H2S Emission and Microbial Community of Chicken Manure and Vegetable Waste in Anaerobic Digestion: A Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design and Sample Preparation
2.2. Determination of Abiotic Factors
2.3. Calculation Formula
2.3.1. H2S Production Prediction Calculation Formula
2.3.2. Formulas for Biogas and H2S Production Potential
2.4. Characterization of the Microbial Community
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of CM, VW, and Inoculum
3.2. Production Characteristics of Biogas, CH4, and H2S
3.2.1. Biogas and CH4
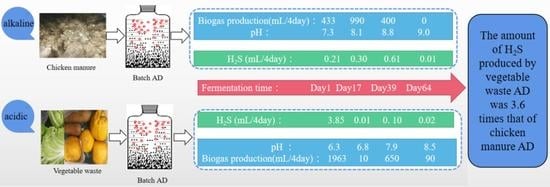
3.2.2. H2S Emission
3.3. The Relationship between H2S, Sulfide, and pH
3.4. Microbial Community Structure and Function
3.4.1. Microbial Community Structure at Phylum and OTUs Levels
3.4.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.4.3. Microbial Community Function Concerning Sulfide Metabolism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, P.; Han, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y. Potential Analysis on High Efficient Utilization of Waste Vegetable Resources in China. China Veg. 2015, 7, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Fu, J.; Li, C.; Tang, J. Research Advance and Prospect on Vermicomposting of Chicken Excrement. China Poult. 2018, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Higgins, M.J.; Beightol, S.M.; Murthy, S.N.; Toffey, W.E. Anaerobically digested biosolids odor generation and pathogen indicator regrowth after dewatering. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2616–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, N.; Guo, B.; Liu, Y. Enhancing the resistance to H2S toxicity during anaerobic digestion of low-strength wastewater through granular activated carbon (GAC) addition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lamont, L.D.; Sedbrook, J.C.; Heller, N.J.; Kopsell, D.E. Anaerobic Digestion of Cereal Rye Cover Crop. Fermentation 2022, 8, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, X.; He, D.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Du, M.; Wang, Y.; Long, S.; Wang, D. Rhamnolipid increases H2S generation from waste activated sludge anaerobic fermentation: An overlooked concern. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akgul, D.; Abbott, T.; Eskicioglu, C. Assessing iron and aluminum-based coagulants for odour and pathogen reductions in sludge digesters and enhanced digestate dewaterability. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzi, V.; Cadena, E.; D’Imporzano, G.; Artola, A.; Davoli, E.; Crivelli, M. Potential odour emission measurement in organic fraction of municipal solid waste during anaerobic digestion: Relationship with process and biological stability parameters. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7330–7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peu, P.; Picard, S.; Diara, A.; Girault, R.; Béline, F.; Bridoux, G.; Dabert, P. Prediction of hydrogen sulphide production during anaerobic digestion of organic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 121, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, I.; Ramos, I.; Fdz-Polanco, M. Economic analysis of microaerobic removal of H2S from biogas in full-scale sludge digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Hao, T.; Sun, B.; Luo, J.; Chen, G.; Crittenden, J.C. Electrochemical Pretreatment for Sludge Sulfide Control without Chemical Dosing: A Mechanistic Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14559–14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y. A new method for the simultaneous enhancement of methane yield and reduction of hydrogen sulfide production in the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Xi, J.; Yeung, M.; Ren, G. Characteristics and mechanisms of H2S production in anaerobic digestion of food waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 137977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, J.; Brandt, K.K.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Holm, P.E.; Hansen, L.H.; Sørensen, S.J. Selection for Cu-tolerant bacterial communities with altered composition, but unaltered richness, via long-term Cu exposure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7438–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Bai, Y. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, M.; Klon, A.E.; Acklin, P.; Davies, J.W. Enrichment of extremely noisy high-throughput screening data using a naive Bayes classifier. J. Biomol. Screen. 2004, 9, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. Peer J. 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.W.; Jeong, C.M.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, M.I.; Chang, H.N. On-site removal of H2S from biogas produced by food waste using an aerobic sludge biofilter for steam reforming processing. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2010, 15, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, R.; Chen, R.; Pu, T.; Huang, C.; He, T.; Tian, G. Feeding controls H2S production in situ in high solid anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Belle, A.J.; Lansing, S.; Mulbry, W.; Weil, R.R. Methane and hydrogen sulfide production during co-digestion of forage radish and dairy manure. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 80, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonknechten, N.; Chaussonnerie, S.; Tricot, S.; Lajus, A.; Andreesen, J.R.; Perchat, N.; Kreimeyer, A. Clostridium sticklandii, a specialist in amino acid degradation: Revisiting its metabolism through its genome sequence. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathani, N.M.; Duggirala, S.M.; Bhatt, V.D.; Patel, A.K.; Kothari, R.K.; Joshi, C.G. Correlation between genomic analyses with metatranscriptomic study reveals various functional pathways of Clostridium sartagoforme AAU1, a buffalo rumen isolate. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2016, 44, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilina, T.N.; Appel, R.; Probian, C.; Brossa, E.L.; Harder, J.; Widdel, F.; Zavarzin, G.A. Alkaliflexus imshenetskii gen. nov. sp. nov., a new alkaliphilic gliding carbohydrate-fermenting bacterium with propionate formation from a soda lake. Arch. Microbiol. 2004, 182, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, H.; Borrion, A.; Yu, Z.; Li, J. Kinetic studies on organic degradation and its impacts on improving methane production during anaerobic digestion of food waste. Appl. Energy 2018, 213, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyuki, M.; Masateru, N.; Yosuke, K. Isolation, Characterization and Physiology of a New Formate-assimilable Methanogenic Strain (A2). J. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 38, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Morii, H.; Nishihara, M.; Koga, Y. Isolation, characterization and physiology of a new formate-assimilable methanogenic strain (A2) of Methanobrevibacter arboriphilus. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1983, 47, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanthongthip, P.; Yagci, N.; Orhon, D.; Novak, J. Generation and fate of volatile organic sulfur compounds during anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 215, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Items | CM | VW | Inoculum |
|---|---|---|---|
| TS (%) | 27.1 ± 1.7 | 7.2 ± 0.4 | 5.2 ± 0.3 |
| VS (%) (dry basis) | 72.3 ± 2.5 | 87.5 ± 1.5 | 56.5 ± 2.2 |
| Ash (%) (dry basis) | 27.7 ± 1.6 | 12.5 ± 2.2 | 43.5 ± 2.1 |
| ORP (mV) | −327 ± 19 | 152 ± 15 | −279 ± 12 |
| DO (mg/L) | 0.15 ± 0.10 | 7.37 ± 1 | 0.16 ± 0.11 |
| pH | 7.37 ± 0.16 | 5.08 ± 0.22 | 8.5 ± 0.10 |
| Protein (%) (dry basis) | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 11.4 ± 1.3 | 1.5 ± 0.15 |
| S-sulfide (mg/kg) (dry basis) | 2566 ± 354 | 264 ± 14 | 8750 ± 279 |
| S-sulfate (mg/kg) (dry basis) | 1922 ± 272 | 1527 ± 220 | 653 ± 37 |
| S-total (mg/kg) (dry basis) | 7509 ± 480 | 3152 ± 317 | 9576 ± 643 |
| S-protein (mg/kg) (dry basis) | 388 | 1139 | 19 |
| CM | VW | |
|---|---|---|
| Biogas production potential (m3/ton (TS)) | 314 + 92 | 240 + 78 |
| Average methane content (%) | 54.9 + 3.1 | 49.7 + 2.2 |
| H2S production potential (g/ton (TS)) | 90 ± 37 | 288 ± 87 |
| Average H2S concentration (ppm) | 198 + 79 | 738 ± 210 |
| Functional Groups | Chicken Manure AD (%) | Vegetable Waste AD (%) | Inoculum (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | A17 | A399 | A67 | B0 | B17 | B399 | B67 | C0 | C17 | C39 | C67 | |
| Methanogenesis | 0.21 | 0.26 | 6.97 | 0.20 | 1.70 | 0.39 | 7.79 | 1.54 | 0.26 | 5.34 | 0.09 | 0.34 |
| Sulfate respiration | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| Sulfur respiration | 0.48 | 0.95 | 0.64 | 1.12 | 0.43 | 2.83 | 1.28 | 1.56 | 0.46 | 0.51 | 1.62 | 0.92 |
| Sulfite respiration | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Thiosulfate respiration | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Respiration of sulfur compounds | 0.52 | 1.05 | 0.66 | 1.18 | 0.50 | 2.89 | 1.30 | 1.57 | 0.54 | 0.57 | 1.69 | 0.96 |
| Dark sulfide oxidation | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Dark sulfur oxidation | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| Dark thiosulfate oxidation | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| Dark oxidation_of_sulfur_compounds | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.013 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Fermentation | 30.05 | 22.85 | 6.27 | 10.28 | 22.27 | 22.38 | 9.45 | 8.82 | 27.15 | 12.53 | 8.82 | 8.013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, G.; Yeung, M.; Xi, J. H2S Emission and Microbial Community of Chicken Manure and Vegetable Waste in Anaerobic Digestion: A Comparative Study. Fermentation 2023, 9, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020169
Tian G, Yeung M, Xi J. H2S Emission and Microbial Community of Chicken Manure and Vegetable Waste in Anaerobic Digestion: A Comparative Study. Fermentation. 2023; 9(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Guangliang, Marvin Yeung, and Jinying Xi. 2023. "H2S Emission and Microbial Community of Chicken Manure and Vegetable Waste in Anaerobic Digestion: A Comparative Study" Fermentation 9, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020169
APA StyleTian, G., Yeung, M., & Xi, J. (2023). H2S Emission and Microbial Community of Chicken Manure and Vegetable Waste in Anaerobic Digestion: A Comparative Study. Fermentation, 9(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020169