The Lifetimes of Evaporating Sessile Droplets of Water Can Be Strongly Influenced by Thermal Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Fully Coupled Model
2.1. Governing Equations and Boundary Conditions
2.2. Numerical Implementation and Validation
2.3. Parameter Values
3. The Physical Mechanism Controlling Evaporation
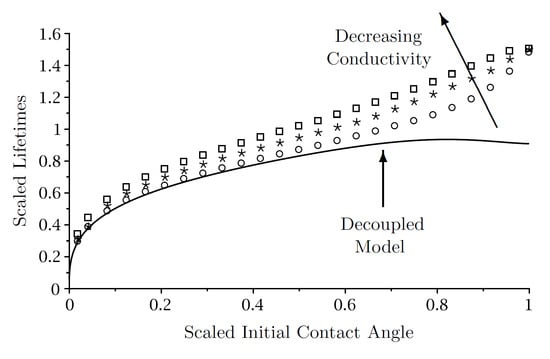
4. The Lifetime of a Droplet
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larson, R.G. Transport and deposition patterns in drying sessile droplets. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 1538–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brutin, D.; Starov, V. Recent advances in droplet wetting and evaporation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 558–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgiutti-Dauphiné, F.; Pauchard, L. Drying drops. Eur. Phys. J. E 2018, 41, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picknett, R.G.; Bexon, R. The evaporation of sessile or pendant drops in still air. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1977, 61, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askounis, A.; Orejon, D.; Koutsos, V.; Sefiane, K.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Nanoparticle deposits near the contact line of pinned volatile droplets: Size and shape revealed by atomic force microscopy. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4152–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orejon, D.; Sefiane, K.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Stick–slip of evaporating droplets: Substrate hydrophobicity and nanoparticle concentration. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12834–12843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.H.; Nguyen, A.V. Increased evaporation kinetics of sessile droplets by using nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16725–16728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Garimella, S.V. Droplet evaporation dynamics on a superhydrophobic surface with negligible hysteresis. Langmuir 2013, 29, 10785–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauber, J.M.; Wilson, S.K.; Duffy, B.R.; Sefiane, K. On the lifetimes of evaporating droplets. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 744, R2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stauber, J.M.; Wilson, S.K.; Duffy, B.R.; Sefiane, K. On the lifetimes of evaporating droplets with related initial and receding contact angles. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 122101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stauber, J.M.; Wilson, S.K.; Duffy, B.R.; Sefiane, K. Evaporation of droplets on strongly hydrophobic substrates. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3653–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitrich, E.; Kooij, E.S.; Zhang, X.; Zandvliet, H.J.W.; Lohse, D. Stick-jump mode in surface droplet dissolution. Langmuir 2015, 31, 4696–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Bao, L.; Dietrich, E.; van der Veen, R.C.A.; Peng, S.; Friend, J.; Zandvliet, H.J.W.; Yeo, L.; Lohse, D. Mixed mode of dissolving immersed nanodroplets at a solid–water interface. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, F.G.H.; Wilson, S.K.; Pritchard, D.; Sefiane, K. The lifetimes of evaporating sessile droplets are significantly extended by strong thermal effects. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 851, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Z.; Weibel, J.A.; Garimella, S.V. Transport mechanisms during water droplet evaporation on heated substrates of different wettability. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 152, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, A.W.; Duffy, B.R.; Wilson, S.K. Competitive evaporation of multiple sessile droplets. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 884, A45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, G.J.; Wilson, S.K.; Duffy, B.R.; David, S.; Sefiane, K. A mathematical model of the evaporation of a thin sessile liquid droplet: Comparison between experiment and theory. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 323, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, G.J.; Wilson, S.K.; Duffy, B.R.; David, S.; Sefiane, K. The strong influence of substrate conductivity on droplet evaporation. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 623, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sefiane, K.; Wilson, S.K.; David, S.; Dunn, G.J.; Duffy, B.R. On the effect of the atmosphere on the evaporation of sessile droplets of water. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 062101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sefiane, K.; Bennacer, R. An expression for droplet evaporation incorporating thermal effects. J. Fluid Mech. 2011, 667, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobac, B.; Brutin, D. Thermal effects of the substrate on water droplet evaporation. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 021602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ait Saada, M.; Chikh, S.; Tadrist, L. Evaporation of a sessile drop with pinned or receding contact line on a substrate with different thermophysical properties. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 58, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.C.; Bonaccurso, E.; Gambaryan-Roisman, T.; Stephan, P. Influence of the substrate thermal properties on sessile droplet evaporation: Effect of transient heat transport. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 432, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diddens, C.; Tan, H.; Lv, P.; Versluis, M.; Kuerten, J.G.M.; Zhang, X.; Lohse, D. Evaporating pure, binary and ternary droplets: Thermal effects and axial symmetry breaking. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 823, 470–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schofield, F.G.H. Mathematical Modelling of Droplet Evaporation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Nagel, S.R.; Witten, T.A. Capillary flow as the cause of ring stains from dried liquid drops. Nature 1997, 389, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, Y.O. Evaporative deposition patterns: Spatial dimensions of the deposit. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 036313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- COMSOLMultiphysics v. 5.4. COMSOL AB, Stockholm, Sweden. Available online: www.comsol.com (accessed on 3 December 2018).
