.H.; Mukherjee, S.; Banerjee, P.; Zhou, S.Q. Magnetic/NIR-thermally responsive hybrid nanogels for optical temperature sensing, tumor cell imaging and triggered drug release. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13001–13011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, S.; Guerin, T.; Toth, I.; Stephenson, R.J. Recent advances in self-assembled peptides: Implications for targeted drug delivery and vaccine engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, Z.Q.; Ma, C.Y.; Yan, H.; Xu, N.; Gang, F.L.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, L.Y.; Sun, X.D. Three-dimensional printing and injectable conductive hydrogels for tissue engineering application. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2019, 25, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.J.; Wang, X.G.; Zhu, Y.L.; Su, W.T.; Lv, Q.Z.; Li, D. Antimicrobial hydrogel microspheres for protein capture and wound healing. Mater. Des. 2022, 215, 110478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.P.; Lv, Q.Z.; Liu, S.Y.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Zhou, C.X.; Liao, W.F. 3D-bioprinted peptide coupling patches for wound healing. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 13, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.J.; Zhu, Y.L.; Qin, X.Y.; Chai, S.L.; Liu, G.X.; Su, W.T.; Lv, Q.Z.; Li, D. Magnetic biohybrid microspheres for protein purification and chronic wound healing in diabetic mice. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Han, Y.; Li, H.; Chang, J. Design of a thermosensitive bioglass/agarose-alginate composite hydrogel for chronic wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8856–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jia, J.; Kim, J.P.; Shen, H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D. Ionic Colloidal Molding as a Biomimetic Scaffolding Strategy for Uniform Bone Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Fan, Z.; Huang, X.; Lu, Q.; Xu, W.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk-Hydroxyapatite Nanoscale Scaffolds with Programmable Growth Factor Delivery for Bone Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2016, 8, 24463–24470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Han, H.; Fan, Z.; Lu, H.; Sang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Lu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Nanoscale Silk-Hydroxyapatite Hydrogels for Injectable Bone Biomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2017, 9, 16913–16921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Weir, M.; Xu, H.H.K. An injectable calcium phosphate-alginate hydrogel-umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell paste for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6502–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Cui, Z.; Kim, P.; Jung, L.; Lee, M. Design of hydrogels to stabilize and enhance bone morphogenetic protein activity by heparin mimetics. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Bian, F.K.; Zhao, Y.J. Ice-inspired lubricated drug delivery particles from microfluidic electrospray for osteoarthritis treatment. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20600–20606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.W.; Yang, J.L.; Liang, J.; Xu, X.Y.; Cui, W.G.; Deng, L.F.; Zhang, H.Y. Bioinspired hyaluronic acid/phosphorylcholine polymer with enhanced lubrication and anti-inflammation. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 4135–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simón-Vázquez, R.; Tsapis, N.; Lorscheider, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Calleja, P.; Mousnier, L.; Villegas, E.D.M.; González-Fernández, A.; Fattal, E. Improving dexamethasone drug loading and efficacy in treating arthritis through a lipophilic prodrug entrapped into PLGA-PEG nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X. Remission of Collagen-Induced Arthritis through Combination Therapy of Microfracture and Transplantation of Thermogel-Encapsulated Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.X.; Sun, L.Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, G.P.; Zhao, Y.J. Biomass Microcapsules with Stem Cell Encapsulation for Bone Repair. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Wan, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, X.; Feng, G. Repair of articular cartilage defects in rabbits through tissue-engineered cartilage constructed with chitosan hydrogel and chondrocytes. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, M.; Liu, K.; Wan, Y.Q.; Li, X.; Feng, G. Novel chitosan hydrogel formed by ethylene glycol chitosan, 1,6-diisocyanatohexan and polyethylene glycol-400 for tissue engineering scaffold: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 25, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Z.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z.; Huang, H.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Dai, L.; Zhang, J.; Fu, X.; Duan, X.; et al. Transplantation of allogenic chondrocytes with chitosan hydrogel-demineralized bone matrix hybrid scaffold to repair rabbit cartilage injury. Biomaterials 2016, 108, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.E.; Mohan, R.R.; Mohan, R.R.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Hong., J.; Lee, J. The Corneal Wound Healing Response: Cytokine-mediated Interaction of the Epithelium, Stroma, and Inflammatory Cells. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2001, 20, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekaris, I.; Mravicić, I.; Barisić, A.; Draca, N.; Pauk, M. Amniotic membrane transplantation in the treatment of persistent epithelial defect on the corneal graft. Coll. Antropol. 2010, 34, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jourdan, C.; Wirostko, B.; Coats, B. Finite Element Design Optimization of a Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Drug Delivery Device for Improved Retention. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Chung, S. Combined Application of Autologous Serum Eye Drops and Silicone Hydrogel Lenses for the Treatment of Persistent Epithelial Defects. Eye Contact Lens 2011, 37, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.X.; Lan, H.Y. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor metastasis: Biological roles and clinical therapeutic applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, J.; Oliva, N.; Atilano, M.; Song, H.S.; Artzi, N. Self-assembled RNA-triple-helix hydrogel scaffold for microRNA modulation in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Mater. 2015, 15, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.S.; Park, T.G. Folate-receptor-targeted delivery of doxorubicin nano-aggregates stabilized by doxorubicin–PEG–folate conjugate. J. Control Release 2004, 100, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariepy, E.R.; Shive, M.; Bichara, A.; Berrada, M.; Garrec, D.L.; Chenite, A.; Leroux, J.C. A thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogel for the local delivery of paclitaxel. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.J.; Sridhar, K.S.; Garewal, H.S.; Mills, G.M.; Wenig, B.L.; Dunphy, F.R.; Costantino, P.D.; Leavitt, R.D.; Stewart, M.E.; Orenberg, E.K. Intratumoral cisplatin/epinephrine gel in advanced head and neck cancer: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase III study in North America. Head Neck 2003, 25, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.-Y.J.; Hung, C.C.; Chang, C.W.; Chao, J.H.; Hsieh, B.T. Evaluation of injectable chitosan-based Co-cross-linking hydrogel for local delivery of 188Re-LIPO-DOX to breast-tumor-bearing mouse model. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 4651–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Dai, W.; Zhang, H.; He, B.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhang, Q. Localized co-delivery of collagenase and trastuzumab by thermosensitive hydrogels for enhanced antitumor efficacy in human breast xenograft. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Yu, Y.R.; Yang, C.Y.; Shao, C.M.; Shi, K.Q.; Shang, L.R.; Ye, F.F.; Zhao, Y.J. Microfluidic 3D printing responsive scaffolds with biomimetic enrichment channels for bone regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatchley, M.R.; Gerecht, S. Acellular implantable and injectable hydrogels for vascular regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Qu, T.; Ding, C.; Ma, C.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Liu, X. Injectable gelatin derivative hydrogels with sustained vascular endothelial growth factor release for induced angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yi, G.H.; Yu, C.Y.; Wei, H. Biotherapeutic-loaded injectable hydrogels as a synergistic strategy to support myocardial repair after myocardial infarction. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 216–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Villain, N.; Frisoni, G.B.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Sabbagh, M.; Cappa, S.; Bejanin, A.; Bombois, S.; Epelbaum, S.; Teichmann, M.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations of the International Working Group. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, R.; Bullock, M. Ross. Traumatic brain injury: Therapeutic challenges and new directions. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, A.M.; De Laporte, L.; Tortelli, F.; Spedden, E.; Staii, C.; Atherton, T.J.; Hubbell, J.A.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Hydrogels as Soft Substrates for Neural Tissue Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5140–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Incitti, T.; Migliaresi, C.; Quattrone, A.; Casarosa, S.; Motta, A. Genipin-crosslinked gelatin-silk fibroin hydrogels for modulating the behaviour of pluripotent cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 10, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meder, D.; Herz, D.M.; Rowe, J.B.; Lehericy, S.; Siebner, H.R. The role of dopamine in the brain-lessons learned from Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage 2019, 190, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, X.; Ma, P.; Guo, B. Injectable hydrogel based on quaternized chitosan, gelatin and dopamine as localized drug delivery system to treat Parkinson’s disease. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.J.; Lv, Q.Z.; Jin, Y.; An, H.; Shi, Z.; Hu, G.; Yang, Y.Z.; Wang, X.G.; Yang, L. Angiogenic microspheres for the treatment of a thin endometrium. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4914–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, A.A.; Gibson-Helm, M.E.; Teede, H.J. Anxiety and depression in polycystic ovary syndrome: A comprehensive investigation. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 93, 2421–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xita, N.; Tsatsoulis, A. Fetal Programming of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by Androgen Excess: Evidence from Experimental, Clinical, and Genetic Association Studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brizel, D.M. Pharmacologic approaches to radiation protection. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4084–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.P.; Qi, H.Y.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, G.Q. Observation and Nursing of the Curative Effect of Ag/TiO2 Nanomaterials on Bacterial Vaginosis and Trichomonal Vaginitis. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 7419–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerasarn, V.; Phromratanapongse, P.; Suntornpong, N.; Lorvidhaya, V.; Chitapanarux, I.; Tesavibul, C.; Kongthanarat, Y.; Shotelersuk, K.; Chiewvit, S.; Pusuwan, P. Effect of amifostine to prevent radiotherapy-induced acute and late toxicity in head and neck cancer patients who had normal or mild impaired salivary gland function. EJC Suppl. 2003, 1, S273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.; Xin, X.; Fei, H.; Cui, Y.C. Meta-analysis of the use of hyaluronic acid gel to prevent intrauterine adhesions after miscarriage. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 244, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, W.B.; Xu, L.J.; Zhao, S.D.; Zheng, J.H.; Tian, Y.P.; Qi, X.J.; Huang, X.H.; Zhang, J.K. Controlled releasing of SDF-1α in chitosan-heparin hydrogel for endometrium injury healing in rat model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, F.F.; Shang, L.R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.R.; Zhao, Y.J. Bioinspired living structural color hydrogels. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, 8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.X.; Shao, C.M.; Bian, F.K.; Zhao, Y.J. Biomimetic enzyme cascade reaction system in microfluidic electrospray microcapsules. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, F.F.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Shang, L.R.; Gu, Z.Z.; Zhao, Y.J. Bio-inspired self-healing structural color hydrogel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5900–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, L.; Bai, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, W.; Lv, Q. Current Understanding of Hydrogel for Drug Release and Tissue Engineering. Gels 2022, 8, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050301
Lei L, Bai Y, Qin X, Liu J, Huang W, Lv Q. Current Understanding of Hydrogel for Drug Release and Tissue Engineering. Gels. 2022; 8(5):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050301
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Lanjie, Yujing Bai, Xinyun Qin, Juan Liu, Wei Huang, and Qizhuang Lv. 2022. "Current Understanding of Hydrogel for Drug Release and Tissue Engineering" Gels 8, no. 5: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050301
APA StyleLei, L., Bai, Y., Qin, X., Liu, J., Huang, W., & Lv, Q. (2022). Current Understanding of Hydrogel for Drug Release and Tissue Engineering. Gels, 8(5), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8050301