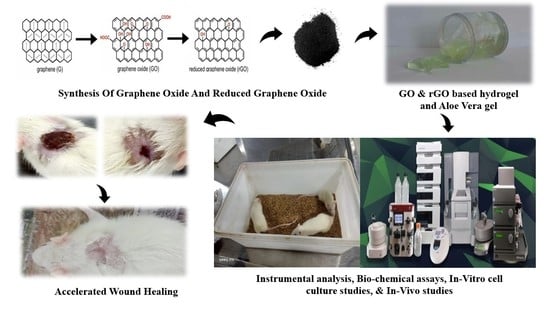
Efficacy of Graphene-Based Nanocomposite Gels as a Promising Wound Healing Biomaterial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fourier–Transform Infra–Red Spectroscopy (FT–IR) Study
2.2. Raman Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.4. Physico–Chemical Parameters of Composite Gels
2.5. Spreadability
2.6. Solubility
2.7. Swellability
2.8. Antioxidant Activity
2.9. Hemocompatibility Assay
2.10. Antibacterial Assay
2.11. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
2.12. Wound Scratch Assay
2.13. In Vivo Studies: Wound Contraction Rate
2.14. Histopathology
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Extraction of Aloe Vera Gel
4.3. Hydrogel Preparation
4.4. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide (GO)
4.5. Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
4.6. Characterization
4.7. Preparation of Composite Wound Healing Gels
4.8. Visual Examination
4.9. Spreadability
4.10. Solubility
4.11. Swellability
4.12. Antibacterial Analysis
4.13. Antioxidant Analysis
4.14. In Vitro Cell Culture Studies
4.14.1. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.14.2. In Vitro Wound Scratch Assay
4.15. In Vivo Wound–Healing Studies
4.15.1. Animals and Experimental Protocol
- Control;
- Aloe vera gel;
- Aloe vera gel + Graphene Oxide (GO);
- Aloe vera gel + Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO);
- Hydrogel;
- Hydrogel + Graphene Oxide (GO);
- Hydrogel + reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO).
4.15.2. Anesthesia and Wound Creation in Rats
4.15.3. Macroscopic Biophysical Analysis
4.15.4. Histopathological Analysis
4.16. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Guo, B. Smart Wound Dressings for Wound Healing. Nano Today 2021, 41, 101290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, P.; Huang, C.; Zeng, R.; Yang, L.; Han, Z.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, C. Photothermal-Promoted Multi-Functional Dual Network Polysaccharide Hydrogel Adhesive for Infected and Susceptible Wound Healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pormohammad, A.; Monych, N.K.; Ghosh, S.; Turner, D.L.; Turner, R.J. Nanomaterials in Wound Healing and Infection Control. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.A.; Abd El-Aziz, S.; Elbadry, H.M.; El-Aassar, S.A.; Tamer, T.M. Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance Profile, and Characterization of Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria from Various Infected Wounds in North Egypt. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 2978–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanikireddy, V.; Varaprasad, K.; Jayaramudu, T.; Karthikeyan, C.; Sadiku, R. Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Materials for Infection Control and Wound Healing: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qin, M.; Xu, M.; Miao, F.; Merzougui, C.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, D. The Fabrication of Antibacterial Hydrogels for Wound Healing. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Lin, C.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, X.; Chen, M.; He, Y.; Peng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cai, K. Copper-Nanoparticle-Embedded Hydrogel for Killing Bacteria and Promoting Wound Healing with Photothermal Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2534–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Pi, W.; Cheng, S.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Min, T.; Zhang, W.; Du, H.; Zhang, P.; Wen, Y. Multifunctional DNA Hydrogels with Hydrocolloid-Cotton Structure for Regeneration of Diabetic Infectious Wounds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Fang, C.W.; Khan, A.; Minhas, M.U.; Wu, P.C. Fabrication and in Vitro Evaluation of Ph-sensitive Polymeric Hydrogels as Controlled Release Carriers. Gels 2021, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettini, R.; Colombo, P.; Peppas, N.A. Controlled Release Solubility Effects on Drug Transport through PH-Sensitive, Swelling-Controlled Release Systems: Transport of Theophylline and Metoclopramide Monohydrochloride. J. Control. Release 1995, 37, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xia, H.