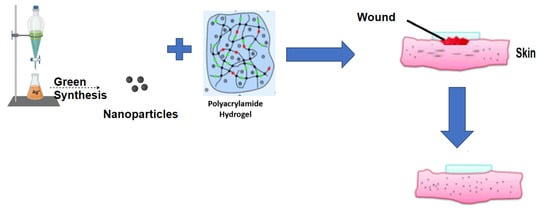
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Wound Healing; Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Top of Form
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.1.1. Bacteria-Facilitated Production of Silver Nanoparticles
2.1.2. Fungi-Facilitated Production of Silver Nanoparticles
2.1.3. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Plants
2.2. Silver Nanoparticles–Polyacrylamide Hydrogel
2.3. Factors Affecting the Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.3.1. Temperature
2.3.2. The pH Value
2.3.3. Reaction Time
2.4. Silver Nanomaterials Characterization
2.4.1. UV–Vis Spectrophotometry
2.4.2. (FT-IR) Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5. Silver Nanoparticles Hydrogel for Wound Healing
2.5.1. Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing
2.5.2. Ensuring the Well-Being of Silver Nanoparticles in the Context of Wound Healing
- Top of Form
2.6. Hydrogel
Types of Hydrogel Used in Wound Healing
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methodology
4.1. Problem Formulation
4.2. Conducting Literature Searches to Gather Information for Research Syntheses
4.3. Extraction of the Data
4.4. Meta-Analysis Processing
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Augustine, R.; Kalarikkal, A.; Thomas, S. PCL membranes incorporated with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles as antibacterial wound dressings. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Villén, F.; Faccendini, A.; Aguzzi, C.; Cerezo, P.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Rossi, S.; Grisoli, P.; Ruggeri, M.; Ferrari, F.; Sandri, G.; et al. Montmorillonite-Norfloxacin nanocomposite intended for healing of infected wounds. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5051–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pang, S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Cao, M.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Song, M.; Jiang, G. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles on wound healing: A case study of zebrafish fin regeneration model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarupa, B.; Kumari, V.; Shatabdi, D.; Moumita.; Dutta, D.M.; Jyotsna, M.; Sandhimita, M.; Arnab, G. Antibacterial, anti-biofilm activity and mechanism of action of pancreatin doped zinc oxide nanoparticles against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 11, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Kardan-Yamchi, J.; Kazemian, H.; Battaglia, S.; Abtahi, H.; Foroushani, A.R.; Hamzelou, G.; Cirillo, D.M.; Ghodousi, A.; Feizabadi, M.M. Whole genome sequencing results associated with minimum inhibitory concentrations of 14 anti-tuberculosis drugs among rifampicin-resistant isolates of mycobacterium tuberculosis from Iran. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natan, M.; Banin, E.N. From Nano to Micro: Using nanotechnology to combat microorganisms and their multidrug resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shehabeldine, A.M.; Ashour, R.M.; Okba, M.M.; Saber, F.R. Callistemon citrinus bioactive metabolites as new inhibitors of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawani, E.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Gad, E.-R.S. Nanoformulation of biogenic cefotaxime-conjugated-silver nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial efficacy against multidrug-resistant bacteria and anticancer studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamida, R.S.; Abdelmeguid, N.E.; Ali, M.A.; Bin-Meferij, M.M.; Khalil, M.I. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a novel cyanobacteria desertifilum sp. extract: Their antibacterial and cytotoxicity effects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Bactericidal and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mounyr, B.; Moulay, S.; Saad, K.I. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, A.; Vranken, T.; Malhotra, A.; Arts, J.J.C.; Habibovic, P. In Vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing methods: Agar dilution to 3D tissue-engineered models. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustapha, T.; Misni, N.; Ithnin, N.R.; Daskum, A.M.; Unyah, N.Z. A review on plants and microorganisms mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles, role of plants metabolites and applications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeep, K.; Ayushi, G.; Praveen, G.; Kulvinder, S.; Vineet, K. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles and their environmental applications. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 29, 100390. [Google Scholar]
- Jaison, J.; Siaw, F.K.; Stephen, B.-A.; Sie, Y.L.; Ahmed, B.; Michael, K.; Danquah, J.R. Green approaches for the synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles using microbial and plant extracts. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 2534–2571. [Google Scholar]
