Development of a New Control System for a Rehabilitation Robot Using Electrical Impedance Tomography and Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Design
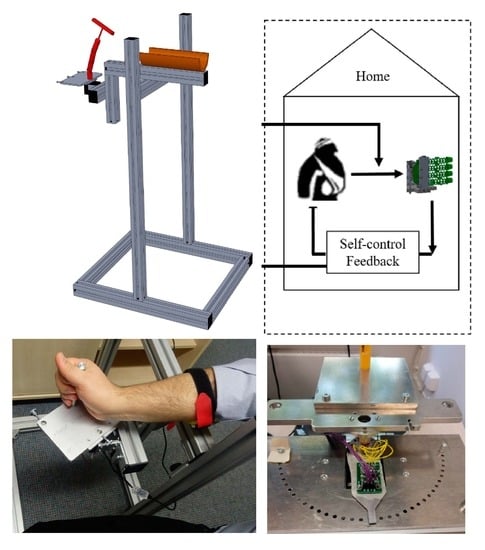
2.1. Mechanical Design
2.2. Mechanical Model of the Forearm and Wrist Rotations

2.3. Control Architecture
2.4. Tomography
2.4.1. Impedance Analyzer Setup
2.4.2. Impedance Calculations
2.4.3. Torque Calculation Based on Hand Impedance
2.4.4. Protocol Description
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Future Work
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouteraa, Y.; Ben Abdallah, I.; Alnowaiser, K.; Islam, M.R.; Ibrahim, A.; Gebali, F. Design and development of a smart IoT-based robotic solution for wrist rehabilitation. Micromachines 2022, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Hacke, W.; Fisher, M.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global stroke fact sheet 2022. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.H.; Kim, Y.H. Robot-assisted therapy in stroke rehabilitation. J. Stroke 2013, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, V.; Fouad, K. Restoration of sensorimotor functions after spinal cord injury. Brain 2014, 137, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Bi, Z. Recent Development of Rehabilitation Robots. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 563062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbbasiMoshaii, A.; Najafi, F. Design, evaluation and prototyping of a new robotic mechanism for ultrasound imaging. J. Comput. Appl. Mech. 2019, 50, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Mohebbi, A. Human-robot interaction in rehabilitation and assistance: A review. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2020, 1, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.; Brooks, D.; Brown, E.; Gebregiorgis, A.; Chen, Y.P. Non-contact versus contact-based sensing methodologies for in-home upper arm robotic rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.S.; Powers, J.P.; Tilton, L.G.; Kriegman, S.; Bongard, J.; Kramer-Bottiglio, R. A soft robot that adapts to environments through shape change. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshaii, A.A.; Masouleh, M.T.; Zarezadeh, E.; Farajzadeh, K. Static analysis of a 3-RRS and a 3-RSR Spherical Parallel Robots. In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd RSI international conference on robotics and mechatronics (ICROM), Tehran, Iran, 7–9 October 2015; pp. 800–804. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H. An Internet of Things Framework Based on Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robots for Rehabilitation. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Interactive Applications: Proceedings of the Advances in Intelligent, Interactive Systems and Applications; Xhafa, F., Patnaik, S., Tavana, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 752–759. [Google Scholar]
- Payedimarri, A.B.; Ratti, M.; Rescinito, R.; Vanhaecht, K.; Panella, M. Effectiveness of Platform-Based Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation for Musculoskeletal or Neurologic Injuries: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niestanak, V.D.; Moshaii, A.A.; Moghaddam, M.M. A new underactuated mechanism of hand tendon injury rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th RSI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), Tehran, Iran, 25–27 October 2017; pp. 400–405. [Google Scholar]
- Burgar, C.G.; Lum, P.S.; Shor, P.C.; Van der Loos, H.M. Development of robots for rehabilitation therapy: The Palo Alto VA/Stanford experience. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2000, 37, 663–674. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Li, G.; Su, E.; Wei, X.; Huang, S.; Ma, K.; Zheng, H.; Xie, L. Real-Time Detection of Compensatory Patterns in Patients With Stroke to Reduce Compensation During Robotic Rehabilitation Therapy. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2630–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahim, K.N.K.A.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Vasant, P.; Ganesan, T. Robotic Assistive System: Development of a Model based on Artificial Intelligent Technique. In Robotic Systems: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 1688–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Matheson Rittenhouse, D.; Abdullah, H.A.; John Runciman, R.; Basir, O. A neural network model for reconstructing EMG signals from eight shoulder muscles: Consequences for rehabilitation robotics and biofeedback. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1924–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Wei, W.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y. Kinematic analysis of a novel exoskeleton finger rehabilitation robot for stroke patients. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Tianjin, China, 3–6 August 2014; pp. 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Holder, D. Electrical Impedance Tomography: Methods, History and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Frerichs, I.; Dargaville, P.A.; van Genderingen, H.; Morel, D.R.; Rimensberger, P.C. Lung volume recruitment after surfactant administration modifies spatial distribution of ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Cortés, J.C.; Díaz-Carmona, J.J.; Padilla-Medina, J.A.; Calderon, A.E.; Gutiérrez, A.I.B.; Gutiérrez-López, M.; Prado-Olivarez, J. Electrical Impedance Tomography Technical Contributions for Detection and 3D Geometric Localization of Breast Tumors: A Systematic Review. Micromachines 2022, 13, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezanejad Gatabi, Z.; Mirhoseini, M.; Khajeali, N.; Rezanezhad Gatabi, I.; Dabbaghianamiri, M.; Dorri, S. The accuracy of electrical impedance tomography for breast cancer detection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast J. 2022, 2022, 8565490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.Y.; Hou, W.; Huang, Q.; Hou, X.; Bao, X.Y.; Kong, W.X.; Li, C.X.; Qiu, Y.Q.; Hu, S.Y.; Dong, L.H. Advances in electrical impedance tomography-based brain imaging. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, S.K.; Hogan, N. Dynamics of wrist rotations. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peaden, A.W.; Charles, S.K. Dynamics of wrist and forearm rotations. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 2779–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leva, P. Adjustments to Zatsiorsky-Seluyanov’s segment inertia parameters. J. Biomech. 1996, 29, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, J.M.M.; Luna, A.M.; Fernández, R.E.H. Characterization and Differentiation between Olive Varieties through Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy, Neural Networks and IoT. Sensors 2020, 20, 5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budoya, D.; Baptista, F. Signal Acquisition from Piezoelectric Transducers for Impedance-Based Damage Detection. Proceedings 2018, 2, 4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, D.; Chen, B.; Wu, H. Integral fuzzy sliding mode impedance control of an upper extremity rehabilitation robot using time delay estimation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 156513–156525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, H.; Qiu, S.; Yao, W.; Xie, P.; Chen, X. An advanced adaptive control of lower limb rehabilitation robot. Front. Robot. AI 2018, 5, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Piece Name | Material | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Forearm holder | Plastic | 1 |
| Motor holder | Steel | 2 |
| Motor | Dynamixel motor | 1 |
| Rotating plate | Aluminium | 1 |
| Horizontal rail | Aluminium | 1 |
| Motor place regulator | Aluminium | 1 |
| Name | Age | Date | Time | Repetition | Flexion | Extension | Ulnar | Radial | Supination | Pronation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27022023 | 09:47:00 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 20 | 15 | ||
| 27022023 | 21:16:00 | 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 23 | 17 | ||
| 28022023 | 08:56:00 | 8 | 13 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 27 | 19 | ||
| 28022023 | 18:34:00 | 12 | 15 | 10 | 9 | 6 | 29 | 19 | ||
| 29022023 | 10:12:00 | 3 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 32 | 21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbasimoshaei, A.; Chinnakkonda Ravi, A.K.; Kern, T.A. Development of a New Control System for a Rehabilitation Robot Using Electrical Impedance Tomography and Artificial Intelligence. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050420
Abbasimoshaei A, Chinnakkonda Ravi AK, Kern TA. Development of a New Control System for a Rehabilitation Robot Using Electrical Impedance Tomography and Artificial Intelligence. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(5):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050420
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbasimoshaei, Alireza, Adithya Kumar Chinnakkonda Ravi, and Thorsten Alexander Kern. 2023. "Development of a New Control System for a Rehabilitation Robot Using Electrical Impedance Tomography and Artificial Intelligence" Biomimetics 8, no. 5: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050420
APA StyleAbbasimoshaei, A., Chinnakkonda Ravi, A. K., & Kern, T. A. (2023). Development of a New Control System for a Rehabilitation Robot Using Electrical Impedance Tomography and Artificial Intelligence. Biomimetics, 8(5), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050420