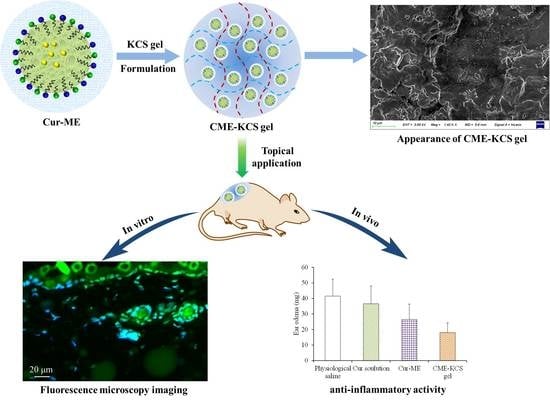
Microemulsion-Based Keratin–Chitosan Gel for Improvement of Skin Permeation/Retention and Activity of Curcumin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of KCS Conjugate
2.2. Characterization of Cur-ME and CME-KCS Gel
2.2.1. Visual Inspection and Dyeing Test
2.2.2. Size and Zeta Potential
2.2.3. SEM Imaging
2.2.4. pH and Viscosity
2.2.5. XRD Study
2.2.6. Spreadability of CME-KCS Gel
2.2.7. Bioadhesion of CME-KCS Gel
2.3. In Vitro Release
2.4. Skin Permeation and Retention
2.5. Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging
2.6. Hematoxylin–Eosin Staining
2.7. Assessment of Analgesic Activity
2.8. Assessment of Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.9. In Vivo Skin Irritation
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis and Characterization of KCS Conjugate
4.3. Development of Cur-ME and CME-KCS Gel
4.4. Characterization of Cur-ME and CME-KCS Gel
4.4.1. Visual Inspection and Dyeing Test
4.4.2. Measurement of Size and Zeta Potential
4.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Imaging
4.4.4. Determination of pH and Viscosity
4.4.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.4.6. Spreadability Test of CME-KCS Gel
4.4.7. Bioadhesion Study of CME-KCS Gel
4.5. In Vitro Drug Release Study
4.6. In Vitro Skin Permeation and Retention Study
4.6.1. Preparation of Rat Skin
4.6.2. In Vitro Skin Permeation Study
4.6.3. Skin Retention Study
4.7. Fluorescence Imaging
4.8. Hematoxylin–Eosin Staining
4.9. Analgesic Activity Evaluation
4.10. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Evaluation
4.11. Skin Irritation Test
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basto, R.; Andrade, R.; Nunes, C.; Lima, S.A.C.; Reis, S. Topical Delivery of Niacinamide to Skin Using Hybrid Nanogels Enhances Photoprotection Effect. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.N.; Mohapatra, D. Nanovesicular transferosomes for the topical delivery of plant bioactives. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 2491–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.R.; Al-Harbi, F.F.; Nawaz, A.; Amin, A.; Farid, A.; Mohaini, M.A.; Alsalman, A.J.; Hawaj, M.A.A.; Alhashem, Y.N. Formulation and Characterization of Chitosan-Decorated Multiple Nanoemulsion for Topical Delivery In Vitro and Ex Vivo. Molecules 2022, 27, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, Y.H. Application of Cellular Resolution Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography in vivo for the Diagnosis of Skin Tumours and Inflammatory Skin Diseases: A Pilot Study. Dermatology 2022, 238, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Sahoo, P.K.; Manchanda, S. Curcumin Loaded Ethosomal Gel for Improved Topical Delivery: Formulation, Characterization and Ex-vivo Studies. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2021, 9, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Ya, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Hyaluronic Acid Micelles for Promoting the Skin Permeation and Deposition of Curcumin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 4009–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.L.; Fan, Z.L.; Yuan, J.D.; Chen, P.P.; Yang, J.J.; Xu, J.; ZhuGe, D.L.; Jin, B.H.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Shen, B.X.; et al. Skin-penetrating polymeric nanoparticles incorporated in silk fibroin hydrogel for topical delivery of curcumin to improve its therapeutic effect on psoriasis mouse model. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, P.; Jain, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Keshari, M.K. Systematic development and characterization of curcumin-loaded nanogel for topical application. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 1443–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, E.; Zeeshan, M.; Ain, Q.U.; Khan, A.U.; Hussain, I.; Khan, S.; Lepeltier, E.; Ali, H. Topical delivery of curcumin-loaded transfersomes gel ameliorated rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting NF-kappabeta pathway. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghule, T.; Gorantla, S.; Rapalli, V.K.; Shah, P.; Dubey, S.K.; Saha, R.N.; Singhvi, G. Emerging Trends in Topical Delivery of Curcumin Through Lipid Nanocarriers: Effectiveness in Skin Disorders. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, N.; Ahmad, I.; Zulfakar, M.H.; Kargarzadeh, H.; Ramli, S. Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-nanocrystalline cellulose (CTAB-NCC) based microemulsions for enhancement of topical delivery of curcumin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, T.M.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Elsewedy, H.S. Curcumin Niosomes Prepared from Proniosomal Gels: In Vitro Skin Permeability, Kinetic and In Vivo Studies. Polymers 2021, 13, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazim, T.; Tariq, A.; Usman, M.; Ayoob, M.F.; Khan, A. Chitosan hydrogel for topical delivery of ebastine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for alleviation of allergic contact dermatitis. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 37413–37425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, B.J.; Garg, N.K.; Beg, S.; Singh, B.; Katare, O.P. Nanosized ethosomes-based hydrogel formulations of methoxsalen for enhanced topical delivery against vitiligo: Formulation optimization, in vitro evaluation and preclinical assessment. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asad, M.I.; Khan, D.; Rehman, A.U.; Elaissari, A.; Ahmed, N. Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Polymeric Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for the Management of Psoriasis. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaia, L.; Olariu, I.; Mut, A.M.; Coneac, G.; Vlaia, V.; Anghel, D.F.; Maxim, M.E.; Stanga, G.; Dobrescu, A.; Suciu, M.; et al. New, Biocompatible, Chitosan-Gelled Microemulsions Based on Essential Oils and Sucrose Esters as Nanocarriers for Topical Delivery of Fluconazole. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Canales, I.C.; Delgado-Buenrostro, N.L.; Chirino, Y.I.; Nava-Arzaluz, G.; Pinon-Segundo, E.; Martinez-Cruz, G.; Ganem-Rondero, A. Curcumin-loaded microemulsion: Formulation, characterization, and in vitro skin penetration. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2023, 49, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir Siddique, M.; Nazar, M.F.; Mahmood, M.; Saleem, M.A.; Alwadai, N.; Almuslem, A.S.; Alshammari, F.H.; Haider, S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Hussain, S.Z.; et al. Microemulsified Gel Formulations for Topical Delivery of Clotrimazole: Structural and In Vitro Evaluation. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13767–13777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Pol, A.; Kalaria, D.; Date, A.A.; Kalia, Y.; Patravale, V. Microemulsion-based gel for the transdermal delivery of rasagiline mesylate: In vitro and in vivo assessment for Parkinson’s therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 165, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payyal, S.P.; Rompicherla, N.C.; Sathyanarayana, S.D.; Shriram, R.G.; Vadakkepushpakath, A.N. Microemulsion Based Gel of Sulconazole Nitrate for Topical Application. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 17, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, T.T.; Ou, G.; Hu, X.B.; Tang, T.T.; Wang, J.M.; Liu, X.Y.; Xiang, D.X. Microemulsions vs chitosan derivative-coated microemulsions for dermal delivery of 8-methoxypsoralen. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, D.A.J.; Amaral, J.G.; Garcia, L.B.; Dos Santos, M.S.; Silva, L.A.O.; Almeida, M.P.; Gomes, A.F.; Barros, D.R.P.; Lopes, N.P.; Pereira, G.R.; et al. Associating chitosan and microemulsion as a topical vehicle for the administration of herbal medicines. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ta, Q.; Ting, J.; Harwood, S.; Browning, N.; Simm, A.; Ross, K.; Olier, I.; Al-Kassas, R. Chitosan nanoparticles for enhancing drugs and cosmetic components penetration through the skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 160, 105765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, S.; Lu, Y.; Lai, R.; Liu, Z.; Luo, W.; Xu, Y. Chitosan/hyaluronan nanogels co-delivering methotrexate and 5-aminolevulinic acid: A combined chemo-photodynamic therapy for psoriasis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojanowska, D.J.; Suarato, G.; Braccia, C.; Armirotti, A.; Fiorentini, F.; Athanassiou, A.; Perotto, G. Wool Keratin Nanoparticle-Based Micropatterns for Cellular Guidance Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 15272–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Ramirez, D.O.; Cruz-Maya, I.; Vineis, C.; Tonetti, C.; Varesano, A.; Guarino, V. Design of Asymmetric Nanofibers-Membranes Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol and Wool-Keratin for Wound Healing Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Han, X.; Wang, L.; Yuan, J.; Meng, X.; Xiao, Y. Preparation and characterization of Keratin-PEG conjugate-based micelles as a tumor microenvironment-responsive drug delivery system. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, T.; Xie, D.; Zhu, R.; Chen, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; He, L. RGD/TAT-functionalized chitosan-graft-PEI-PEG gene nanovector for sustained delivery of NT-3 for potential application in neural regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yi, Z.; Cui, X.; Chen, X.; Su, W.; Ren, X.; Li, X. Tumor-targeted and nitric oxide-generated nanogels of keratin and hyaluronan for enhanced cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12109–12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, A.A.S.; Kumar, G.S.V. PEG grafted chitosan scaffold for dual growth factor delivery for enhanced wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikumbh, K.V.; Sevankar, S.G.; Patil, M.P. Formulation development, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of microemulsion-based gel loaded with ketoprofen. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Prabhavalkar, K.S.; Bhatt, L.K. Preparation, optimization, and evaluation of Zaltoprofen-loaded microemulsion and microemulsion-based gel for transdermal delivery. J. Liposome Res. 2016, 26, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Yuan, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ya, H.; Fan, Y. Silk peptide-hyaluronic acid based nanogels for the enhancement of the topical administration of curcumin. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1028372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Iscaro, A.; Zambito, G.; Mijiti, Y.; Minicucci, M.; Essand, M.; Lowik, C.; Muthana, M.; Censi, R.; Mezzanotte, L.; et al. Development of a New Hyaluronic Acid Based Redox-Responsive Nanohydrogel for the Encapsulation of Oncolytic Viruses for Cancer Immunotherapy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.E.; Elgammal, W.E.; Eid, A.M.; Dawaba, A.M.; Ibrahim, A.G.; Fouda, A.; Hassan, S.M. Synthesis and characterization of new functionalized chitosan and its antimicrobial and in-vitro release behavior from topical gel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgountzou, A.; Papadopoulos, N.G. Postnatal Innate Immune Development: From Birth to Adulthood. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, T.; Xu, T.; Pan, J.; Qin, M.; Pan, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Z.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y. Microemulsion based gel for topical dermal delivery of pseudolaric acid B: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 493, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, H.; Novitasari, E.; Purnami, N.L.W.; Mahbub, A.W.; Sari, R.; Setyawan, D. Formulation Design and Cell Cytotoxicity of Curcumin-Loaded Liposomal Solid Gels for Anti-Hepatitis C Virus. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 2022, 3336837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, W.E.; Shehata, T.M.; Mohamed, M.E.; Younis, N.S.; Elsewedy, H.S. Enhancement of Curcumin Anti-Inflammatory Effect via Formulation into Myrrh Oil-Based Nanoemulgel. Polymers 2021, 13, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.K.; Barot, B.S.; Parejiya, P.B.; Shelat, P.K.; Shukla, A. Topical delivery of clobetasol propionate loaded microemulsion based gel for effective treatment of vitiligo--part II: Rheological characterization and in vivo assessment through dermatopharmacokinetic and pilot clinical studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 119, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.M.; de Oliveira, E.G.; Coradini, K.; Bruinsmann, F.A.; Aguirre, T.; Lorenzoni, R.; Barcelos, R.C.S.; Roversi, K.; Rossato, D.R.; Pohlmann, A.R.; et al. Chitosan hydrogels containing nanoencapsulated phenytoin for cutaneous use: Skin permeation/penetration and efficacy in wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 96, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contri, R.V.; Katzer, T.; Ourique, A.F.; da Silva, A.L.; Beck, R.C.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Combined effect of polymeric nanocapsules and chitosan hydrogel on the increase of capsaicinoids adhesion to the skin surface. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Su, W.; Ma, L.; Tan, Y.; Yi, Z.; Li, X. Developing exquisite collagen fibrillar assemblies in the presence of keratin nanoparticles for improved cellular affinity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moqejwa, T.; Marimuthu, T.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E. Development of Stable Nano-Sized Transfersomes as a Rectal Colloid for Enhanced Delivery of Cannabidiol. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshiri, M.K.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Shahraky, M.K.; Rahimi, F. Lecithin soybean phospholipid nano-transfersomes as potential carriers for transdermal delivery of the human growth hormone. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 9023–9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryab, M.; Faizi, M.; Mahboubi, A.; Aboofazeli, R. Preparation and Characterization of Lidocaine-Loaded, Microemulsion-Based Topical Gels. Iran J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2022, 21, e123787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.; Pani, N.R.; Sahoo, S.K. Effect of microemulsion in topical sertaconazole hydrogel: In vitro and in vivo study. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, F.; Ragno, G.; Muzzalupo, R.; Occhiuzzi, M.A.; Mazzotta, E.; Luca, M.; Garofalo, A.; Ioele, G. Gel Formulation of Nabumetone and a Newly Synthesized Analog: Microemulsion as a Photoprotective Topical Delivery System. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.B.; Kang, R.R.; Tang, T.T.; Li, Y.