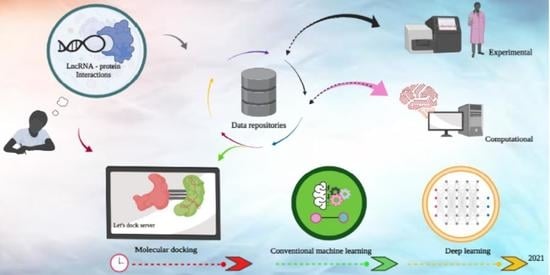
A Survey of Current Resources to Study lncRNA-Protein Interactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LPI Laboratory Assays
3. LncRNA-Protein Resource Databases
4. LPI Prediction Algorithms
4.1. Molecular Docking Approaches
4.2. Machine Learning Approaches
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lowe, R.; Shirley, N.; Bleackley, M.; Dolan, S.; Shafee, T. Transcriptomics technologies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.-C.; Fang, S.-S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.-H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, B.; Wu, J.-R.; Li, E.-M.; Xu, L.-Y.; et al. CNIT: A fast and accurate web tool for identifying protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts based on intrinsic sequence composition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W516–W522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, L. LncRNA Structural Characteristics in Epigenetic Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazimierczyk, M.; Kasprowicz, M.K.; Kasprzyk, M.E.; Wrzesinski, J. Human Long Noncoding RNA Interactome: Detection, Characterization and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jalali, S.; Bhartiya, D.; Lalwani, M.K.; Sivasubbu, S.; Scaria, V. Systematic Transcriptome Wide Analysis of lncRNA-miRNA Interactions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Jones, J.; Tiwari, M.; Ling, J.; Wang, Y.; Harismendy, O.; Sen, G.L. HNRNPK maintains epidermal progenitor function through transcription of proliferation genes and degrading differentiation promoting mRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Fullwood, M.J. Roles, Functions, and Mechanisms of Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piccolo, L.L.; Mochizuki, H.; Nagai, Y. The lncRNA hsrω regulates arginine dimethylation of FUS to cause its proteasomal degradation in Drosophila. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs.236836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Militti, C.; Maenner, S.; Becker, P.; Gebauer, F. UNR facilitates the interaction of MLE with the lncRNA roX2 during Drosophila dosage compensation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardou, F.; Ariel, F.; Simpson, C.G.; Romero-Barrios, N.; Laporte, P.; Balzergue, S.; Brown, J.W.; Crespi, M. Long Noncoding RNA Modulates Alternative Splicing Regulators in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2014, 30, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigo, R.; Bazin, J.; Romero-Barrios, N.; Moison, M.; Lucero, L.; Christ, A.; Benhamed, M.; Blein, T.; Huguet, S.; Charon, C.; et al. The Arabidopsis lnc RNA ASCO modulates the transcriptome through interaction with splicing factors. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e48977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Lian, B.; Gu, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y. Global identification of Arabidopsis lncRNAs reveals the regulation of MAF4 by a natural antisense RNA. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Zhu, B.; Leng, D.; Ge, W.; Zhang, X.D. Long noncoding RNAs implicated in embryonic development in Ybx1 knockout zebrafish. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 1259–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Cai, M.; Liu, M.; Su, G.; An, D.; Moon, B.; Lyu, G.; Si, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, W. lncRNA 5430416N02Rik Promotes the Proliferation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells by Activating Mid1 Expression through 3D Chromatin Architecture. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 14, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Yang, G.; Luo, L.; Ling, L.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Lan, J.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Q.; Long, Z.; et al. lncRNA THAP9-AS1 Promotes Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Growth and Leads to a Poor Clinical Outcome via Sponging miR-484 and Interacting with YAP. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1736–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, Q.; Gong, C.; Yao, Y.; Lv, X.; Lin, L.; Yao, H.; Su, F.; Li, D.; et al. A Cytoplasmic NF-κB Interacting Long Noncoding RNA Blocks IκB Phosphorylation and Suppresses Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yang, W.I.; Yoon, S.O.; Kim, S.J. Association of the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 with the polycomb repressive complex pathway in T and NK cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31305–31317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turjya, R.R.; Khan, A.-A.-K.; Islam, A.B.M.M.K. Perversely expressed long noncoding RNAs can alter host response and viral proliferation in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Futur. Virol. 2020, 15, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, S.; Saha, C.; Dutta, S.; Basu, M.; Chatterjee, R.; Ghosh, S.; Bhattacharyya, N.P. In silico analysis of altered expression of long non-coding RNA in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells and their possible regulation by STAT1, STAT3 and interferon regulatory factors. