Metagenomic Binning Revealed Microbial Shifts in Anaerobic Degradation of Phenol with Hydrochar and Pyrochar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate and Inoculum
2.2. Hydrochar and Pyrochar Preparatio
2.3. Experimental Set-Up
2.4. Metagenomic Analysis
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Different Carbon Materials on Methane Production from Phenol
3.2. Metagenomic Analysis
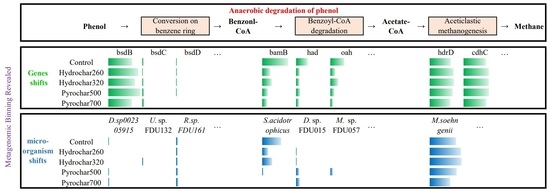
3.2.1. Genes Involved in Phenol Anaerobic Degradation
3.2.2. Genome Reconstruction and Metabolic Potential
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, S.L.; Ren, S.; Zhou, N.; Chen, H.H.; Usman, M.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S.C. Molecular composition of hydrothermal liquefaction wastewater from sewage sludge and its transformation during anaerobic digestion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, S.; Bize, A.; Bureau, C.; Bouchez, T.; Chapleur, O. Community shifts within anaerobic digestion microbiota facing phenol inhibition: Towards early warning microbial indicators? Water Res. 2016, 100, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ren, S.; Ji, M.; Sompong, O.; Qian, Y.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S. Characterization and biogas production potentials of aqueous phase produced from hydrothermal carbonization of biomass–Major components and their binary mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, F.; Cabrol, L.; Carballa, M.; Donoso-Bravo, A.; Cruz, L.; Ruiz-Filippi, G.; Chamy, R.; Lema, J.M. Relationship between phenol degradation efficiency and microbial community structure in an anaerobic SBR. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6739–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Berardinelli, S.; Resini, C.; Arrighi, L. Technologies for the removal of phenol from fluid streams: A short review of recent developments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 265–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Godoi, L.A.G.; Fuess, L.T.; Delforno, T.P.; Foresti, E.; Damianovic, M.H.R.Z. Characterizing phenol-removing consortia under methanogenic and sulfate-reducing conditions: Potential metabolic pathways. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 3216–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leven, L.; Nyberg, K.; Schnurer, A. Conversion of phenols during anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste—A review of important microorganisms and impact of temperature. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S99–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigou, C.; Poirier, S.; Bureau, C.; Chapleur, O. Acclimation strategy to increase phenol tolerance of an anaerobic microbiota. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schie, P.M.; Young, L.Y. Biodegradation of Phenol: Mechanisms and Applications. Bioremediation J. 2000, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, R. Redox-based electron exchange capacity of biowaste-derived biochar accelerates syntrophic phenol oxidation for methanogenesis via direct interspecies electron transfer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieg, L.M.; Fowler, S.J.; Berdugo-Clavijo, C. Syntrophic biodegradation of hydrocarbon contaminants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos-Hernandez, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Guenne, A.; Mazeas, L. Elucidation of the thermophilic phenol biodegradation pathway via benzoate during the anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste. Chemosphere 2014, 97, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canada. Environment Canada; Canada. Health Canada. Priority Substances List Assessment Report: Phenol; Environment Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2000; pp. 7, 66.
