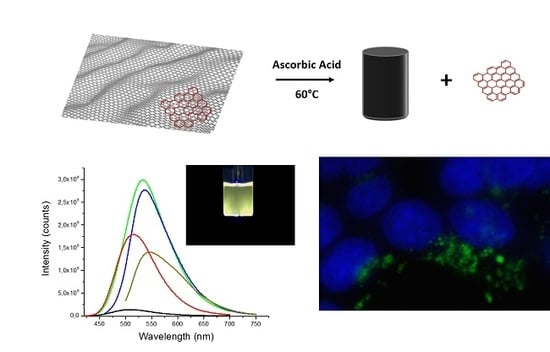
Facile Synthesis of Water-Soluble, Highly-Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Graphene Oxide Reduction for Efficient Cell Labelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of GO Hydrogel and Isolation of GQDs
2.3. Cell Treatment
2.4. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Synthesis and Optical Characterization of GQDs
3.2. Chemical and Morphological Characterization of GQDs
3.3. Biological Imaging with GQDs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koutsioukis, A.; Belessi, V.; Georgakilas, V. Fluorescent Carbon Dots Ink for Gravure Printing. C 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasouni, A.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Stalikas, C. Bioimaging Applications of Carbon Nanodots: A Review. C J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Baker, G. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Lu, K.; Tang, Z.; Xu, Y. Recent progress in carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, properties and applications in photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3717–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, A. Carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Tiwari, P.; Mobin, S. Sustainable carbon-dots: Recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8904–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xu, Y.; Che, Y.; Liao, X.; Jiang, Y. A type of novel fluorescent magnetic carbon quantum dots for cells imaging and detection. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 3956–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wei, C.; Zeng, X. Origin of green luminescence in carbon quantum dots: Specific emission bands originate from oxidized carbon groups. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 4603–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Chen, B.B.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Carbon dots: Synthesis, formation mechanism, fluorescence origin and sensing applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, J.E.; Guo, Z.L.; Carroll, D.; Sun, Y.P. Strong Luminescence of Solubilized Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 5879–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Weng, W.; Guo, H.; Guo, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T.; Hong, X.; et al. Large scale synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots and their application for bioimaging. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Carbon Dots Prepared by Hydrothermal Treatment of Dopamine as an Effective Fluorescent Sensing Platform for the Label-Free Detection of Iron(III) Ions and Dopamine. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 7243–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, P.; Tian, F.; Li, W.; Li, F.; Liu, W. One-step synthesis of surface passivated carbon nanodots by microwave assisted pyrolysis for enhanced multicolor photoluminescence and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 13163–13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Cao, L.; Luo, P.G.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Qi, G.; Sun, Y.P. Carbon Dots for Optical Imaging in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11308–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ye, T.; Mao, C. Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles Derived from Candle Soot. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6473–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Liu, J.; Yan, X.; Kang, L. The graphene oxide derived graphene quantum dots with different photoluminescence properties and peroxidase-like catalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50609–50617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, S.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Lin, H. A facile and high-efficient approach to yellow emissive graphene quantum dots from graphene oxide. Carbon 2017, 124, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, G.; Canteri, R. RxpsG a new open project for Photoelectron and Electron Spectroscopy data processing. SoftwareX 2019, 46, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minati, L.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F.; Micheli, V.; Speranza, G. Palladium nanoparticle functionalized graphene xerogel for catalytic dye reduction. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 14573–14579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeret, C.; Cousseau, J.; Fernandez, V.J.; Mevellec, Y.; Lefrant, S.J. Spectroscopic Evidence of Carbon Nanotubes’ Metallic Character Loss Induced by Covalent Functionalization via Nitric Acid Purification. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 11, 16411–16416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minati, L.; Torrengo, S.; Maniglio, D.; Migliaresi, C.; Speranza, G. Luminescent graphene quantum dots from oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, D.B.; Pillai, V.K. Electrochemical Preparation of Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 12522–12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Haddad, R.E.