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, A.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Lei, J.; Xu, H.; Leng, Z.; Li, T.; et al. LncTarD: A manually-curated database of experimentally-supported functional lncRNA–target regulations in human diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D118–D126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, M.; Porter, D.F.; Khavari, P.A. Methods to study RNA–protein interactions. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faoro, C.; Ataide, S.F. Ribonomic approaches to study the RNA-binding proteome. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3649–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramanathan, M.; Majzoub, K.; Rao, D.; Neela, P.H.; Zarnegar, B.J.; Mondal, S.; Roth, J.; Gai, H.; Kovalski, J.R.; Siprashvili, Z.; et al. RNA–protein interaction detection in living cells. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kretz, M.; Siprashvili, Z.; Chu, C.; Webster, D.; Zehnder, A.; Qu, K.; Lee, C.S.; Flockhart, R.J.; Groff, A.F.; Chow, J.; et al. Control of somatic tissue differentiation by the long non-coding RNA TINCR. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 493, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.D.; Wang, C.I.; Kharchenko, P.V.; West, J.A.; Chapman, B.A.; Alekseyenko, A.A.; Borowsky, M.L.; Kuroda, M.I.; Kingston, R.E. Te genomic binding sites of a noncoding RNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20497–20502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.; Qu, K.; Zhong, F.; Artandi, S.E.; Chang, H.Y. Genomic Maps of Long Noncoding RNA Occupancy Reveal Principles of RNA-Chromatin Interactions. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, B.P.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Waterman, M.L. Quantitative profiling of in vivo–assembled RNA-protein complexes using a novel integrated proteomic approach. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M110.007385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Peritz, T.; Kannanayakal, T.J.; Kilk, K.; Eiríksdóttir, E.; Langel, Ü.; Eberwine, J. A protocol for PAIR: PNA-assisted identification of RNA binding proteins in living cells. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, C.A.; Guttman, M. RAP-MS: A Method to Identify Proteins that Interact Directly with a Specific RNA Molecule in Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1649, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matia-González, A.M.; Iadevaia, V.; Gerber, A.P. A versatile tandem RNA isolation procedure to capture in vivo formed mRNA-protein complexes. Methods 2017, 118–119, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ule, J.; Jensen, K.B.; Ruggiu, M.; Mele, A.; Ule, A.; Darnell, R. CLIP Identifies Nova-Regulated RNA Networks in the Brain. Science 2003, 302, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kim, V.N. fCLIP-seq for transcriptomic footprinting of dsRNA-binding proteins: Lessons from DROSHA. Methods 2019, 152, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, C.O.; Friedersdorf, M.B.; Keene, J.D. Quantifying RNA binding sites transcriptome-wide using DO-RIP-seq. RNA 2016, 23, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMahon, A.; Rahman, R.; Jin, H.; Shen, J.L.; Fieldsend, A.; Luo, W.; Rosbash, M. TRIBE: Hijacking an RNA-Editing Enzyme to Identify Cell-Specific Targets of RNA-Binding Proteins. Cell 2016, 165, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinodoz, S.; Guttman, M. Long noncoding RNAs: An emerging link between gene regulation and nuclear organization. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulitsky, I. Interactions between short and long noncoding RNAs. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 2874–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishnaiah, Y.; Kuhlmann, L.; Tyagi, S. Towards a comprehensive pipeline to identify and functionally annotate long noncoding RNA (lncRNA). Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 127, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H.; Yang, J.-H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein–RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, Z.J. POSTAR: A platform for exploring post-transcriptional regulation coordinated by RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D104–D114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, A.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Garde, C.; Pan, X.; Santos, A.; Alkan, F.; Anthon, C.; von Mering, C.; Workman, C.T.; Jensen, L.J.; et al. RAIN: RNA-protein Association and Interaction Networks. Database 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, T.; Cui, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, P.; Huang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, D. RNAInter in 2020: RNA interactome repository with increased coverage and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D189–D197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Chen, X.; Xue, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Kang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y.; He, S. NPInter v4.0: An integrated database of ncRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D160–D165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, G.