A Review of the Contribution of Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials Towards Addressing the Upcoming Challenges of Asphalt Pavements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
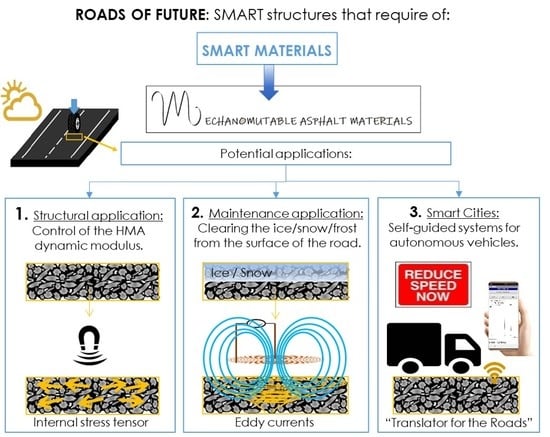
2. Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials
2.1. Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials as Improved Materials for Constructing Pavements
2.2. Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials for Improving Road Safety and Service Conditions
2.3. Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials for the Guidance of Autonomous Vehicles
3. Conclusions
- The first potential application in which MAMs aim to improve the mechanical performance of asphalt pavements showed that the magnetically susceptible materials used in their manufacture tended to be aligned to the forces of activated magnetic fields. This movement improves the mechanical properties of these materials, which depends on the temperature, the amount of magnetically susceptible materials and the intensity of the magnetic field. The mechanisms of action involved in the process are associated with: (1) the development of an internal structure in the material at high temperatures and (2) the generation of a stress field inside the bituminous matrix at low temperatures;
- In the case of the second application, the concept of MAMs can be extended to their use as thermomutable materials. The electrical properties of the magnetically susceptible materials used in their manufacture allow for the production of parasite currents which produce energy losses and increments in the temperature of the material and the surrounding layers. This thermal capacity could be taken into account when proposing new strategies for improving the safety and service conditions of the road;
- With regard to the third application, the development of a better means of transportation means that the road infrastructure should be prepared to respond to the associated advances in technology, and mechanomutable asphalt materials provide a tool for developing roads that can be used for the guidance of autonomous vehicles;
- Finally, it should be noted that further research is required with regard to the development of these materials. In particular, there is a need is to replicate the results obtained in the laboratory in a real-scale study. More results are needed to provide inputs for validating numerical models, which can be useful in the parametrization—and, therefore, the extrapolation—of the uses of MAMs in practice. This will allow for validating and adjusting the tested designs, a step that is necessary for the future implementation of MAMs as smart materials that can be used in the construction of smart pavements.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Development of new smart materials for the pavements of the future. Carreteras 2018, 4, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Iglesias, G.R.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Encoded asphalt materials for the guidance of autonomous vehicles. Autom. Constr. 2019, 99, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Iglesias, G.R.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Experimental evaluation of using stainless steel slag to produce mechanomutable asphalt mortars for their use in smart materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Iglesias, G.R.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Mechanical performance of mechanomutable asphalt binders under cyclic creep and recovery loads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Iglesias, G.R.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Development of mechanomutable asphalt binders for the construction of smart pavements. Mater. Des. 2015, 84, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva-Padilla, P.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Iglesias, G.R.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Analysis of the mechanical response of asphalt materials manufactured with metallic fibres under the effect of magnetic fields. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 29, 015033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Iglesias, G.R.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Ligante modificado con propiedades mecánicas controlables por campos magnéticos. International Patent Application No. PCT/ES2014/071002, 31 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Skaf, M.; Manso, J.M.; Aragón, Á.; Fuente-Alonso, J.A.; Ortega-López, V. EAF slag in asphalt mixes: A brief review of its possible re-use. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 120, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Wen, J.; Zhao, M.; Yi, M.; Wan, J. Utilization of gneiss coarse aggregate and steel slag fine aggregate in asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, D. Study on the effective composition of steel slag for asphalt mixture induction heating purpose. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Meijide, B.; Ajam, H.; Garcia, A.; Vansteenkiste, S. Effect of bitumen properties in the induction healing capacity of asphalt mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Meijide, B.; Ajam, H.; Lastra-González, P.; Garcia, A. Effect of air voids content on asphalt self-healing via induction and infrared heating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhong, S.; Zhu, X.; Chen, H. High-efficiency heating characteristics of ferrite-filled asphalt-based composites under microwave irradiation. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabiun, N.; Khabiri, M.M. Mechanical and moisture susceptibility properties of HMA containing ferrite for their use in magnetic asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhong, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, H. Self-healing efficiency of ferrite-filled asphalt mixture after microwave irradiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, Á.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M.; van Vliet, D. Induction heating of mastic containing conductive fibers and fillers. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2011, 44, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pamulapati, Y.; Elseifi, M.A.; Cooper, S.B.; Mohammad, L.N.; Elbagalati, O. Evaluation of self-healing of asphalt concrete through induction heating and metallic fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, P.; Wu, S.; Xiao, F.; Pang, L.; Xiao, Y. Conductive asphalt concrete: A review on structure design, performance, and practical applications. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Garcia, A. Self-healing of asphalt mixture by microwave and induction heating. Mater. Des. 2016, 106, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Wang, Z.; Hasan, M.R.M. Investigation of induction healing effects on electrically conductive asphalt mastic and asphalt concrete beams through fracture-healing tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Partl, M.N. Experimental evaluation of dense asphalt concrete properties for induction heating purposes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 46, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, Á.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M.; Liu, Q. A simple model to define induction heating in asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 31, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; García, Á.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M. Induction healing of asphalt mastic and porous asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3746–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Ai, T. Utilization of magnetite tailings as aggregates in asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; An, D.; Ai, T.; Zhao, P. Laboratory investigation on deicing characteristics of asphalt mixtures using magnetite aggregate as microwave-absorbing materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, F.; Mansour, K.; Pannirselvam, M.; Giustozzi, F. Mining materials to generate magnetically-triggered induction healing of bitumen on smart road pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of asphalt carbon coated reduced graphene oxide/magnetic CoFe2O4 hollow particles modified multi-wall carbon nanotube composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 723, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.; Shin, H.O. Self-healing capability of asphalt concrete with carbon-based materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, J.V.S.; Trichês, G.; de Rosso, L.T. Experimental evaluation of the influence of reinforcement with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) on the properties and fatigue life of hot mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, A.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Sassani, A.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Mina, M. Electrically-conductive asphalt mastic: Temperature dependence and heating efficiency. Mater. Des. 2018, 157, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahanbakhsh, H.; Karimi, M.M.; Jahangiri, B.; Nejad, F.M. Induction heating and healing of carbon black modified asphalt concrete under microwave radiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Q.; Porter, D.; You, Z. Investigation of microwave healing performance of electrically conductive carbon fiber modified asphalt mixture beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, B.; Gao, Y.; Ling, T.C.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z. Investigation on electrically conductive aggregates produced by incorporating carbon fiber and carbon black. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Q.; Guo, S. Laboratory performance evaluation of both flake graphite and exfoliated graphite nanoplatelet modified asphalt composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, G.R.; Ahualli, S.; Otero, J.E.; Ruiz-Morón, L.F.; Durán, J.D.G. Theoretical and experimental evaluation of the flow behavior of a magnetorheological damper using an extremely bimodal magnetic fluid. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 085028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubieta, M.; Eceolaza, S.; Elejabarrieta, M.J.; Bou-Ali, M.M. Magnetorheological fluids: Characterization and modeling of magnetization. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 095019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalski, P.; Kalita, K. Role of magnetorheological fluids and elastomers in today’s world. Acta Mech. ET Autom. 2017, 11, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Sol-Sánchez, M.; Gámiz, F.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Mechanical and thermal properties of graphene modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, S. Study on the graphite and carbon fiber modified asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1807–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Ye, Q.; Qiu, J.; Li, B. Properties evaluation of asphalt-based composites with graphite and mine powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Cortavitarte, M.; Jato-Espino, D.; Tabakovic, A.; Castro-Fresno, D. Optimizing the valorization of industrial by-products for the induction healing of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenberg, D.; Warner, K.E. Effects of snowfalls on motor vehicle collisions, injuries, and fatalities. Am. J. Public Health 2005, 95, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmert, H.M.; Osso, J.D.; Twiss, M.R.; Langen, T.A. Winter road management effects on roadside soil and vegetation along a mountain pass in the Adirondack Park, New York, USA. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Cuthbert, M.O.; Gamble, R.; Connon, L.E.; Pearson, A.; Shepley, M.G.; Davis, J. Highway deicing salt dynamic runoff to surface water and subsequent infiltration to groundwater during severe UK winters. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.; Akin, M.; Pan, T.; Fay, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z. Deicer impacts on pavement materials: Introduction and recent developments. Open Civ. Eng. J. 2009, 3, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mensah, K.; Choi, J.M. Review of technologies for snow melting systems. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 5507–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, Y.; Yoneda, Y.; Mori, K. Far-Infrared Ray Snow Melting System; West Nippon Expressway Facilities Company Limited: Osaka, Japan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yehia, S.; Tuan, C.Y. Bridge Deck Deicing. In Proceedings of the Transportation Conference Proceedings, Des Moines, IA, USA, 19–20 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z. Experimental investigation of hydronic snow melting process on the inclined pavement. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 63, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Che, G. Concrete pavement deicing with carbon fiber heating wires. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 65, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. Study of ice and snow melting process on conductive asphalt solar collector. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 3241–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Jang, D.-U.; Hong, J.-S.; Kim, T. Thermal modeling of railroad with installed snow melting system. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2015, 109, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdualla, H.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Mina, M.; Cetin, K.S.; Taylor, P.C.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Cetin, B.; Yang, S.; Vidyadharan, A. Design and construction of the world’s first full-scale electrically conductive concrete heated airport pavement system at a U.S. airport. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Xie, X.-M.; Wang, L.-Q.; Su, J.-F.; Guo, Y.-D.; Mu, R. Rheological behaviour of bitumen blending with self-healing microcapsule: Effects of physical and chemical interface structures. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 586, 124212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.F.; Guo, Y.D.; Xie, X.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Mu, R.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tan, Y.Q. Smart bituminous material combining anti-icing and self-healing functions using electrothermal graphene microcapsules containing oily rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Yalcin, E.; Hudson-Griffiths, R.; García, A. Mechanical and self-healing properties of stone mastic asphalt containing encapsulated rejuvenators. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarro, F.; Sol-Sánchez, M.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Exploring the recovery of fatigue damage in bituminous mixtures: The role of healing. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Preliminary Statement of Policy Concerning Automated Vehicles. 2013. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwiZ2J3g6qDoAhWMKqYKHRbPD28QFjAAegQIAhAB&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.nhtsa.gov%2Fstaticfiles%2Frulemaking%2Fpdf%2FAutomated_Vehicles_Policy.pdf&usg=AOvVaw1kzgMhDIOOc-olHnCFb4os (accessed on 27 May 2018).