- Deng, S.; Jothinathan, L.; Cai, Q.; Li, R.; Wu, M.; Ong, S.L.; Hu, J. FeOx@GAC catalyzed microbubble ozonation coupled with biological process for industrial phenolic wastewater treatment: Catalytic performance, biological process screening and microbial characteristics. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Wang, R.; Geng, P.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z. Enhancing effects of activated carbon supported nano zero-valent iron on anaerobic digestion of phenol-containing organic wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Tabassum, S.; Sun, J.; Hong, Y. Enhanced phenols removal and methane production with the assistance of graphene under anaerobic co-digestion conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, Z.B.; Siddique, M.N.I.; Nayeem, A.; Adyel, T.M.; Ismail, S.B.; Ibrahim, M.Z. Biochar application as sustainable precursors for enhanced anaerobic digestion: A systematic review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Li, Y.; Quan, X.; Zhang, Y.B. Towards engineering application: Potential mechanism for enhancing anaerobic digestion of complex organic waste with different types of conductive materials. Water Res. 2017, 115, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.Y.; Ding, L.J.; Zama, E.F.; Liu, P.P.; Hozzein, W.N.; Zhu, Y.G. Biochar Modulates Methanogenesis through Electron Syntrophy of Microorganisms with Ethanol as a Substrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12198–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, K.; Ren, S.; Clark, J.H.; Fan, J.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S. Characterization and utilization of aqueous products from hydrothermal conversion of biomass for bio-oil and hydro-char production: A review. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1553–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wan, J.; Chen, K.; Luo, G.; Fan, J.; Clark, J.; Zhang, S. Biogas production from hydrothermal liquefaction wastewater (HTLWW): Focusing on the microbial communities as revealed by high-throughput sequencing of full-length 16S rRNA genes. Water Res. 2016, 106, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. A review of the hydrothermal carbonization of biomass waste for hydrochar formation: Process conditions, fundamentals, and physicochemical properties. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Usman, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; O-Thong, S.; Angelidaki, I.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Luo, G. Hydrochar-Facilitated Anaerobic Digestion: Evidence for Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer Mediated through Surface Oxygen-Containing Functional Groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5755–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucian, M.; Volpe, M.; Gao, L.H.; Piro, G.; Goldfarb, J.L.; Fiori, L. Impact of hydrothermal carbonization conditions on the formation of hydrochars and secondary chars from the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Fuel 2018, 233, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Yang, L.; Ouyang, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.Y.; Gu, M.Y.; Li, J.; Chen, M.F.; Huang, L.H.; Qian, L.B. Enhanced removal of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene by modified biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron and palladium. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomei, M.C.; Mosca Angelucci, D.; Clagnan, E.; Brusetti, L. Anaerobic biodegradation of phenol in wastewater treatment: Achievements and limits. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2195–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wiegel, J. Purification and characterization of an oxygen-sensitive, reversible 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from Clostridium hydroxybenzoicum. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 3539–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabus, R.; Widdel, F. Anaerobic degradation of ethylbenzene and other aromatic hydrocarbons by new denitrifying bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 163, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schie, P.M.; Young, L.Y. Isolation and characterization of phenol-degrading denitrifying bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Wu, J.H.; Tseng, I.C.; Liang, T.M.; Liu, W.T. Characterization of active microbes in a full-scale anaerobic fluidized bed reactor treating phenolic wastewater. Microbes Environ. 2009, 24, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.G.; Lee, M.K.; Yun, Y.M.; Moon, C.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, D.H. Microbial community analysis of anaerobic granules in phenol-degrading UASB by next generation sequencing. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 112, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tabassum, S.; Yu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Chu, C.; Zhang, Z. Effect of effluent recirculation rate on the performance of anaerobic bio-filter treating coal gasification wastewater under co-digestion conditions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 87926–87934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.R.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, M. Performance and microbial community composition in a long-term sequential anaerobic-aerobic bioreactor operation treating coking wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 8191–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.G.; Koo, T.; Lee, J.; Han, G.; Cho, K.; Kim, W.; Hwang, S. Correlations between bacterial populations and process parameters in four full-scale anaerobic digesters treating sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tringe, S.G.; Rubin, E.M. Metagenomics: DNA sequencing of environmental samples. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanaro, S.; Treu, L.; Kougias, P.G.; Luo, G.; Angelidaki, I. Metagenomic binning reveals the functional roles of core abundant microorganisms in twelve full-scale biogas plants. Water Res. 2018, 140, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.H.; Campanaro, S.; Kougias, P.; Treu, L.; Angelidaki, I.; Zhang, S.C.; Luo, G. Anaerobic granular sludge for simultaneous biomethanation of synthetic wastewater and CO with focus on the identification of CO-converting microorganisms. Water Res. 2017, 126, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Sanders, W. Assessment of the anaerobic biodegradability of macropollutants. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2004, 3, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.J.; Jing, Y.H.; Zhang, S.C.; Angelidaki, I.; Luo, G. Mesophilic and thermophilic alkaline fermentation of waste activated sludge for hydrogen production: Focusing on homoacetogenesis. Water Res. 2016, 102, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Wei, W.; Sun, J.; Xu, Q.X.; Dai, X.H.; Ni, B.J. Medium-Chain fatty acids and long-chain alcohols production from waste activated sludge via two-stage anaerobic fermentation. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Lv, N.; Cai, G.; Zhou, M.; Wang, R.; Li, C.; Ning, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ye, Z.; et al. Carbon- and metal-based mediators modulate anaerobic methanogenesis and phenol removal: Focusing on stimulatory and inhibitory mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Cai, T.; Liu, Z. Hydrochar and pyrochar for sorption of pollutants in wastewater and exhaust gas: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.D. Comparison of hydrochar- and pyrochar-based solid acid catalysts from cornstalk: Physiochemical properties, catalytic activity and deactivation behavior. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Dispensa, M.; Harwood, C.S. 4-hydroxybenzoyl coenzyme A reductase (dehydroxylating) is required for anaerobic degradation of 4-hydroxybenzoate by Rhodopseudomonas palustris and shares features with molybdenum-containing hydroxylases. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupa, B.; Lyon, D.; Shaw, L.N.; Sieprawska-Lupa, M.; Wiegel, J. Properties of the reversible nonoxidative vanillate/4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breese, K.; Boll, M.; Alt-Morbe, J.; Schagger, H.; Fuchs, G. Genes coding for the benzoyl-CoA pathway of anaerobic aromatic metabolism in the bacterium Thauera aromatica. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 256, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, M.Y.; Liang, B.; Mbadinga, S.M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Gu, J.D.; Mu, B.Z. Molecular diversity of bacterial bamA gene involved in anaerobic degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons in mesophilic petroleum reservoirs. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2016, 114, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntze, K.; Shinoda, Y.; Moutakki, H.; McInerney, M.J.; Vogt, C.; Richnow, H.H.; Boll, M. 6-Oxocyclohex-1-ene-1-carbonyl-coenzyme A hydrolases from obligately anaerobic bacteria: Characterization and identification of its gene as a functional marker for aromatic compounds degrading anaerobes. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, K.; Brown, C.T.; Hug, L.A.; Sharon, I.; Castelle, C.J.; Probst, A.J.; Thomas, B.C.; Singh, A.; Wilkins, M.J.; Karaoz, U.; et al. Thousands of microbial genomes shed light on interconnected biogeochemical processes in an aquifer system. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Rinke, C.; Chuvochina, M.; Chaumeil, P.A.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Evans, P.N.