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Torroja, C.; Lara-Pezzi, E. ATtRACT—A database of RNA-binding proteins and associated motifs. Database 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouvrette, L.P.B.; Bovaird, S.; Blanchette, M.; Lécuyer, E. oRNAment: A database of putative RNA binding protein target sites in the transcriptomes of model species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D166–D173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular Docking: A Powerful Approach for Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Curr. Comput. Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suravajhala, R.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, N.; Suravajhala, P. Deciphering LncRNA–protein interactions using docking complexes. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Xiao, Y. 3dRPC: A web server for 3D RNA–protein structure prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 1238–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghoorah, A.W.; Devignes, M.-D.; Smaïl-Tabbone, M.; Ritchie, D.W. Protein docking using case-based reasoning. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2013, 81, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrusier, N.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. FireDock: Fast interaction refinement in molecular docking. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 69, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zundert, G.; Rodrigues, J.; Trellet, M.; Schmitz, C.; Kastritis, P.; Karaca, E.; Melquiond, A.; van Dijk, M.; de Vries, S.; Bonvin, A.M. The HADDOCK2.2 Web Server: User-Friendly Integrative Modeling of Biomolecular Complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duhovny, D.; Nussinov, R.; Wolfson, H.J. Efficient Unbound Docking of Rigid Molecules. In Algorithms in Bioinformatics, Proceedings of Second International Workshop, WABI 2002, Rome, Italy, 17-21 September 2002; Guigo, R., Gusfield, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 2452, pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Tao, H.; He, J.; Huang, S.-Y. The HDOCK server for integrated protein–protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1829–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Tao, H.; Huang, S.-Y. Protein-ensemble–RNA docking by efficient consideration of protein flexibility through homology models. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4994–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Hong, X.; Xie, J.; Tong, X.; Liu, S. P3DOCK: A protein–RNA docking webserver based on template-based and template-free docking. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuszynska, I.; Magnus, M.; Jonak, K.; Dawson, W.; Bujnicki, J.M. NPDock: A web server for protein–nucleic acid docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W425–W430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Tyagi, S. Integrative computational epigenomics to build data-driven gene regulation hypotheses. GigaScience 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. Multivariate information fusion with fast kernel learning to kernel ridge regression in predicting lncrna-protein interactions. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Jiang, L.; Guo, F. LPI-KTASLP: Prediction of lncRNA-protein interaction by semi-supervised link learning with multivariate information. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 13486–13496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ren, G.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ai, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Q. LPI-NRLMF: lncRNA-protein interaction prediction by neighborhood regularized logistic matrix factorization. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103975–103984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wu, C.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Z.; Liu, J. LPI-IBNRA: Long Non-coding RNA-Protein Interaction Prediction Based on Improved Bipartite Network Recommender Algorithm. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, H.; Ming, Z.; Hu, H.; Ren, G.; Liu, H. The Bipartite Network Projection-Recommended Algorithm for Predicting Long Non-coding RNA-Protein Interactions. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ai, H.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, H. HLPI-Ensemble: Prediction of human lncRNA-protein interactions based on ensemble strategy. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Deng, L. Prediction of lncRNA-protein interactions using HeteSim scores based on heterogeneous networks. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Ren, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H. IRWNRLPI: Integrating random walk and neighborhood regularized logistic matrix factorization for lncRNA-protein interaction prediction. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Yue, X.; Tang, G.; Wu, W.; Huang, F.; Zhang, X. SFPEL-LPI: Sequence-based feature projection ensemble learning for predicting LncRNA-protein interactions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekesa, J.S.; Meng, J.; Luan, Y. A deep learning model for plant lncRNA-protein interaction prediction with graph attention. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 295, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. The linear neighborhood propagation method for predicting long non-coding RNA–protein interactions. Neurocomputing 2018, 273, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-N.; Zhang, S.-W. LPI-BLS: Predicting lncRNA-protein interactions with a broad learning system-based stacked ensemble classifier. Neurocomputing 2019, 370, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipanahi, B.; Delong, A.; Weirauch, M.T.; Frey, B.J. Predicting the sequence specificities of DNA- and RNA-binding proteins by deep learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Zhang, X.X.; Fan, X.N.; Li, W.N. LPI-CNNCP: Prediction of lncRNA-protein interactions by using convolutional neural network with the copy-padding trick. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 601, 113767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.; Chen, H.; Xie, M.; Jiang, T. DeepLPI: A multimodal deep learning method for predicting the interactions between lncRNAs and protein isoforms. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; He, T.; Jiang, X. Projection-Based Neighborhood Non-Negative Matrix Factorization for lncRNA-Protein Interaction Prediction. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-K.; Shen, Z.-A.; Yu, H.; Luo, T.; Gao, Y.; Du, P.-F. Predicting lncRNA–Protein Interactions With miRNAs as Mediators in a Heterogeneous Network Model. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-K.; Hu, J.; Shen, Z.-A.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Du, P.-F. LPI-SKF: Predicting lncRNA-Protein Interactions Using Similarity Kernel Fusions. Front. Genet. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Ren, S.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, T. Computational prediction of associations between long non-coding RNAs and proteins. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agostini, F.; Zanzoni, A.; Klus, P.; Marchese, D.; Cirillo, D.; Tartaglia, G.G. catRAPIDomics: A web server for large-scale prediction of protein–RNA interactions. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2928–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacq, C.; Miller, J.; Brownlee, G. A pseudogene structure in 5S DNA of Xenopus laevis. Cell 1977, 12, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, W.; Ding, B.; Fu, P. Pseudogene-Derived lncRNAs and Their miRNA Sponging Mechanism in Human Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denning, G.M.; Anderson, M.P.; Amara, J.F.; Marshall, J.; Smith, A.E.; Welsh, M. Processing of mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is temperature-sensitive. Nat. Cell Biol. 1992, 358, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB.version 7.10.0 (R2010a); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2010. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Ramakrishnaiah, Y.; Kuhlmann, L.; Tyagi, S. Linc2function: A deep learning model to identify and assign function to long noncoding RNA (lncRNA). bioRxiv 2021. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.01.29.428785v1.abstract (accessed on 27 May 2021). [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, R.; Sugawara, H.; Shumway, M. On behalf of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration the Sequence Read Archive. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D19–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RNAcentral Consortium; Sweeney, B.A.; Petrov, A.I.; Ribas, C.E.; Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Szymanski, M.; Karlowski, W.M.; Seemann, S.E.; Gorodkin, J.; et al. RNAcentral 2021: Secondary structure integration, improved sequence search and new member databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D212–D220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, O.; Kodama, Y.; Mashima, J.; Kosuge, T.; Fujisawa, T. DDBJ Database updates and computational infrastructure enhancement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D45–D50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sl:No | Resource | Resource Type | Advantages and Disadvantages | Weblink | Reference Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P3DOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Free docking and template-based docking strategies in a hybrid approach, results in an accurate classification | http://www.rnabinding.com/P3DOCK/P3DOCK.html | [55] |
| 2 | HDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Integrates template-based modelling as well as ab initio free docking, with a scope that extends to both proteins and nucleic acids | http://hdock.phys.hust.edu.cn | [53] |
| 3 | PATCHDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Low-level geometric features into higher-level features, FireDOCK and PatchDOCK both complement each other, where PatchDOCK can feed output directly into FireDOCK. | https://bioinfo3d.cs.tau.ac.il/PatchDock/ / | [52] |
