Slug Translational Velocity for Highly Viscous Oil and Gas Flows in Horizontal Pipes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Description of Test Facility
3.2. Flow Facility Instrumentation, Data Acquisition and Processing
3.2.1. Thermocouples and Pressure Transducers
3.2.2. Gamma Densitometers
3.3. Fluid Properties
4. Results
4.1. Flow Regime Map
4.2. Mechanism of Slug Flow Formation and Liquid Viscosity on Translational Velocity
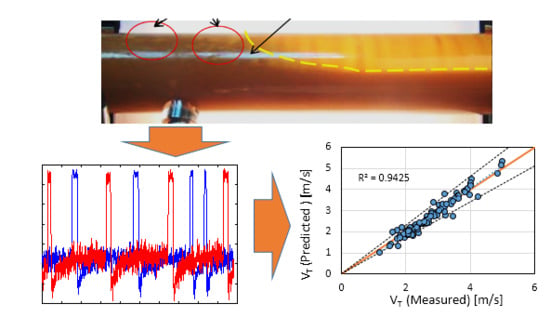
5. Correlation of Slug Translational Velocity Data
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbols | Denotes | Units |
| A | Area | m2 |
| C | Constant | [-] |
| D | Pipe diameter | m |
| Fr | Froude number | [-] |
| fs | Slug Frequency | s−1 |
| g | Acceleration due to gravity | m. s−2 |
| L | length | m |
| N | Viscosity number | [-] |
| HL | Holdup | [-] |
| HF | Average film holdup | [-] |
| HS | Average slug holdup | [-] |
| N | Inverse viscosity number | [-] |
| Re | Reynolds number | [-] |
| St | Strouhal number | [-] |
| Vm | Mixture Velocity | m/s |
| Ls | Liquid slug length | m |
| VT | Translational velocity | m/s |
| Greek letters | ||
| Viscosity | cP | |
| Density | kg/m3 | |
| Shear stress | Pa | |
| Relative error | [-] | |
| Subscripts | ||
| f | Film zone | |
| g | Gas phase | |
| l | Liquid phase | |
| m | Mixture phase | |
| s | Superficial | |
| t | Translational |
Appendix A
References
- Baba, Y.D.; Aliyu, A.M.; Archibong, A.E.; Almabrok, A.A.; Igbafe, A.I. Study of high viscous multiphase phase flow in a horizontal pipe. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 54, 651–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.; Behnia, M. Pressure drop calculation and modelling of inclined intermittent gas–liquid flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 4699–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.J.; Shonham, O.; Brill, J.P. A Comprehensive Mechanistic Model for Two-Phase Flow in Pipelines. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–26 September 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Sarica, C.; Pereyra, E. A Mechanistic Slug Liquid Holdup Model for Wide Ranges of Liquid Viscosity and Pipe Inclination Angle. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 6–9 May 2013; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.-Q.; Wang, Q.; Sarica, C.; Brill, J.P. Unified Model for Gas-Liquid Pipe Flow via Slug Dynamics−Part 1: Model Development. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2003, 125, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibong-Eso, A.; Okeke, N.; Baba, Y.; Aliyu, A.; Lao, L.; Yeung, H. Estimating slug liquid holdup in high viscosity oil-gas two-phase flow. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2019, 65, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibong-Eso, A.; Baba, Y.; Aliyu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, W.; Yeung, H. On slug frequency in concurrent high viscosity liquid and gas flow. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 163, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokcal, B. Effects of High Oil Viscosity on Oil/Gas Flow Behavior in Horizontal Pipes. Master’s Thesis, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gokcal, B. An Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of Slug Flow for High Oil Viscosity in Horizontal Pipes. Ph.D. Thesis, The University Tulsa, Tulsa, OK, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. High Viscosity Liquid Two-Phase Flow. Ph.D Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Archibong, A. Viscous Multiphase Flow Characteristics in Pipelines. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, Y.D. Experimental Investigation of High Viscous Multiphase Flow in Horizontal Pipelines. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, Y.D.; Archibong, A.E.; Aliyu, A.M.; Ameen, A.I. Slug frequency in high viscosity oil-gas two-phase flow: Experiment and prediction. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2017, 54, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklin, D.; Wilkes, J.; Davidson, J. Two Phase Flow in Vertical tubes. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1962, 40, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, G. a.; Scott, D.S. Correlation of liquid slug velocity and frequency in horizontal cocurrent gas-liquid slug flow. AIChE J. 1969, 15, 933–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, L.; Gregory, G.A. Air-Oil slug flow in an upward-inclined pipe-I: Slug velocity, holdup and pressure gradient. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 1974, 13, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukler, A.E.; Hubbard, M.G. A Model for Gas-Liquid Slug Flow in Horizontal and Near Horizontal Tubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1975, 14, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, M.K.; Aziz, K.; Gregory, G.A. Intermittent Two Phase Flow in Horizontal Pipes: Predictive Models. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1978, 56, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukler, A.E.; Maron, D.M.; Brauner, N. A Physical Model For Predicting The Minimum Stable Slug Length. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1985, 40, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, G.E.; Jepson, W.P. The Flow of Slugs in Horizontal, Two-Phase Pipelines. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1990, 112, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J. Gas Entrainment in Two-Phase Gas-Liquid Slug Flow. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, R.; Pereyra, E.; Sarica, C. Experimental study to characterize slug flow for medium oil viscosities in horizontal pipes. In Proceedings of the 9th North American Conference on Multiphase Technology, Banff, AB, Canada, 11–13 June 2014; pp. 403–417. [Google Scholar]
- Al Awadi, H. Multiphase Characteristics of High Viscosity Oil. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyachandra, B.C.; Gokcal, B.; Al-Sarkhi, A.; Serica, C.; Sharma, A.K. Drift-Velocity Closure Relationships for Slug Two-Phase High-Viscosity Oil Flow in Pipes. Soc. Pet. Eng. 2012, 17, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-kayiem, H.H.; Mohmmed, A.O.; Al-hashimy, Z.I.; Time, R.W. Statistical assessment of experimental observation on the slug body length and slug translational velocity in a horizontal pipe. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 105, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendiksen, K.H.; Langsholt, M.; Liu, L. An experimental investigation of the motion of long bubbles in high viscosity slug flow in horizontal pipes. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 104, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moissis, R.; Griffith, P. Entrance Effects in Slug Flow. In Proceedings of the Transaction of American Society of Mechanical Engineers (A.S.M.E.), New York, NY, USA, 1 February 1962; pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fabre, J.; Line, A. Modeling of Two-Phase Slug Flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1992, 24, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, I.G. High Pressure Gas-Liquid Slug Flow. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, B.D.; Hanratty, T.J. Relation of slug stability to shedding rate. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1996, 22, 809–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petalas, N.; Aziz, K. A Mechanistic Model for Multiphase Flow in Pipes. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2000, 39, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Pereyra, E.; Sarica, C.; Park, C.; Kang, J. An Efficient Drift-Flux Closure Relationship to Estimate Liquid Holdups of Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flow in Pipes. Energies 2012, 5, 5294–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.W.; Aydin, T.B.; Pereyra, E.; Sarica, C. Detailed flow field measurements and analysis in highly viscous slug flow in horizontal pipes. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 106, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y.D.; Aliyu, A.M.; Archibong, A.E.; Abdulkadir, M.; Lao, L.; Yeung, H. Slug length for high viscosity oil-gas flow in horizontal pipes: Experiments and prediction. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 165, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, D.H.; Brill, J.P. A Study of Two-Phase Flow in Inclined Pipes. J. Pet. Technol. 1973, 25, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taitel, Y.; Dukler, A.E. A model for predicting flow regime transitions in horizontal and near horizontal gas-liquid flow. AIChE J. 1976, 22, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.; Pereyra, E.; Sarica, C. Effect of Medium Oil Viscosity on Two-Phase Oil-Gas Flow Behavior in Horizontal Pipes. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 6–9 May 2013; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lao, L.; Yeung, H. Investigation and prediction of slug flow characteristics in highly viscous liquid and gas flows in horizontal pipes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 102, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-safran, E.; Gokcal, B.; Sarica, C. High Viscosity Liquid Effect on Two-Phase Slug Length in Horizontal Pipes. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Multiphase Production Technology, Cannes, France, 15–17 June 2011; pp. 257–276. [Google Scholar]
