Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as key regulators in a wide range of biological processes. Here, we identified a mouse miRNA-host gene lncRNA (
Lnc-Nr6a1) upregulated early during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). We show that when lncRNA is processed, it gives rise
[...] Read more.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as key regulators in a wide range of biological processes. Here, we identified a mouse miRNA-host gene lncRNA (
Lnc-Nr6a1) upregulated early during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). We show that when lncRNA is processed, it gives rise to two abundant polyadenylated isoforms, lnc-
Nr6a1-1 and lnc-
Nr6a1-2, and a longer non-polyadenylated microprocessor-driven lnc-pri-miRNA containing clustered pre-miR-181a2 and pre-miR-181b2 hairpins. Ectopic expression of the lnc-
Nr6a1-1 or lnc-
Nr6a1-2 isoform enhanced cell migration and the invasive capacity of the cells, whereas the expression of the isoforms and miR-181a2 and miR-181b2 conferred anoikis resistance.
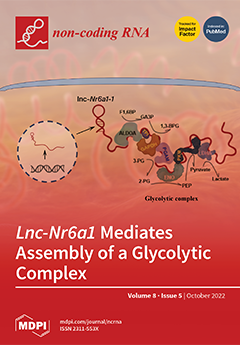
Lnc-Nr6a1 gene deletion resulted in cells with lower adhesion capacity and reduced glycolytic metabolism, which are restored by lnc-
Nr6a1-1 isoform expression. We performed identification of direct RNA interacting proteins (iDRIP) to identify proteins interacting directly with the lnc-
Nr6a1-1 isoform. We defined a network of interacting proteins, including glycolytic enzymes, desmosome proteins and chaperone proteins; and we demonstrated that the lnc-
Nr6a1-1 isoform directly binds and acts as a scaffold molecule for the assembly of ENO1, ALDOA, GAPDH, and PKM glycolytic enzymes, along with LDHA, supporting substrate channeling for efficient glycolysis. Our results unveil a role of
Lnc-Nr6a1 as a multifunctional lncRNA acting as a backbone for multiprotein complex formation and primary microRNAs.
Full article