- Wang, K.; Akar, G. Effects of neighborhood environments on perceived risk of self-driving: Evidence from the 2015 and 2017 Puget Sound Travel Surveys. Transportation (Amst) 2019, 46, 2117–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, T. Autonomous vehicle implementation predictions: Implications for transport planning. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 8–12 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Kumar, A.; Priyadharshini, M. Smart city: Traffic management system using smart sensor network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Physics and Photonics Processes in Nano Sciences, Eluru, India, 20–22 June 2019; Volume 1362. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Isabel, A.; Fuentes-Fernández, R.; de Diego, I.M. Modeling multi-agent systems to simulate sensor-based Smart Roads. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2020, 99, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, S.; Wazid, M.; Singh, D.P.; Das, A.K.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Park, Y. Intrusion detection protocols in wireless sensor networks integrated to internet of things deployment: Survey and future challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 3343–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudev, H.; Das, D.; Vasilakos, A.V. Secure message propagation protocols for IoVs communication components. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 82, 106555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, D. ICT based smart traffic management system ‘iSMART’ for smart cities. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 3920–3928. [Google Scholar]
- Nallaperuma, D.; Nawaratne, R.; Bandaragoda, T.; Adikari, A.; Nguyen, S.; Kempitiya, T.; De Silva, D.; Alahakoon, D.; Pothuhera, D. Online incremental machine learning platform for big data-driven smart traffic management. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 4679–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Material | Parameters studied | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Steel slag (coarse aggregate and powdered), steel grit. | Permanent deformation, fracture energy, moisture damage, Marshall stability. | [8,9,10,11,12]. |
| Ferrite fillers. | Permanent deformation, healing, moisture damage, Marshall stability | [13,14,15,16]. |
| Fibers (carbon, steel, steel wood and carbon nanofibers) | Fracture energy, moisture damage, Marshall stability. | [2,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. |
| Magnetite (tailings and powdered) | Moisture damage, Marshall stability. | [24,25,26] |
| Carbonyl iron powder | Permanent deformation, fatigue cracking, complex modulus and phase angle. | [4,5] |
| Carbon (carbon fiber, flake graphite and exfoliated graphite, graphene, carbon black and carbon nanotubes) | Electrical resistivity, healing, rheology, electrical conductivity, temperature changes. | [18,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34] |
| System | Components | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrared heating | Energy source, sensors, infrared heaters and control system. | Power consumption: 75 W/m2. Areas of application: pedestrian walkways, emergency entrances, loading dock ramps and hotel lobby entry. | [46,47,48] |
| Hydronic heating systems | heat source, heat exchanging tubes usually embedded in the pavements (floor heating), heat transfer fluid, sensors and a system control. | Power consumption: 473 W/m2. Areas of application: bridge decks, sidewalks, inclined pavements. | [48,49,50,51] |
| Embedded heating wires | energy source, sensors, heating element (cables and electric mats) and system controllers. | Power consumption: 323 to 3430 W/m2. Areas of application: railroad, bridge deck, pavements. | [48,50,52] |
| Electrically conductive materials | heat source (induction, microwave, electricity), sensors, magnetically susceptible materials and system controllers. | Power consumption: 516 W/m2 Areas of application: pavements, bridge decks. | [30,48,53] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leiva-Padilla, P.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Iglesias, G.; Rubio-Gamez, M.C. A Review of the Contribution of Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials Towards Addressing the Upcoming Challenges of Asphalt Pavements. Infrastructures 2020, 5, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures5030023
Leiva-Padilla P, Moreno-Navarro F, Iglesias G, Rubio-Gamez MC. A Review of the Contribution of Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials Towards Addressing the Upcoming Challenges of Asphalt Pavements. Infrastructures. 2020; 5(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures5030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeiva-Padilla, Paulina, Fernando Moreno-Navarro, Guillermo Iglesias, and Maria Carmen Rubio-Gamez. 2020. "A Review of the Contribution of Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials Towards Addressing the Upcoming Challenges of Asphalt Pavements" Infrastructures 5, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures5030023
APA StyleLeiva-Padilla, P., Moreno-Navarro, F., Iglesias, G., & Rubio-Gamez, M. C. (2020). A Review of the Contribution of Mechanomutable Asphalt Materials Towards Addressing the Upcoming Challenges of Asphalt Pavements. Infrastructures, 5(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures5030023