- El Shafey, A.M. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles from plant leaf extracts and their applications: A review. Green Process Synth. 2020, 9, 304–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunday, A.A.; Aderonke, S.F.; Olabisi, T.A. Instrumental characterization and antibacterial investigation of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Garcinia kola leaf. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Nanoparticles in the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant organisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigo, C.; Maria, B. Do age and professional rank influence the order of authorship in scientific publications? Some evidence from a micro-level perspective. Scientometrics 2011, 88, 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.; Alison, C.K. The overview of reviews: Unique challenges and opportunities when research syntheses are the principal elements of new integrative scholarship. Am. Psychol. 2012, 67, 446. [Google Scholar]
- Saeid, T.F.; Ali, R.; Sajjad, M. A novel green synthesis of nickel oxide nanoparticles using Arabic gum. Chem. J. Mol. 2017, 12, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Raktima, C.; Sarkar, S.; Amit, K.D.; Yuksel, A.; Saumya, D.; Madhumita, M. Scope and challenges for green synthesis of functional nanoparticles. In Novel Applications of Carbon Based Nano-Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, M.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Lakshmi, T.; Pugazhendhi, A. Saravanan. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from phenerochaete chrysosporium (MTCC-787) and their antibacterial activity against human pathogenic bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehnal, K.; Hosnedlova, B.; Docekalova, M.; Stankova, M.; Uhlirova, D.; Tothova, Z.; Kepinska, M.; Milnerowicz, H.; Fernandez, C.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; et al. An assessment of the effect of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using sage leaves (Salvia officinalis L.) on germinated plants of maize (Zea mays L.). Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amr, E.-W.; Ghada, S.; Abd, E.-G.; Sabah, A.; Abo, E.; Mervet, G.H. Cytotoxicity and promising anti-biofilm of Curcuma silver nanoparticles against Candida albicans. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2022, 15, 3355–3359. [Google Scholar]
- Oves, M.M.O.; Mohd, A.R.; Mohammad, A.; Huda, A.Q.; Hana, S.; Irfan, A.; Gaffar, S.Z.; Mohd, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Conocarpus lancifolius plant extract and their antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eva, S.-H.; Vicente, G.-G.; Adriana, C.-G.; José, C.-G.; Jesús, M.-G.; Pablo, M.-R. Phytochemical profle and activity against Fusarium species of Tamarix gallica bark aqueous ammonia extract. Agronomy 2023, 13, 496. [Google Scholar]
- Chinnappan, S.; Kandasamy, S.; Arumugam, S.; Seralathan, K.K.; Thangaswamy, S.; Muthusamy, G. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using fower extract of Bauhinia purpurea and its antibacterial activity against clinical pathogens. Env. Sci. Poll. Res. 2018, 25, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.; Priscyla, D.; Marcato, G.I.H.S.; Oswaldo, L.A. Antibacterial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Fungal Process on Textile Fabrics and Their Effluent Treatment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaramoorthi, C.; Dhivya, M.M.; Palanisamy, S.; Vivekanandan, K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Aspergillus niger and evaluation of its wound healing activity in experimental rat model. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2009, 1, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Wankar, S.; Walake, S.; Gumathannavar, R.; Sapre, N.; Kulkarni, A. The era of green nanomaterials for sensing. In Innovations in Green Nanoscience and Nanotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 209–225. [Google Scholar]
- Dat, N.M.; Thinh, D.B.; Huong, L.M.; Tinh, N.T.; Linh, N.T.T.; Hai, N.D.; Viet, N.D.; Dat, N.T.; Phong, M.T.; Hieu, N.H. Facile synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles-modifed graphene oxide hybrid material: The assessment, utilization, and anti-virus potentiality. Mat. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, B.; David, L.; Vulcu, A.; Olenic, L.; Perde-Schrepler, M.; Fischer-Fodor, E.; Baldea, I.; Clichici, S.; Filip, G.A. In vitro and in vivo anti-infammatory properties of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Viburnum opulus L. fruits extract. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanja, K.; Joerger, R.; Olsson, E.; Claes-Göran, G. Silver-based crystalline nanoparticles, microbially fabricated. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 96, 13611–13614. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, L.M.; Chopade, B.A. Plasmid mediated silver resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Biometals 1994, 7, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Ali, N.; Wang, L.; Waseem, H.; Pan, G. Revisiting the mechanistic pathways for bacterial mediated synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 159, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galvez, A.M.; Ramos, K.M.; Alexis, J.T.; Baculi, R. Bacterial exopolysaccharide-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their application on bacterial biofilms. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2019, 9, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hina, S.; Juan, D.; Priyanka, S.; Tae, H.Y. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Pseudomonas sp. THG-LS1. 4 and their antimicrobial application. J. Pharm. Anal. 2018, 8, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniappan, S.; Palaniappan, S.; Subramaniam, P.; Murugesan, S.; Tamilselvi, M.; Loganathan, S.; Kannan, S.; Thangavel, B. Characterization, antimicrobial and antioxidant property of exopolysaccharide mediated silver nanoparticles synthesized by Streptomyces violaceus MM72. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 752–759. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Hamzah, H.; Maaroof, M. Analyzing formation of silver nanoparticles from the filamentous fungus Fusarium oxysporum and their antimicrobial activity. Turk. J. Biol. 2018, 42, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivani, T.J.; Gade, A.C. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Bacillus sp. for Microbial Disease Control: An in-vitro and in-silico approach. Sch. Acad. J. Pharm. 2015, 4, 389–397. [Google Scholar]
- Anima, N.; Saef, M.; Mohammed, T.A.; Gouri, K.D. Fungal mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles andits role in enhancing the bactericidal property of Amoxicillin. Der. Pharm. Lett. 2015, 7, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Salaheldin, T.A.; Husseiny, S.M.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Elzatahry, A.; Cowley, A.H. Evaluation of the cytotoxic behavior of fungal extracellular synthesized Ag nanoparticles using confocal laser scanning microscope. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neethu, S.; Midhun, S.J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K.; Jyothis, M. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles by marine endophytic fungus Penicillium polonicum and its antibacterial efficacy against biofilm forming, multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumanii. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahideh, A.; Iman, S.; Morteza, Y.; Zahra, G. Mangrove-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using native Avicennia marina plant extract from southern Iran. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 205, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Tippayawat, P.; Phromviyo, N.; Boueroy, P.; Chompoosor, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles in aloe vera plant extract prepared by a hydrothermal method and their synergistic antibacterial activity. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siddhant, J.; Mohan, S.M. Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15867. [Google Scholar]
- Gulamnabi, L.; Vanti, V.B.; Nargund, B.K.N.; Rajinikanth, V.; Mahantesh, K.; Sikandar, I.M.; Suresh, T.; Rajashekar, R.P. Synthesis of Gossypium hirsutum-derived silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial efficacy against plant pathogens. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4630. [Google Scholar]
- Dziedzic, A.; Kubina, R.; Bułdak, R.J.; Skonieczna, M.; Cholewa, K. Silver nanoparticles exhibit the dose-dependent anti-proliferative effect against human squamous carcinoma cells attenuated in the presence of berberine. Molecules 2016, 21, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haleem, A.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.-X.; Wang, J.-Y.; Li, H.-J.; Li, P.-Y.; Chen, S.-Q.; He, W.-D. Hybrid cryogels composed of P(NIPAM-co-AMPS) and metal nanoparticles for rapid reduction of p-nitrophenol. Polymer 2020, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldakheel, F.M.; Mohsen, D.; El Sayed, M.M.; Alawam, K.A.; Binshaya, A.S.; Alduraywish, S.A. Silver Nanoparticles Loaded on Chitosan-g-PVA Hydrogel for the Wound-Healing Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, A.; Mohammad, S.; Eskandar, A. Design of AgNPs-Base Starch/PEG-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel for Removal of Mercury (II). J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narjes, N.D.; Mohammad, S. Free radical synthesis of nanosilver/gelatin-poly (acrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogels employed for antibacterial activity and removal of Cu (II) metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 351, 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, J.; Kanoujia, J.; Parashar, P.; Tripathi, C.B.; Saraf, S.A. Wound healing applications of sericin/chitosan-capped silver nanoparticles incorporated hydrogel. Drug Deliv. Translat. Res. 2017, 7, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Vichayarat, R.; Nuttaporn, P.; Pitt, S. In Vitro efficacy and toxicology evaluation of silver nanoparticle-loaded gelatin hydrogel pads as antibacterial wound dressings. J. Appl. Polymer. Sci. 2012, 124, 1668–1682. [Google Scholar]
