In Silico Identification and Characterization of circRNAs as Potential Virulence-Related miRNA/siRNA Sponges from Entamoeba histolytica and Encystment-Related circRNAs from Entamoeba invadens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Computational Identification of Entamoeba circRNAs
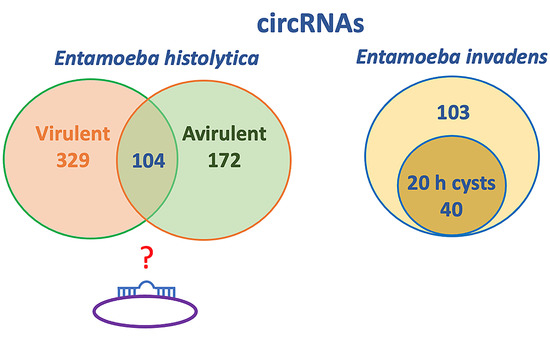
2.2. E. histolytica circRNAs
2.3. E. invadens circRNAs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Libraries
4.2. Identification of Linear and Circular RNAs
4.3. Differential Expression of RNAs
4.4. Gene Ontology Analysis
4.5. Identification of circRNAs as miRNAs Sponges
4.6. CIRI-Full Control
4.7. RNA Isolation, Retrotranscription, and Polymerase Chain Reactions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.T.; Coca-Prados, M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature 1979, 280, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasda, E.; Parker, R. Circular RNAs: Diversity of form and function. RNA 2014, 20, 1829–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L. The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, L.M.; Kohlmaier, A.; Teupser, D. Molecular roles and function of circular RNAs in eukaryotic cells. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasman, Z.; Been, M.D.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. Exon circularization in mammalian nuclear extracts. RNA 1996, 2, 603–610. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The biogenesis of nascent circular RNAs. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhouarne, G.J.; Gall, J.G. Lariat intronic RNAs in the cytoplasm of Xenopus tropicalis oocytes. RNA 2014, 20, 1476–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C.; Munk, R.; Grammatikakis, I.; Dudekula, D.B.; De, S.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Martindale, J.L.; et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legnini, I.; Di Timoteo, G.; Rossi, F.; Morlando, M.; Briganti, F.; Sthandier, O.; Fatica, A.; Santini, T.; Andronache, A.; Wade, M.; et al. Circ-ZNF609 is a circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 22–37.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Feng, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Irwin, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. Identification of candidate circular RNAs underlying intramuscular fat content in the donkey. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 587559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Xiao, L.; Chung, H.K.; Ma, X.X.; Liu, X.; Song, J.L.; Jin, C.Z.; Rao, J.N.; Gorospe, M.; Wang, J.Y. Interaction between HuR and circPABPN1 modulates autophagy in the intestinal epithelium by altering ATG16L1 translation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00492-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhouarne, G.J.S.; Gall, J.G. Lariat intronic RNAs in the cytoplasm of vertebrate cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7970–E7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; De, S.; Grammatikakis, I.; Munk, R.; Yang, X.; Piao, Y.; Dudekula, D.B.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. High-purity circular RNA isolation method (RPAD) reveals vast collection of intronic circRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turkeltaub, J.A.; McCarty, T.R., 3rd; Hotez, P.J. The intestinal protozoa: Emerging impact on global health and development. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Figueroa, M.S.; Alfonso-Maqueira, E.E.; Velez, C.; Azuara-Liceaga, E.I.; Zarate, S.; Villegas-Sepulveda, N.; Saucedo-Cardenas, O.; Valdes, J. Postsplicing-derived full-length intron circles in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggart, A.J.; Lin, C.L.; Shrestha, B.; Heintzelman, C.; Kim, S.; Fairbrother, W.G. Large-scale analysis of branchpoint usage across species and cell lines. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.L.; Bao, Y.; Yee, M.C.; Barrett, S.P.; Hogan, G.J.; Olsen, M.N.; Dinneny, J.R.; Brown, P.O.; Salzman, J. Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar-Aguilar, F.; Trevino, V.; Salinas-Hernandez, J.E.; Tamez-Guerrero, M.M.; Barron-Gonzalez, M.P.; Morales-Rubio, E.; Trevino-Neavez, J.; Verduzco-Martinez, J.A.; Morales-Vallarta, M.R.; Resendez-Perez, D. Identification and characterization of microRNAs from Entamoeba histolytica HM1-IMSS. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Pal, D.; Ghosh, S.K. Entamoeba histolytica: Computational identification of putative microRNA candidates. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 113, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avesson, L.; Reimegard, J.; Wagner, E.G.; Soderbom, F. MicroRNAs in Amoebozoa: Deep sequencing of the small RNA population in the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum reveals developmentally regulated microRNAs. RNA 2012, 18, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Panigrahi, S.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Self-circularizing 5′-ETS RNAs accumulate along with unprocessed pre-ribosomal RNAs in growth-stressed Entamoeba histolytica. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Singh, N.; Bhattacharya, A.; Bhattacharya, S. The ribosomal RNA transcription unit of Entamoeba invadens: Accumulation of unprocessed pre-rRNA and a long noncoding RNA during encystation. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2013, 192, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, K.M.; Broadbent, J.C.; Ribacke, U.; Wirth, D.; Rinn, J.L.; Sabeti, P.C. Strand-specific RNA sequencing in Plasmodium falciparum malaria identifies developmentally regulated long non-coding RNA and circular RNA. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.L.; Liu, T.L.; Yao, Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Wu, X.M.; Wang, X.T.; Yang, X.; Song, J.K.; Zhao, G.H. Circular RNA ciRS-7 affects the propagation of Cryptosporidium parvum in HCT-8 cells by sponging miR-1270 to activate the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, S.; Diao, J.; Liu, H.; Su, B.; Li, C. Identification of potential immune-related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in intestine of Paralichthys olivaceus during Edwardsiella tarda infection. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ji, P.; Chen, S.; Hou, L.; Zhao, F. Reconstruction of full-length circular RNAs enables isoform-level quantification. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, C.C.; Weber, C.; Sismeiro, O.; Proux, C.; Koutero, M.; Deloger, M.; Das, S.; Agrahari, M.; Dillies, M.A.; Jagla, B.; et al. Quantification of stochastic noise of splicing and polyadenylation in Entamoeba histolytica. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1936–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Amado, D.; Avila-Lopez, P.A.; Hernandez-Montes, G.; Briseno-Diaz, P.; Vargas, M.; Lopez-Rubio, J.J.; Carrero, J.C.; Hernandez-Rivas, R. A class I histone deacetylase is implicated in the encystation of Entamoeba invadens. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhuang, B.; Yu, Z.; Han, S. Changing expression profiles of mRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, and miRNA in lung tissue reveal the pathophysiological of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in mouse model. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9369–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Manna, D.; Hall, N.; Singh, U. High throughput sequencing of Entamoeba 27nt small RNA population reveals role in permanent gene silencing but no effect on regulating gene expression changes during stage conversion, oxidative, or heat shock stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, J.M.; Cho, K.R.; Fearon, E.R.; Kern, S.E.; Ruppert, J.M.; Oliner, J.D.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Scrambled exons. Cell 1991, 64, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Chen, R.E.; Olsen, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Brown, P.O. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Lerena, J.A.; Gonzalez-Blanco, G.; Saucedo-Cardenas, O.; Valdes, J. Promoter-bound full-length intronic circular RNAs-RNA polymerase II complexes regulate gene expression in the human parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Noncoding RNA 2022, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Alramini, H.; Tran, V.; Singh, U. Nucleus-localized antisense small RNAs with 5′-polyphosphate termini regulate long-term transcriptional gene silencing in Entamoeba histolytica G3 strain. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44467–44479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Hall, N.; Singh, U. Small RNA pyrosequencing in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica reveals strain-specific small RNAs that target virulence genes. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Serum stress-responsive gene EhslncRNA of Entamoeba histolytica is a novel long noncoding RNA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, P.B.K.; Suravajhala, R.; Rajasheker, G.; Marka, N.; Shridhar, K.K.; Dhulala, D.; Scinthia, K.P.; Divya, K.; Doma, M.; Edupuganti, S.; et al. Lysine, lysine-rich, serine, and serine-rich proteins: Link between metabolism, development, and abiotic stress tolerance and the role of ncrnas in their regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 546213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisardi, M.; Ghosh, S.K.; Field, J.; Van Dellen, K.; Rogers, R.; Robbins, P.; Samuelson, J. The most abundant glycoprotein of amebic cyst walls (Jacob) is a lectin with five Cys-rich, chitin-binding domains. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4217–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mornico, D.; Hon, C.C.; Koutero, M.; Weber, C.; Coppee, J.Y.; Dillies, M.A.; Guillen, N. Genomic determinants for initiation and length of natural antisense transcripts in Entamoeba histolytica. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, J.A.; Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Singh, U. Identification of putative transcriptional regulatory networks in Entamoeba histolytica using Bayesian inference. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 2141–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F. CIRI: An efficient and unbiased algorithm for de novo circular RNA identification. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.; Wright, P.R.; Backofen, R. IntaRNA 2.0: Enhanced and customizable prediction of RNA-RNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W435–W439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.; Hess, W.R.; Borner, T. Precise branch point mapping and quantification of splicing intermediates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 2030–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houseley, J.; Tollervey, D. Apparent non-canonical trans-splicing is generated by reverse transcriptase in vitro. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Entamoeba histolytica | Entamoeba invadens | |
|---|---|---|
| Total circRNAs | 958 | 188 |
| Without duplicates | 605 | 143 |
| mono elements | 570 | 143 |
| 2+ elements | 35 | 0 |
| Exonic | 585 | 131 |
| Intronic | 0 | 2 |
| Intergenic | 20 | 10 |
| Virulent-specific | 329 | nd 1 |
| Shared between virulent and avirulent | 104 | nd |
| Avirulent-specific | 172 | nd |
| Cyst-specific | nd | 40 |
| circRNA | Element | Product | C/L 2 | DE 3 | Ehi-miR-like Sites In 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01_169670 | exon | GRIP domain RUD3 | ↓/↓ | ↓ | Ehi-miR-18, Ehi-miR-136, Ehi-miR-160, Ehi-miR-50, Ehi-miR-88, Ehi-miR-82 |
| 02_169670 | exon | GRIP domain RUD3 | ↓/↓ | ↓ | |
| 03_169670 | exon | GRIP domain RUD3 | ↓/↓ | ↓ | |
| 04_130700 | exon | Enolase | ↑/⎯ | ↑ | Ehi-miR-56 |
| 05_146110 | exon | hp 5 | ↑/↑ | ↑ | |
| 06_DS571557 | intergenic | nd 6 | na 6 | ↑ | Ehi-miR-193, Ehi-miR-39 |
| 07_036530 | exon | Ribosomal S27a | ↑/⎯ | ↑ | Ehi-miR-69 |
| 08_130700 | exon | Enolase | ↑/⎯ | ↑ | |
| 09_146110 | exon | hp | ↑/↑ | ↑ | |
| 10_146370 | exon | Ribosomal L27 | ↑/↑ | ↑ | |
| 11_014170 | exon | GRIP domain RUD3 | ↓/↑ | ↓ | |
| 12_026410 | intergenic | Ribosomal S20 | ↑/↓ | ↓ | |
| 13_086110 | exon | HMG domain | ↑/⎯ | ↑ | |
| 14_116360 | exon | Serine-rich | ↑/↑ | ↓ | Ehi-miR-23, Ehi-miR-51 |
| 15_193440 | exon | hp | ↑/↑ | ↑ | |
| 16_183480 | exon | Ribosomal L27 | ↓/↓ | ↓ | |
| 17_027380 | exon | hp | ↑/↑ | ↑ | |
| 18_169670 | exon | GRIP domain RUD3 | ↓/↓ | ↓ | Ehi-miR-17, Ehi-miR-18, Ehi-miR-160, Ehi-miR-50 |
| 19_125950 | exon | ADH | ↑/⎯ | ↑ | Ehi-miR-177 |
| 20_DS571344 | intergenic | nd | na | ↑ | Ehi-miR-150, Ehi-miR-7 |
| 20 h Cysts (#) 1 | Gene Annotation in E. invadens/Gene Annotation in Orthologs 2 | Orthologs 2 |
|---|---|---|
| EIN_023210 | Jacob/na 3 | |
| EIN_031580 | hp/hp 4 | EHI_030890 |