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y. In Vitro Evaluation of Kaempferol-Loaded Hydrogel as PH-Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2022, 14, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubaid, M.; Ilyas, S.; Mir, S.; Khan, A.K.; Rashid, R.; Khan, M.Z.U.; Kanwal, Z.G.; Nawaz, A.; Shah, A.; Murtaza, G. Formulation and in Vitro Evaluation of Carbopol 934-Based Modified Clotrimazole Gel for Topical Application. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2016, 88, 2303–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.D.; Yin, J.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Que, Z.Q.; Nie, S.P. Structural and Conformational Characterization of Linear O-Acetyl-Glucomannan Purified from Gel of Aloe Barbadensis Miller. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kased, R.F.; Amer, R.I.; Attia, D.; Elmazar, M.M. Honey-Based Hydrogel: In Vitro and Comparative in Vivo Evaluation for Burn Wound Healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; Guan, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, J. Aloe Vera: A Medicinal Plant Used in Skin Wound Healing. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2021, 27, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilip Kumar, S.; Aashabharathi, M.; KarthigaDevi, G.; Subbaiya, R.; Saravanan, M. Insights of CRISPR-Cas Systems in Stem Cells: Progress in Regenerative Medicine. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H. Reduced Graphene Oxide Incorporated Acellular Dermal Composite Scaffold Enables Efficient Local Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Accelerating Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4054–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Islam, R.; Rana, M.M.; Spitzhorn, L.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Adjaye, J.; Asaduzzaman, S.M. Characterization of Burn Wound Healing Gel Prepared from Human Amniotic Membrane and Aloe Vera Extract. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pulingam, T.; Thong, K.L.; Appaturi, J.N.; Lai, C.W.; Leo, B.F. Mechanistic Actions and Contributing Factors Affecting the Antibacterial Property and Cytotoxicity of Graphene Oxide. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, P.; Ramachandran, B.; Kannan, R.; Muthuvijayan, V. Biomimetic Hydrogel Loaded with Silk and L-Proline for Tissue Engineering and Wound Healing Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Owens, A.C.E.; Kulaots, I.; Chen, Y.; Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H. Antioxidant Chemistry of Graphene-Based Materials and Its Role in Oxidation Protection Technology. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11744–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drabczyk, A.; Kudłacik-Kramarczyk, S.; Głab, M.; Kedzierska, M.; Jaromin, A.; Mierzwiński, D.; Tyliszczak, B. Physicochemical Investigations of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels Containing Aloe Vera Designed for Biomedical Use. Materials 2020, 13, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, P.; Kumar, A. Development of a Microbial Coating for Cellulosic Surface Using Aloe Vera and Silane. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2020, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShammari, A.S.; Halim, M.M.; Yam, F.K.; Kaus, N.H.M. Effect of Precursor Concentration on the Performance of UV Photodetector Using TiO2/Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) Nanocomposite. Results Phys. 2020, 19, 103630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponrasu, T.; Vishal, P.; Kannan, R.; Suguna, L.; Muthuvijayan, V. Isabgol-Silk Fibroin 3D Composite Scaffolds as an Effective Dermal Substitute for Cutaneous Wound Healing in Rats. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 73617–73626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, J.; Muñoz-Camargo, C.; Cruz, J.C. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds as a Multifunctional and Highly Biocompatible Nanocomposite for Wound Healing: Insights into Characterization and Electroconductive Potential. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnana Kumar, G.; Justice Babu, K.; Nahm, K.S.; Hwang, Y.J. A Facile One-Pot Green Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Composites for Non-Enzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 7944–7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, F.C.; Sykam, N.; Selvakumar, M.; Mahesha, M.G. Green Reduction of Graphene Oxide Using Indian Gooseberry (Amla) Extract for Gas Sensing Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Raza, A.; Imran, M.