- Sudheesh Kumar, P.T.; Abhilash, S.; Manzoor, K.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H.; Jayakumar, R. Preparation and characterization of novel β-chitin/nanosilver composite scaffolds for wound dressing applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Kumar, A.; Patil, N.B.; Viswanathan, C.; Ghosh, D. Preparation and characterization of silver nanoparticle loaded amorphous hydrogel of carboxymethylcellulose for infected wounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, K.; Varaprasad, Y.; Murali, M.S.; Ravindra, N.; Narayana, R.; Vimala, K.; Monika, K.; Sreedhar, B.; Mohana, R.K. Hydrogel–Silver nanoparticle composites: A new generation of antimicrobials. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 2010, 115, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, X.L.; Gu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, G.W. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their potential applications to treat cancer. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpita, R.; Chetan, P.; Amel, G.; Mohammed, S.; Alqahtani, M.B.; Saiful, I.; Jamal, H.M.; Mohammed, J. Biologically derived gold nanoparticles and their applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- AMosquera-Romero, S.; Anaya-Garzon, J.; Garcia-Timermans, C.; Van, D.J.; Hoorens, A.; Commenges-Bernole, N.; Verbeken, K.; Rabaey, K.; Varia, J. Combined gold recovery and nanoparticle synthesis in microbial systems using fractional factorial design. Nanomaterials 2022, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karade, V.C.; Dongale, T.D.; Subasa, C.S.; Kollu, P.; Chougale, A.D.; Patil, P.S.; Patil, P. B. Effect of reaction time on structural and magnetic properties of green-synthesized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phy. Chem. Sol. 2018, 120, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, Z.; Norrizah, J.S.; Abdullah, S. Impact of temperature and pH on antioxidant activity of green silver nanoparticles fabricated from Ananas comosus peel extracts. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1019, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, R.H.; Dhandapani, R.; Narayanan, S.; Palanivel, V.; Paramasivam, R.; Subbarayalu, R.; Thangavelu, S.; Muthupandian, S. Medicinal plants mediated the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 16, 114–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd, Q.K.; Praveen, K.; Rais, A.K.; Khursheed, A. Fabrication of sulfur-doped reduced graphene oxide modifed glassy carbon electrode (S@ rGO/GCE) based acetaminophen sensor. Inorganics 2022, 10, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Liyana, R.; Kamalrul, A.A.; Rajinder, S.; Sharifah, N.S.J.; Abrizah, O.; Wolfram, W.; Umi, S.R. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy approach combined with discriminant analysis and prediction model for crude palm oil authentication of diferent geographical and temporal origins. Food Control. 2023, 146, 109509. [Google Scholar]
- Naganthran, A.; Verasoundarapandian, G.; Khalid, F.E.; Masarudin, M.J.; Zulkharnain, A.; Nawawi, N.M.; Karim, M.; Che Abdullah, C.A.; Ahmad, S.A. Synthesis, characterization and biomedical application of silver nanoparticles. Materials 2022, 15, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahari, M.H.; Al, A.A.; Asiri, A.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Shaikh, I.A.; Shettar, A.K.; Hoskeri, J. Green synthesis and characterization of iron nanoparticles synthesized from aqueous leaf extract of Vitex leucoxylon and its biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fang, F.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.; Zhang, K. Biogenic silver nanoparticles-modifed forward osmosis membranes with mitigated internal concentration polarization and enhanced antibacterial properties. NPJ Clean Water 2022, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisreen, J.A.; Ekhlas, A.A.A.G.; Nuha, A.I. Eco-friendly approach for silver nanoparticles synthesis from lemon extract and their anti-oxidant, anti-bacterial, and anti-cancer activities. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect A Chem. 2023, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- Leila, C.; Sanjeev, N.; Julie, M.; Wendy, H.; Karina, D.; Roy, M.K. A retrospective cohort study of ActicoatTM versus SilvazineTM in a paediatric population. Burns 2007, 33, 701–707. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.A.; Bowler, P.G.; Walker, M.; Parsons, D. Controlling wound bioburden with a novel silver-containing HydrofiberR dressing. Wound Repair Regen. 2004, 12, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira, C.; Manisha, P.; Yan, Q.L.; Chea, Y.L.; Cheng, T.L.; Tee, C.L.M.; Huai, S.L.; Yee, P.L.; Cheng, F.L.; Subrat, K.B.; et al. Silver nanoparticles: Advanced and promising technology in diabetic wound therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110925. [Google Scholar]