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Liu, X.Y.; Xiang, D.X. Topical delivery of 3,5,4’-trimethoxy-trans-stilbene-loaded microemulsion-based hydrogel for the treatment of osteoarthritis in a rabbit model. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrotriya, S.; Ranpise, N.; Satpute, P.; Vidhate, B. Skin targeting of curcumin solid lipid nanoparticles-engrossed topical gel for the treatment of pigmentation and irritant contact dermatitis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almawash, S.; Quadir, S.S.; Al Saqr, A.; Sharma, G.; Raza, K. Dual Delivery of Fluticasone Propionate and Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride for the Management of Atopic Dermatitis Using a Microemulsion-Based Topical Gel. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7696–7705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Lv, Y.; Huang, W.; Fang, Z.; Qi, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y. Enhanced transdermal delivery of curcumin nanosuspensions: A mechanistic study based on co-localization of particle and drug signals. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhai, G. Ropivacaine loaded microemulsion and microemulsion-based gel for transdermal delivery: Preparation, optimization, and evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulvi, F.A.; Pillai, L.V.; Patel, K.P.; Desai, A.R.; Shukla, M.R.; Desai, D.T.; Patel, H.P.; Ranch, K.M.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, D.O. Lidocaine tripotassium phosphate complex laden microemulsion for prolonged local anaesthesia: In vitro and in vivo studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Liang, Q.; Feng, P.; Li, C.; Yang, C.; Liang, H.; Tang, H.; Shuai, C. A Novel Brucine Gel Transdermal Delivery System Designed for Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Luo, D.D.; Xie, J.H.; Xian, Y.F.; Lai, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, W.H.; Chen, J.N.; Lai, X.P.; Lin, Z.X.; et al. Curcumin’s Metabolites, Tetrahydrocurcumin and Octahydrocurcumin, Possess Superior Anti-inflammatory Effects in vivo Through Suppression of TAK1-NF-kappaB Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Yang, Y.; Du, S.; Yang, X.; Pang, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, S. Preparation of a recombinant collagen-peptide (RHC)-conjugated chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 119, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qindeel, M.; Ahmed, N.; Sabir, F.; Khan, S.; Ur-Rehman, A. Development of novel pH-sensitive nanoparticles loaded hydrogel for transdermal drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shen, B.D.; Shen, C.Y.; Zhong, R.N.; Wang, X.H.; Yuan, H.L. Nanoparticle-loaded gels for topical delivery of nitrofurazone: Effect of particle size on skin permeation and retention. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukale, S.S.; Sharma, S.; Dalela, M.; Singh, A.K.; Mohanty, S.; Mittal, A.; Chitkara, D. Multi-component clobetasol-loaded monolithic lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles ameliorate imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in Swiss albino mice. Acta Biomater. 2020, 115, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Yaqoob, S.; Madni, A.; Akhtar, M.F.; Sohail, M.F.; Saleem, A.; Tahir, N.; Khan, K.U.; Qureshi, O.S. Development and In Vitro/Ex Vivo Evaluation of Lecithin-Based Deformable Transfersomes and Transfersome-Based Gels for Combined Dermal Delivery of Meloxicam and Dexamethasone. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8170318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurakula, M.; Ahmed, O.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, T.A. Solid lipid nanoparticles for transdermal delivery of avanafil: Optimization, formulation, in-vitro and ex-vivo studies. J. Liposome Res. 2016, 26, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, J.; Yuan, M.; Gao, P.; Wang, L.; Qi, Y.; Chen, J.; Bai, K.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X. Microemulsion-Based Keratin–Chitosan Gel for Improvement of Skin Permeation/Retention and Activity of Curcumin. Gels 2023, 9, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070587
Niu J, Yuan M, Gao P, Wang L, Qi Y, Chen J, Bai K, Fan Y, Liu X. Microemulsion-Based Keratin–Chitosan Gel for Improvement of Skin Permeation/Retention and Activity of Curcumin. Gels. 2023; 9(7):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070587
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Jiangxiu, Ming Yuan, Panpan Gao, Liye Wang, Yueheng Qi, Jingjing Chen, Kaiyue Bai, Yanli Fan, and Xianming Liu. 2023. "Microemulsion-Based Keratin–Chitosan Gel for Improvement of Skin Permeation/Retention and Activity of Curcumin" Gels 9, no. 7: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070587
APA StyleNiu, J., Yuan, M., Gao, P., Wang, L., Qi, Y., Chen, J., Bai, K., Fan, Y., & Liu, X. (2023). Microemulsion-Based Keratin–Chitosan Gel for Improvement of Skin Permeation/Retention and Activity of Curcumin. Gels, 9(7), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9070587