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Shahbaz, A.; Ali, S. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Silver Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) Nanoflakes with Effective Photocatalytic Activity for Wastewater Treatment. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, R.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Anbu, P.; Salimi, M.N.; Yaakub, A.R.W.; Lakshmipriya, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Reduced Graphene Oxide Using the Aqueous Extract of Eclipta Prostrata. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, W.C.; Zhang, F.J. Preparation and Characterization of Graphene Oxide Reduced from a Mild Chemical Method. Asian J. Chem. 2011, 23, 875–879. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.H.; de Silva, K.K.H.; Kumara, G.R.A.; Yoshimura, M. Structural Evolution of Hydrothermally Derived Reduced Graphene Oxide. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alavi, M.; Nokhodchi, A. Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Activities of Electrospun Nanofibers Based on Functionalized Carbohydrates and Proteins. Cellulose 2022, 29, 1331–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, W.; Hardiansyah, A.; Randy, A.; Asri, L.A.T.W. Physically Crosslinked PVA/Graphene-Based Materials/Aloe Vera Hydrogel with Antibacterial Activity. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 29029–29041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Hu, Y.; Tang, P.; Wang, H.; Bin, Y. High Stretchable, PH-Sensitive and Self-Adhesive RGO/CMCNa/PAA Composite Conductive Hydrogel with Good Strain-Sensing Performance. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.; Pathan, N. Potential of Carbohydrate-Conjugated Graphene Assemblies in Biomedical Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; Chauhan, G.; Kumar, A. Augmented Healing of Full Thickness Chronic Excision Wound by Rosmarinic Acid Loaded Chitosan Encapsulated Graphene Nanopockets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyana, B.; Aderibigbe, B.A.; Ray, S.S.; Ndinteh, D.T.; Fonkui, Y.T. Development, Characterization, and in Vitro Evaluation of Water Soluble Poloxamer/Pluronic-mastic Gum-gum Acacia-based Wound Dressing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liu, S.; Hou, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Graphene-Based Nanomaterials as Lubricant Additives: A Review. Lubricants 2022, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Jiang, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, P. Effects of Graphene Oxide on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Graphene Oxide-Geopolymer Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsi, H.A.; Ali, S.K.; Altaa, S.H.A. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) Using Sabdarriffa L Extract and Its Solubility Property. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1664, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhong, L.; Xue, J. Preparation and Properties of Conductive Bacterial Cellulose-Based Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanoparticles Antibacterial Dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aycan, D.; Selmi, B.; Kelel, E.; Yildirim, T.; Alemdar, N. Conductive Polymeric Film Loaded with Ibuprofen as a Wound Dressing Material. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 121, 109308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, M.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Wang, K.; Yao, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, W.; et al. Engineering Bioactive M2 Macrophage-Polarized Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Scaffolds for Rapid Angiogenesis and Diabetic Wound Repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Two-Pronged Strategy of Biomechanically Active and Biochemically Multifunctional Hydrogel Wound Dressing to Accelerate Wound Closure and Wound Healing. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 9937–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, G.; Kim, S.W.; Park, J.