- Meekul, J.; Chotirosniramit, A.; Himakalasa, W.; Orrapin, S.; Wongthanee, A.; Pongtam, O.; Kulprachakarn, K.; Rerkasem, K. A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Outcome in Comparing an Alginate Silver Dressing with a Conventional Treatment of a Necrotizing Fasciitis Wound. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2017, 16, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, H.M.; Lee, I.J.; Woo, K.J.; Park, B.Y. Silver-Impregnated Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy for the Treatment of Lower-Extremity Open Wounds: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Study. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2019, 32, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zou, Q.; Hamblin, M.R.; Wen, X. A preliminary clinical trial comparing wet silver dressings versus wet-to-dry povidone-iodine dressings for wound healing in pemphigus vulgaris patients. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M.; Elmasry, M.; Steinvall, I.; Sjöberg, F.; Olofsson, P.; Thorfinn, J. Superiority of silver-foam over porcine xenograft dressings for treatment of scalds in children: A prospective randomised controlled trial. Burns 2019, 45, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, T.; Kendirci, M.; Akgün, A.E.; Cetinkaya, E.; Er, S.; Akin, M.; Yasti, A.C. Applying a Silver-containing Dressing to the Incision Site and Its Effect on the Development of Surgical Site Infection After Ostomy Closure: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Pilot Study. Wound Manag. Prev. 2022, 68, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, P.; Gogoi, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Gopinath. Implications of silver nanoparticle induced cell apoptosis for in vitro gene therapy. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 075104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borm, P.J.; Kreyling, W. Toxicological hazards of inhaled nanoparticles—Potential implications for drug delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megan, E.M.; Melissa, J.P. Are nanoparticles potential male reproductive toxicants? A literature review. Nanotoxicology 2007, 1, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.M.; Javorina, A.K.; Schrand, A.M.; Duhart, H.M.; Ali, S.F.; Schlager, J.J. The interaction of manganese nanoparticles with PC-12 cells induces dopamine depletion. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S.M.; Hess, K.L.; Gearhart, J.M.; Geiss, K.T.; Schlager, J. In Vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2005, 19, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braydich-Stolle, L.; Hussain, S.; Schlager, J.J.; Hofmann, M.C.B.-S. In Vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 88, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, D. In Situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by sodium alginate to obtain silver-loaded composite wound dressing with enhanced mechanical and antimicrobial property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, M.; Lui, S.L.; Poon, V.K.M.; Lung, I.; Burd, A. Antimicrobial activities of silver dressings: An in vitro comparison. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sougata, S.; Atish, D.J.; Samir, K.S.; Golam, M. Facile synthesis of silver nano particles with highly efficient anti-microbial property. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 4419–4426. [Google Scholar]
- Kokura, S.; Handa, O.; Takagi, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Silver nanoparticles as a safe preservative for use in cosmetics. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zeng, W.; Yang, T.; Cao, Y.; Mei, C.; Kuang, Y. Toxicity assessment of nanoparticles in various systems and organs. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhanu, W.Z. A review of stabilized silver nanoparticles–synthesis, biological properties, characterization, and potential areas of applications. Nanomed 2016, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, M.K.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Ingle, A.P.; Gade, A.K. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyeh, B.S.; Costagliola, M.; Hayek, S.N.; Dibo, S.A. Effect of silver on burn wound infection control and healing: Review of the literature. Burns. Burns 2007, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franková, J.; Pivodová, V.; Vágnerová, H.; Juráňová, J.; Ulrichová, J. Effects of silver nanoparticles on primary cell cultures of fibroblasts and keratinocytes in a wound-healing model. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2016, 14, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajalekshmi, R.; Sivan, U.; Lissy, K.K.; Kalliyana, K.V. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle incorporated gelatin-hydroxypropyl methacrylate hydrogels for wound dressing applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44529. [Google Scholar]
- Katayoon, K.; Ebrahim, M.; Thomas, J.W.; Amalina, B.M.A. Wound dressings functionalized with silver nanoparticles: Promises and pitfalls. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2268–2291. [Google Scholar]
