Magnetorheological Finishing of Chemically Treated Electroless Nickel Plating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Electroless Plating
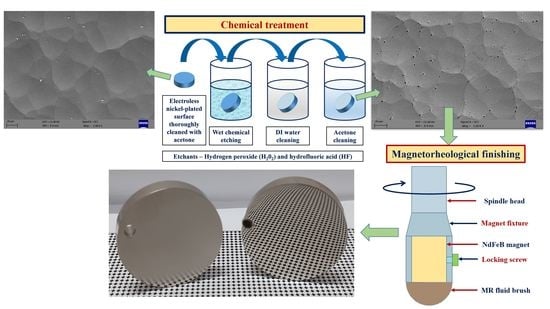
2.2. Chemical Treatment of Plated Surface
2.3. Magnetorheological Finishing of Chemically Treated Surface
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of the As-Plated Surface
3.2. Characterization of Chemically Treated Surface
3.3. Surface Roughness
4. Conclusions
- The surface topography of the chemically treated surfaces revealed that the pits are formed and grown in size with an increase in chemical treatment duration with 15% H2O2. The surface chemically treated with 1% HF is relatively smooth having mild reaction. A higher concentration of HF (5%) results in aggressive reaction on the surface and cluster of pits are formed after a chemical treatment duration of 30 min.
- The microhardness of the chemically treated surface decreases after chemical treatment irrespective of chemical and exposure duration. The surface roughness of the chemically treated surfaces increases with 15% H2O2 and 5% HF whereas it decreases with 1% HF. This is related to the formation of pits and surface film. The minimum and maximum surface roughness after chemical treatment is achieved on surfaces chemically treated with 1% HF for 30 min and 5% HF for 30 min, respectively.
- The percentage reduction in surface roughness for chemically treated surfaces after MRF is higher than the same for an as-plated surface. The finishing rate is lowest for surface treated with 1% HF for 30 min. The drastic reduction in surface roughness after chemical treatment is the sole reason for this. All other surfaces have a higher finishing rate when compared with an as-plated surface.
- The normal and tangential forces are mainly dependent on hardness and surface roughness of the surfaces. Moreover, the formation of pits, deposition and intergranular attack also affect these finishing forces.
- A minimum roughness of 10 nm is achieved on a surface chemically treated with 1% HF for a duration of 30 min. There is a reduction of 99% in surface roughness in a two-step process (chemical treatment and MRF). It can be concluded that material removal becomes easy after chemical treatment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loto, C.A. Electroless nickel plating–a review. Silicon 2016, 8, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudagar, J.; Lian, J.; Sha, W. Electroless nickel, alloy, composite and nano coatings–A critical review. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 571, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitry, V.; Sens, A.; Delaunois, F. Comparison of various electroless nickel coatings on steel: Structure, hardness and abrasion resistance. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 783–786, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, Y.; Shimomura, T.; Fushiki, A.; Beaucamp, A.; Inasaki, I.; Kunieda, H.; Ogasaka, Y.; Yamashita, K. Ultra-precision polishing of electroless nickel molding dies for shorter wavelength applications. CIRP Ann. 2008, 57, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Singh, H. Chemomechanical magnetorheological finishing: Process mechanism, research trends, challenges and opportunities in surface finishing. J. Micromanuf. 2021, 5(2), 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Xu, M.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Tang, G.; Yue, X. The magnetorheological finishing (MRF) of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) crystal with Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sidpara, A.M.; Jain, V.K. Nanofinishing of freeform surfaces of prosthetic knee joint implant. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B J. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 226, 1833–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Jang, K.I.; Min, B.K.; Lee, S.J. A study on the fabrication of curved surfaces using magnetorheological fluid finishing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 2077–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.; Jang, K.I.; Min, B.K.; Lee, S.J.; Seok, J. Magnetorheological finishing process for hard materials using sintered iron-CNT compound abrasives. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2009, 49, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, Y.; Li, Z.; Dong, J.; Cui, H. Steady-State and Dynamic Rheological Properties of a Mineral Oil-Based Ferrofluid. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socoliuc, V.; Peddis, D.; Petrenko, V.I.; Avdeev, M.V.; Susan-Resiga, D.; Szabó, T.; Turcu, R.; Tombácz, E.; Vékás, L. Magnetic nanoparticle systems for nanomedicine—A materials science perspective. Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, X.; Qu, J.; Zhang, X. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of the Assisted Abrasive Flow of Magnetic Particles on the Polishing of Fuel Injection Nozzles. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Guo, M.; Yin, S.; Chen, F.; Huang, S.; Lu, A.; Guo, Y. An atomic-scale and high efficiency finishing method of zirconia ceramics by using magnetorheological finishing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Lambropoulos, J.C.; Jacobs, S.D. Process parameter effects on material removal in magnetorheological finishing of borosilicate glass. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafrir, S.N.; Lambropoulos, J.C.; Jacobs, S.D. A magnetorheological polishing-based approach for studying precision microground surfaces of tungsten carbides. Precis. Eng. 2007, 31, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.A.; Jha, S. Synthesis of polishing fluid and novel approach for nanofinishing of copper using ball-end magnetorheological finishing process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhong, M.; Rushing, K.J.; Li, Y.; Shipp, D.A. Benzotriazole as a passivating agent during chemical mechanical planarization of Ni–P alloy substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 315, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.L.; Wang, R.M.; Hu, T.; Yin, L.H.; Pu, Y.P.; Lin, P.H.; Wu, S.L.; Chung, C.Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Chu, P.K. Surface structure and biomedical properties of chemically polished and electropolished NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liao, L.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Guo, D. Development of a novel chemical mechanical polishing slurry and its polishing mechanisms on a nickel alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Hu, H.; Lai, T.; Yang, Q.; Xiong, Y. A High Efficiency and Precision Smoothing Polishing Method for NiP Coating of Metal Mirror. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xu, C.; Lai, T.; Yang, Q.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Qiu, J. Sub-Nanometer Accuracy Combination Processing Technology for Nickel–Phosphorus Modified Surfaces Based on Aluminum Reflector Mirror. Micromachines 2022, 13, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Sidpara, A.; Bandyopadhyay, P.P. High efficiency chemical assisted nanofinishing of HVOF sprayed WC-Co coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Kumar, M.; Sidpara, A.M.; Bandyopadhyay, P.P. Tribological aspects of different machining processes. In Machining and Tribology, 1st ed.; Pramanik, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Sidpara, A.; Bandyopadhyay, P.P. Magnetorheological finishing of WC-Co coating using iron-B4C-CNT composite abrasives. Tribol. Int. 2021, 155, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sidpara, A.M.; Racherla, V. Finishing of OFHC copper using fluid filled open-cell porous flexible abrasive impregnated tools. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B J. Eng. Manuf. 2022, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Cho, J.H.; Jung, J.H.; Duy, P.P.; Le, A.H.T.; Yi, J. A review of wet chemical etching of glasses in hydrofluoric acid based solution for thin film silicon solar cell application. Curr. Photovolt. Res. 2017, 5, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.D.; Chou, C.T. The influence of phosphorus content on the microstructure and specific capacitance of etched electroless Ni-P coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 368, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibińska, K.; Kutyła, D.; Yang, X.; Krause, L.; Marzec, M.M.; Żabiński, P. Rhodium-decorated nanoconical nickel electrode synthesis and characterization as an electrochemical active cathodic material for hydrogen production. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 592, 153326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Lee, W. XPS study of CMP mechanisms of NiP coating for hard disk drive substrates. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; Guo, Z.; Wu, K.H.; Tan, C.; Wang, Z. Bimetallic metal-organic framework derived metal-carbon hybrid for efficient reversible oxygen electrocatalysis. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Lau, L.W.; Gerson, A.; Smart, R.S.C. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic chemical state quantification of mixed nickel metal, oxide and hydroxide systems. Surf. Interface Anal. 2009, 41, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivet, L.; Joudrier, A.L.; Bouttemy, M.; Vigneron, J.; Tan, K.L.; Morelle, J.M.; Etcheberry, A.; Chalumeau, L. Wettability and XPS analyses of nickel–phosphorus surfaces after plasma treatment: An efficient approach for surface qualification in mechatronic processes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 274, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Gu, C.D.; Wang, X.L.; Tu, J.P. Ionothermal synthesis and lithium storage performance of core/shell structured amorphous@ crystalline Ni–P nanoparticles. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 7942–7950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zu, X.; Jiang, X.; Xiang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, W.; Li, L. Effect of HF etching on the surface quality and laser-induced damage of fused silica. Opt. Laser Technol. 2012, 44, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, L.; Yan, Y. Effects of HF etching on nanoindentation response of ion-exchanged aluminosilicate float glass on air and tin sides. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 4367–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sidpara, A.M.; Racherla, V. Surface finishing of aluminium 6061 using fabricated flexible abrasive tool. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Parameter | Levels |
|---|---|
| Chemicals | Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) hydrofluoric acid (HF) |
| Concentration | H2O2–15%
HF–1%, 5% |
| Exposure time | 10, 20, and 30 min |
| Constituents | Vol. % |
|---|---|
| Carbonyl iron particles (CIPs) | 40 |
| Boron carbide abrasive | 5 |
| Glycerol | 5 |
| Benzotriazole (BTA) | 4 |
| Deionized water | Balance |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Tool rotational speed | 800 RPM |
| Working gap | 1.5 mm |
| Tool feed rate | 30 mm/min |
| Travel length in single pass | 60 mm |
| No. of passes | 5 |
| Finishing duration | 10 min |
| Total no. of experiments | 10 |
| Experiment No. | Input Parameters | Output Responses | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemicals | Conc. (% v/v) | Exposure Time | Areal Surface Roughness (nm) | Finishing Forces (N) | |||
| Initial | Final | Normal Fz | Tangential Ft | ||||
| 1 | H2O2 | 15 | 10 | 1026 | 100 | 17.66 | 4.24 |
| 2 | H2O2 | 15 | 20 | 1075 | 114 | 17.44 | 4.94 |
| 3 | H2O2 | 15 | 30 | 1151 | 116 | 13.12 | 2.48 |
| 4 | HF | 1 | 10 | 925 | 83 | 6.46 | 2.01 |
| 5 | HF | 1 | 20 | 918 | 79 | 6.51 | 2.42 |
| 6 | HF | 1 | 30 | 370 | 59 | 13.73 | 3.91 |
| 7 | HF | 5 | 10 | 1013 | 129 | 12.12 | 1.65 |
| 8 | HF | 5 | 20 | 1044 | 143 | 16.72 | 4.54 |
| 9 | HF | 5 | 30 | 1209 | 173 | 14.19 | 2.93 |
| 10 | As-plated surface | 960 | 200 | 13.13 | 3.51 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, M.; Bhavani, T.; Rawal, S.; Sidpara, A. Magnetorheological Finishing of Chemically Treated Electroless Nickel Plating. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120184
Kumar M, Bhavani T, Rawal S, Sidpara A. Magnetorheological Finishing of Chemically Treated Electroless Nickel Plating. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(12):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120184
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Mayank, Tharra Bhavani, Sunil Rawal, and Ajay Sidpara. 2022. "Magnetorheological Finishing of Chemically Treated Electroless Nickel Plating" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 12: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120184
APA StyleKumar, M., Bhavani, T., Rawal, S., & Sidpara, A. (2022). Magnetorheological Finishing of Chemically Treated Electroless Nickel Plating. Magnetochemistry, 8(12), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8120184