Artifacts’ Detection for MRI Non-Metallic Needles: Comparative Analysis for Artifact Evaluation Using K-Means and Manual Quantification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
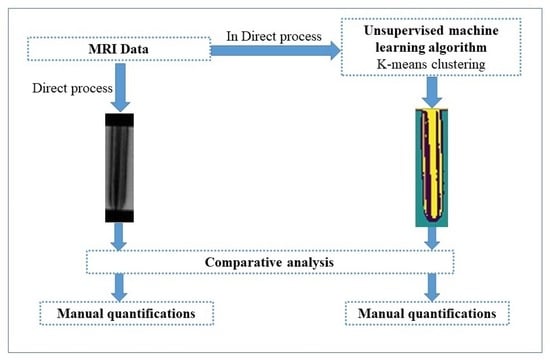
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Manual Quantification
2.3. K-Means Quantification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Artifacts Quantification: Needles’ Widths
3.2. Artifacts’ Quantification: Needles’ Shafts
3.3. Cluster Validation: Silhouette Coefficient
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adam, G.; Bücker, A.; Nolte-Ernsting, C.; Tacke, J.; Günther, R.W. Interventional MR imaging: Percutaneous abdominal and skeletal biopsies and drainages of the abdomen. Eur. Radiol. 1999, 9, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariniemi, J.; Blanco Sequeiros, R.; Ojala, R.; Tervonen, O. MRI-guided abdominal biopsy in a 0.23-T open-configuration MRI system. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bücker, A.; Adam, G.; Neuerburg, J.M.; Glowinski, A.; Tacke, J.; Günther, R.W. Interventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging—Non-Invasive Imaging for Interventions. Rofo Fortschr. Auf Dem Geb. Der Rontgenstrahlen Und Der Nukl. 2000, 172, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frahm, C.; Gehl, H.-B.; Melchert, U.H.; Weiss, H.-D. Visualization of magnetic resonance-compatible needles at 1.5 and 0.2 Tesla. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 1996, 19, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangos, S.; Kiefl, D.; Eichler, K.; Engelmann, K.; Heller, M.; Herzog, C.; Mack, M.G.; Jacobi, V.; Vogl, T.J. MR-guided biopsies of undetermined liver lesions: Technique and results. Rofo Fortschr. Auf Dem Geb. Der Rontgenstrahlen Und Der Nukl. 2003, 175, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.; Thomas, C.; Clasen, S.; Claussen, C.D.; Lewin, J.S.; Pereira, P.L. Freehand real-time MRI-guided lumbar spinal injection procedures at 1.5 T: Feasibility, accuracy, and safety. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 192, W161–W167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, H.H. Mr-compatible instruments for interventional mri. In Interventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 35–51. [Google Scholar]
- Genant, J.W.; Vandevenne, J.E.; Bergman, A.G.; Beaulieu, C.F.; Kee, S.T.; Norbash, A.M.; Lang, P. Interventional Musculoskeletal Procedures Performed by Using MR Imaging Guidance with a Vertically Open MR Unit: Assessment of Techniques and Applicability. Radiology 2002, 223, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehranzadeh, J.; Tao, C.; Browning, C.A. Percutaneous needle biopsy of the spine. Acta Radiol. 2007, 48, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, M.; Detert, M.; Rube, M.A.; El-Tahir, A.; Elle, O.J.; Melzer, A.; Schmidt, B.; Rose, G.H. Resonant marker design and fabrication techniques for device visualization during interventional magnetic resonance imaging. Biomed. Eng./Biomed. Tech. 2015, 60, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maatoq, M.; Boese, A.; Henke, H.W.; Friebe, M. Primary Design Concept for Non-metallic Needle for MRI Guided Spinal Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 1994–1997. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, Y.; Sakurai, J.; Hiraki, T.; Okamoto, S.; Iguchi, T.; Tomita, K.; Uka, M.; Gobara, H.; Kanazawa, S. MRI-guided percutaneous needle biopsy with 1.2 T open MRI: Study protocol for a prospective feasibility study (SCIRO-1701). Nagoya J. Med Sci. 2019, 81, 463. [Google Scholar]
- Garnon, J.; Ramamurthy, N.; Caudrelier, J.J.; Erceg, G.; Breton, E.; Tsoumakidou, G.; Rao, P.; Gangi, A. MRI-Guided Percutaneous Biopsy of Mediastinal Masses Using a Large Bore Magnet: Technical Feasibility. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 39, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehl, H.B.; Frahm, C.; Melchert, U.H.; Weiss, H.D. Suitability of different MR-compatible needle and magnet designs for MR-guided punctures. In Proceedings of the SMR 3rd Annual Meeting, Nice, France, 19–25 August 1995; Volume 1156. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, G.; Dewey, C. Study of new Titanium alloy needles for interventional MRI procedures. In Proceedings of the SMR 3rd Annual Meeting, Paris, France, 18–22 August 1995; Volume 1159. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Maatoq, M.; Krug, J.W.; Friebe, M.H. The tip is the key-rfa needle modification using peek for reduced susceptibility artifact in mri. In Proceedings of the Conference of the International Society for Medical Innovation and Technology, (SMIT), Delft, The Netherlands, 5–8 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fantini, I.; Rittner, L.; Yasuda, C.; Lotufo, R. Automatic detection of motion artifacts on MRI using Deep CNN. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Neuroimaging (PRNI), Singapore, 2–14 June 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ladd, M.E.; Erhart, P.; Debatin, J.F.; Romanowski, B.J.; Boesiger, P.; McKinnon, G.C. Biopsy needle susceptibility artifacts. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, J.S.; Duerk, J.L.; Haaga, J.R. Needle localization in MR guided therapy: Effect of field strength, sequence design, and magnetic field orientation. In Proceedings of the SMR 3rd Annual Meeting, Nice, France, 19–25 August 1995; Volume 1155. [Google Scholar]
- Penzkofer, T.; Peykan, N.; Schmidt, K.; Krombach, G.; Kuhl, C.K. How MRI compatible is “MRI compatible”? A systematic comparison of artifacts caused by biopsy needles at 3.0 and 1.5 T. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holton, A.; Walsh, E.; Anayiotos, A.; Pohost, G.; Venugopalan, R. Comparative mri compatibility of 316l stainless steel alloy and nickel–titanium alloy stents: Original article technical. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2002, 4, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, A. Materials and biomaterials for interventional radiology. Biomed. Pharmacother. 1998, 52, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.-E.; Cho, N.B.; Iordachita, I.I.; Guion, P.; Fichtinger, G.; Whitcomb, L.L. A study of needle image artifact localization in confirmation imaging of MRI-guided robotic prostate biopsy. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alamooti, H.Y.; Ganji, Y.; Farimani, F.S.; Rostami, M. Primary design of MRI compatible needle for the purpose of soft tissue insertion. In Proceedings of the 2010 17th Iranian Conference of Biomedical Engineering (ICBME), Isfahan, Iran, 3–4 November 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrtash, A.; Ghafoorian, M.; Pernelle, G.; Ziaei, A.; Heslinga, F.G.; Tuncali, K.; Fedorov, A.; Kikinis, R.; Tempany, C.M.; Wells, W.M.; et al. Automatic Needle Segmentation and Localization in MRI With 3-D Convolutional Neural Networks: Application to MRI-Targeted Prostate Biopsy. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2018, 38, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Deserno, T.M.; Spitzer, K. Evaluation of free non-diagnostic DICOM software tools. Medical Imaging 2008: PACS and Imaging Informatics. Proc. SPIE 2008, 6919, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illanes, A.; Krug, J.W.; Friebe, M. Assessing MRI susceptibility artefact through an indicator of image distortion. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 2, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhankhar, S.; Tyagi, S.; Prasad, T. Brain MRI segmentation using K-means algorithm. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Advances in Knowledge Management, Kerala, India, 21–22 December 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, H. Research on K-means clustering segmentation method for MRI brain image based on selecting multi-peaks in gray histogram. J. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 30, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.G.; Park, S.J.; Moon, W.K. K-means clustering approach for kinetic pattern analysis of dynamic contrast enhancement breast MRI. APAMI 2006, 2006, 336. [Google Scholar]
- Allman, D.; Reiter, A.; Bell, M.A.L. A machine learning method to identify and remove reflection artifacts in photoacoustic channel data. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pourtaherian, A. Robust Needle Detection and Visualization for 3D Ultrasound Image-Guided Interventions; Technische Universiteit Eindhoven: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.-E.; Cho, N.B.; Iordachita, I.I.; Guion, P.; Fichtinger, G.; Kaushal, A.; Camphausen, K.; Whitcomb, L.L. Biopsy Needle Artifact Localization in MRI-Guided Robotic Transrectal Prostate Intervention. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Understanding K-Means Clustering in Machine Learning. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-k-means-clustering-in-machine-learning-6a6e67336aa1 (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Calthorpe, N. The history of spinal needles: Getting to the point. Anaesthesia 2004, 59, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, W.-S.; Bahk, J.