- Ágnes, S.; Margarita, P.; Krassimira, Y.; Judit, M.; Judith, M.; Pavletta, S. Silver-and sulfadiazine-loaded nanostructured silica materials as potential replacement of silver sulfadiazine. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6283–6292. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, M.; Cochrane, C.A.; Bowler, P.G.; Parsons, D.; Bradshaw, P. Silver deposition and tissue staining associated with wound dressings containing silver. Ostomy Wound Manag. 2006, 52, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Trop, M.; Novak, M.; Rodl, S.; Hellbom, B.; Kroell, W.; Goessler, W. Silver-Coated dressing acticoat caused raised liver enzymes and argyria-like symptoms in burn patient. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2006, 60, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisha, B.S.; Biswas, R.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Jayakumar, R. Chitosan–Hyaluronic acid/nano silver composite sponges for drug resistant bacteria infected diabetic wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geewoo, N.; Sabarinathan, R.; Baskaran, P.; Joon, M.S. The application of bactericidal silver nanoparticles in wound treatment. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2015, 5, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Horbett, T.A.; Ratner, B.D.; Jiang, S. Blood compatibility of surfaces with superlow protein adsorption. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4285–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, T.; Zhao, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Antifouling zwitterionic hydrogel coating improves hemocompatibility of activated carbon hemoadsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 503, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensheng, C.; Eric, C.A.; Ram, B.G. Separation of lignin from aqueous mixtures by ionic and nonionic temperature-sensitive hydrogels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 2283–2288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. In situ synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles on sulfhydryl-functionalized poly(glycidyl methacrylate) micro-spheres for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 6480–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, M.Y.; Kyungjae, L.; Thathan, P.; Kurt, E.G. Hydrogel networks as nanoreactors: A novel approach to silver nanoparticles for antibacterial applica-tions. Polymer 2007, 48, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Mu, J.; Guo, Z.; Liua, Y. “In situ assembly of well-dispersed Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) on electrospun carbon nanofibers (CNFs) for catalytic re-duction of 4-nitrophenol. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3357–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Du, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Encapsulation of AgNPs within Zwitterionic hydrogels for highly efficient and antifouling catalysis in biological environ-ments. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; John, A.J.; Walboomers, X.F.; Yang, F. Antibacterial effect and wound healing ability of silver nanoparticles incorporation into chitosan-based nanofibrous mem-branes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 98, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Bacteria | Precursor | Functional Groups/Organic Components | Condition | Size by (nm) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas | AgNO3 | Amines (Aromatic and Aliphatic) | shaking 28 °C | 10–40 | [38] |
| Streptomyces violaceus | AgNO3 | Exopolysaccharide | shaking; 37 °C pH 7.0 | 10–60 | [39] |
| Fungi | Precursor | Functional Groups/Organic Components | Condition | Size by (nm) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillium polonicum | AgNO3 | Proteins | Shaking Room temp.light | 10–15 | [44] |
| Fusarium oxysporum | AgNO3 | Proteins | shaking 28 °C | 21.3–37.3 | [40] |
| Bacteria | Precursor | Functional Groups/Organic Components | Condition | Size by (nm) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aloe vera (leaf) | AgNO3 | Hemicellulose, lignin, and pectin | 100 °C or 200 °C; shaking | 70.70 ± 22, 192.02 ± 53 | [46] |
| Ocimum sanctum (leaf) | AgNO3 | Quercetin | – | 250–600 | [47] |
| Gossypium hirsutum (shoot) | AgNO3 | – | Shaking 60 °C | 20–100 | [48] |
| Coptis chinensis (leaf) | AgNO3 | – | Room temp.; dark 6–45 | Room temp.; dark 6–45 | [49] |
| Preparation of AgNPs | Size by (nm) for AgNPs | Used Polymer | Method of Incorporation | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green-Synthesized chitosan | 240–970 | Polyacrylamide (chitosan) | The chitosan solution was mixed with the silver nanoparticles | Hydrogel (S/C-SNPs G-1) demonstrated bactericidal activity [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldakheel, F.M.; Sayed, M.M.E.; Mohsen, D.; Fagir, M.H.; El Dein, D.K. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Wound Healing; Systematic Review. Gels 2023, 9, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070530
Aldakheel FM, Sayed MME, Mohsen D, Fagir MH, El Dein DK. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Wound Healing; Systematic Review. Gels. 2023; 9(7):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070530
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldakheel, Fahad M., Marwa M. El Sayed, Dalia Mohsen, Mohammed H. Fagir, and Dalia K. El Dein. 2023. "Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Wound Healing; Systematic Review" Gels 9, no. 7: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070530
APA StyleAldakheel, F. M., Sayed, M. M. E., Mohsen, D., Fagir, M. H., & El Dein, D. K. (2023). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Wound Healing; Systematic Review. Gels, 9(7), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070530