Constructal Design of a Rectangular Fin in a Mixed Convective Confined Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical and Numerical Modeling
2.1. Governing Equations
- (i)
- the heat due to friction between the nanoparticles and base fluid is negligible compared to conduction at the heated surface, i.e., the viscous dissipation of energy is negligible,
- (ii)
- both the fluid phase and nanoparticles are in a thermal equilibrium and flowing at the same velocity,
- (iii)
- nanofluid is Newtonian whose thermophysical properties are assumed to be constant, and
- (iv)
- the Brownian motion of nanoparticles, aggregation of nanoparticles, and the nanoparticle size effects are neglected for simplification by considering low operating temperature and low nanoparticle concentration.
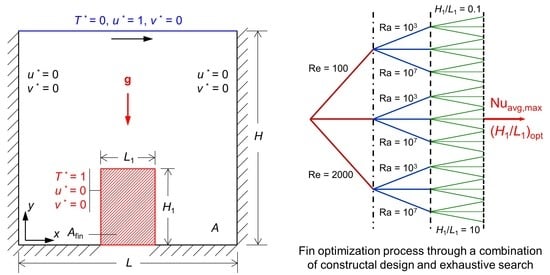
2.2. Problem Description
3. Numerical Methods and Model Verification
3.1. Mesh Sensitivity Test
3.2. Model Verification
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effect of Fin Shape on Local Heat Transfer
4.2. Effects of Reynolds and Rayleigh Numbers on Average Nusselt Number
4.3. Effect of Nanoparticles Concentration
4.4. Effect of Fin Area Fraction
4.5. Optimization of Fin Aspect Ratio
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaluria, Y.; Gupta, S.K. A numerical study of mixed convection flow in enclosures. Int. J. Energy Res. 1983, 7, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peric, M. Natural-convection in trapezoidal cavities. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A-Appl. 1993, 24, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.; Das, P.K.; Hyder, N.; Islam, A.K.M.S. Free convection in an enclosure with vertical wavy walls. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2002, 41, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.; Das, P.K.; Hyder, N. Laminar natural convection around an isothermal square cylinder at different orientations. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2002, 29, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, S.H.; Mahmud, S.; Das, P.K. Effect of aspect ratio and eccentricity on heat transfer from a cylinder in a cavity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2002, 12, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Mahmud, S. Numerical investigation of natural convection inside a wavy enclosure. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2003, 42, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Mahmud, S.; Tasnim, S.H.; Islam, A.K.M.S. Effect of surface waviness and aspect ratio on heat transfer inside a wavy enclosure. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2003, 13, 1097–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.A.R.; Mohammad, T.R. Natural convection in cavities with constant flux heating at the bottom wall and isothermal cooling from the sidewalls. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2005, 44, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amiri, A.; Khanafer, K.; Bull, J.; Pop, I. Effect of sinusoidal wavy bottom surface on mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Sharif, M.A.R. Mixed convection in rectangular cavities at various aspect ratios with moving isothermal sidewalls and constant flux heat source on the bottom wall. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2004, 43, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, T.; Roy, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Pop, I. Analysis of mixed convection flows within a square cavity with uniform and non-uniform heating of bottom wall. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2009, 48, 891–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.H.; Yan, H.; Massoudi, M.; Chen, Z.H.; Wu, W.T. Numerical simulation of nanofluid suspensions in a geothermal heat exchanger. Energies 2018, 11, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.A.; Choi, U.S.; Li, S.; Thompson, L.J.; Lee, S. Enhanced thermal conductivity through the development of nanofluids. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1997, 457, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Choi, S.U.S.; Patel, H.E. Heat transfer in nanofluids—A review. Heat Transf. Eng. 2006, 27, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, B.; Aminossadati, S.M. Natural convection heat transfer in an inclined enclosure filled with a water-CuO nanofluid. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A-Appl. 2009, 55, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Vafai, K. A critical synthesis of thermophysical characteristics of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 4410–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhalleb, M.; Abbassi, H. Numerical investigation of heat transfer by CuO–water nanofluid in rectangular enclosures. Heat Transf. Eng. 2016, 37, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, N.; Roetzel, W.; Das, S.K. Natural convection of nano-fluids. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 39, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, R.Y.; Tzeng, S.C. Numerical research of nature convective heat transfer enhancement filled with nanofluids in rectangular enclosures. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2006, 33, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Nada, E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, F.; Mahmoudi, A.H.; Shahi, M. Numerical study of mixed convection flows in a square lid-driven cavity utilizing nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2010, 37, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.K.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Pop, I. Numerical study on mixed convection and entropy generation of a nanofluid in a lid-driven square enclosure. J. Heat Transf. 2016, 138, 012503–012511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Vafai, K.; Lightstone, M. Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 46, 3639–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrach, S. Natural convection in enclosures. Adv. Heat Transf. 1972, 8, 161–227. [Google Scholar]