- Al-safran, E.M.; Gokcal, B.; Sarica, C. Investigation and Prediction of High-Viscosity Liquid Effect on Two-Phase Slug Length in Horizontal Pipelines. SPE Prod. Oper. 2013, 28, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokcal, B.; Sarica, C. Analysis and Prediction of Heavy Oil Two-Phase Slug Length in Horizontal Pipelines. In Proceedings of the SPE Heavy Oil Conference and Exhibition, Kuwait City, Kuwait, 12–14 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wallis, G.B. One-Dimensional Two-Phase Flow; American Institute of Chemical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Lacy, C.E. Applicability of Slug Flow Models to Heavy Oils. In Proceedings of the SPE Heavy Oil Conference Canada, Calgary, AB, Canada, 12–14 June 2012; pp. 266–275. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, M.G. An Analysis of Horizontal Gas-liquid Slug Flow. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Houston, Houston, TX, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, W.P. Modelling the transition to slug flow in horizontal conduit. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1989, 67, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, G.E. Horizontal Slug Flow Modeling and Metering; University of Tulsa: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, B. Gravity currents and related phenomena. J. Fluid Mech 1968, 31, 209–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokcal, B.; Al-Sarkhi, A.; Sarica, C.; Alsafran, E.M. Prediction of Slug Frequency for High Viscosity Oils in Horizontal Pipes. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 4–7 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Safran, E. Investigation and prediction of slug frequency in gas/liquid horizontal pipe flow. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2009, 69, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, C.; Sarica, C.; Zhang, H.; Al-Sarkhi, A.; Al-Safran, E. Effects of High Oil Viscosity on Slug Liquid Holdup in Horizontal Pipes. In Proceedings of the Canadian Unconventional Resources Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–17 November 2011. [Google Scholar]









| Authors/Year | Experimental Conditions | Model/Correlations Developed for Slug Translational Velocity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nicklin et al. [14] | Theoretical model | 1.2 at high Reynolds numbers and 2.0 at low Reynolds numbers | |
| Moissis and Griffith [27] | Theoretical model | – | |
| Gregory and Scott [15] | Theoretical model | 1.35 | |
| Mattar and Gregory [16] | Air-oil(9 cP) horizontal to 10o incline | 1.32 | – |
| Dukler and Hubbard [17] | Air-water; 3.75 m horizontal pipe | . | |
| Nicholson et al. [18] | Theoretical model validated with air-oil horizontal flow data | ||
| Dukler et al. [19] | 1.225 | ||
| Kouba and Jepson [20] | Air-water, Diameter= 0.15 m, | – | . |
| Fabre and Line [28] | – | – | |
| Manolis [29] | – | – | |
| Woods and Hanratty [30] | Horizontal air-water in a 0.0953-m pipe at atmospheric pressure | ||
| Petalas and Aziz [31] | – | – | |
| Choi et al. [32] | Air-water/light oil inclinations of -10o to 10o | – | |
| Archibong [11] | Air-oil in two horizontal pipes of 0.0508, 0.0762 m internal diameter | , and were respectively obtained as 0.272, 0.236, 0.471 and 17.143 | – |
| Kim et al. [33] | Air-oil in a horizontal pipe of internal diameters: 0.0508 and 0.0762 m | Where are and are the in-situ maximum liquid and superficial liquid velocities at each PIV x-grid. | – |
| ; ;; | |||
| Density (kg/m3) | Test Fluids | Viscosity (cP) | Interfacial Tension (25 °C, N/m) | Test Matrix (m/s) | API Gravity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.293 | Air | 0.017 | 0.033 | 0.3–9.0 | - |
| ≈918 | CYL680 | 1000~6000 | 0.033 | 0.06–0.3 | 22.67 |
| Measurement | Uncertainty (%) | ||||
| Superficial liquid velocity | ±0.5 | ||||
| Superficial gas velocity | ±2.1 | ||||
| Liquid viscosity | ±1 | ||||
| Pressure drop | ±2 | ||||
| Liquid holdup | ±10 | ||||
| Nicklin [14] | Hubbard [44] | Benjamin, [47] | Kouba [46] | Jepson [45] | Jeyachandra et al. [24] | Choi et al. [32] | Eqn. 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −19.85 | −58.20 | −19.85 | −57.63 | −54.32 | −33.22 | −7.67 | −0.31 | |
| 20.96 | 58.20 | 20.96 | 57.63 | 54.32 | 33.35 | 17.79 | 8.05 | |
| 10.61 | 8.64 | 10.61 | 6.95 | 14.96 | 12.16 | 31.31 | 6.55 | |
| −0.54 | −1.59 | −1.59 | −1.59 | −1.44 | −0.88 | −0.11 | 0.00 | |
| 0.56 | 1.59 | 1.59 | 1.59 | 1.44 | 0.89 | 0.54 | 0.21 | |
| 0.29 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 1.43 | 0.26 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baba, Y.D.; Archibong-Eso, A.; Aliyu, A.M.; Fajemidupe, O.T.; Ribeiro, J.X.F.; Lao, L.; Yeung, H. Slug Translational Velocity for Highly Viscous Oil and Gas Flows in Horizontal Pipes. Fluids 2019, 4, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids4030170
Baba YD, Archibong-Eso A, Aliyu AM, Fajemidupe OT, Ribeiro JXF, Lao L, Yeung H. Slug Translational Velocity for Highly Viscous Oil and Gas Flows in Horizontal Pipes. Fluids. 2019; 4(3):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids4030170
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaba, Yahaya D., Archibong Archibong-Eso, Aliyu M. Aliyu, Olawale T. Fajemidupe, Joseph X. F. Ribeiro, Liyun Lao, and Hoi Yeung. 2019. "Slug Translational Velocity for Highly Viscous Oil and Gas Flows in Horizontal Pipes" Fluids 4, no. 3: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids4030170
APA StyleBaba, Y. D., Archibong-Eso, A., Aliyu, A. M., Fajemidupe, O. T., Ribeiro, J. X. F., Lao, L., & Yeung, H. (2019). Slug Translational Velocity for Highly Viscous Oil and Gas Flows in Horizontal Pipes. Fluids, 4(3), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids4030170