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Analysis of the effects of Marangoni stresses on the microflow in an evaporating sessile droplet. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidzadeh-Bonn, N.; Rafaï, S.; Azouni, A.; Bonn, D. Evaporating droplets. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 549, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristenpart, W.D.; Kim, P.G.; Domingues, C.; Wan, J.; Stone, H.A. Influence of substrate conductivity on circulation reversal in evaporating drops. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 234502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, G.J.; Duffy, B.R.; Wilson, S.K.; Holland, D. Quasi-steady spreading of a thin ridge of fluid with temperature-dependent surface tension on a heated or cooled substrate. Quart. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 2009, 62, 365–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, E.; Wildeman, S.; Visser, C.W.; Hofhuis, K.; Kooij, E.S.; Zandvliet, H.J.W.; Lohse, D. Role of natural convection in the dissolution of sessile droplets. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 794, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diddens, C.; Li, Y.; Lohse, D. Competing Marangoni and Rayleigh convection in evaporating binary droplets. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 914, A23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfle, C.; Bechinger, C.; Rinn, B.; David, C.; Leiderer, P. Cooperative evaporation in ordered arrays of volatile droplets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 5302–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokuler, M.; Auernhammer, G.K.; Liu, C.J.; Bonaccurso, E.; Butt, H.J. Dynamics of condensation and evaporation: Effect of inter-drop spacing. Europhys. Lett. 2010, 89, 36004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, O.; Shahidzadeh-Bonn, N.; Zargar, R.; Aytouna, M.; Habibi, M.; Eggers, J.; Bonn, D. Evaporation of water: Evaporation rate and collective effects. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 798, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schofield, F.G.H.; Wray, A.W.; Pritchard, D.; Wilson, S.K. The shielding effect extends the lifetimes of two-dimensional sessile droplets. J. Eng. Math. 2020, 120, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wray, A.W.; Wray, P.S.; Duffy, B.R.; Wilson, S.K. Contact-line deposits from multiple evaporating droplets. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.07221. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schofield, F.G.H.; Pritchard, D.; Wilson, S.K.; Sefiane, K. The Lifetimes of Evaporating Sessile Droplets of Water Can Be Strongly Influenced by Thermal Effects. Fluids 2021, 6, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6040141
Schofield FGH, Pritchard D, Wilson SK, Sefiane K. The Lifetimes of Evaporating Sessile Droplets of Water Can Be Strongly Influenced by Thermal Effects. Fluids. 2021; 6(4):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6040141
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchofield, Feargus G. H., David Pritchard, Stephen K. Wilson, and Khellil Sefiane. 2021. "The Lifetimes of Evaporating Sessile Droplets of Water Can Be Strongly Influenced by Thermal Effects" Fluids 6, no. 4: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6040141
APA StyleSchofield, F. G. H., Pritchard, D., Wilson, S. K., & Sefiane, K. (2021). The Lifetimes of Evaporating Sessile Droplets of Water Can Be Strongly Influenced by Thermal Effects. Fluids, 6(4), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids6040141