| 4 | FIREDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Focuses on exploiting side chain information, optimises the minimum free energy of the lncRNA-protein complex | http://bioinfo3d.cs.tau.ac.il/FireDock/ / | [50] |
| 5 | NPDOCK | Exclusively lncRNA-protein docking server, developed for nucleic acid docking only | Chains multiple methods into a pipeline of tools, which implement mostly FFT-based methods. | http://genesilico.pl/NPDock / | [56] |
| 6 | HADDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | It averages ambiguous interaction restraints, and it can generalise to multi-body problems as well as other biomolecular interactions, optimises the minimum free energy of the lncRNA-protein complex | https://wenmr.science.uu.nl/haddock2.4/ | [51] |
| 7 | MPRDOCK | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | Implies protein flexibility by applying FFT and considering sequence homology of the target of interest to generate a repertoire of structures for “ensemble docking” | http://huanglab.phys.hust.edu.cn/mprdock/ | [54] |
| 8 | Hexserver | LncRNA–protein docking server (adapted from conventional docking servers) | FFT-based algorithm to exploit shape complementarity as a feature for optimisation | http://hexserver.loria.fr/ | [49] |
| Sl:no | Resource | Scope | Advantages and Disadvantages | Strategy | Problem Formulation | Model Training Data | Weblink/Source Code | Reference Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LPI-FKLKRR (lncRNA-protein interaction kernel ridge regression, based on fast kernel learning) | Prediction | Effective in datasets with imbalanced classes. | Kernel ridge regression | Similarity matrices formulated as kernels | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA expression, protein ontology, lncRNA sequence, protein sequence | https://github.com/6gbluewind/LPI_FKLKRR | [58] |
| 2 | LPI-KTASLP (prediction of lncRNA-protein interaction by semi-supervised link learning with multivariate information) | Prediction, discovery | Effective in datasets with imbalanced classes. | Multiple kernel learning | Similarity matrices formulated as kernels | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA expression, lncRNA sequence | https://github.com/6gbluewind/LPI_KTASLP | [59] |
| 3 | LPI-NRLMF (lncRNA-protein interaction prediction by neighbourhood regularised logistic matrix factorisation) | Prediction, discovery | Prediction bias is expected due to the sparsity of the training dataset. | Matrix factorisation | Similarity matrices | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, protein sequence | NA | [60] |
| 4 | LPI-INBRA (long non-coding RNA–protein interaction prediction based on improved bipartite network recommender algorithm) | Prediction | Robust against false positives. | Matrix factorisation | Similarity matrices | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, protein sequence | NA | [61] |
| 5 | LPI-BNPRA (long non-coding RNA–protein interaction bipartite network projection recommended algorithm) | Prediction | Effective in humans and closely related species. | Bipartite network recommendation | Similarity matrices | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, protein sequence | NA | [62] |
| 6 | PBLPI (path-based lncRNA-protein interaction) | Prediction, discovery | Prediction accuracy limited due to technical limitations. | Graph | Similarity matrices | lncRNA-protein interactions, protein semantic similarity, lncRNA functional similarity, Gaussian interaction profile kernel similarity, integrated similarity for lncRNAs and proteins | NA | [63] |
| 7 | PLPIHS (predicting lncRNA-protein interactions using HeteSim scores) | Prediction, discovery | Performance is improved by preserving information regarding the biological network, taking into account lncRNA-protein interactions similar to the target. | Graph | Similarity matrices | Co-expression data of lncRNA-protein pairs, lncRNA-protein interaction data | NA | [64] |
| 8 | IRWNRLPI (integrating random walk and neighbourhood regularised logistic matrix factorisation for lncRNA-protein interaction prediction) | Prediction | Robust due to hybrid approach, but known to be unstable. | Hybrid: random walk, neighbourhood regularised logistic matrix factorisation algorithm | Similarity matrices | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, protein sequence | NA | [65] |
| 9 | SFPEL-LPI (sequence-based feature projection ensemble learning method) | Prediction, discovery | Multimodal approach boosts prediction accuracy. | Ensemble: graph Laplacian regularisation | Similarity matrices | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, protein sequence | http://www.bioinfotech.cn/SFPEL-LPI/ | [66] |
| 10 | HLPI-Ensemble (human lncRNA-protein interactions ensemble) | Prediction | Scope restricted to humans. | Ensemble: support vector machines (SVM), random forests (RF) and extreme gradient boosting (XGB) | Recoded feature vectors | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, lncRNA features, protein sequence, protein features | NA | [63] |