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. Recovery of nearly 8,000 metagenome-assembled genomes substantially expands the tree of life. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Uchiyama, T.; Ishii, S.; Enoki, M.; Imachi, H.; Kamagata, Y.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H.; Ikenaga, H.; Watanabe, K. Reconstruction and regulation of the central catabolic pathway in the thermophilic propionate-oxidizing syntroph Pelotomaculum thermopropionicum. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juteau, P.; Cote, V.; Duckett, M.F.; Beaudet, R.; Lepine, F.; Villemur, R.; Bisaillon, J.G. Cryptanaerobacter phenolicus gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobe that transforms phenol into benzoate via 4-hydroxybenzoate. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, B.E.; Bhupathiraju, V.K.; Tanner, R.S.; Woese, C.R.; McInerney, M.J. Syntrophus aciditrophicus sp. nov., a new anaerobic bacterium that degrades fatty acids and benzoate in syntrophic association with hydrogen-using microorganisms. Arch. Microbiol. 1999, 171, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, J.R.; Le, H.M.; McInerney, M.J. The importance of hydrogen and formate transfer for syntrophic fatty, aromatic and alicyclic metabolism. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, M.J.; Rohlin, L.; Mouttaki, H.; Kim, U.; Krupp, R.S.; Rios-Hernandez, L.; Sieber, J.; Struchtemeyer, C.G.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Campbell, J.W.; et al. The genome of Syntrophus aciditrophicus: Life at the thermodynamic limit of microbial growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7600–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.J.F.; Nevin, K.P.; Holmes, D.E.; Rotaru, A.E.; Ward, J.E.; Woodard, T.L.; Zhu, J.; Ueki, T.; Nonnenmann, S.S.; McInerney, M.J.; et al. Syntrophus conductive pili demonstrate that common hydrogen-donating syntrophs can have a direct electron transfer option. ISME J. 2020, 14, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.L.; Shou, L.B.; Lin, D.D.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.Z.; Liu, J.F.; Li, W.; Gu, J.D.; et al. Anaerobic Degradation of Paraffins by Thermophilic Actinobacteria under Methanogenic Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10610–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aromokeye, D.A.; Oni, O.E.; Tebben, J.; Yin, X.; Richter-Heitmann, T.; Wendt, J.; Nimzyk, R.; Littmann, S.; Tienken, D.; Kulkarni, A.C.; et al. Crystalline iron oxides stimulate methanogenic benzoate degradation in marine sediment-derived enrichment cultures. ISME J. 2021, 15, 965–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobu, M.K.; Narihiro, T.; Liu, M.; Kuroda, K.; Mei, R.; Liu, W.T. Thermodynamically diverse syntrophic aromatic compound catabolism. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4576–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huser, B.A.; Wuhrmann, K.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Methanothrix-Soehngenii Gen-Nov-Sp-Nov, a New Acetotrophic Non-Hydrogen-Oxidizing Methane Bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 1982, 132, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Measured Methane Production at the End of Batch Experiments (mL) | P (mL) | Rm (mL/d) | λ (d) | R2 | Increasing Rate of Rm (%) * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 49.5 ± 2.9 | 54.0 ± 7.1 | 2.49 ± 0.41 | 74.2 ± 1.5 | 0.951 | |
| H260 | 51.3 ± 1.8 | 50.3 ± 1.0 | 4.40 ± 0.51 | 59.4 ± 0.7 | 0.988 | 76.7 |
| H320 | 48.2 ± 1.3 | 49.4 ± 0.7 | 4.46 ± 0.42 | 57.6 ± 0.5 | 0.993 | 79.1 |
| P500 | 50.2 ± 0.2 | 51.0 ± 6.0 | 2.07 ± 0.32 | 66.8 ± 1.6 | 0.960 | −16.9 |
| P700 | 46.1 ± 1.7 | 54.0 ± 9.2 | 1.59 ± 0.21 | 63.2 ± 1.8 | 0.952 | −36.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, T.; He, J.; Shi, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, G. Metagenomic Binning Revealed Microbial Shifts in Anaerobic Degradation of Phenol with Hydrochar and Pyrochar. Fermentation 2023, 9, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040387
Luo T, He J, Shi Z, Shi Y, Zhang S, Liu Y, Luo G. Metagenomic Binning Revealed Microbial Shifts in Anaerobic Degradation of Phenol with Hydrochar and Pyrochar. Fermentation. 2023; 9(4):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040387
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Tao, Jun He, Zhijian Shi, Yan Shi, Shicheng Zhang, Yan Liu, and Gang Luo. 2023. "Metagenomic Binning Revealed Microbial Shifts in Anaerobic Degradation of Phenol with Hydrochar and Pyrochar" Fermentation 9, no. 4: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040387
APA StyleLuo, T., He, J., Shi, Z., Shi, Y., Zhang, S., Liu, Y., & Luo, G. (2023). Metagenomic Binning Revealed Microbial Shifts in Anaerobic Degradation of Phenol with Hydrochar and Pyrochar. Fermentation, 9(4), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040387