Study of Hybrid Modification with Humic Acids of Environmentally Safe Biodegradable Hydrogel Films Based on Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- research the physicochemical features resulting from the hybrid modification of environmentally safe biodegradable hydrogels based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose with humic acids;
- -
- detect the effect of modification with humic acids on a set of strength-based and operational properties regarding environmentally safe, biodegradable hybrid hydrogel films based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Samples Preparation
2.3. Characterization
- -
- Specific conductivity: from 0 to 9990 mkS/cm;
- -
- Temperatures: from 0 to 55 °C;
- -
- Error: ±2%.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological and Physical Studies of the Mechanism of Hybrid Modification of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Hydrogels with Humic Acids
- -
- -
- the formation of a larger number of agglomerates in HESBHM due more intensive hydration process by a high-density and rigid network of HESBHM, because an increase in specific electrical conductivity is actually a measure of the hydration level by the high-density and rigid network in water-soluble polymeric hydrogel materials [31,32].
3.2. Study of the Effect of Hybrid Modification of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose with Humic Acids on a Set of Characteristics of Biodegradable Hydrogel Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabrera, F.C. Eco-friendly polymer composites: A review of suitable methods for waste management. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 2653–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ge, J.; Yu, X.; Li, H. Environmental fate and impacts of microplastics in soil ecosystems: Progress and perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Preziosi, R.; Robson, G.D. Abiotic and biotic environmental degradation on the bioplastic polymer poly(lactic acid): A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 137, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasi, S.; Ammar Haeri, S. Biodegradable materials and their applications in sample preparation techniques–A review. Microchem. J. 2021, 171, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukiruthika, T.; Sethupathy, P.; Wilson, A.; Kashampur, K.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Multilayer packaging: Advances in preparation techniques and emerging food applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1156–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falguera, V.; Quintero, J.P.; Jimenez, A.; Munoz, J.A.; Ibarz, A. Edible films and coatings: Structures, active function and trends in their use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.; Tykhomyrova, T.; Litvinenko, I.; Avina, S.; Saimbetova, Z. Design and Research of Eco-Friendly Polymer Composites. Mater. Sci. Forum 2020, 1006, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.; Tykhomyrova, T.; Filenko, O.; Cherkashina, A.; Lytvynenko, O. Sorption Resistance Studying of Environmentally Friendly Polymeric Materials in Different Liquid Mediums. Mater. Sci. Forum 2021, 1038, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.; Miroshnichenko, D.; Bilets, D.; Mysiak, V. Investigation of Hybrid Modification of Eco-Friendly Polymers by Humic Substances. Solid State Phenom. 2022, 334, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickelbick, G. Hybrid Materials: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pyshyev, S.; Demchuk, Y.; Gunka, V.; Sidun, I.; Shved, M.; Bilushchak, H.; Obshta, A. Development of mathematical model and identification of optimal conditions to obtain phenol-cresol-formaldehyde resin. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2019, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prysiazhnyi, Y.; Borbeyiyong, G.I.; Pyshyev, S. Preparation and application of coumarone-indene-carbazole resin as a modifier of road petroleum bitumen 1. Influence of carbazole:raw materials ratio. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2022, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Hu, Y.; Ma, D.; Ge, J.; Huang, S. Reconfigurable Mechanochromic Patterns into Chameleon-Inspired Photonic Papers. Research 2022, 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, X.; Xie, C.; Chen, Q.; Liu, W.; Gao, Z.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Q.; He, D.; et al. Improved Comprehensive Photovoltaic Performance and Mechanisms by Additive Engineering of Ti3C2Tx MXene into CsPbI2Br. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 40930–40938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, D.; Ma, D.; Huang, S. Liquid, Transparent, and Antideformable Thermochromic Photonic Crystals for Displays. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2200769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, D.; Ma, D.; Huang, S. Extremely sensitive mechanochromic photonic crystals with broad tuning range of photonic bandgap and fast responsive speed for high-resolution multicolor display applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Wang, M.; Xu, F. Preparation of covalently crosslinked sodium alginate/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose pH-sensitive microspheres for controlled drug release. BioResources 2018, 13, 8614–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Han, M.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Shin, S.W.; Nam, S.Y.; Park, J.H. Tip-loaded dissolving microneedles for transdermal delivery of donepezil hydrochloride for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 105, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, P.; Zhu, J.; Lan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Tao, J. Hyaluronic acid-based dissolving microneedle patch loaded with methotrexate for improved treatment of psoriasis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43588–43598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistilis, M.J.; Bommarius, A.