Experimental Investigation on the Effect of Size and Pitch of Hydrophobic Square Patterns on the Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Performance of Cylindrical Copper Surface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Process
2.1. Surface Modification
2.1.1. Copper Test Piece Cleaning Procedure
2.1.2. Preparation of the Polymer Mixture for Screen Printing
2.1.3. Preparation of the Heterogeneous Wettable Surfaces with Various Sized and Pitched Square Patterns
2.2. Test Section
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Data Reduction and Uncertainty Analysis
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
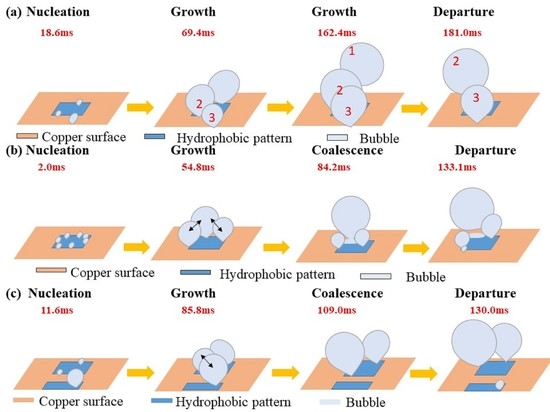
3.1. Bubble Dynamics
3.2. Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Performance
4. Conclusions
- Three types of the development behaviors were observed on the heterogeneous wettable surfaces: the isolated development of a bubble, the internal coalescence of bubbles, and the inter coalescence of bubbles in the axial and circumferential directions. The isolated bubble development had a longer departure time and was most frequent at low heat fluxes. However, internal and inter coalescences in the circumferential direction took less departure time due to the influence of the merging of the bubbles.
- The 2 mm size square pattern (Ratio = 0.4) produced a superior pool boiling heat transfer performance compared to all other aspect ratios studied. This is due to the presence of more bubbles at the interfaces, internal coalescence, the inter coalescence in the circumferential direction, and the inter coalescence of bubbles in the axial direction at the time of departure. Therefore, the 2 mm size square pattern (Ratio = 0.4) is the best design.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, B.; Yamada, M.; Hidaka, S.; Liu, J.; Shiomi, J.; Amberg, G.; Do-Quang, M.; Kohno, M.; Takahashi, K.; Takata, Y. Early Onset of Nucleate Boiling on Gas-covered Biphilic Surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, N.S.; Buongiorno, J.; Varanasi, K.J. Critical heat flux maxima during boiling crisis on textured surfaces. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hanley, H.; Coyle, C.; Buongiorno, J.; McKrell, T.; Hu, L.; Rubner, M.; Cohen, R. Separate effects of surface roughness, wettability, and porosity on the boiling critical heat flux. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 024102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garimella, S.V.; Fleischer, A.S.; Murthy, J.Y.; Keshavarzi, A.; Prasher, R. Thermal Challenges in Next-Generation Electronic Systems. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 2008, 31, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienhard, J.H., IV; Lienhard, J.H., V. A Heat Transfer Textbook, 3rd ed.; Phlogiston Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmendra, M.; Suresh, S.; Kumar, C.S.S.; Yang, Q. Pool Boiling Heat Transfer enhancement using vertically aligned Carbon Nanotube Coatings on a copper substrate. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 99, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouh, M.; Gualous, H.L.; de Labachelerie, M. Local convective boiling heat transfer and pressure drop of nanofluid in narrow rectangular channels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 2619–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottoff, S.; Gorenflo, D.; Danger, E.; Luke, A. Heat transfer and bubble formation in pool boiling: Effect of basic surface modifications for heat transfer enhancement. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2006, 3, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Genk, M.S.; Ali, A.F. Enhanced nucleate boiling on copper micro-porous surfaces. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2010, 36, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.S.; Suresh, S.; Yang, L.; Yang, Q.; Aravind, S. Flow boiling heat transfer enhancement using carbon nanotube coatings. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 65, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.T.; Caney, N.; Marty, P.; Colasson, S.; Gavillet, J. How does Surface Wettability Influence Nucleate Boiling? CR Mécanique 2009, 337, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Latour, B.; Li, C.H.; Li, C.; Lee, Y.; Yang, R. Enhanced Bubble Nucleation and Liquid Rewetting for Highly Efficient Boiling Heat Transfer on Two-level Hierarchical Surfaces with Patterned Copper Nanowire Arrays. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.-J.; Ahn, H.S.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, M.H. A Study of Nucleate Boiling Heat Transfer on Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic and Heterogeneous Wetting Surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 5643–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-H.; David, M.; Gao, Z.; Chang, A.; Allen, M.; Wang, H.; Chang, C.-H. Large-scale Generation of Patterned Bubble Arrays on Printed Bi-functional Boiling Surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.S.S.; Chang, Y.W.; Chen, P.H. Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Enhancement on Cylindrical Surfaces with Hybrid Wettable Patterns. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.J.; Leu, T.Z.-S. Fabrication of high wettability gradient on copper substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Lee, M.R.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, P.H. Effect of interlaced wettability on horizontal copper cylinders in nucleate pool boiling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 112, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.R. An Introduction to Error Analysis: The Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements, 2nd ed.; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Pollack, J.; McCarthy, M. Increasing boiling heat transfer using low conductivity materials. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.S.S.; Chang, Y.W.; Chen, P.H. Effect of heterogeneous wettable structures on pool boiling performance of cylindrical copper surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 127, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Advancing Contact Angle (°) | Receding Contact Angle (°) | |
|---|---|---|
| Plain copper surface | 104.79 | 3.22 |
| Hydrophobic surface | 124.32 | 54.79 |
| Aspect Ratio | Size (mm) | Pitch (mm) | Number of Patterns | Area Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case: Various sizes of pattern | ||||
| 0.20 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 105 | 3.34 |
| 0.30 | 1.5 | 5.0 | 105 | 7.52 |
| 0.40 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 105 | 13.37 |
| 0.50 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 105 | 20.89 |
| 0.60 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 105 | 30.08 |
| Case: Various pitches of pattern | ||||
| 0.36 | 2.0 | 5.5 | 98 | 12.48 |
| 0.40 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 105 | 13.37 |
| 0.44 | 2.0 | 4.5 | 136 | 17.32 |
| Definition aspect ratio = the size of pattern/pitch between the pattern | ||||
| Definition of area ratio = total area of hydrophobic patterns/heating area | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
C. S., S.K.; Chang, Y.W.; Arenales, M.R.M.; Kuo, L.-S.; Chuang, Y.H.; Chen, P.-H. Experimental Investigation on the Effect of Size and Pitch of Hydrophobic Square Patterns on the Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Performance of Cylindrical Copper Surface. Inventions 2018, 3, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3010015
C. S. SK, Chang YW, Arenales MRM, Kuo L-S, Chuang YH, Chen P-H. Experimental Investigation on the Effect of Size and Pitch of Hydrophobic Square Patterns on the Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Performance of Cylindrical Copper Surface. Inventions. 2018; 3(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleC. S., Sujith Kumar, Yao Wen Chang, Mario R. Mata Arenales, Long-Sheng Kuo, Yu Hsuan Chuang, and Ping-Hei Chen. 2018. "Experimental Investigation on the Effect of Size and Pitch of Hydrophobic Square Patterns on the Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Performance of Cylindrical Copper Surface" Inventions 3, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3010015
APA StyleC. S., S. K., Chang, Y. W., Arenales, M. R. M., Kuo, L. -S., Chuang, Y. H., & Chen, P. -H. (2018). Experimental Investigation on the Effect of Size and Pitch of Hydrophobic Square Patterns on the Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Performance of Cylindrical Copper Surface. Inventions, 3(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3010015