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, Y.; Jung, D.W.; Williams, D.R.; Lee, J.Y. Anti-Oxidant Activity Reinforced Reduced Graphene Oxide/Alginate Microgels: Mesenchymal Stem Cell Encapsulation and Regeneration of Infarcted Hearts. Biomaterials 2019, 225, 119513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baali, N.; Khecha, A.; Bensouici, A.; Speranza, G.; Hamdouni, N. Assessment of Antioxidant Activity of Pure Graphene Oxide (GO) and ZnO-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) Using DPPH Radical and H2O2 Scavenging Assays. C 2019, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; He, J.; Shi, M.; Liang, Y.; Guo, B. Injectable Self-Healing Supramolecular Hydrogels with Conductivity and Photo-Thermal Antibacterial Activity to Enhance Complete Skin Regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamrai, M.; Banerjee, S.L.; Paul, S.; Ghosh, A.K.; Sarkar, P.; Kundu, P.P. A Mussel Mimetic, Bioadhesive, Antimicrobial Patch Based on Dopamine-Modified Bacterial Cellulose/RGO/Ag NPs: A Green Approach toward Wound-Healing Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12083–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Ye, J.; Yang, Y.C.; Huang, Y.Y.; Xiao, M.T. Self-Healing Polysaccharide-Based Injectable Hydrogels with Antibacterial Activity for Wound Healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Rath, T.; De, J.; Adhikary, A.; Basu, R.K.; Kundu, P.P. Polyhydroxybutyrate-Co-Hydroxyvalerate Copolymer Modified Graphite Oxide Based 3D Scaffold for Tissue Engineering Application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Fang, W.W.; Xue, J.; Sun, T.C.; Dong, L.; Zha, Z.; Qian, H.; Song, Y.H.; Zhang, M.; Gong, X.; et al. Thermoresponsive in Situ Forming Hydrogel with Sol-Gel Irreversibility for Effective Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infected Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10074–10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandhakumar, M.; Thangaian, D.T.; Sundaram, S.; Roy, A.; Subramanian, B. An Enduring in Vitro Wound Healing Phase Recipient by Bioactive Glass-Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jales, S.T.L.; Barbosa, R.D.M.; de Albuquerque, A.C.; Duarte, L.H.V.; da Silva, G.R.; Meirelles, L.M.A.; da Silva, T.M.S.; Alves, A.F.; Viseras, C.; Raffin, F.N.; et al. Development and Characterization of Aloe Vera Mucilaginous-Based Hydrogels for Psoriasis Treatment. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, U.F.; Abou-Taleb, H.A.; Abdellatif, A.H.; Tolba, N.S. Formulation and Evaluation of Simvastatin Polymeric Nanoparticles Loaded in Hydrogel for Optimum Wound Healing Purpose. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.; Garg, P.; Goyal, R.; Khan, A.; Negi, P.; Li, X.; Kulshrestha, S. An Efficient Wound Healing Hydrogel Based on a Hydroalcoholic Extract of Moringa Oleifera Seeds. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 145, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayah, N.M.S.; Liu, W.W.; Lai, C.W.; Noriman, N.Z.; Khe, C.S.; Hashim, U.; Lee, H.C. Comparison on Graphite, Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide: Synthesis and Characterization. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics Inc.: College Park, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 1892, p. 150002. [Google Scholar]
- Habte, A.T.; Ayele, D.W.; Hu, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) Started from Graphene Oxide (GO) Using the Tour Method with Different Parameters. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5058163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, N.H.; Amin, M.C.I.M.; Ng, S.F. Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Hydrogels Containing Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) as a Functional Antibiofilm Wound Dressing. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subtil, E.L.; Gonçalves, J.; Lemos, H.G.; Venancio, E.C.; Mierzwa, J.C.; dos Santos de Souza, J.; Alves, W.; Le-Clech, P. Preparation and Characterization of a New Composite Conductive Polyethersulfone Membrane Using Polyaniline (PANI) and Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavel, P.K.; Kumar, N.; Parmar, H.S.; Das, A.K. Evaluation of a Peptide-Based Coassembled Nanofibrous and Thixotropic Hydrogel for Dermal Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 3326–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, A.A.; Arigela, B.; Giduturi, A.K.; Komaravolu, R.K.; Mangamuri, U.; Poda, S. Pterocarpus Marsupium Roxburgh Heartwood Extract/Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel as an Innovative Wound Healing Agent in the Diabetic Rat Model. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternullo, S.; Werning, L.V.S.; Holsæter, A.M.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Curcumin-in-Deformable Liposomes-in-Chitosan-Hydrogel as a Novel Wound Dressing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Fan, D.