- Poulikakos, D.; Bejan, A. Natural convection experiments in a triangular enclosure. J. Heat Transf. 1983, 105, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, E.; Jaluria, Y. Mixed convection from an isolated heat-source in a rectangular enclosure. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A-Appl. 1990, 18, 427–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, G.; Paroncini, M.; Corvaro, F. Effect of heat transfer on natural convection in a square cavity with two source pairs. Heat Transf. Eng. 2014, 35, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Meng, X.; Zeng, M.; Ozoe, H.; Wang, Q.W. Natural convection heat transfer of copper-water nanofluid in a square cavity with time-periodic boundary temperature. Heat Transf. Eng. 2014, 35, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 2002–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Mondal, B. Mixed convective transport in a lid-driven cavity containing a nanofluid and a rotating circular cylinder at the center. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2014, 56, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Nada, E.; Chamkha, A.J. Mixed convection flow of a nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity with a wavy wall. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2014, 57, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A. From heat transfer principles to shape and structure in nature: Constructal theory. J. Heat Transf. 2000, 122, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, G.; Moretti, S. A cfd application to optimize t-shaped fins: Comparisons to the constructal theory’s results. J. Electron. Packag. 2007, 129, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, G.; Medici, M.; Rocha, L.A.O. Convective analysis of constructal t-shaped fins. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2014, 23, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, G.; Machado, B.S.; Isoldi, L.A.; dos Santos, E.D.; Rocha, L.A.O. Constructal design of rectangular fin intruded into mixed convective lid-driven cavity flows. J. Heat Transf. 2016, 138, 102501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, D.; Xie, G.N. Heat transfer enhancement and entropy generation of nanofluids laminar convection in microchannels with flow control devices. Entropy 2016, 18, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, H.H.; Hou, S.S. Numerical study of laminar flow and convective heat transfer utilizing nanofluids in equilateral triangular ducts with constant heat flux. Materials 2016, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, R.; Zhou, X.; Machado, B.D.S.; Das, P.K. Mixed convection flow of nanofluid in a square enclosure with an intruded rectangular fin. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1754, 050017. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, M.S.; Seo, J.H.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, M.Y. Review on synthesis, thermo-physical property, and heat transfer mechanism of nanofluids. Energies 2016, 9, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, H.C. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solution. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. The effect of Brownian motion on the bulk stress in a suspension of spherical particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 83, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell-Garnett, J.C. Colours in metal glasses and in metallic films. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1904, 203, 385–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.L.; Crosser, O.K. Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two-component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1962, 1, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.S. Effective transport coefficients in PEM fuel cell catalyst and gas diffusion layers: Beyond Bruggeman approximation. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2785–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.S. Analytical approach to polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell performance and optimization. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 604, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Li, X.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Z.S. Effects of catalyst layer structure and wettability on liquid water transport in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Energy Res. 2011, 35, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Weber, A.Z.; Bender, G.; Manak, A.; Bittinat, D.; Herring, A.M.; Ulsh, M. Rapid detection of defects in fuel-cell electrodes using infrared reactive-flow-through technique. J. Power Sour. 2014, 261, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Das, P.K.; Song, X.G.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. Numerical analysis of the optimum membrane/ionomer water content of PEMFCs: The interaction of Nafion ionomer content and cathode relative humidity. Appl. Energy 2015, 138, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenyuk, I.V.; Das, P.K.; Weber, A.Z. Understanding impacts of catalyst-layer thickness on fuel-cell performance via mathematical modeling. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F691–F703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A.; Lorente, S. Design with constructal theory. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2006, 22, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Bejan, A.; Lorente, S. Natural design with constructal theory. Mech. Eng. 2009, 131, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ansys® Academic Research Mechanical, Release 18.1. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/academic/terms-and-conditions (accessed on 25 March 2018).
- Patankar, S.V. Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, G.D. Natural-convection of air in a square cavity—A bench-mark numerical-solution. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 1983, 3, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallasamy, M.; Prasad, K.K. On cavity flow at high Reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 79, 391–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsinezhad, H.; Sharifpur, M.; Meyer, J.P. Experimental investigation on cavity flow natural convection of Al2O3–water nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2016, 76, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















| Physical Properties | Base Fluid | Nanoparticles |
|---|---|---|
| cp (J/kg·K) | 4179 | 765 |
| ρ (kg/m3) | 997.10 | 3970 |
| k (W/m·K) | 6.13 × 10−1 | 40 |
| β (1/K) | 2.10 × 10−4 | 8.5 × 10−6 |
| μ (kg/m) | 1.002 × 10−3 | – |
| Pr | 6.83 | – |
| Rayleigh Number | Nuavg | Percentage of Error (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benchmark Data | Present Study | ||
| Ra = 103 | 1.116 | 1.110 | 0.541 |
| Ra = 104 | 2.243 | 2.247 | 0.178 |
| Ra = 105 | 4.519 | 4.537 | 0.397 |
| Ra = 106 | 8.799 | 8.925 | 1.412 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cong, R.; Ozaki, Y.; Machado, B.S.; Das, P.K. Constructal Design of a Rectangular Fin in a Mixed Convective Confined Environment. Inventions 2018, 3, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3020027
Cong R, Ozaki Y, Machado BS, Das PK. Constructal Design of a Rectangular Fin in a Mixed Convective Confined Environment. Inventions. 2018; 3(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleCong, Ran, Yu Ozaki, Bruno S. Machado, and Prodip K. Das. 2018. "Constructal Design of a Rectangular Fin in a Mixed Convective Confined Environment" Inventions 3, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3020027
APA StyleCong, R., Ozaki, Y., Machado, B. S., & Das, P. K. (2018). Constructal Design of a Rectangular Fin in a Mixed Convective Confined Environment. Inventions, 3(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3020027