| EIN_044390 | hp/hp | EHI_054800 |
| EIN_057320 | hp/C2-DCP 5 | EHI_069320 + 6 |
| EIN_061000 (3) | hp/Neuroendocrine convertase 1-like | MBAL_005770 |
| EIN_065890 | hp/hp | EHI_166920 + |
| EIN_065940 | Sphingomyelinase C precursor/Endo- exonuclease, phosphatase-DCP | EHI_125790 + |
| EIN_082550 (3) | hp/Zinc finger protein | EHI_055700 |
| EIN_092220 | hp/Actin | EHI_198930 |
| EIN_093520 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DBP6/DEAD/DEAH box helicase | EHI_052790 |
| EIN_118080 | hp/hp | EHI_016340 + |
| EIN_129500 | 60S ribosomal protein L21/60S ribosomal protein L21 | EHI_069110 + |
| EIN_145900 | DNA topoisomerase/DNA topoisomerase | EHI_120640 |
| EIN_153430 | Pyruvate phosphate dikinase/Pyruvate phosphate dikinase | EHI_009530 + |
| EIN_162170 (3) | hp/Deoxycytidine triphosphate deaminase | EHI_140240 |
| EIN_176430 | Vesicle-fusing ATPase/Vesicle-fusing ATPase | EHI_004640 |
| EIN_230150 (3) | hp/WD-DCP | EHI_135040 |
| EIN_231040 | hp/hp | EHI_160980 + |
| EIN_274360 | hp/hp | EHI_002780 |
| EIN_281330 (3) | hp/hp | EHI_012130 + |
| EIN_284560 | High mobility group protein B3/na | |
| EIN_284970 | GAPDH/GAPDH | EHI_187020 + |
| EIN_327660 | Caldesmon/Glutamic acid-rich protein precursor | EHI_182620 |
| EIN_335410 | Phospholipase D/Phospholipase D | EHI_082560 + |
| EIN_369450 | hp/hp | EHI_152970 |
| EIN_369520 | hp/hp | EHI_091120 |
| EIN_369710 | hp/hp | MBAL_010850 |
| EIN_377620 | hp/hp | EHI_142970 |
| EIN_381500 | Cadmium metallothionein precursor/na | |
| EIN_398110 | hp/hp | EHI_030480 |
| EIN_403300 | Myosin-2 heavy chain/Myosin heavy chain | EHI_110180 |
| EIN_409300 | 60S ribosomal protein L4/60S ribosomal protein L4 | EHI_000510 + |
| EIN_409670 | hp/hp | EHI_024550 |
| EIN_416970 | Actin binding protein/Actin binding protein | EHI_094030 + |
| EIN_424210 | dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase/dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase | EHI_125700 + |
| EIN_461630 (3) | U1-70 kDa/U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein subunit | EHI_153670 + |
| EIN_468500 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase/Pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase | EHI_051060 |
| EIN_475930 | Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase/Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase | MBAL_004253 |
| EIN_486020 | hp/hp | EHI_196570 |
| EIN_487250 (5) | Rho GTPase/Rho family GTPase | EHI_178680 + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Luis, M.Á.; Padrón-Manrique, C.J.C.; García-Lerena, J.A.; Lozano-Amado, D.; Hernández-Rivas, R.; Saucedo-Cárdenas, O.; Méndez-Tenorio, A.; Valdés, J. In Silico Identification and Characterization of circRNAs as Potential Virulence-Related miRNA/siRNA Sponges from Entamoeba histolytica and Encystment-Related circRNAs from Entamoeba invadens. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8050065
López-Luis MÁ, Padrón-Manrique CJC, García-Lerena JA, Lozano-Amado D, Hernández-Rivas R, Saucedo-Cárdenas O, Méndez-Tenorio A, Valdés J. In Silico Identification and Characterization of circRNAs as Potential Virulence-Related miRNA/siRNA Sponges from Entamoeba histolytica and Encystment-Related circRNAs from Entamoeba invadens. Non-Coding RNA. 2022; 8(5):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8050065
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Luis, Mario Ángel, Cristian Julio César Padrón-Manrique, Jesús Alberto García-Lerena, Daniela Lozano-Amado, Rosaura Hernández-Rivas, Odila Saucedo-Cárdenas, Alfonso Méndez-Tenorio, and Jesús Valdés. 2022. "In Silico Identification and Characterization of circRNAs as Potential Virulence-Related miRNA/siRNA Sponges from Entamoeba histolytica and Encystment-Related circRNAs from Entamoeba invadens" Non-Coding RNA 8, no. 5: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8050065
APA StyleLópez-Luis, M. Á., Padrón-Manrique, C. J. C., García-Lerena, J. A., Lozano-Amado, D., Hernández-Rivas, R., Saucedo-Cárdenas, O., Méndez-Tenorio, A., & Valdés, J. (2022). In Silico Identification and Characterization of circRNAs as Potential Virulence-Related miRNA/siRNA Sponges from Entamoeba histolytica and Encystment-Related circRNAs from Entamoeba invadens. Non-Coding RNA, 8(5), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8050065