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Fu, R.; Li, X. Non-Stick Hemostasis Hydrogels as Dressings with Bacterial Barrier Activity for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamer, T.M.; Alsehli, M.H.; Omer, A.M.; Afifi, T.H.; Sabet, M.M.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Hassan, M.A. Development of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Kaolin Sponges Stimulated by Marjoram as Hemostatic, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Dressings for Wound Healing Promotion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Degradable Conductive Injectable Hydrogels as Novel Antibacterial, Anti-Oxidant Wound Dressings for Wound Healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.I.; Ghosh, S.; Vinothkumar, K.; Ramesh, B.; Kumari, P.H.; Mohan, K.V.M.; Sukumar, E. Fumaric Acid Incorporated Ag/Agar-Agar Hybrid Hydrogel: A Multifunctional Avenue to Tackle Wound Healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, P.; Kannan, R.; Ramachandran, B.; Moorthy, G.; Suguna, L.; Muthuvijayan, V. Development of Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO)-Isabgol Nanocomposite Dressings for Enhanced Vascularization and Accelerated Wound Healing in Normal and Diabetic Rats. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2018, 517, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Gao, M.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.O.; Ho, W.; Yu, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.Q. An Intrinsically Bioactive Hydrogel with On-Demand Drug Release Behaviors for Diabetic Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4592–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, F.; Ashraf, I.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmad, T.; Anjum, S. 6-Deoxy-Aminocellulose Derivatives Embedded Soft Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels for Improved Wound Healing Applications: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, B.; Pandiyan, N.; Kasinathan, K.; Rajaiah, A.; Arumuga, M.; Subramanian, P.; Sonamuthu, J.; Samayanan, S.; Arumugam, V.R.; Marimuthu, K.; et al. Fabrication of Heteroatom Doped NFP-MWCNT and NFB-MWCNT Nanocomposite from Imidazolium Ionic Liquid Functionalized MWCNT for Antibiofilm and Wound Healing in Wistar Rats: Synthesis, Characterization, in-Vitro and in-Vivo Studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfeek, H.M.; Abou-Taleb, D.A.E.; Badary, D.M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abdellatif, A.A.H. Pharmaceutical, Clinical, and Immunohistochemical Studies of Metformin Hydrochloride Topical Hydrogel for Wound Healing Application. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



















| Composite Gels | Pseudomonas aeruginosa (A) | Bacillus subtilis (B) | Staphylococcus aureus (C) | E. coli (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogel | − | 10.01 | 12.56 | 12.43 |
| Hydrogel + GO | 3.77 | 8.46 | 6.32 | 11.82 |
| Hydrogel + rGO | 4.27 | 7.92 | 6.47 | 12.19 |
| Aloe vera Gel | − | 9.81 | 6.92 | 10.89 |
| Aloe vera Gel + GO | 3.06 | 9.76 | 5.93 | 11.10 |
| Aloe vera Gel + rGO | 15.75 | 8.13 | 3.82 | 13.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shanmugam, D.K.; Madhavan, Y.; Manimaran, A.; Kaliaraj, G.S.; Mohanraj, K.G.; Kandhasamy, N.; Amirtharaj Mosas, K.K. Efficacy of Graphene-Based Nanocomposite Gels as a Promising Wound Healing Biomaterial. Gels 2023, 9, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010022
Shanmugam DK, Madhavan Y, Manimaran A, Kaliaraj GS, Mohanraj KG, Kandhasamy N, Amirtharaj Mosas KK. Efficacy of Graphene-Based Nanocomposite Gels as a Promising Wound Healing Biomaterial. Gels. 2023; 9(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleShanmugam, Dilip Kumar, Yasasve Madhavan, Aashabharathi Manimaran, Gobi Saravanan Kaliaraj, Karthik Ganesh Mohanraj, Narthana Kandhasamy, and Kamalan Kirubaharan Amirtharaj Mosas. 2023. "Efficacy of Graphene-Based Nanocomposite Gels as a Promising Wound Healing Biomaterial" Gels 9, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010022
APA StyleShanmugam, D. K., Madhavan, Y., Manimaran, A., Kaliaraj, G. S., Mohanraj, K. G., Kandhasamy, N., & Amirtharaj Mosas, K. K. (2023). Efficacy of Graphene-Based Nanocomposite Gels as a Promising Wound Healing Biomaterial. Gels, 9(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010022