| 11 | GPLPI (graph predict lncRNA-protein interaction) | Prediction | Scope restricted to plants. | Deep learning, ensemble learning, graph attention LSTM autoencoder | Recoded sequence and structure vectors | lncRNA sequences, protein sequences, structural features from predicted secondary structures from lncRNA and protein sequences. | https://github.com/Mjwl/GPLPI | [67] |
| 12 | LPI-BLS (predicting lncRNA-protein interactions with a broad learning system-based stacked ensemble classifier) | Prediction | Flat network architecture boosts speed and accuracy. Effective in several model organisms. | Ensemble: broad learning system (flat neural network) | Recoded feature vectors | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, lncRNA features, protein sequence, protein features | https://github.com/NWPU-903PR/LPI_BLS | [69] |
| 13 | LPI-CNNCP (lncRNA-protein interactions convolutional neural network copy-padding trick) | Prediction | Can be extended to predict other biomolecular interactions, effective across different species. | Deep learning (convolutional neural network) | Recoded feature vectors | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, protein sequence | https://github.com/NWPU-903PR/LPI-CNNCP | [71] |
| 14 | DeepLPI (deep lncRNA-protein interactions) | Prediction, discovery | Can be extended to other biomolecular interactions, unique capability to predict lncRNA interaction with different protein isoforms. | Deep learning (embedding, convolution, LSTM) | Recoded feature tensors | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, lncRNA structure, protein sequence, protein structure | https://github.com/dls03/DeepLPI | [72] |
| 15 | LPI-SKF (lncRNA-protein interaction similarity kernel fusion) | Prediction, discovery | Aggregating multiple similarities increases robustness against noise. | Similarity kernel fusion, manifold learning | Similarity matrices | lncRNA-protein interactions, pairwise similarities for lncRNAs, pairwise similarities for proteins | https://github.com/zyk2118216069/LPI-SKF | [75] |
| 16 | PMKDN (projection-based neighbourhood non-negative matrix decomposition model) | Prediction | Strategy avoids overfitting and sparsity issues, allowing more generalisability to different datasets. | Neighbourhood regularised matrix factorisation algorithm | Similarity matrices | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, lncRNA expression, protein sequence, protein annotation | NA | [73] |
| 17 | LPI-miRNA | Prediction, discovery | Can operate on datasets without prior knowledge of lncRNA interactions but relies on known miRNA–lncRNA and miRNA–protein interactions. | Heterogeneous network model | Similarity matrices | lncRNA–miRNA interactions, protein–miRNAs interactions | https://github.com/zyk2118216069/LncRNA-protein-interactions-prediction | [74] |
| 18 | lncPro | Prediction | Training dataset limited, effective on short sequences. | Fourier transform, matrix factorisation | Recoded feature tensors | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, lncRNA features, protein sequence, protein features | http://cmbi.bjmu.edu.cn/lncpro/ | [76] |
| 19 | catRAPID | Prediction | Visualisation is available, prediction accuracy may be limited by reliance on very old lncRNA annotations. | Discrete Fourier transform | lncRNA and protein secondary structure, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces | NA | http://s.tartaglialab.com/page/catrapid_group | [77] |
| 20 | 3dRPC | Prediction | Effective on well-characterised molecules, may have lower accuracy if this is not the case. | Fast Fourier transform, root mean square deviation | Conformations of nucleotide-amino-acid pairs | NA | http://biophy.hust.edu.cn/3dRPC.html | [48] |
| 21 | DeepBind | Prediction | Effective, generalisable across species, but more effective at predicting protein–DNA binding than protein–RNA binding. | Deep learning (convolutional neural network) | Recoded feature tensors | lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, protein sequence | http://tools.genes.toronto.edu/deepbind/ | [70] |
| 22 | LPLNP | Prediction, discovery | Effective and robust in humans, capable of discovering novel interactions. | Ensemble: linear neighbourhood similarity | Similarity matrices | lncRNA expression, lncRNA features lncRNA-protein interactions, lncRNA sequence, protein features, protein sequence | https://github.com/BioMedicalBigDataMiningLabWhu/lncRNA-protein-interaction-prediction | [68] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Philip, M.; Chen, T.; Tyagi, S. A Survey of Current Resources to Study lncRNA-Protein Interactions. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020033
Philip M, Chen T, Tyagi S. A Survey of Current Resources to Study lncRNA-Protein Interactions. Non-Coding RNA. 2021; 7(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020033
Chicago/Turabian StylePhilip, Melcy, Tyrone Chen, and Sonika Tyagi. 2021. "A Survey of Current Resources to Study lncRNA-Protein Interactions" Non-Coding RNA 7, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020033
APA StylePhilip, M., Chen, T., & Tyagi, S. (2021). A Survey of Current Resources to Study lncRNA-Protein Interactions. Non-Coding RNA, 7(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020033