-H.; Lim, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-C. The effect of introducer gauge, design and bevel direction on the deflection of spinal needles. Anaesthesia 2002, 57, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damianou, C. The role of phantoms in magnetic resonance imaging-guided focused ultrasound surgery. Digit. Med. 2019, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, A.I.; Odéen, H.; de Bever, J.; Coats, B.; Parker, D.L.; Payne, A.; Christensen, D.A. Characterization and evaluation of tissue-mimicking gelatin phantoms for use with MRgFUS. J. Ther. Ultrasound 2015, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Küçükkülahli, E.; Erdoğmuş, P.; Polat, K. Brain MRI segmentation based on different clustering algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 155, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.R.; Dixit, P.; Singh, N.; Gupta, J.P. Infected Fruit Part Detection using K-Means Clustering Segmentation Technique. Int. J. Interact. Multimed. Artif. Intell. 2013, 2, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Franco-Penya, H.-H.; Kelleher, J.D.; Pugh, J.; Ross, R. An analysis of the application of simplified silhouette to the evaluation of k-means clustering validity. In Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition, MLDM 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 291–305. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanachandra, N.; Manglem, K.; Chanu, Y.J. Image Segmentation Using K -means Clustering Algorithm and Subtractive Clustering Algorithm. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 54, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mamat, A.R.; Mohamed, F.S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Rawi, N.M.; Awang, M.K. Silhouette index for determining optimal k-means clustering on images in different color models. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinh, D.-T.; Fujinami, T.; Huynh, V.-N. Estimating the optimal number of clusters in categorical data clustering by silhouette coefficient. In Knowledge and Systems Sciences, KSS 2019; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Burney, S.M.A.; Tariq, H. K-means cluster analysis for image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Seraj, R.; Islam, S.M.S. The k-means Algorithm: A Comprehensive Survey and Performance Evaluation. Electronics 2020, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbelaitz, O.; Gurrutxaga, I.; Muguerza, J.; Pérez, J.M.; Perona, I. An extensive comparative study of cluster validity indices. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, A.; Velmurugan, T. Identification of Calcification in MRI Brain Images by k-Means Algorithm. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Labeled Needles | Materials Used for Needles’ Fabrication | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | Inner core (3FB) + outer sheet (PTFE AWG 21) | OD: 1.00 mm, TW: 0.15 mm |
| L2 | Inner core (3FB) + outer sheet (PTFE AWG 22) | OD: 1.00 mm, TW: 0.15 mm |
| L3 | Inner core (3FB) + outer sheet (PTFE AWG 20) | OD: 1.00 mm, LW: 0.15 mm |
| L4 | ITP Standard needle (inner core + outer sheet) = NiTi | OD: 1.00 mm. LW: 0.15 mm |
| L5 | Inner core (3FB) + outer sheet (PTFE AWG 22) | OD: 1.00 mm, TW: 0.25 mm |
| L6 | Inner core (3FB) + outer sheet (PTFE AWG 21) | OD: 1.00 mm, LW: 0.15 mm |
| L7 | Inner core (3FB) + outer sheet (PEEK) | OD: 0.78 mm, TW: 0.25 mm |
| L8 | Inner core (3FB) + outer sheet (FEP AWG 22) | OD: 1.00 mm, TW: 0.25 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AL-Maatoq, M.; Fachet, M.; Rao, R.; Hoeschen, C. Artifacts’ Detection for MRI Non-Metallic Needles: Comparative Analysis for Artifact Evaluation Using K-Means and Manual Quantification. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9030079
AL-Maatoq M, Fachet M, Rao R, Hoeschen C. Artifacts’ Detection for MRI Non-Metallic Needles: Comparative Analysis for Artifact Evaluation Using K-Means and Manual Quantification. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleAL-Maatoq, Marwah, Melanie Fachet, Rajatha Rao, and Christoph Hoeschen. 2023. "Artifacts’ Detection for MRI Non-Metallic Needles: Comparative Analysis for Artifact Evaluation Using K-Means and Manual Quantification" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9030079
APA StyleAL-Maatoq, M., Fachet, M., Rao, R., & Hoeschen, C. (2023). Artifacts’ Detection for MRI Non-Metallic Needles: Comparative Analysis for Artifact Evaluation Using K-Means and Manual Quantification. Magnetochemistry, 9(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9030079