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Development of a thermostable microneedle patch for influenza vaccination. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, K.; Ye, Y.; Su, T.; Qiao, L.; Hensley, M.T.; Caranasos, T.G.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Z.; et al. Cardiac cell-integrated microneedle patch for treating myocardial infarction. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, R.; Laffitte, Y.; Schmill, U.; Hu, W.; Kaddoura, M.; Blondeel, E.J.M.; Cui, B. Fabrication of sharp silicon hollow microneedles by deep -reactive ion etching towards minimally invasive diagnostics. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebedev, V.; Miroshnichenko, D.; Xiaobin, Z.; Pyshyev, S.; Savchenko, D. Technological Properties of Polymers Obtained from Humic Acids of Ukrainian Lignite. Pet. Coal 2021, 63, 646–654. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, V.; Miroshnichenko, D.; Xiaobin, Z.; Pyshyev, S.; Savchenko, D.; Nikolaichuk, Y. Use of Humic Acids from Low-Grade Metamorphism Coal for the Modification of Biofilms Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol. Pet. Coal 2021, 63, 953–962. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, V.; Sizhuo, D.; Xiaobin, Z.; Pyshyev, S.; Dmytro, S. Hybrid Modification of Eco-Friendly Biodegradable Polymeric Films by Humic Substances from Low-Grade Metamorphism Coal. Pet. Coal 2022, 64, 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Miroshnichenko, D.V.; Pyshyev, S.V.; Lebedev, V.V.; Bilets, D.Y. Deposits and quality indicators of brown coal in Ukraine. Nauk. Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu 2022, 3, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornaya, L.P.; Cherkashyna, G.M.; Lebedev, V.V. Theory and Methods of Research and Testing of Plastics, Adhesives and Sealants, 1st ed.; Textbook of NTU “KhPI”: Kharkiv, Ukraine, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Feroz, S.; Dias, G. Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose (HPMC) crosslinked keratin/hydroxyapatite (HA) scaffold fabrication, characterization and in vitro biocompatibility assessment as a bone graft for alveolar bone regeneration. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Rubina Gilani, S.; Iqbal Durani, A.; Naseem, S. Materials Diversity of Hydrogel: Synthesis, Polymerization Process and Soil Conditioning Properties in Agricultural Field. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 33, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacopardo, L.; Guazzelli, N.; Nossa, R.; Mattei, G.; Ahluwalia, A. Engineering hydrogel viscoelasticity. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 89, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaklamani, G.; Kazaryan, D.; Bowen, J.; Iacovella, F.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Deligeorgis, G. On the electrical conductivity of alginate hydrogels. Regen. Biomater. 2018, 5, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konsta, A.; Daoukaki, D.; Pissis, P.; Vartzeli, K. Hydration and conductivity studies of polymer–Water interactions in polyacrylamide hydrogels. Solid State Ion. 1999, 125, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Proximate Analysis, % wt. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wa (%) | Ad (%) | Sdt (Sdaft) (%) | Vdaf (Vd) (%) |
| 16.8 | 48.7 | 2.08 (2.50) | 56.7 (29.1) |
| Range (cm−1) | Functional Groups |
|---|---|
| 3380–3400 | phenolic −OH hydroxyl groups |
| 2920–2940 | aliphatic bands C–H |
| 2750–2900 | –CH3 |
| 1650–1660 | fluctuation νC=O |
| 1540–1580 | asymmetric νCOO– carboxyl |
| 1400, 1600 | C–C |
| 1380–1400 | symmetric νCOO– carboxyl |
| 1100 | νCO (phenolic), νOH (aliphatic) |
| 1040 | νC–N |
| 1005 | νCO |
| 910 | out-of-phase δCH (aromatic) |
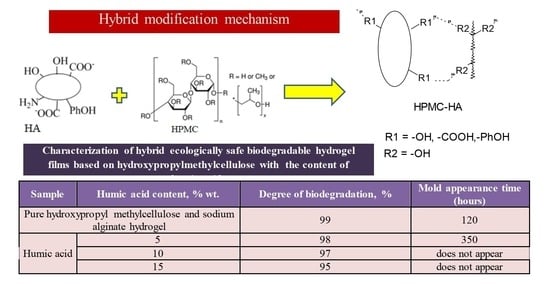
| Sample | Humic Acid Content, % wt. | Degree of Biodegradation, % | Mold Appearance Time (Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and sodium alginate hydrogel | 0 | 99 | 120 |
| Humic acid | 5 | 98 | 350 |
| 10 | 97 | does not appear | |
| 15 | 95 | does not appear |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miroshnichenko, D.; Lebedeva, K.; Cherkashina, A.; Lebedev, V.; Tsereniuk, O.; Krygina, N. Study of Hybrid Modification with Humic Acids of Environmentally Safe Biodegradable Hydrogel Films Based on Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose. C 2022, 8, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/c8040071
Miroshnichenko D, Lebedeva K, Cherkashina A, Lebedev V, Tsereniuk O, Krygina N. Study of Hybrid Modification with Humic Acids of Environmentally Safe Biodegradable Hydrogel Films Based on Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose. C. 2022; 8(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/c8040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiroshnichenko, Denis, Katerina Lebedeva, Anna Cherkashina, Vladimir Lebedev, Oleksandr Tsereniuk, and Natalia Krygina. 2022. "Study of Hybrid Modification with Humic Acids of Environmentally Safe Biodegradable Hydrogel Films Based on Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose" C 8, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/c8040071
APA StyleMiroshnichenko, D., Lebedeva, K., Cherkashina, A., Lebedev, V., Tsereniuk, O., & Krygina, N. (2022). Study of Hybrid Modification with Humic Acids of Environmentally Safe Biodegradable Hydrogel Films Based on Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose. C, 8(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/c8040071