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minati, L.; Speranza, G.; Bernagozzi, I.; Torrengo, S.; Chiasera, A.; Ferrari, M. Luminescent short thiol-functionalized multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2011, 20, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Facile preparation and upconversion luminescence of graphene quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2580–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal Route for Cutting Graphene Sheets into Blue-Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Shao, J.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Chi, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, G. Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 2012, 12, 4738–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Cai, B.; Cao, Q.; Su, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Facile synthesis of amine-functionalized graphene quantum dots with highly pH-sensitive photoluminescence. Fullerenes Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2017, 25, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tian, F.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.X. Fabrication of highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots using L-glutamic acid for in vitro/in vivo imaging and sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 31, 4676–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Xue, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhang, B.; Hao, J.; Feng, W. Facile synthesis of analogous graphene quantum dots with sp2 hybridized carbon atom dominant structures and their photovoltaic application. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13043–13052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guin, J.P.; Guin, S.K.; Debnath, T.; Ghosh, H.N. Chemically clean single-step oxido-reductive synthesis of green luminescent graphene quantum dots as impending electrocatalyst. Carbon 2016, 109, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.F.; Chen, S.J.; Teng, H. Synergistic effect of oxygen and nitrogen functionalities for graphene-based quantum dots used in photocatalytic H2 production from water decomposition. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, C.M.; Chen, B.L.; Teng, K.S.; Tang, L.B.; Lau, S.P. Optically and electrically tunable graphene quantum dot–polyaniline composite films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 4526–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | BE (eV) | Conc. at. % | Bond |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1s1 | 288.8 | 2.3 | COOH |
| C1s2 | 286.3 | 12.8 | C–OH, C–O–C |
| C1s3 | 284.4 | 69 | sp2C |
| O1s1 | 534.1 | 2.1 | COOH |
| O1s2 | 532.4 | 11.3 | C–OH, C–O–C |
| O1s3 | 531.4 | 2.5 | COOH |
| Synthesis | Source | Dimension | QY | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonization | sucrose | 1.8 nm | 21% | Cell imaging | [11] |
| Hydrothermal | Dopamine | 3.8 nm | - | Detection of Iron(III) Ions | [12] |
| Acid oxidation | GO | 3–4 nm | - | peroxidase-like catalytic activity | [17] |
| Hydrazine reduction | GO | 10–20 nm | 7.4% | Blue emitting GQDs | [26] |
| Hydrothermal | GO | 12 nm | 6,9% | Blue emitting GQDs | [27] |
| Hydrothermal | Citric acid | 6–12 nm | 9% | Blue emitting GQDs | [28] |
| Hydrothermal | 1,5-dinitronaphthalene | 1.5 nm | - | Green-yellow emitting GQDs | [29] |
| Hydrothermal | L-glutamic acid | 5 nm | 54.5% | NIR emitting GQDs | [30] |
| Microwave assisted hydrothermal | glucose | 4 nm | 5.2% | Green-red emitting GQDs | [31] |
| Liquid exfoliation | GO | 3 nm | 0.9% | Green emitting GQDs | [32] |
| Liquid exfoliation | GO | 5 nm | 12.8% | photocatalytic H2 production | [33] |
| Nanolithography | Graphene | 10 nm | - | Molecular-scale electronics | [34] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minati, L.; Del Piano, A. Facile Synthesis of Water-Soluble, Highly-Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Graphene Oxide Reduction for Efficient Cell Labelling. C 2019, 5, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5040077
Minati L, Del Piano A. Facile Synthesis of Water-Soluble, Highly-Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Graphene Oxide Reduction for Efficient Cell Labelling. C. 2019; 5(4):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5040077
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinati, Luca, and Alessia Del Piano. 2019. "Facile Synthesis of Water-Soluble, Highly-Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Graphene Oxide Reduction for Efficient Cell Labelling" C 5, no. 4: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5040077
APA StyleMinati, L., & Del Piano, A. (2019). Facile Synthesis of Water-Soluble, Highly-Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Graphene Oxide Reduction for Efficient Cell Labelling. C, 5(4), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5040077